Macroeconomics final section 1 questions
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
A budget surplus means that:
Government revenues are greater than expenditures in a given year
Which of the following fiscal policy changes would be the most contractionary?
A $10 billion increase in taxes and a $30 billion cut in government spending
Automatic stabilizers smooth fluctuations in the economy because they produce changes in the government's budget that:
Help offset changes in GDP
A major advantage of the built-in or automatic stabilizers is that they:
require no legislative action by Congress to be made effective.
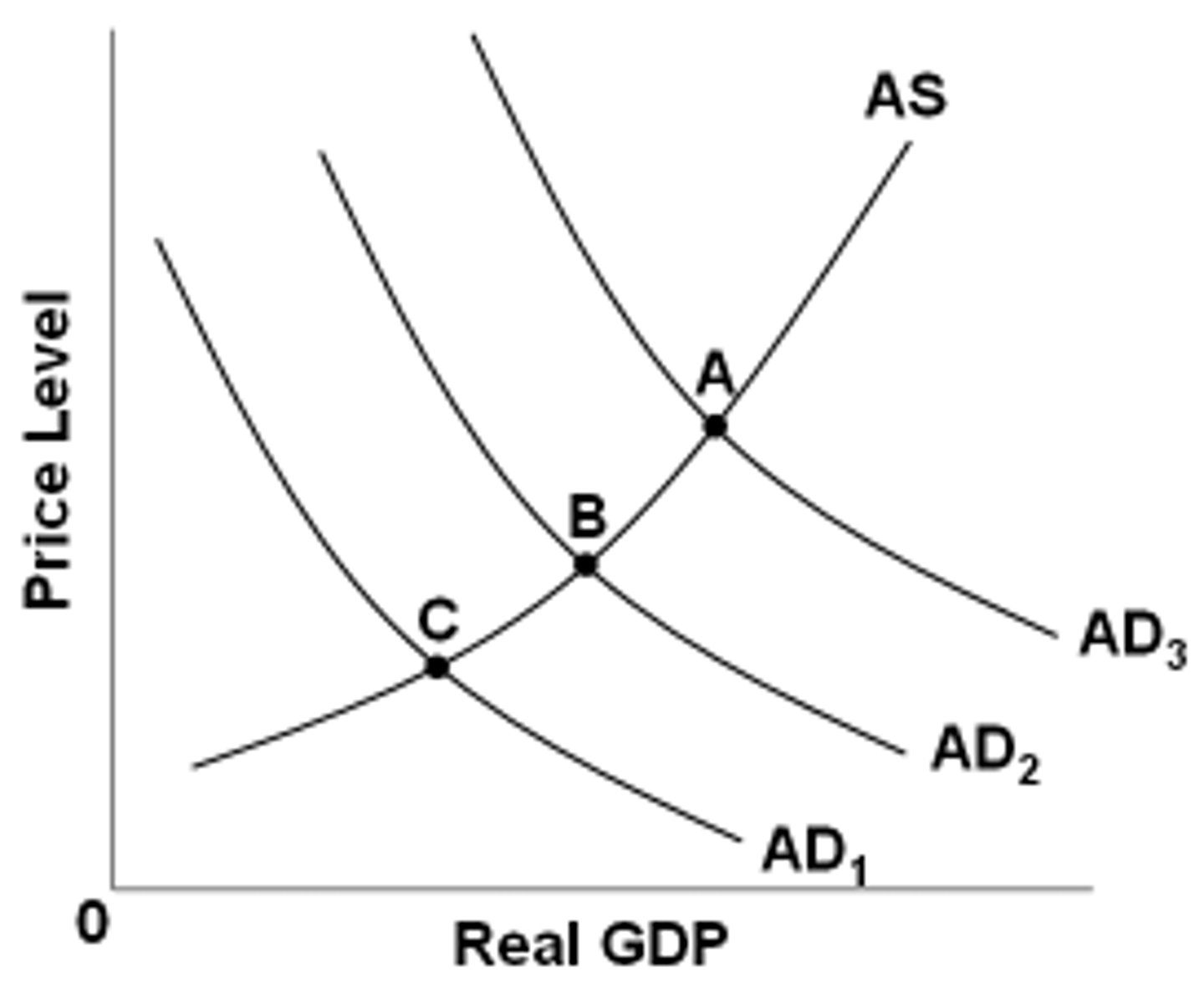
Refer to the figure above. The economy is at equilibrium at point B. What would expansionary fiscal policy do?
Move the economy from point B towards point A
Demand-pull inflation can be restrained by increasing government spending and reducing taxes.
