AS-A level Physics Practice Questions (theory)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
State what is meant by the threshold frequency of the incident light(1)
Explain why the photoelectric effect is not observed below the threshold frequency.(2)
minimum frequency for electrons to overcome work function.
energy of a photon depends on frequency.
below threshold frequency, the photon does not have enough energy to liberate an electron.
When monochromatic light is shone on a clean metal surface, electrons are emitted from the surface
due to the photoelectric effect.
(a) State and explain the effect on the emitted electrons when
(i) increasing the frequency of the light, (2)
(ii) increasing the intensity of the light. (2)
the (maximum) kinetic energy/speed/velocity/momentum
of released electrons increases.
this is because increasing the frequency of the photons increases their energy.
Increases the amount of electrons released from the surface of the metal per second.
As there are more 1-1 interactions between the photons and the electrons.
(b) The wave model was once an accepted explanation for the nature of light. It was rejected when validated evidence was used to support a particle model of the nature of light. Explain what is meant by validated evidence. (2)
Experiment/observation needs to be performed (to test a theory) .
the results of (the experiment) need to be proved repeatable.
At a fixed frequency of radiation, emitted electrons are collected and a current is recorded. State and explain a change that may be made to increase this current. (3)
Increase the intensity of light.
This will increase the amount of photons released from the source and the amount of 1-1 interactions with the electrons.
So will increase the amount of electrons released per second (The frequency).
4 (a) When monochromatic light is incident on a metal plate, electrons are emitted only when the frequency of the light exceeds a certain threshold frequency.
Explain, in terms of energy, why this threshold frequency exists. (3)
the energy of each photon/the light increases with frequency.
electrons need a minimum amount of energy to leave the metal.
this amount of energy is equal to the work function.

Experiments based on the photoelectric effect support the particle theory of light. State one conclusion drawn from these experiments and explain how it supports the theory. (2)
conclusion: light below a threshold frequency does not release electrons.
explanation: photons carry quanta of energy.
Alternate answer: electrons are emitted immediately the light hits the metal surface explanation photons carry quanta of energy.
When monochromatic light is incident on a particular metal plate, electrons are emitted. The intensity of the light is then increased.
Explain:
why the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons does not change,
why the number of electrons emitted per second increases. (3)
Energy of a photon does not depend on intensity.
So electrons gain no extra energy.
Intensity of light depends on number of photons emitted per second.
So more 1-1 interactions with the electrons.
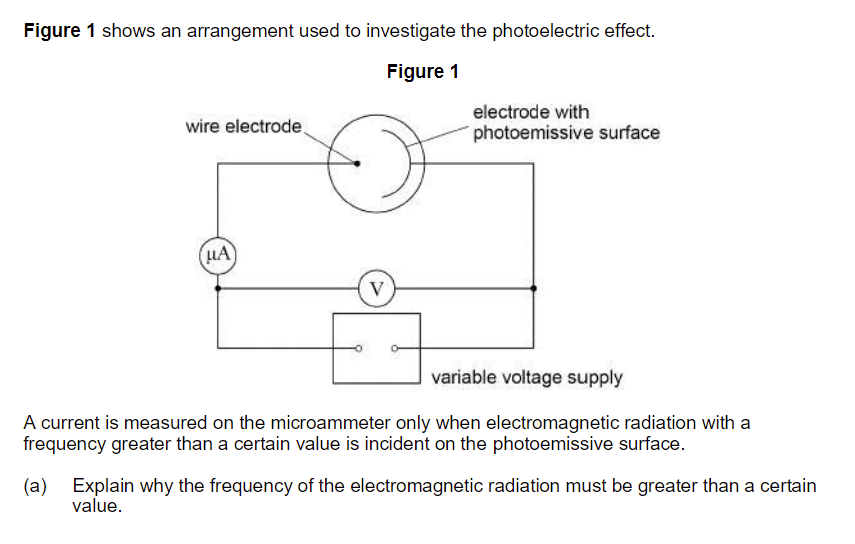
Explain why the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation must be greater than a certain value.
Frequency is proportional to energy of a photon.
There is a minimum energy (of a photon) required to remove photoelectron; (minimum energy relates to minimum frequency).
(Paper 2-Fields-Uses of Magnetic Fields in Devices – Electric Generators 6 marks)
Explain how the principle of electromagnetic induction is used in electric generators.

(Paper 2-Thermal-Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution & Kinetic Theory – 5 marks)
Explain how the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution changes when temperature increases.
The peak of the distribution shifts right, indicating higher average kinetic energy.
The number of particles with very high speeds increases.
The curve flattens, meaning a wider range of speeds is present.
The most probable speed increases as temperature increases.
The area under the curve remains constant, as the number of molecules is unchanged.