Maxillary Techniques
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Infiltration Techniques
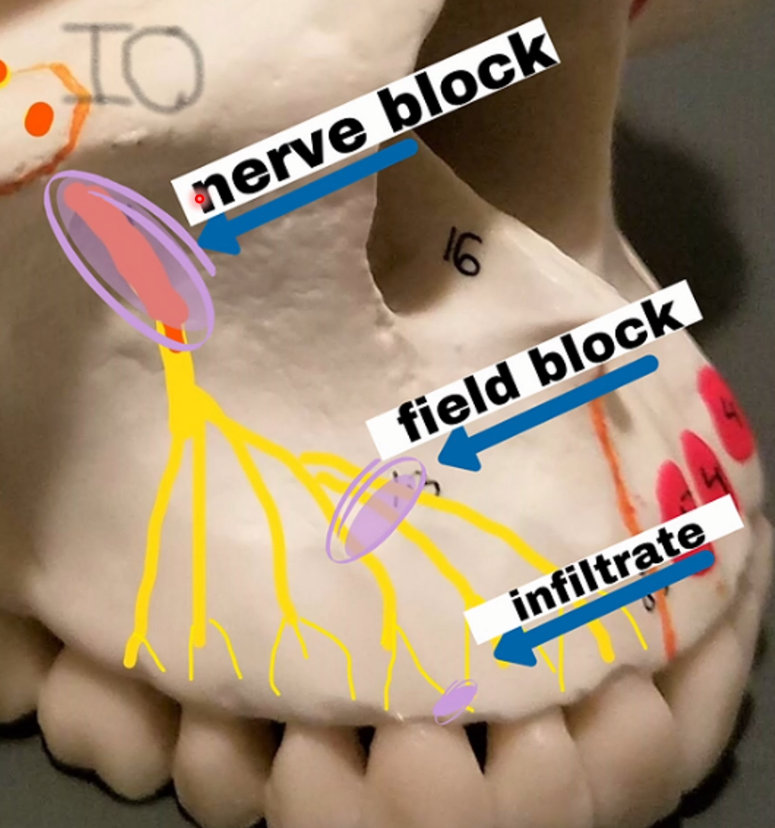
Local Infiltration: Small terminal nerve endings in the area are flooded with anesthetic → PDl Injections or pulpal → Tx is done on same area in which L.A is deposited
Field Block: L.A is deposited near the larger terminal nerve branch so the area will be circumscribed and preventing the passage of impulses from the tooth to the CNS
Nerve blocks: L.A deposited close to the main nerve trunk at a distance to prevent operative intervention
Supraperiosteal
Areas anesthetized
Contraindication
Armamentarium recommendations
Technique
Amount of anesthetic
Most frequently used for pulpal anesthesia in maxillary teeth → but used when only 1-2 teeth are being treated