False
The goal of expansionary fiscal policy is to increase:
Real GDP
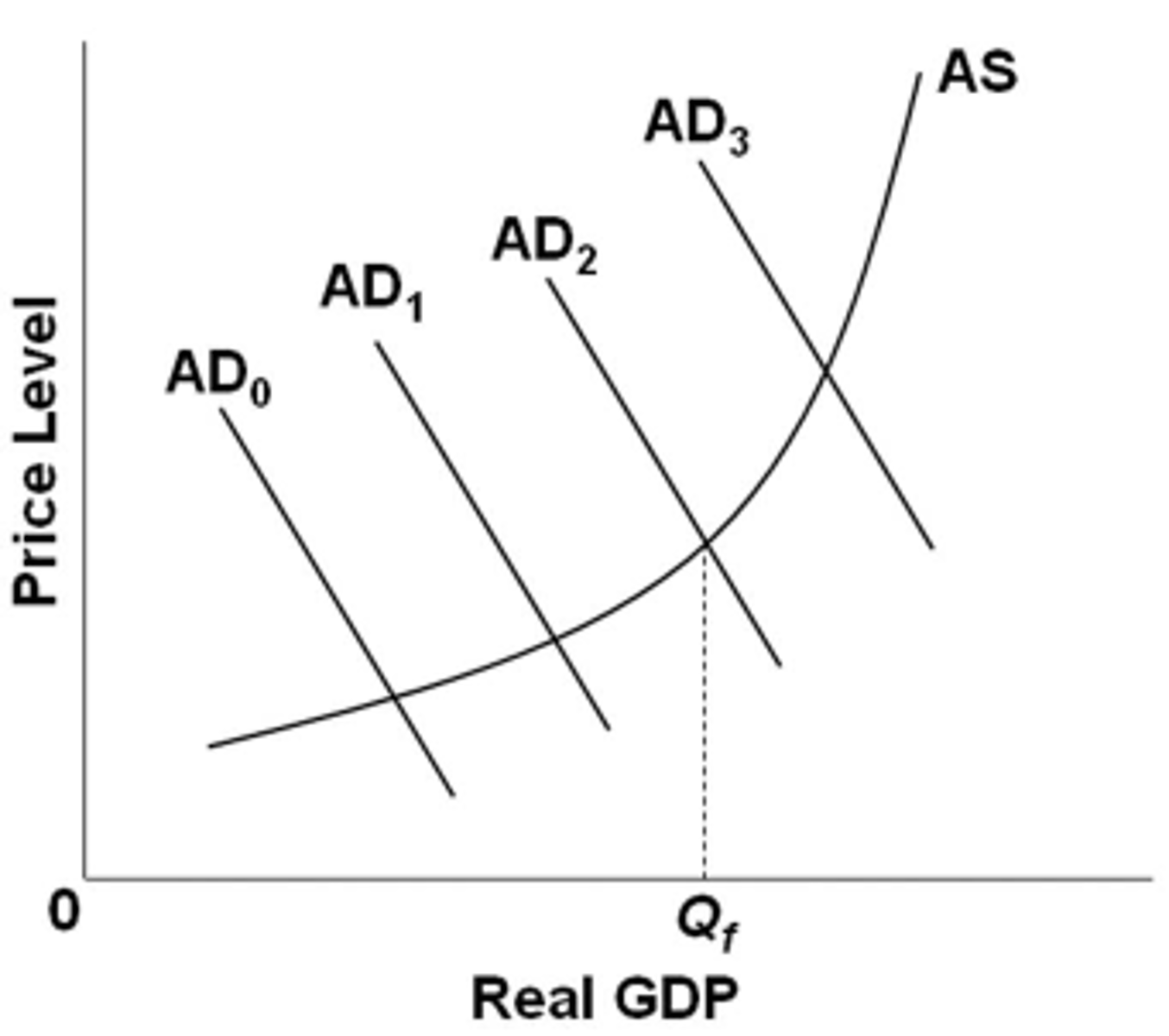
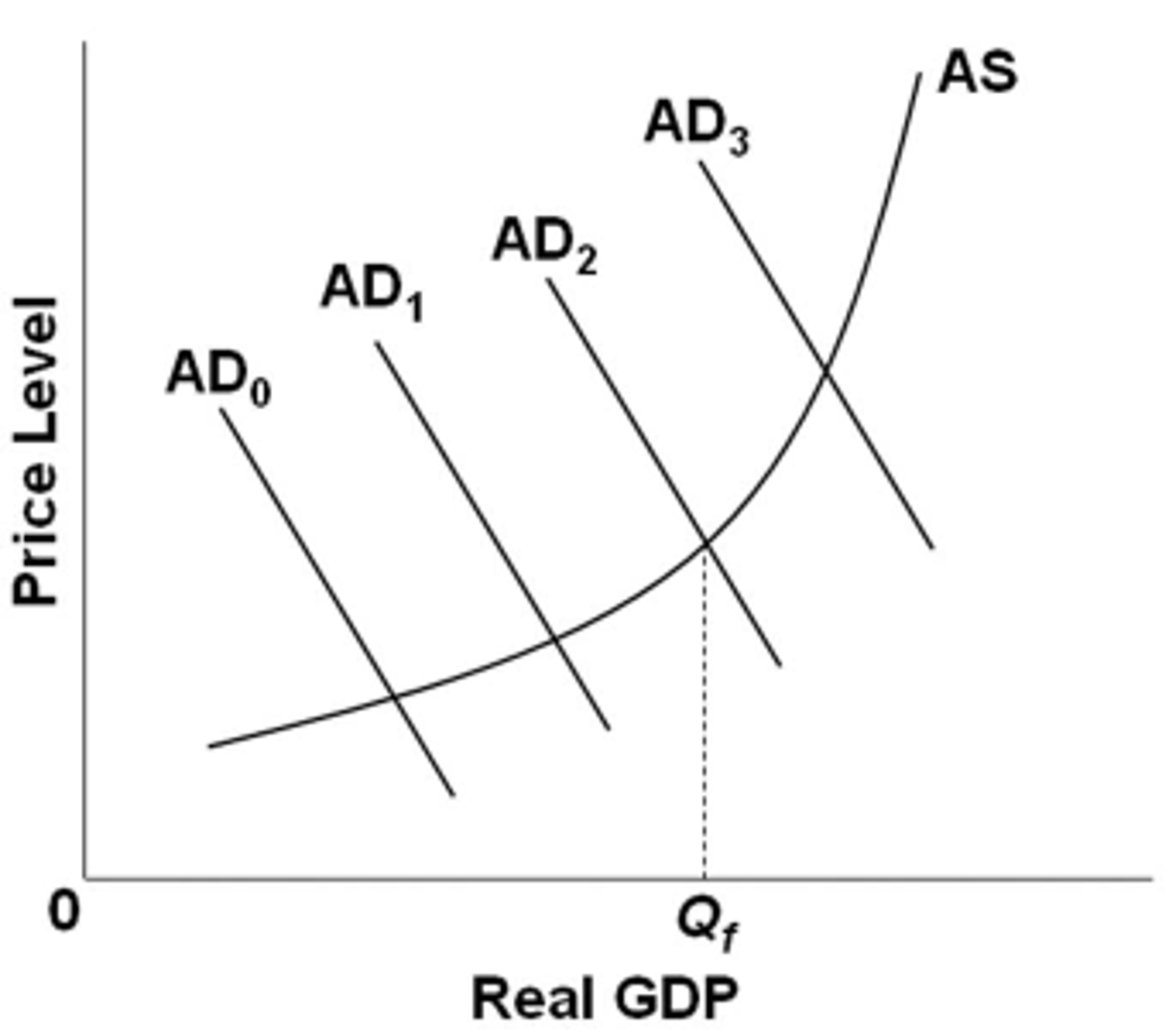
Refer to the diagram, in which Qf is the full-employment output. If the economy's current aggregate demand curve is AD0, it would be appropriate for the government to:
increase government expenditures or reduce taxes.
