Chapter 16 SG
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Spinal nerves functions:
-Pathway for sensory and motor impulses
-Responsible for reflexes (quickest)
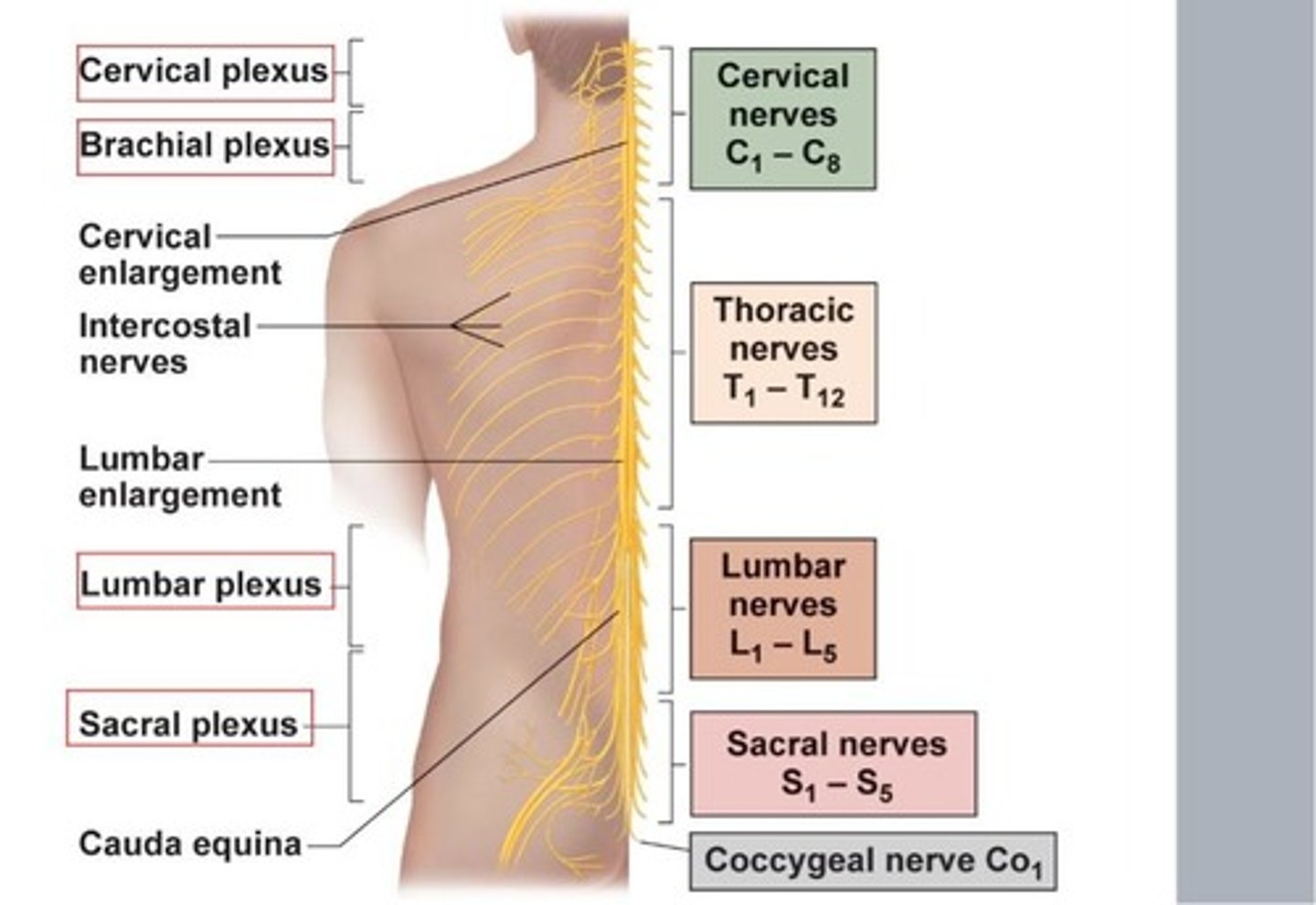
Parts of Spinal cord:
-Cervical part (nerves C1-C8)
-Thoracic part (nerves T1-T12)
-Lumbar part (nerves L1-L5)
-Sacral part (nerves S1-S5)
-Coccygeal part (nerve Co1)