Areas anesthetized: crown, root, pulp, periodontium
Contraindication: Acute inflammation to the area or dense bone on top of tooth
Very high success
Armamentarium recommendations: 27 gauge, short needle, bevel towards bone
Technique: Inject at height of mucobuccal fold about the apex of the tooth, bevel down
Amount of anesthetic: 0.6ml
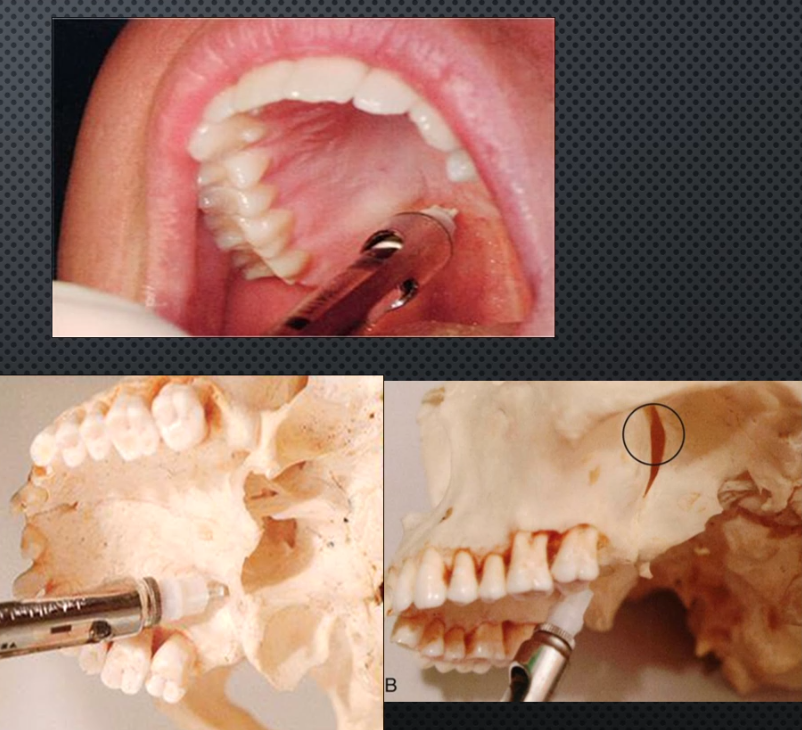
Posterior superior AN BLOCK
Area anesthetized
Success rate
Procedure
Onset of action
Indications
Complications
Amount of anesthetic
Area anesthetized: Max molar buccal gingiva, mucous membrane of sinus, pulpal tissue (except B cusp of 1st molar in 28% of patients →> use MSA block)
Success rate: 95%
Procedure: Insert at height of mucobuccal fold of Max 2nd molar (upward inwards and backward), insert 16mm (2/3 of short needle or half of long needle), bevel oriented to bone, aspirate twice, inject L.A
