Bio Chapter 2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Element
found in all materials of nature, only has one type of atom
atoms
basic unit of matter, contains Protons (+), Neutrons, (neutral), and Electrons (-)
Valence shell
outer most shell
The ___ the electrons are, the ___ ____ it has
father, more energy
the max amount an electron can have on the first shell is
2
the max amount an electron can have on the outer shells are
8
True or False: Can only fill next shell when shells are all full (either 2 or 8)
True
molecule
2 or more atoms linked by chemical bonds
singe bond
2 E shared
double bond
4 E shared
triple bond
6 E shared
nonpolar covalent
when atoms equally share their electrons with same electronegative atoms (methane/CH4)
polar covalent
when atoms unequally share electrons with atoms with different electronegativities (H2O; O is partially neg bc E is drawn to it and H is partially positive bc E is far away)
Oxygen is very ___, which means _____
Electronegative, electrons are attracted to it
Ionic bonds
Strongest bond. atom donates/gains E because electronegativites are very different. When one atom donates an E it has a cation (pos) charge and the other one, with an E now, has a anion (neg) charge
Hydrogen bond
weakest bond. partially positive hydrogen atoms interact with partially negative atoms of a different molecule. constantly breaking and reforming.
Hydrophobic
molecules that hate water (oil)
Hydrophilic
molecules that love water (salt)
pH scale
0-14
in pH scale, 0-6 is ____
acidic
in pH scale, 8-14 is ____
basic
in pH scale, 7 is ____
neutral
Dehydration synthesis
removing water to create bonds, adding ATP Energy
Hydrolysis
adding water to break bond
Cohesion
hydrogen bond ONLY between water molecules (water droplets)
Adhesion
Hydrogen bond between water molecules and other atoms
Hydrogen bonds ___ when temp ____
break, changes
4 Major chemicals
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen
functional groups
amino, carboxyl, carbonyl, hydroxyl, methyl, phosphate
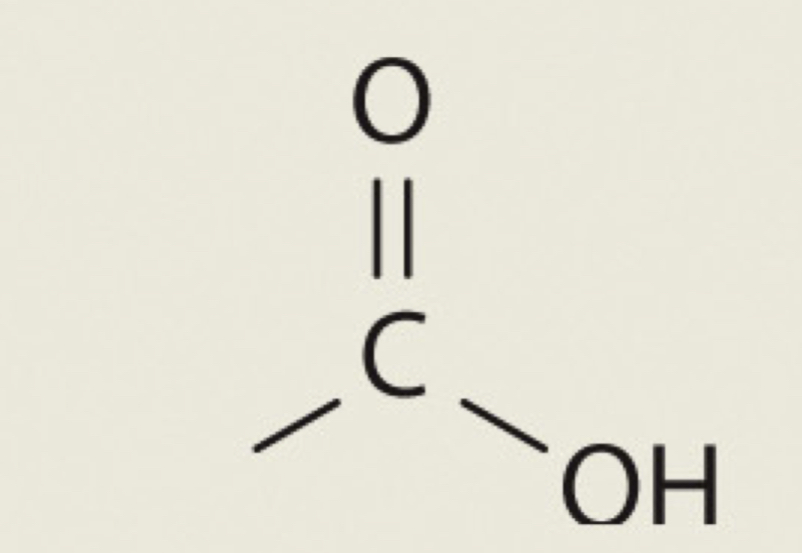
Carboxyl
COOH
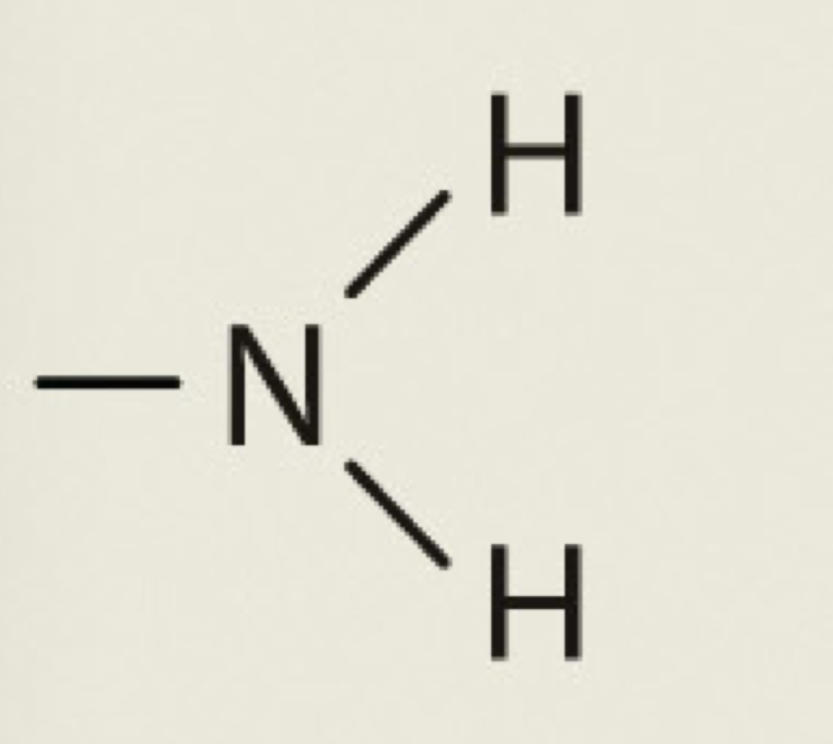
Amino
NH2
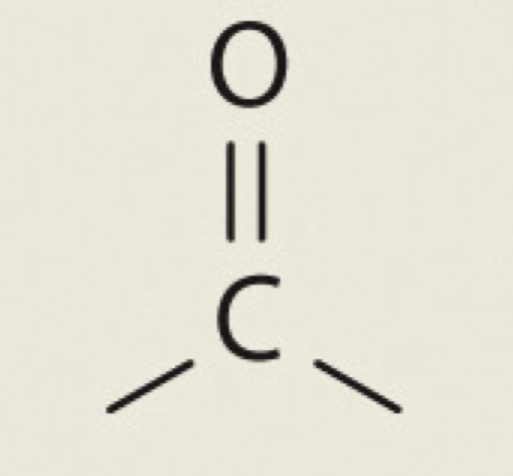
Carbonyl
C=0
Hydroxyl
OH
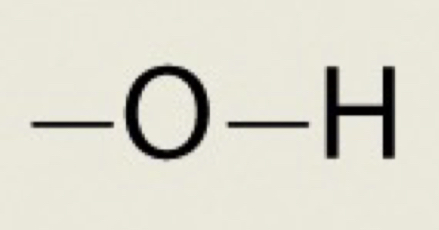
Methyl
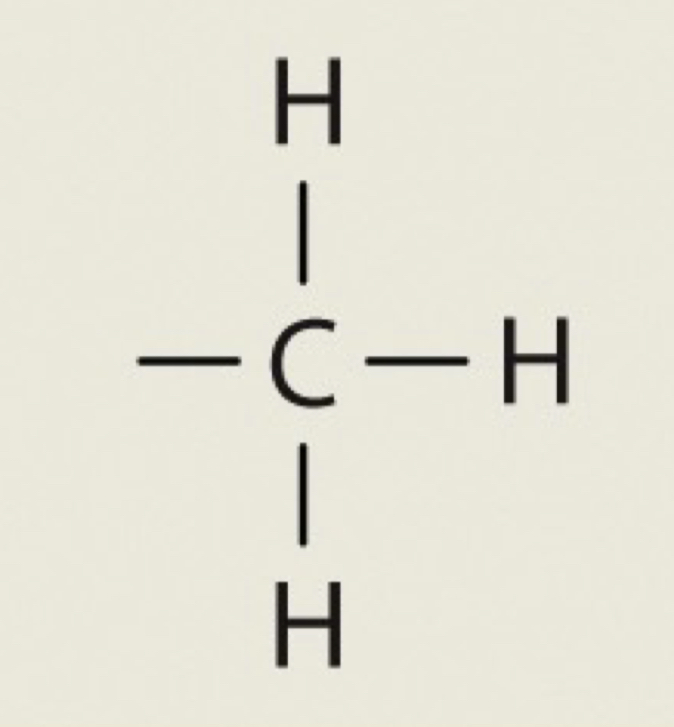
CH3
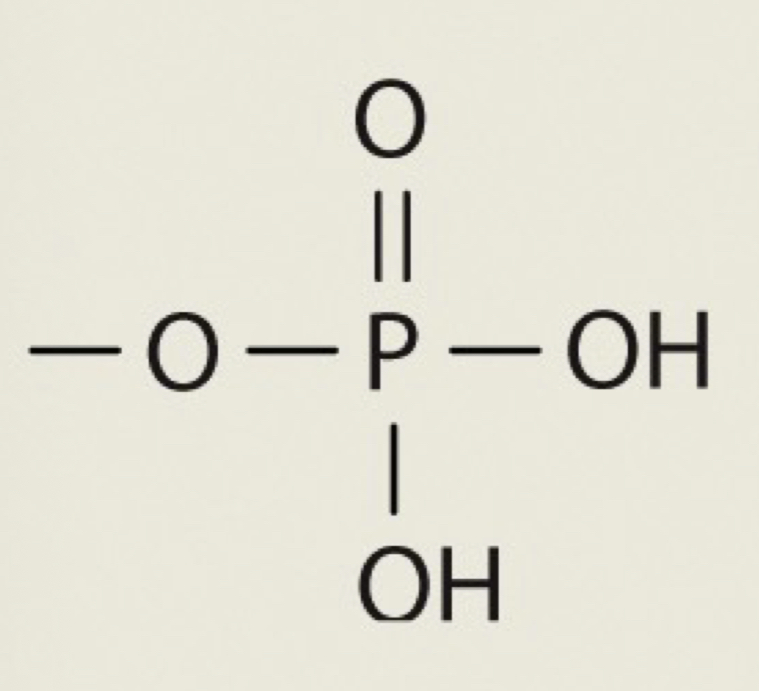
Phosphate
OPO3H2
organic molecules
proteins, nucleic acid, lipids, carbohydrates
proteins (polypeptides)
does most work, catalysts for chemical reactions, structural support
protein is a ____ formed by amino acid monomers liked by ____
polymer, peptides
Nucleic Acid
encodes and transmits genetic info (DNA)
nucleic acid is a ____ and is made of _____
Polymer, phosphate bonds