The following are important problems associated with the public debt, except:
Government borrowing to finance the debt may lead to too much private investment
If the government wants to reduce unemployment using fiscal policy, it may do so by increasing government spending.
True
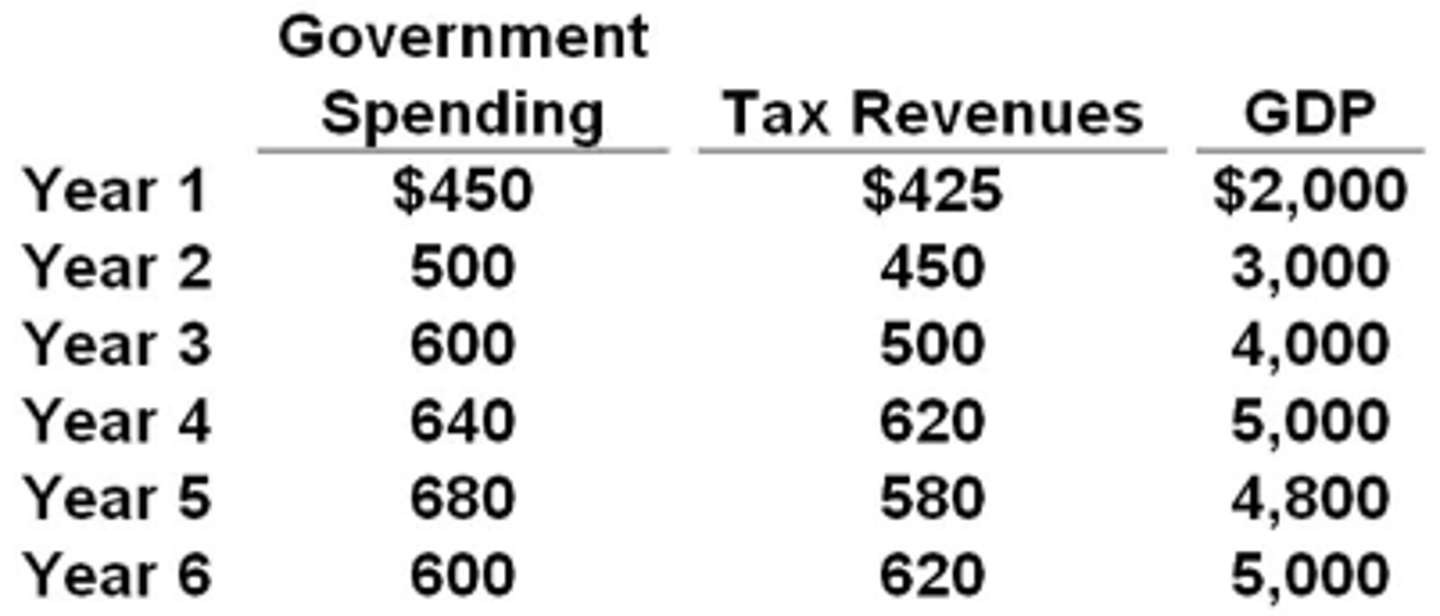
Answer the question using the following budget information for a hypothetical economy. Assume that all budget surpluses are used to pay down the public debt.
$100 billion.
If the MPC in the economy is .75, government could shift the aggregate demand curve rightward by $30 billion by cutting taxes by $10 billion.
True
A specific reduction in government spending will dampen demand-pull inflation by a greater amount the:
smaller is the economy's MPS.
A tax reduction of a specific amount will be more expansionary the:
larger is the economy's MPC.
Built-in stability is exemplified by the fact that with a progressive tax system, net tax revenues decrease when GDP decreases.
