3 - Fluids + Textures
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
volatile content _____ (increases/decreases) with increasing metamorphic grade
decreases
what is LOI
loss of ignition (h2o, co2, so3)
what temperature and pressure are the critical end points at for h2o?
P = 2MPa
T = 374 C
what temperature and pressure are the critical end points at for CO2
P = 3 MPa
T = 31.1 C
above the h2o critical point, it is a _______ fluid
supercritical
what is an isochore
lines of constant density
what happens to a fluid inclusion during cooling and exhumation?
the mass/volume of the inclusion is constant, so density is constant
it will follow the isochore until it intersects the LV curve then the phases will separate (boiling),
Then it fully follows the LV curve
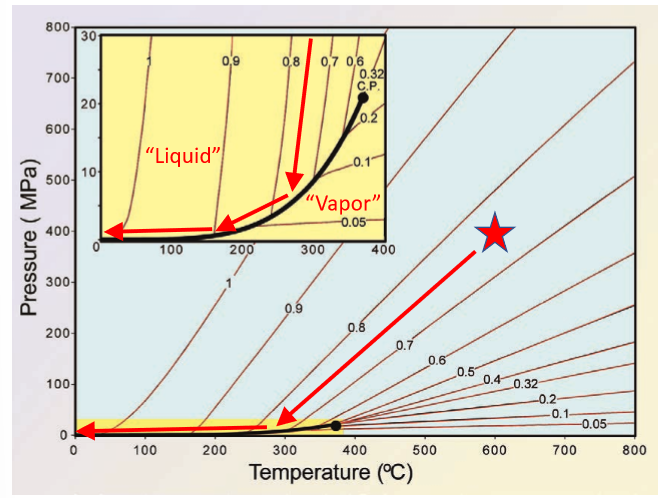
what is the LV curve?
liquid-vapour curve
whats the symbol for stress
sigma σ
definition of stress
an applied force acting on a rock over a cross-sectional area
what is strain
the response of a rock to an applied stress (deformation)
how do rocks beneath the earths surface experience stressed
uniform in all directions
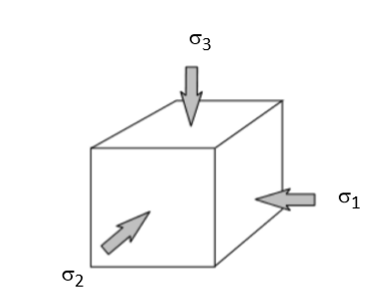
what does the equilibrium mineral assemblage depend on
the pressure of the lithosphere (as well as the T, fluid and protolith)
how to find differential stress
σ1-σ3 (mohrs circles!!!!)
what is the mohr failure criterion
where shear failure occurs
what caused shear failure
increasing fluid pressure
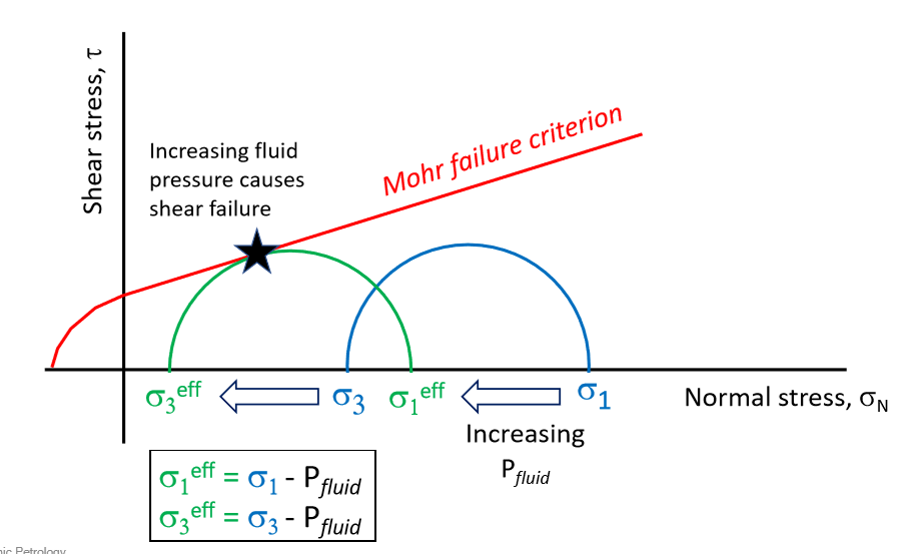
x and y axis of a mohr circle diagram
y = shear stress τ
x = normal stress σN
what is σ1eff (an equation)
(σ1 minus pressure of fluid)
what is σ3eff (an equation)
(σ3 minus pressure of fluid)
what reduces effective stresses and what kind of failure does it cause
increasing pore fluid, causes brittle failure
what is deviatoric stress and what does it result in
unequal stresses, results in rock deformation and development of metamorphic foliation
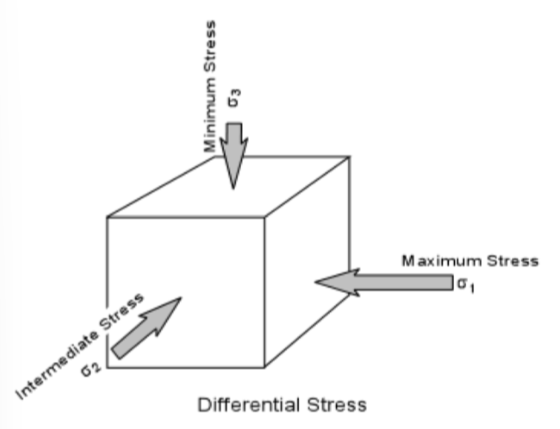
describe the order of principle stresses (___>___>___)
σ1 > σ2 > σ3
what is the maximum stress?