Onset of action: 3-5 min
Indications: Quadrant or sextant dentistry
Complications: Hematoma from pterygoid plexus
Amount of anesthetic: 0.9-1.8ml

Middle superior AN BLOCK (if present! 28% of pts)
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
Amount of anesthetic
Area anesthetized: Both max premolars +MB cusp of 1st molar
Procedure: same as PSA but start above 2nd premolar
Onset of action: 3-5 min
Amount of anesthetic: 0.9-1.2ml
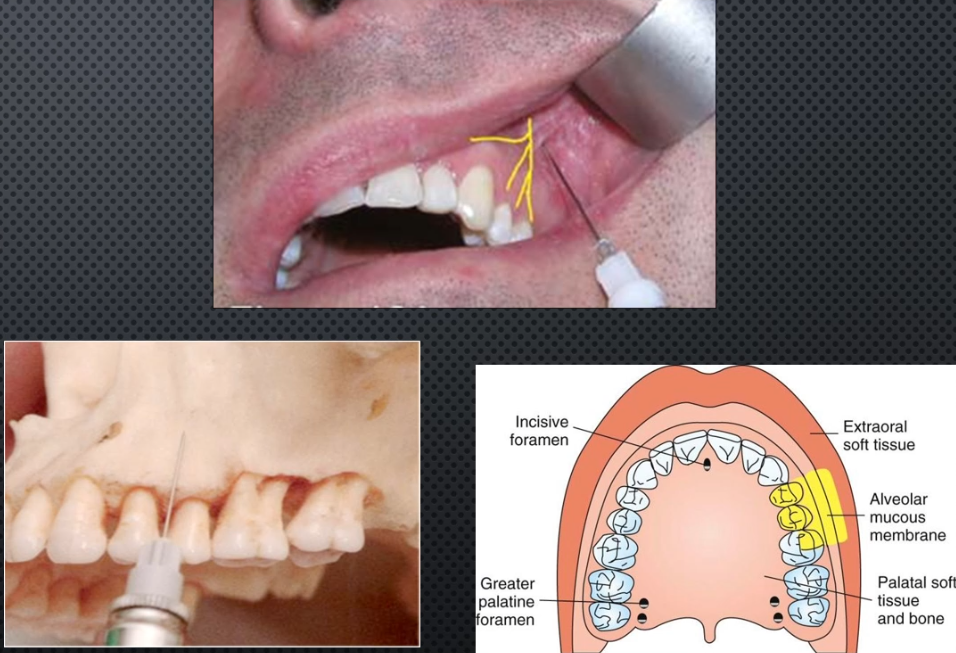
Anterior Superior AN BLOCK
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
Amount of anesthetic:
Area anesthetized: Max Incisors and canine + Premolars and MB cusp of 1st molar ( in 72% of pts- those w/o MSA)
