Forensic Science Fingerprints
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
fingerprints are unchanged throughout a lifetime
second principle of fingerprints
fingerprints can be classified
third principle of fingerprints
fingerprints are unique
first principle of fingerprints
pattern if ridges enter and exit on the same side
pattern with one delta and one core
loop
ulnar
ridges enter and leave towards the pinky
radial
ridges enter and leave towards the thumb
pattern with one or more cores and at least 2 deltas
whorl
pattern when ridges enter and leave on opposite sides
pattern with no deltas or cores
arch
bifurcation
the division of something into two branches
Type of whorl that looks like there is a spoon in the center
type of whorl when deltas are on different ridges
type of whorl when deltas are on the same/very close ridges
pattern if ridges are less than 45 degrees in an arch
plain whorl
pattern if ridges are more than 45 degrees in an arch
tented
3D prints left in soft material
plastic
visible prints
patent
prints that are not visible to the naked eye
latent
fingerprints are created by the ____ on our skin
oil or sweat
prints on biological material (skin) are best developed with ___
chemicals
prints on non-biological material are best developed with ___
powder
Dactyloscopy
study of fingerprints
dactylogram
fingerprint
plain arch
ridges enter on one side and exit on the other side

tented arch
similar to the plain arch, but has a spike in the center

accidental whorl
A mix of different patterns. Cannot be classified as any other pattern.

pocket loop
None of the center core touches the line.

plain whorl
Two deltas, a line drawn between the deltas goes through the central pocket

double whorl
made up of any two loops combined into one print (looks like a wave)

LEFT hand - ulnar loop
opens toward the pinky

RIGHT hand - radial loop
opens toward the thumb

eye
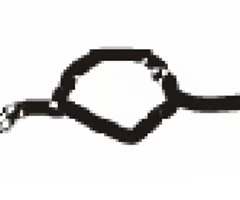
dot/island
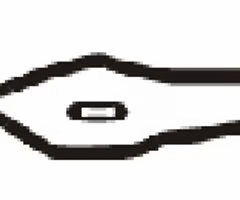
fork/bifurcation

bridge

crossover
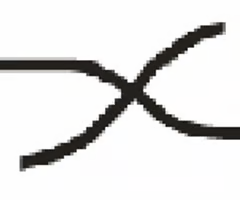
hook/spur

ridge ending

AFIS stands for...
Automated Fingerprint Identification System
How many minutiae are used to identify fingerprints?
12
An example of a plastic fingerprint is...
soap, wax, or playdoh
An example of a patent fingerprint is...
blood, grease, or oil
3 fundamental principles of fingerprints
a fingerprint is an individual characteristic
a fingerprint pattern will remain unchanged for the life of an individual
fingerprints have general characteristic and ridge patters
remember about ulnar and radial loops
on the left hand a loop that opens to the right would be an ulnar loop, while one that opens to the left would be a radial loop
difference between a plain vs central pocket whorl
if some of the curved ridges touch the line, it is a plain whorl.
If none of the center core touches the line it is a central pocket whorl
difference between a double vs accidental whorl
double loop whorls are made up of any 2 loops combined into one print
accidental whorls contain 2 or more patterns not including the plain arch or does not clearly fall under any of the other categories
fingerprint factoid
60 of people have loop
35 have whorls
5 have arches