True
If the government wishes to increase the level of real GDP, it might reduce:
Taxes
Due to automatic stabilizers, when the nation's total income rises, government transfer spending:
Decreases and tax revenues increase
A contractionary fiscal policy is shown as a:
leftward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
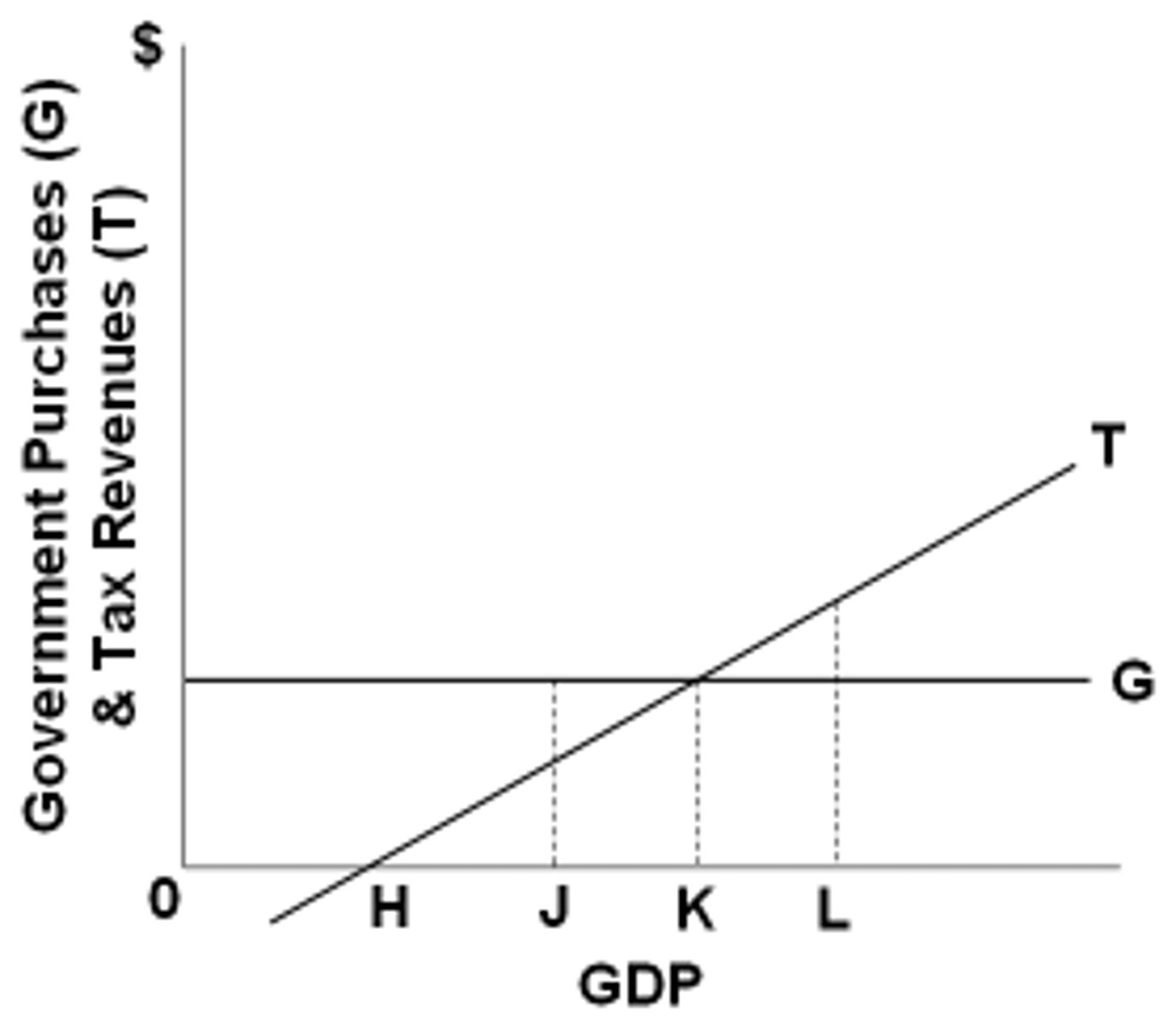
Refer to the graph above. A budget surplus would be associated with GDP level:
L
Refer to the diagram, in which Qf is the full-employment output. If the economy's current aggregate demand curve is AD3, it would be appropriate for the government to:
reduce government expenditures or increase taxes.
If the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System increases the legal reserve ratio, this change will:
Decrease the excess reserves of member banks and thus decrease the money supply
Which best describes how banks create money?
by lending out money and collecting interest
What is one of the functions of the Federal Reserve?
promote economic stability
What is required reserves?
the percent that banks must hold by law
What is expansionary monetary policy?
expanding the money supply or lowering short-term interest rates
What is open market operations?
The Fed buying and selling government securities
how does an expansionary monetary policy affect investment expenditure?
it increases investment
Which are tools of Monetary Policy?
reserve requirement and discount rate
An appropriate fiscal policy for a severe recession is:
a decrease in tax rates
A expansionary fiscal policy is shown as a:
rightward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
What is one formula of the spending multiplier?
1/mps
Expansionary fiscal policy is so named because it:
is designed to expand real GDP
The tax multiplier is always
negative
What is government spending multiplier?
1 / 1- MPC = 1 / MPS
Fiscal policy is carried out primarily by:
federal government
The asset demand for money:
varies inversely with the rate of interest
If the economy were encountering a severe recession, proper monetary and fiscal policies would call for:
buying government securities, reducing the reserve ratio, reducing the discount rate, reducing interest paid on reserves held at Fed banks, and a budgetary deficit.
Lowering the reserve ratio:
Turns required reserves into excess reserves
A restrictive monetary policy reduces investment spending and shifts the economy's aggregate demand curve to the right.
False
Assume the economy is operating at less than full employment. An expansionary monetary policy will cause interest rates to ________, which will ___________ investment spending.
decrease; increase
Interest paid on reserves held at the Fed:
incentivizes financial institutions to hold more reserves and reduce risky lending.
Answer the question on the basis of the following consolidated balance sheet of the commercial banking system. Assume that the reserve requirement is 20 percent. All figures are in billions and each question should be answered independently of changes specified in all preceding ones.