Procedure: same as PSA but insert bove 1st premolar until contacting bone
Onset of action
Amount of anesthetic: 0.9-1.2ml
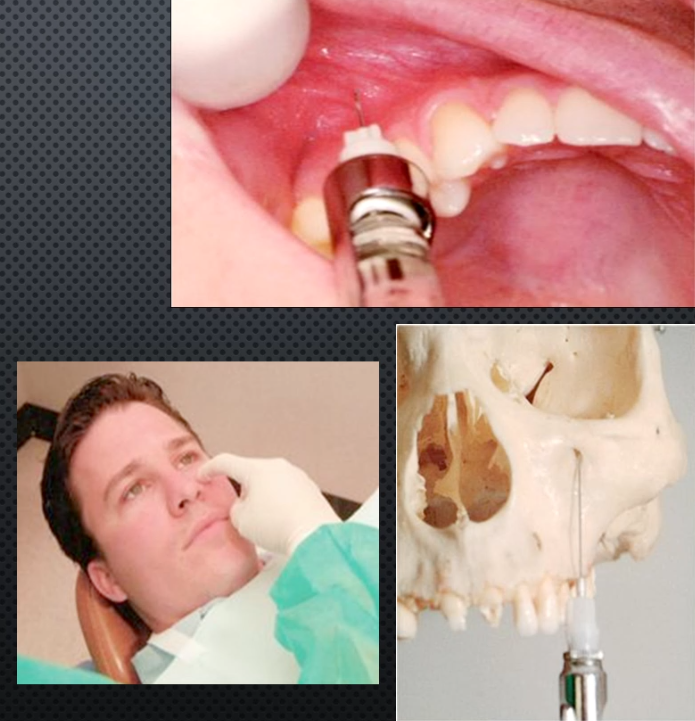
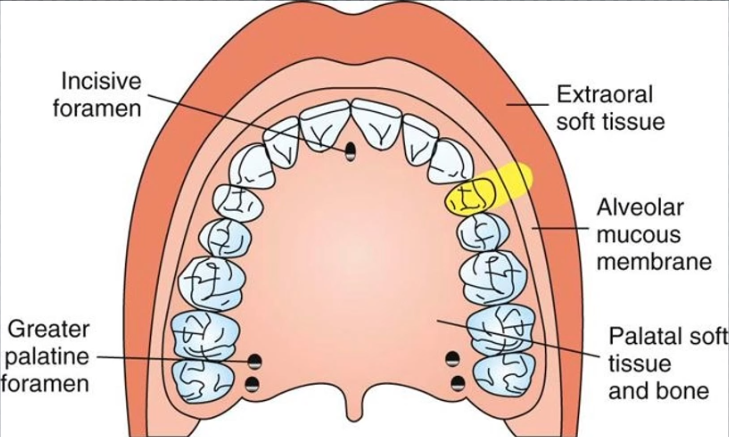
Greater palatine N Block
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
How to make it less traumatic
Amount of anesthetic
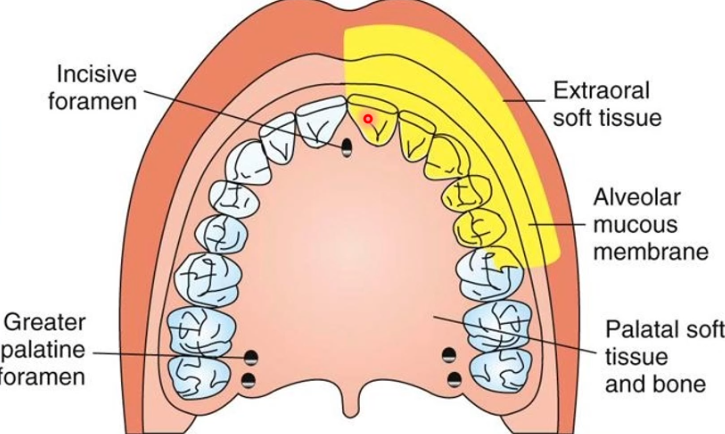
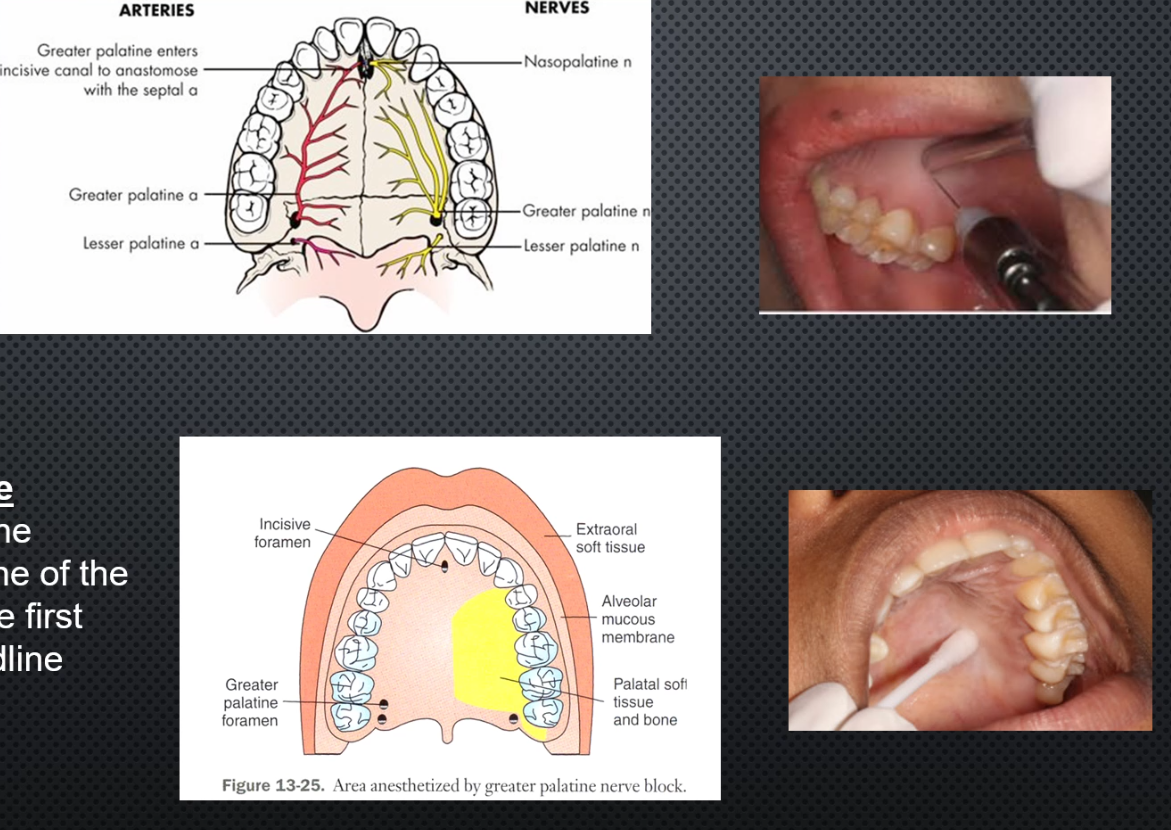
Area anesthetized: palatal mucosa behind maxillary premolars and molars
Procedure: Insert needle slightly anterior to greater Palatine Foramen until contacting bone, deposit 0.5ml (or until blanching)
Onset of action:3-5 min
Apply pressure at site before and during injection
Amount of anesthetic: 0.45-0.6 or blanching
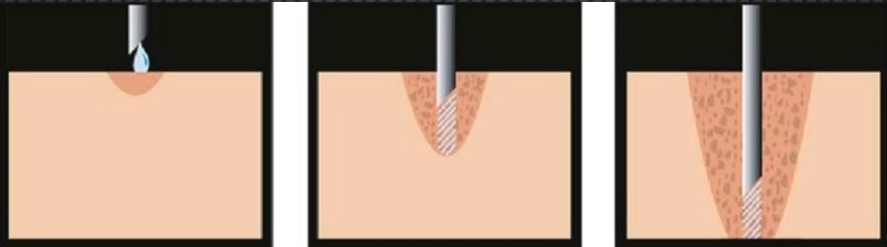
Pre-puncture Technique
Technique used to minimize pain of greater palatine n block