Spinal Cord characteristics:
-Extends from Foramen magnum to L1 vertebra
-The inferior end (conus medullaris)
-Cervical enlargement is at inferior cervical part
-Lumbosacral enlargement through lumbar, sacral parts to lower limbs
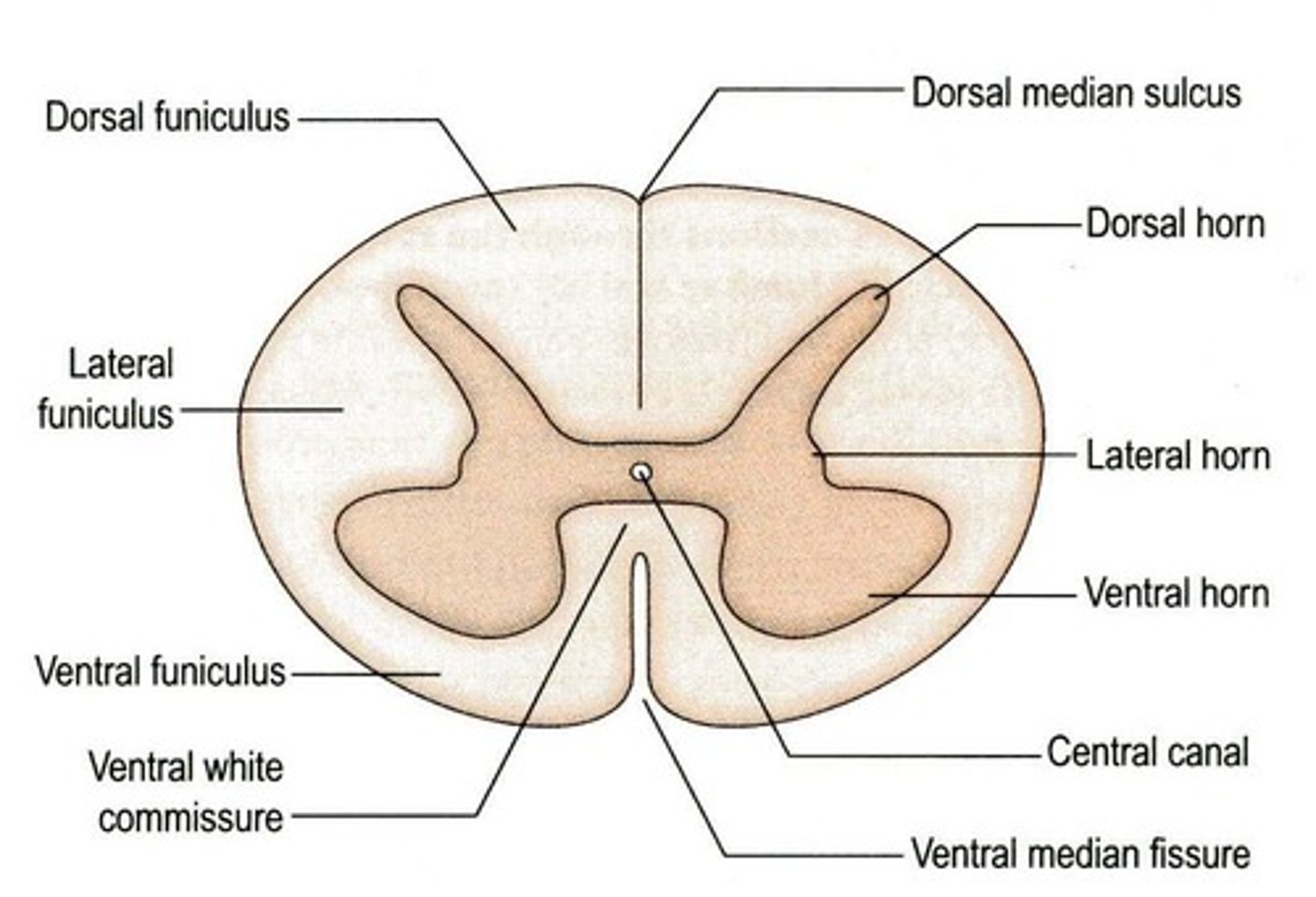
Spinal cord features
External depressions
-Posterior median sulcus
-Anterior median fissure