Refer to the given data. The commercial banking system has excess reserves of:
zero

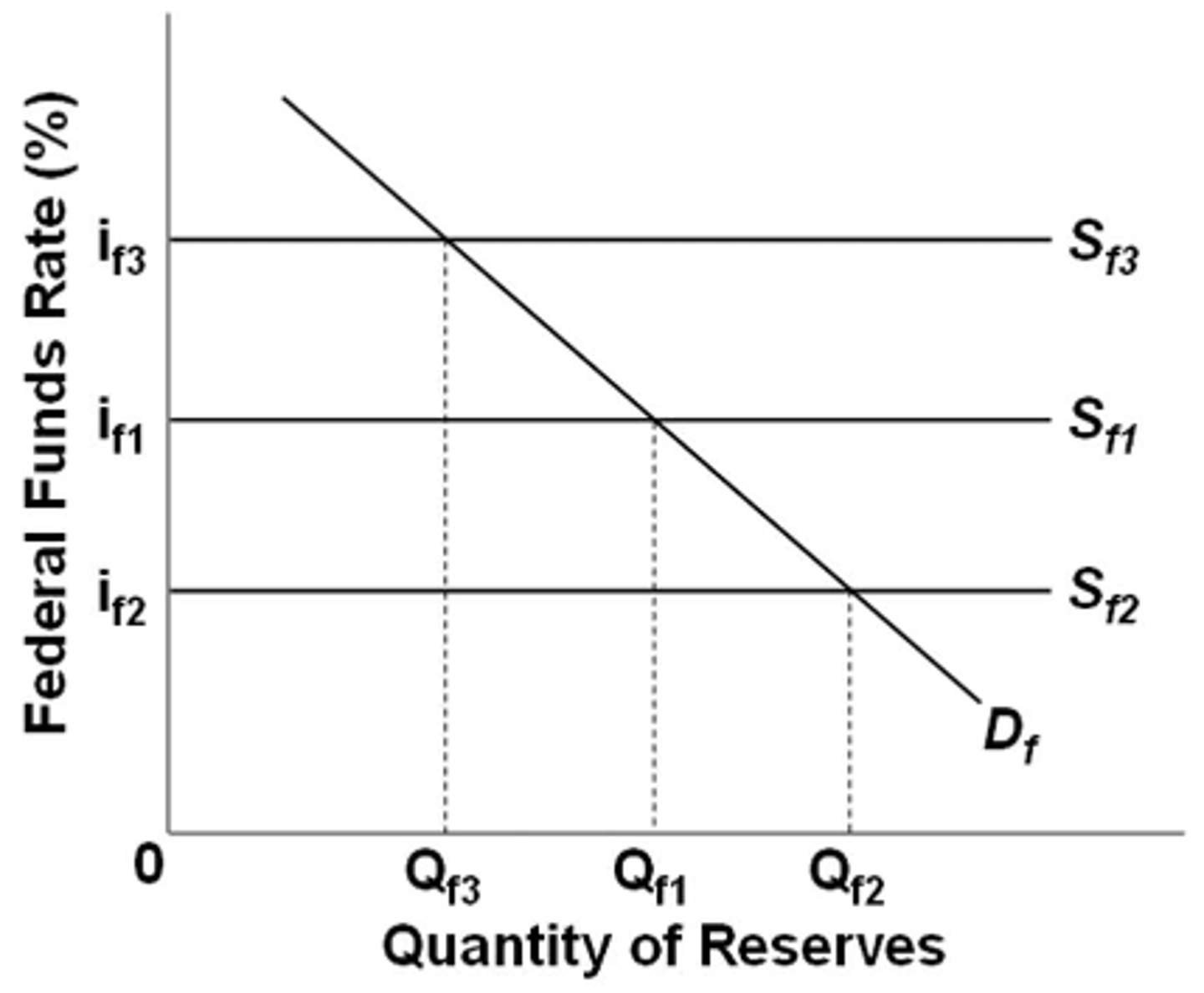
Refer to the diagram for the federal funds market. If the Fed wants the federal funds rate to fall from if1 to if2, it can use open-market operations to:
increase the supply of federal funds.
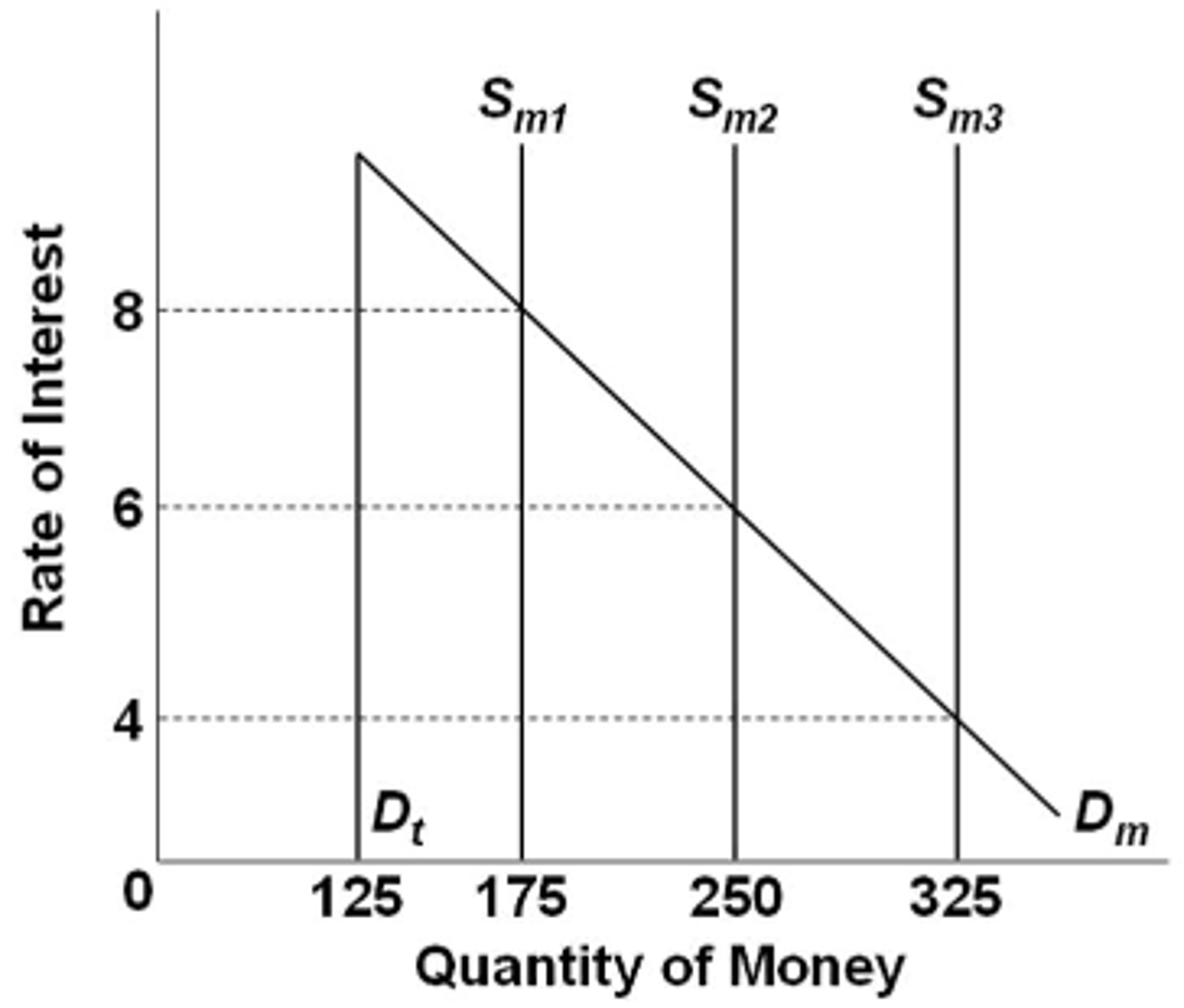
Refer to the graph above, in which Dt is the transactions demand for money, Dm is the total demand for money, and Sm is the supply of money. The market is initially in equilibrium at a 6 percent rate of interest. If the supply of money increases as shown, then the asset demand for money will increase by:
$75
An increase in nominal GDP will:
Increase the transactions demand and the total demand for money
Refer to the diagram for the federal funds market. An expansionary monetary policy would be shown by:
a shift from Sf3 to Sf2.