Bevel towards tissue and force L.A in before needle enters
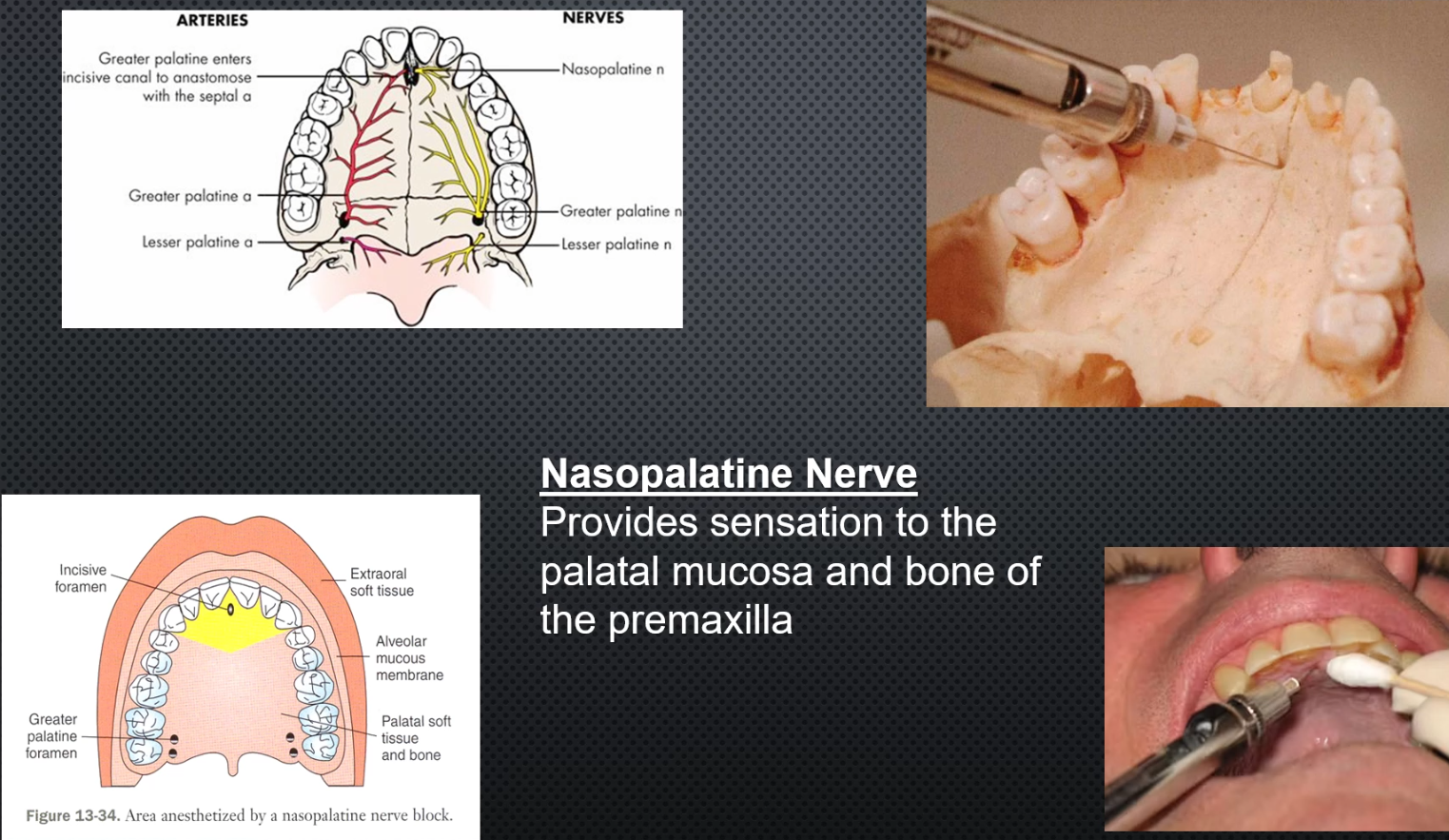
Nasopalatine Nerve Block
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
Amount of anesthetic
Epi
Area anesthetized: palatal mucosa and bone of the pre-maxilla
Procedure: Insert lateral to incisive papilla, do not enter foramen; asprate and deposit 0.5ml or until blanching
Onset of action:3-5min
Amount of anesthetic: max 0.45ml
Epi: 1:50,000 not recommended!
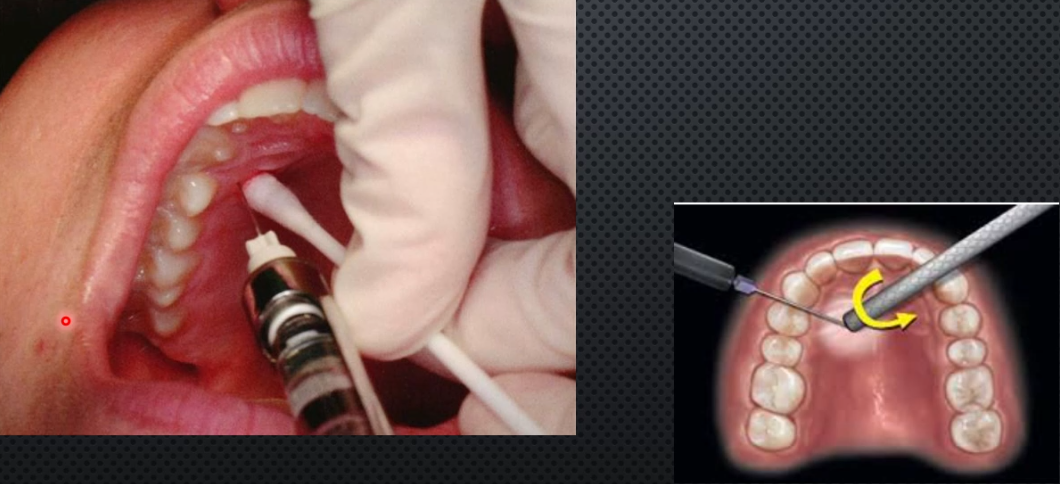
Multiple injection technique for Nasopalatine N block
If the buccal mucosa is already anesthetized, inject incisive papilla slowly from buccal aspect, then you can do nasopalatine N. block as normal but with less pain

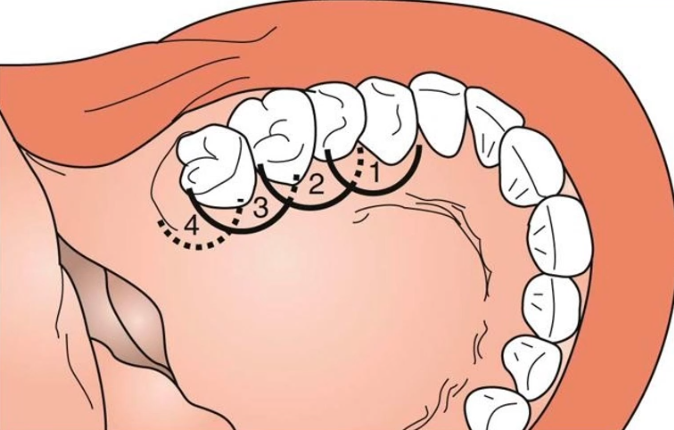
Local Infiltration of the palate
