Chapter 7 Nervous system
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Objectives - Spell and define, using the glossary, all the Words to Know in this chapter. Apply medical terminology for the neurological system. Describe the purpose of the autonomic nervous system. Describe the normal function of the neurological system. List the major organs in the neurological system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The Central nervous system consists of what
the brain and the spinal cord
What does the Peripheral nervous system consist of
the nerves that connect the CNS to every organ and the area around the body
this also consists of the autonomic nervous system
What is the Autonomic nervous system?>
• Specialized part of the peripheral system and controls internal organs and other self-regulating body functions
In the nervous system the basic function unit is?
a nerve cell or neuron
What are the three types of neurons in nerve tissue
Sensory neuron
Internuncial neurons
Motor neurons
define Senrory neuron
Nerves that receive and transmit stimuli from the sense organs.
define internuncial neurons
connecting neuron in a neural pathway, usually serving as a link between two other neurons.
define motor neuron
nerves that permit the body to respond to stimuli.
All nerve cells have what?
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
cell membrane
define Nissl bodies
the function of these?
Scattered throughout the cytoplasm are little microscopic granular “dots”
Protein synthesis and metabolism.
The cell body has processes that are extensions of cytoplasm called what two things?
dendrites and axons.
define dendrites
an extension from a nerve cell.

define axons
an extension from a nerve cell.
A nerve is composed of bundles of nerve fibers bound together by what kind of tissue
Connective tissue
define sensory or afferent nerve
nerve is composed of fibers going from the sense organs to the spinal cord or brain
define motor or efferent nerve
carrying impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle, organ, or gland,
define membrane excitability
Nerves carry impulses by creating electric charges
define action potential
When a neuron is stimulated, ions move across the membrane, creating a current that, if large enough, will briefly change the area inside of the neuron to be more positive than the outside area.
define synapse
the minute space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes how many pairs and what type of nerve?
What organs do they connect to ?
12 pairs of cranial nerves
the brain directly to the sense organs
(eye, ear, tongue, nose, and skin), the heart, the lungs,
The peripheral system also includes how many pairs of what nerves
31 pairs of spinal nerves.
define neurotransmitters
impulses that release chemicals that either speed up or slow down the transmission
define interneurons
neurons connecting sensory to motor neurons.
define ganglion
a mass of nerve tissue that receives and sends out nerve impulses.
What is the Autonomic Nervous system consist of
Nerves, ganglia and Plexuses
define plexuses
a network of nerves.
What are the two divisions of the autonomic system called?
The sympathetic division
and
the parasympathetic division
Are nerves in the autonomic nervous system involuntary or voluntary? What do they control?
These nerves are involuntary and control
unconsciously control breathing, heartbeat, and digestion
the parasympathetic nerves dilate the —————— and slow down the ————-.
blood vessels
heartbeat
The sympathetic division accelerates activity in the?
the smooth, involuntary muscles of the body’s organs,
The parasympathetic system has two important nerves, which are
the vagus and the pelvic nerve.
Within the sympathetic nervous system what are the two tracts consist of?
Nerve fibers and ganglia
Where is the pelvic nerve
The pelvic nerve exits the spinal cord around the hip area and branches into the lower abdominal and pelvic organs.
Where is the vagus?
extends from the medulla oblongata of the brain and branches to the neck, chest, and upper abdominal organs.
Both the sympathetic and parasympathetic are strongly affected by what emotions?
fear, anger, and stress.
The brain is protected and supported by surrounding membranes known as
meninges
the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
The elevated ridges between the sulci are called
convolutions.
The cerebral surface is covered with ridges and furrows known as
fissures
What does the cerebrum controll
Controls sensory and motor activities
Where is the frontal lobel located?
what is the function of the frontal lobe?
behind the forehead
related to emotions, personality, moral traits, and intellectual functions
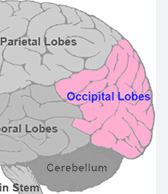
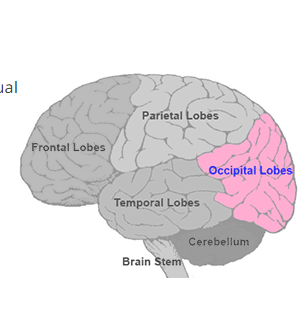
where is the occipital lobe?
function?
far back portion of the cerebrum
associated with vision
transmitted by the optic nerve fibers to the occipital lobe for interpretation
Where is the parietal lobe
function?