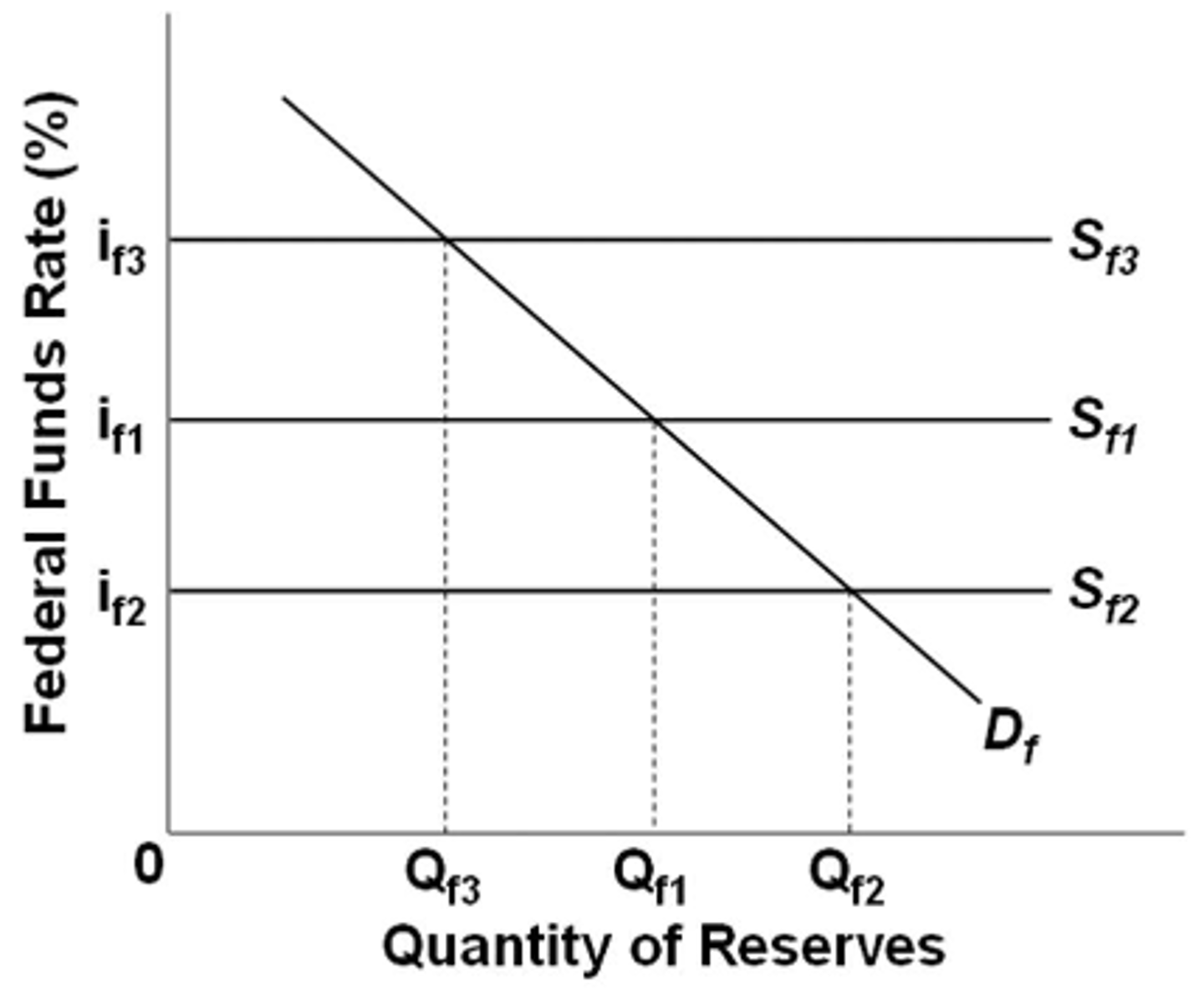
An expansionary monetary policy is one that reduces the supply of money.