Used when only 1-2 teeth are to be anesthetized
Use overlapping sequence of needle penetrations
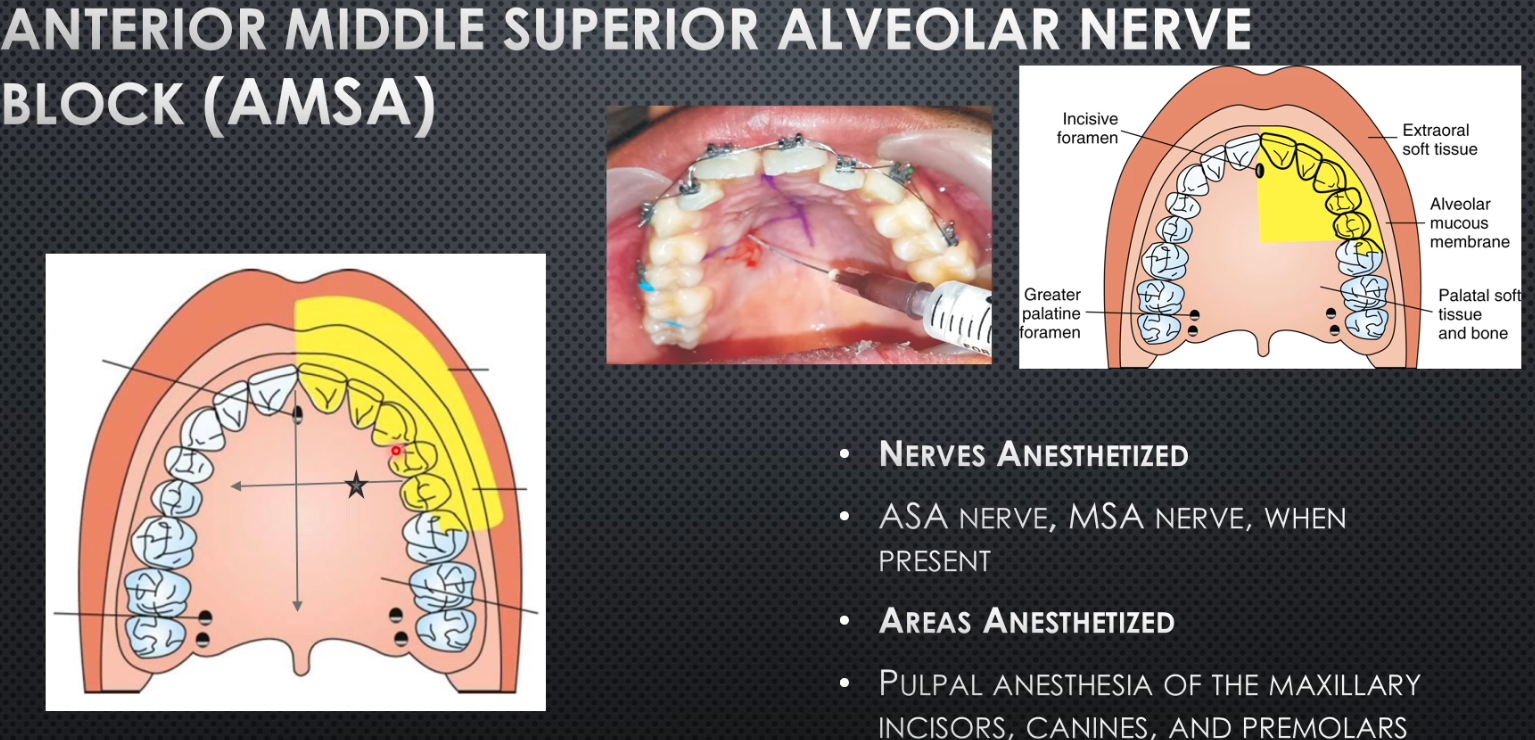
Anterior Middle Superior Alveolar Nerve block
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
Complications
When is it useful
Amount of anesthetic
Area anesthetized: palatal mucosa and bone of the pre-maxilla + behind premolars and MB cusp or 1st molar
Procedure: Insert less than half way between bisecting line of incisive papilla and premolars; use whole cartridge over 2 min
Onset of action:3-5min
Complications: ulcer that lasts 2 days
When is it useful: Cosmetic Procedures where lip must not be anesthetized
Amount of anesthetic:1.4-1.8ml
Palatal Approach to Anterior Superior Alveolar
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