Between the frontal and occipital lobes
Receives impulses from receptors in the hands, feet, and tongue, among others, and sends impulses that cause movement in all these parts in response.
• where is the Cerebellum found what is the function?
Found beneath the cerebrum;
responsible for smooth muscle movement, muscle tone, and coordination of sensory impulses
Where is the brain stem
Lying in front of and below the cerebellum, and connecting the brain to the spinal cord, this is the brain stem
What are the three sections that make up the brain stem?
the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain.
define medulla oblongata
what is the function
• Adjoins the spinal cord;
influences the function of the heart and lungs, stomach secretions, and size of the openings in blood vessels
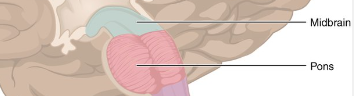
define pons
what is the function
- located just above the medulla
helps to regulate breathing. It is the reflex center for chewing, tasting, and secreting saliva.
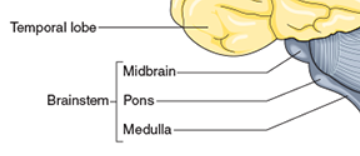
define Midbrain
what is the function
located superior to the pons;
control center for reflex movements and pupil dilation of the eyes
Define Thalamus
what is the function
- located between the cerebrum and the midbrain
•acts as a relay station for impulses going to and from the brain
Define Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus lies below the thalamus and is connected to the pituitary gland, midbrain, and thalamus by a bundle of nerve fibers.
What is the function of the Hypothalamus
Controlling the autonomic nervous system
Controlling blood pressure by regulating the heartbeat and blood vessel constriction and dilation
Maintaining body temperature
Stimulating the production of an antidiuretic hormone to conserve water in the body and to cause thirst to maintain normal water balance
Assisting in the regulation of appetite
Increasing secretions and motility in the intestinal tract
Playing a role in emotions such as fear and pleasure
Helping maintain wakefulness when it is necessary
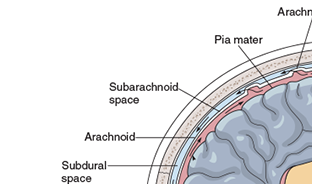
What are Meninges
the coverings on the brain and the spinal cord; made up of 3 layers
What are the three layers that make up Meninges
Pia mater
Arachnoid
Dura Mater
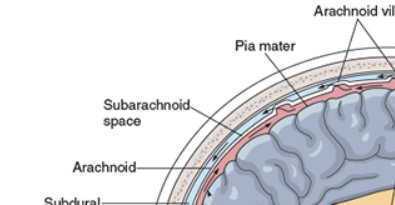
define Pia mater
inner layer contains nerve tissue
define Arachnoid
middle layer made of delicate, lacelike membranes
Define Dura mater
outer layer that protects CNS from damage from contact with bony surfaces of the skull and spine
define subdural
The space between the dura mater and the arachnoid
Define subarachnoid
pace is between the arachnoid and the pia mater.
Define Ventricles
- spaces or cavities within the brain
What is the function of Ventricles
Come back
define Cerebrospinal Fluid
• Acts as a watery cushion or shock absorber to provide additional protection for the CNS
What is the function of Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
•Transports nutrients, primarily proteins and carbohydrates, to the brain and spinal cord
How much is CSF formed within the brain?
• Formed continuously within the ventricles of the brain at the rate of 450 mL (15 oz) per day
Define Arteriography (cerebral angiography)
A catheter is inserted into an artery and then threaded up to the carotid artery in the neck
A dye is injected through the catheter to show the cerebral blood vessels when X-rays are taken
What is the function / purpose of a Arteriography
This test can detect an aneurysm, hemorrhage, evidence of a cerebrovascular accident, (stroke) arteriosclerosis, and a tumor.
define Glasgow coma scale (GCS)
is an assessment tool used to describe the level of consciousness
What is the function or purpose of Glasgow coma scale (GCS)
The scale assesses three things: eye movement, verbal response, and motor response.