false
Refer to the graph above. If the supply of money was $200 billion, the interest rate would be:
2 percent
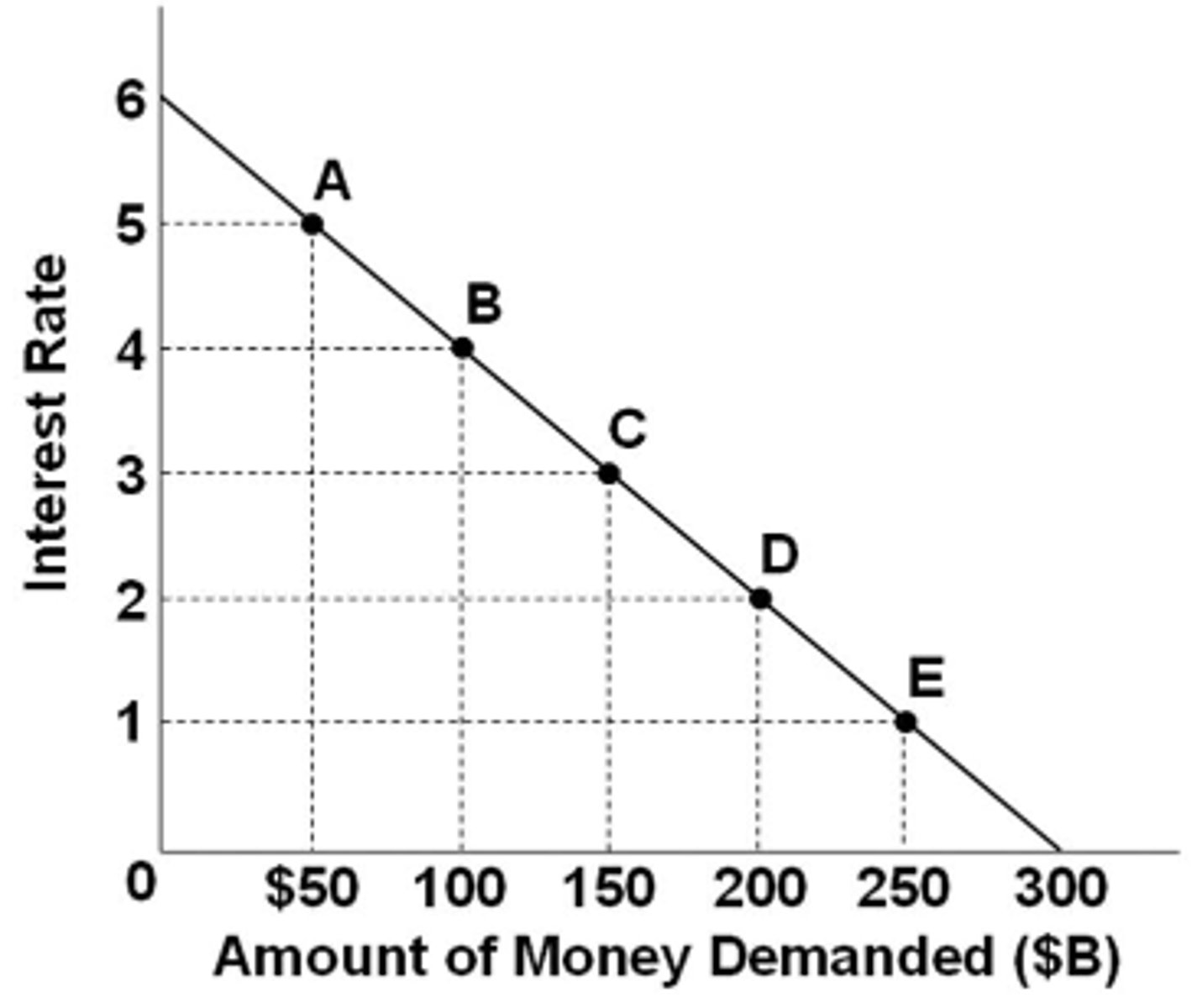
Monetary policy is expected to have its greatest impact on:
Ig.
A commercial bank can add to its actual reserves by:
borrowing from a Federal Reserve Bank.
The federal funds rate target is the most frequently used monetary policy tool.
false
A consumer holds money to meet spending needs. This would be an example of the:
Transactions demand for money
A decrease in the reserve ratio increases the:
amount of excess reserves in the banking system.
A change in the reserve ratio will affect both the amount of the banking system's excess reserves and the multiple by which the system can lend on the basis of excess reserves.
true
An increase in the money supply will:
lower interest rates and increase the equilibrium GDP.
A wealthy executive is holding money, waiting for a good time to invest in the stock market. This action would be an example of the:
Asset demand for money
Refer to the graph above, in which Dt is the transactions demand for money, Dm is the total demand for money, and Sm is the supply of money. The market is initially in equilibrium at a 6 percent interest rate. If the money supply increases, then Sm2 will shift to:
Sm3 and the interest rate will be 4 percent
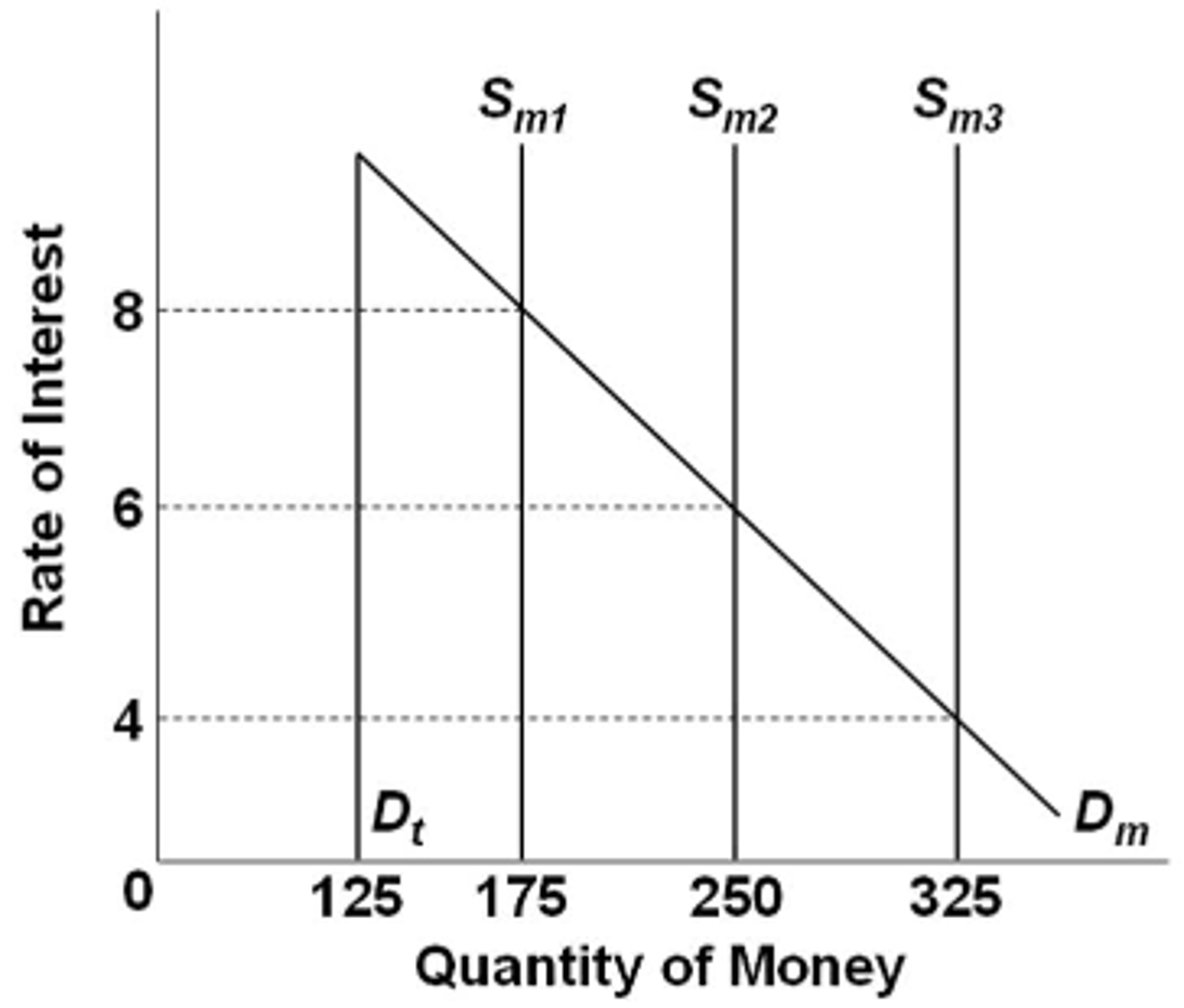
A restrictive monetary policy is designed to shift the:
aggregate demand curve leftward.
A newspaper headline reads: "Fed Raises Discount Rate for Third Time This Year." This headline indicates that the Federal Reserve is most likely trying to:
Reduce inflationary pressures in the economy
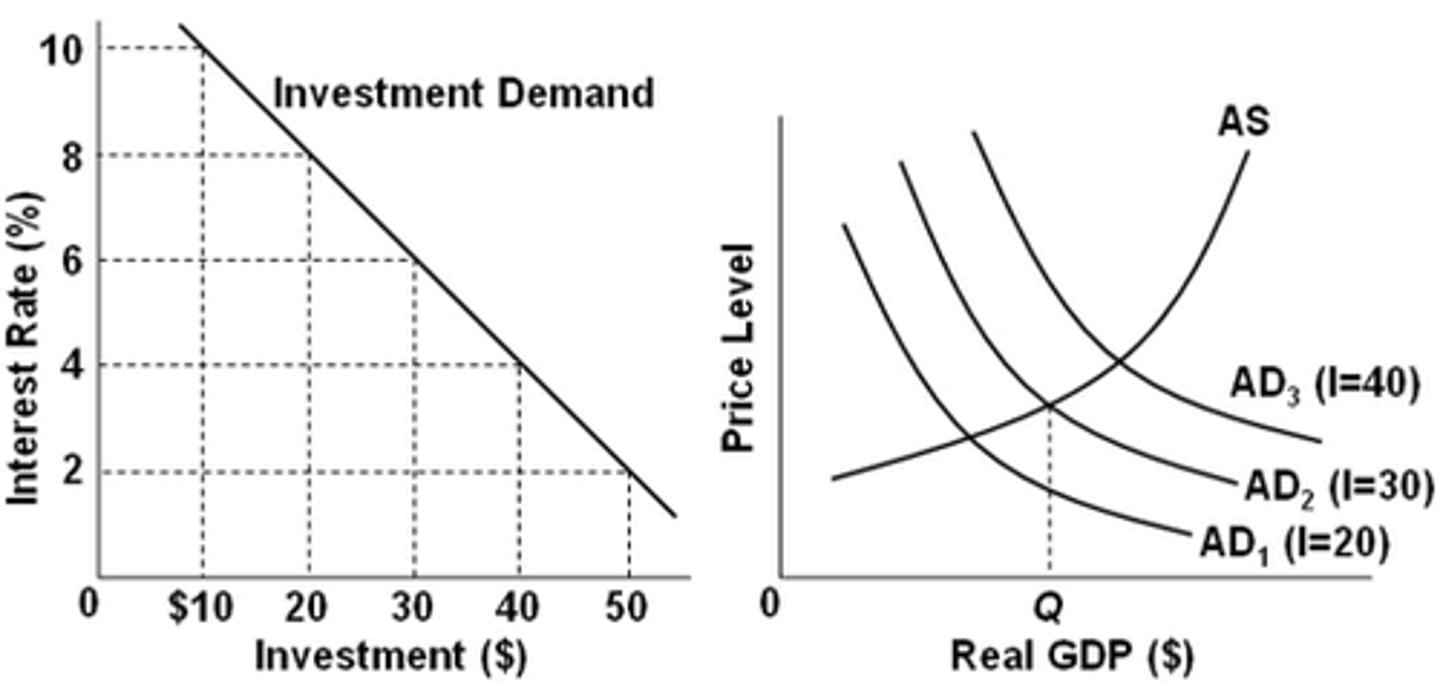
Refer to the diagrams. The numbers in parentheses after the AD1, AD2, and AD3, labels indicate the levels of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. If the interest rate is 8 percent and the goal of the Fed is full-employment output of Qf, it should:
decrease the interest rate from 8 percent to 6 percent.