2.4 Organic Compounds
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Alkane functional group
R-H
Alkene functional group
C=C
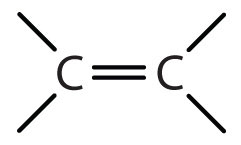
Alcohol functional group
R-OH
What is a primary alcohol?
the carbon the -OH is attached to is attached to 0 or 1 other carbons
What is a secondary alcohol?
the carbon the -OH is attached to is attached to 2 other carbons
What is a tertiary alcohol?
the carbon the -OH is attached to is attached to 3 other carbons
Halogenoalkane functional group
R-X
where X represents
R-F
R-Cl
R-Br
R-I
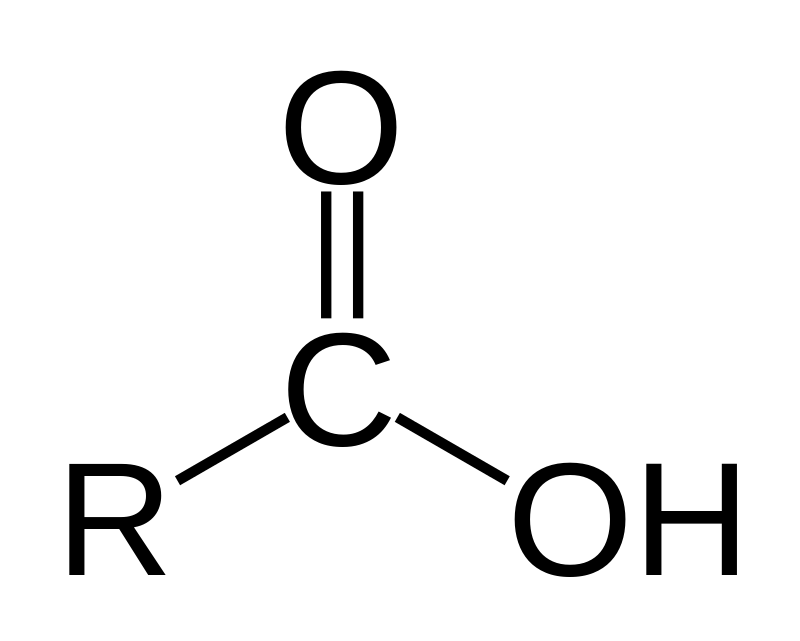
How to identify a carboxylic acid
contains a -COOH group at the end
Carboxylic acid functional group
R-COOH
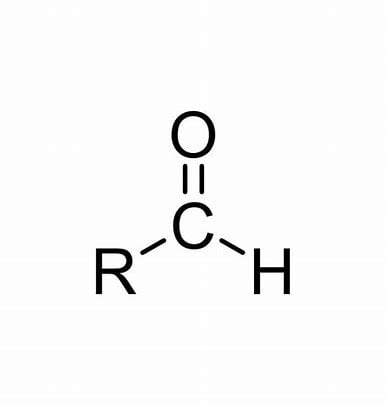
How to identify an aldehyde
carbonyl group
functional group must be at end
Aldehyde functional group
How to identify a ketone
carbonyl group
functional group must be in the middle
Ketone functional group

Name of 1 carbon chain
meth
Name of 2 carbon chain
eth
Name of 3 carbon chain
prop
Name of 4 carbon chain
but
Name of 5 carbon chain
pent
Name of 6 carbon chain