σ1'
what is the intermediate stress?
σ2
what is the minimum stress?
σ3
how do the 3 principle stresses act on a unit? like what direction do they face
like dis
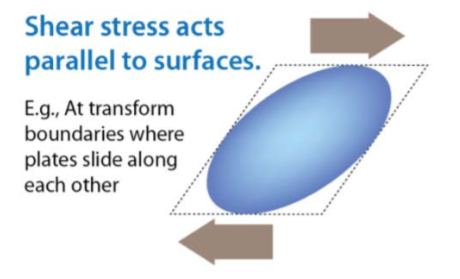
what is simple shear
parallel to surfaces, pushing like a deck of cards
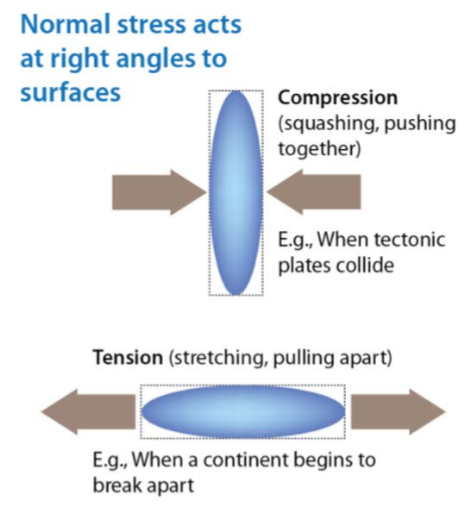
what is pure shear
acts at right angles to surfaces, compression/extension
how does deviatoric stress result in metamorphic foliations (4 ways)
Platy minerals growing perpendicular to σ1 = slaty cleavage
Rotation of mineral grains
Pressure solution
Dislocation glide
what is pressure solution
dissolution-precipitation (minerals dissolve at grain contacts under high stress—> then reprecipitate in lower stress areas)
higher temperatures tend to _____ (increase/decrease) grain size
increase
how does slow heating impact grain size
fewer nuclei, coarser grained
how does rapid heating impact grain size
many nuclei, fine grained textures
deformation tends to _____ (increase/decrease) grain size
decrease
how do low strain rates impact grain size
more time to reduce accumulated strain energy
how do high strain rates impact grain size
less time to reduce accumulated strain energy
what does the final grain size depend on? (6 reasons)
the protolith, temperature, rate of heating, strain, strain rate, and ability to reduce strain energy
rocks will ____ (fine/coarsen) if high temperatures outlast high strain rates
coarsen
what are the 5 categories we can put rock names into
foliated (planar fabric)
non foliated
metabasalts
monomineralic rocks
other special names
4 examples of foliated (planar fabric) rocks
slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss
2 examples of non-foliated rocks
hornfels, granulite (granofels)
4 examples of metabasalts
greenschist, blueschist, amphibole, eclogite
3 examples of monomineralic rocks
quartzite, marble, serpentinite
3 examples other “special” named rocks
migmatite, mylonite, pseudotachylite
from low to high metamorphic grade, rank the foliated rocks
slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss
in the foliated rocks, what do we call them if there are important minerals like garnet or staurolite in them?
just call them garnet-schist or staurolite schist
what is a hornfel and how does it form
fine grained, non foliated rock formed by contact metamorphism
what is a granofel and what do we typically call it
coarse grained non foliated rock, usually call it gneiss or granulite
how are metabasaltic rocks named
based on their metamorphic facies
what mineral dominated in blueschist
glaucophane
what mineral dominated in greenschist
epidote, chlorite, actinolite
what mineral dominated in eclogite
garnet, omphacite
what mineral dominated in amphibolite
hornblende and plag
what mineral dominated in mafic granulite/gneiss
hornblende, clinopyroxene, plag
what is a migmatite
underwent partial melting
what is a mylonite
shear zone rock, highly deformed, indicative of ductile stress
what is a pseudotachlite
a frictional melt layer, indicative of a brittle regime