Complications
When is it useful
Amount of anesthetic:
Area anesthetized: palatal mucosa, pulp, crown and bone of the pre-maxilla
Procedure: Insert needle at incisive foramen
Onset of action:3-5min
Complications: ulcer that lasts 2 days
When is it useful: Cosmetic Procedures where lip must not be anesthetized
Amount of anesthetic: 1.4-1.8ml

Maxillary Nerve Block High Tuberosity Approach
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
Complications
Amount of anesthetic
Area anesthetized: all palatal mucosa of the quadrant, pulpal for all but max molars (except MB cusp), all buccal mucosa except that of Max molars (except MB cusp) → ONLY BLOCK THAT CAN ANESTHETIZE MOST OF THE QUADRAT AT ONCE
Procedure: same exact thing as PSA except insertion is 30mm
Onset of action:3-5 min
Complications: Highest risk of hematoma and intravascular injection of all blocks, not recommended for inexperienced clinicians
Amount of anesthetic: 1.8ml
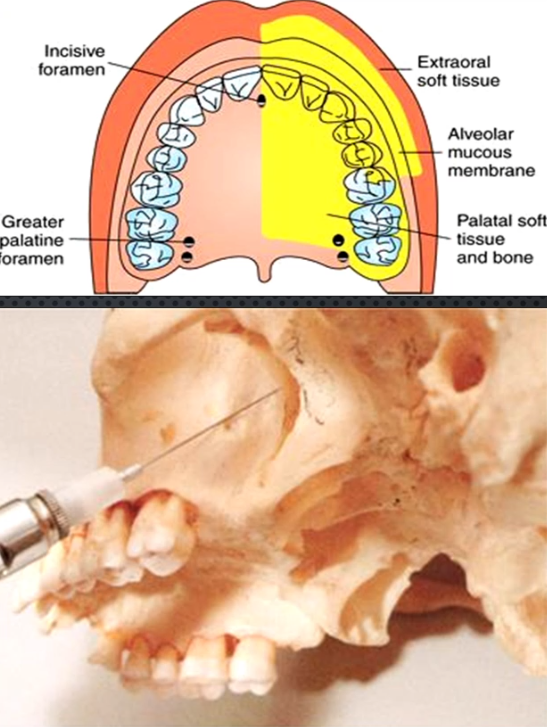
Maxillary Nerve Block Greater Palatine Approach
Area anesthetized
Procedure
Onset of action
Complications
Amount of anesthetic
Area anesthetized: all palatal mucosa of the quadrant, pulpal for all but max molars (except MB cusp), all buccal mucosa except that of Max molars (except MB cusp) → ONLY BLOCK THAT CAN ANESTHETIZE MOST OF THE QUADRANT AT ONCE
Procedure: Insert at greater palatine foramen, go 30mm and deposit cartridge slowly
Onset of action: 3-5 min
Complications: perioptical swelling, diplopia and ophthalmoplegia from possible optic nerve block, horner’s syndrome, L.A going into nose
Amount of anesthetic: 1.8ml