hex
Name of 7 carbon chain
hept
Name of 8 carbon chain
oct
Name of 9 carbon chain
non
Name of 10 carbon chain
dec
How to name alkanes
end in _ane
How to name alkenes
end in -1-_ene
1 is where double bond is

How to name halogenoalkanes
1-fluro/chloro/bromo/iodo
1 is where halogen is
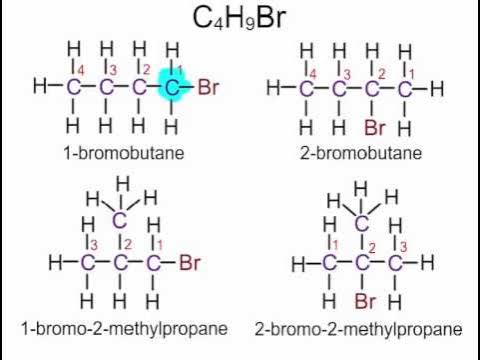
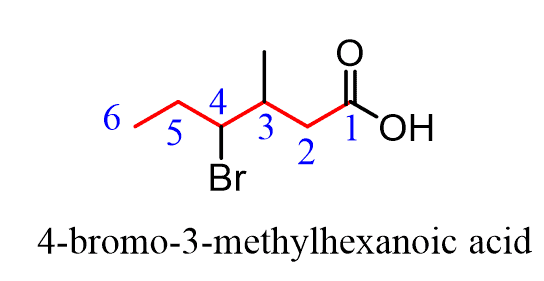
How to name carboxylic acids
always on carbon 1
ends in _anoic acid
How to name alcohols
ends in _an-1-ol
if end is taken 1-hydroxy_
1 is where -OH is

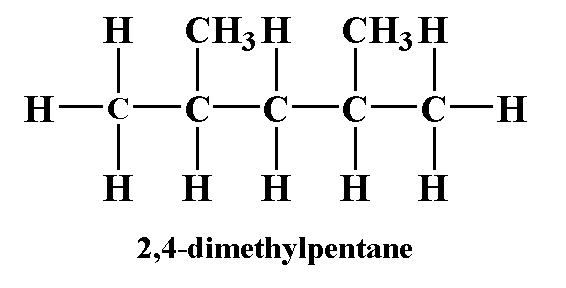
What is structural formula?
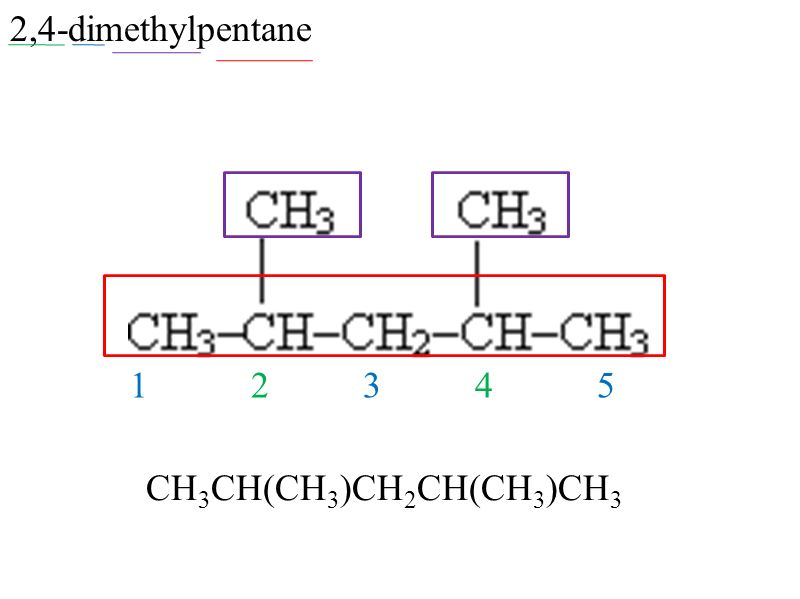
What is shortened structural formula?
What is skeletal formula?
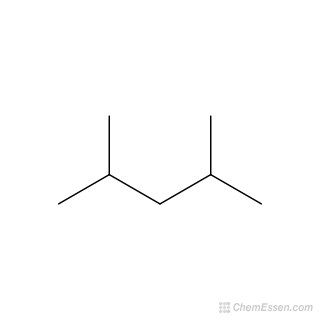
What is structural isomerism?
have same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms
What is stereoisomerism?
same structural formula but have a different arrangement of atoms in a 3d space
Why can stereoisomerism only happen in alkenes?
can only occur in alkenes as no rotation around the fixed carbon-carbon double bond
What is geometric isomerism?