The scale is based on the need for more stimulation to induce a response in the patient.
define Computerized axial tomography (CAT or CT scan)
A series of X-rays of layers of the brain to construct a three-dimensional picture.
What is the purpose of Computerized axial tomography (CAT or CT scan)
It is useful for identifying tumors, bleeding, blood clots, decrease in brain size, and brain edema.
define what is a Electroencephalography (EEG)
A brain wave test that measures the brain’s electrical signals, both normal and abnormal.
Purpose of a Electroencephalography (EEG)
•Can detect abnormalities caused by epilepsy, a tumor, stroke, head injury, or infection
•Can document sleep disorders
define Electromyography (EMG)
• Uses electrical stimulation passed through small needles inserted into the muscle to demonstrate the electrical activity of peripheral muscles
purpose of Electromyography (EMG)
diagnose disorders such as diabetic neuropathy and carpal tunnel syndrome
define Genetic testing or counseling
•Performed to help patients who have a family history of a neurological disease determine if they are carrying one of the known genes that cause the disorder
purpose of Genetic testing or counseling
•Can detect many neurological disorders, including spina bifida while child is in mother’s womb
define Lumbar puncture
• A spinal needle is inserted into a small space in the lower back to remove small amounts of cerebrospinal fluid
purpose of Lumbar Puncture
• Can help diagnose bleeding or infection and can measure fluid pressure in the spine
Define Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
•Uses powerful magnets to generate pictures
When images of the brain and spine are needed, MRI is the method of choice as long as the patient has no ferrous (iron) metal implants or pacemakers
Purpose of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
• Can image from numerous angles, and it imparts no radiation
Define •Myelography
• Imaging examination that involves the introduction of a spinal needle into the spinal canal and the injection of contrast material in the space around the spinal cord and nerve roots (the subarachnoid space) using a real-time form of X-ray called fluoroscopy
purpose of Myelography
•Shows irregularities or compression of the spinal cord
define •Positron emission tomography (PET scan)
•Uses agents, such as glucose or hormones; agents are mixed with chemicals and injected into the blood; records images of where the material ends up in the body
Purpose of Positron emission tomography (PET scan)
• Can help diagnose epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease
Define ultrasound imaging
•X-rays of the patient’s chest and skull are often taken as part of a neurological work-up.
•Can be used to view any part of the body, such as a joint or major organ system
Purpose of ultrasound imaging
• Can identify fractures and abnormal bone structures that may indicate a tumor or increased pressure within the skull
Define X-rays
•X-rays of the patient’s chest and skull are often taken as part of a neurological work-up.
•Can be used to view any part of the body, such as a joint or major organ system
Purpose of X-rays
•Can identify fractures and abnormal bone structures that may indicate a tumor or increased pressure within the skull
What is Alzheimer’s disease
A progressive, degenerative disease that attacks the brain and results in impaired memory, thinking, and behavior.
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease
gradual memory loss,
decline in ability to perform routine tasks
impairment of judgment
disorientation
personality change, .
difficulty in learning,
and loss of language skills.
What is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
progressive, fatal neurologic disease that causes degeneration of motor neurons of the brain and spinal cord.
What age group does ALS affect
ages 40 to 60
What are the symptoms of ALS
(slow and unnoticed) with muscle weakness or stiffness
Muscle atrophy
difficulties with speech, chewing and swallowing
What is the other name for ALS
•Lou Gehrig’s Disease
What is Bell’s Palsy
disease affects the seventh cranial nerve of the face. It occurs suddenly and will usually spontaneously subside within one to nine weeks.
What are the symptoms of Bell’s Palsy
weakness or paralysis on one side of the face,
causes the mouth to droop on the affected side
distorted sense of taste and not being being able to close eye
What is the treatment for Bell’s Palsy
Early treatment with steroids and an antiviral medication, such as valacyclovir (Valtrex)
what is cerebral palsy
nonprogressive brain injury that occurs during fetal development, perinatally, or in early infancy
what are the 4 forms of cerebral palsy
There are four forms of the disorder: spastic (80 percent of the cases), dyskinetic, ataxic, and mixed.
Symptoms for Cerebral Palsy
hyperactive tendon reflexes,
rapid alteration between muscular contraction and relaxation,
contracture tendency (permanent muscle shortening),
underdevelopment of the affected extremities.