Nuclei acids are polymers, and their monomers are_____ and are linked together with _____
Nucleotides , phosphodiester bonds
DNA
double helix, thymine, adeline, guamine
RNA
single strand, uracil, guamine, adeine
pyrmide
1 ring, CTU
Purine
2 rings, G, A
Carbohydrates
structural support, provides energy
carb is a ___ and its monomer is a _____, linked with ______
polymer, monosaccharide, glycosidic bonds
Monosaccharide formula
Cn H2n On
Lipids
make up cell membrane, store energy, help with communication in the cell
Lipids are ___ a _____ and are _____
not, polymer, hydrophobic
3 types of lipids
Triglycerides, steroids, phospholipids
Triglycerides contain
glycerol and fatty acids
fatty acids in TG
long chain of carbon with carboxyl (COOH) group at the end
Saturated FA
single bond carbon, max # of hydrogens, solid at room temperature, straight structure (eg is butter)
Unsaturated FA
double bond carbon, less max # hydrogen, bent structure, liquid at room temperature (eg olive oil)
Steroids
4 rings, eg cholesterol
Cholestorl is ____ which is
amphipatic, when hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules are in structure tg
nonpolar molecules are
hydrophobic
polar molecules are
hydrophilic
phospholipids
make up the cell membrane, spontaneously form liposomes in water
polar head is ___ so its ___
hydrophilic, facing the outside
nonpolar tail is ____ so its____
hydrophobic, facing the inside