molecule must have two different groups attached to each carbon either side of the double bond
Steps to name E-Z geometric isomer
look at two bonds at the end of the double bond and rank the two groups in terms of the atomic number, double bonds count as two bonds
the atom with the higher atomic number takes priority
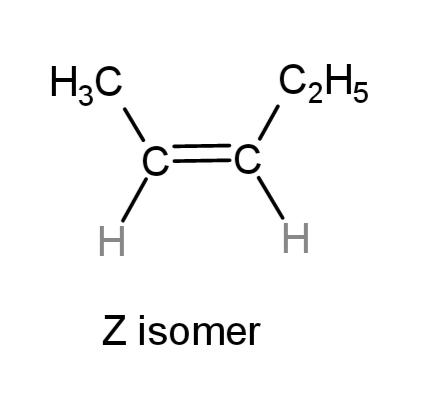
if the higher priority groups are on the same side of the double bond, it is a Z isomer
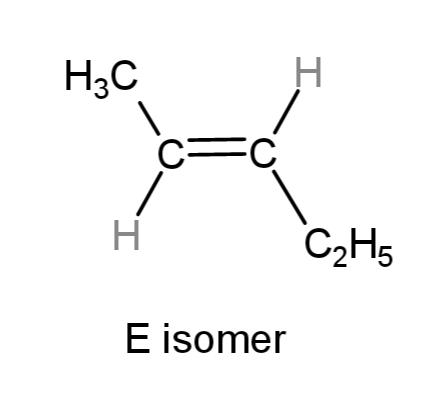
if the higher priority groups are on opposite sides of the double bond, it is an E isomer
Z isomer
if the higher priority groups are on the same side
E isomer
if the higher priority groups are on opposite sides
Why do E isomers tend to have higher boiling points?
they pack together more so have stronger intermolecular forces
What is an organic reaction?
way to break a covalent bond
What is heterolytic bond fission?
occurs when elements have different electronegativities
once the bond is broken, an iron is formed as electrons are closer to one molecule
What is homolytic bond fission?
occurs when two elements have same/similar electronegativities
both gain their electrons back
forms a radical
Examples of attacking species
radicals
electrophiles
nucleophiles
Radicals
a highly reactive species with an unpaired electron
formed by homolytic fission
molecule has a dot next to it (X•)
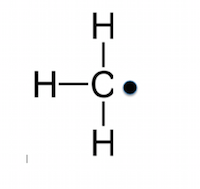
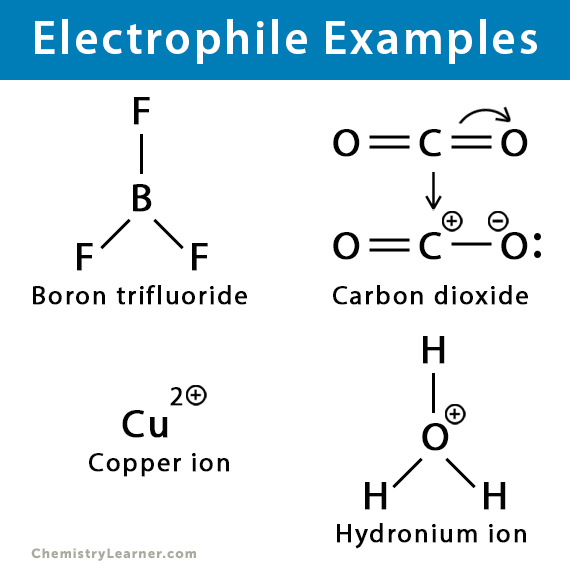
Electrophiles
an electron deficient species that attack electron rich sites
love electrons
positive charge and empty orbitals
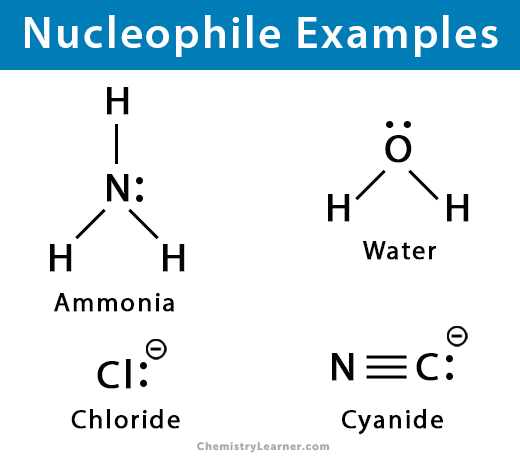
Nucleophiles
an electron rich species that attack electron deficient sites
love protons
negative charge or a lone pair of electrons
Disadvantages of the use of fossil fuels
finite resoruce
acid rain - SO2 emitter
CO2 emitter