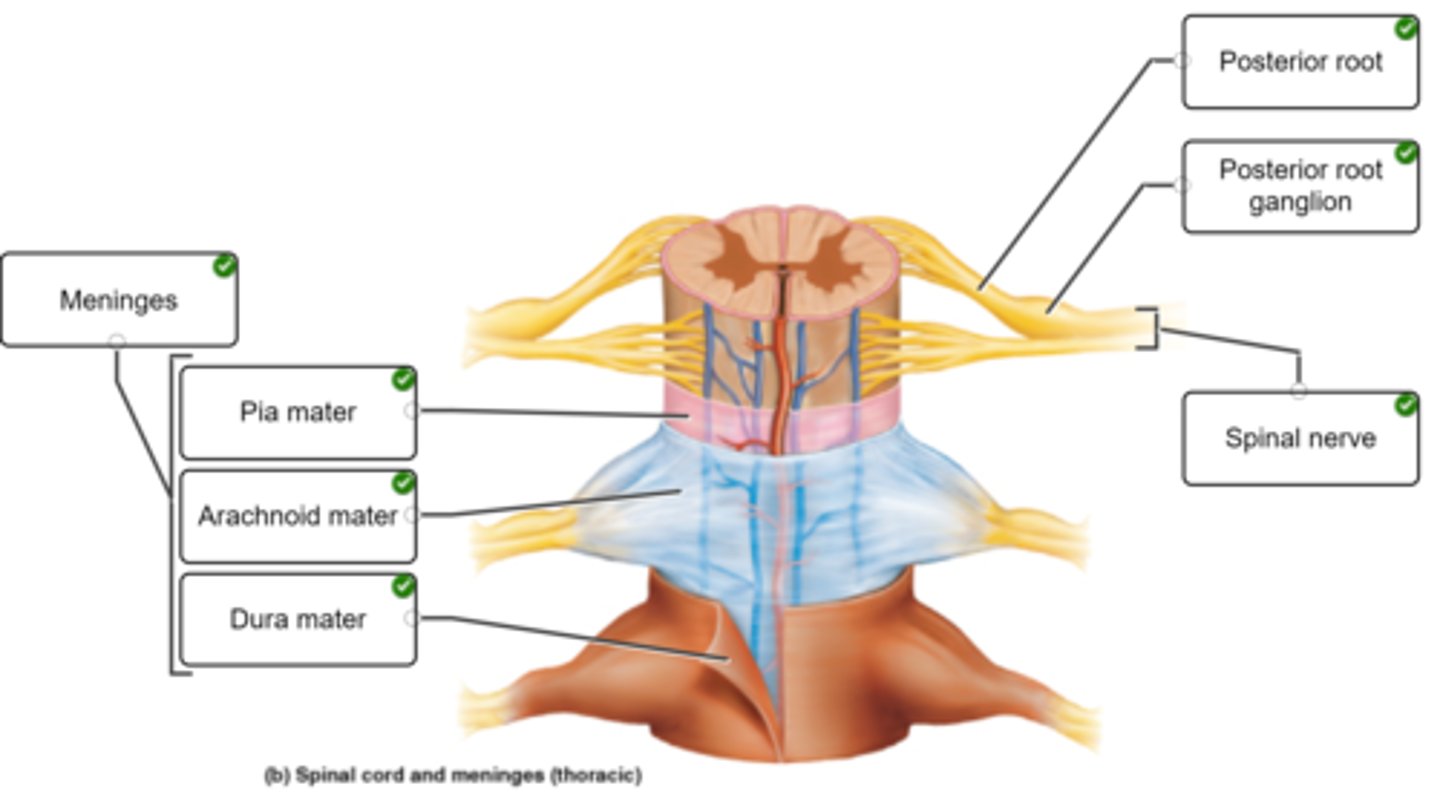
Spinal cord meninges:
dura , arachnoid, pia mater
-Epidural Space between dura & periosteum of vertebra
-Dura mater single layer around
-Subarachnoid space filled w/CSF
-Pia mater has Denticulate ligaments suspend and anchor cord
Gray Matter of spinal cord
-Most inner
-Resembles butterfly
-Dendrites, cell body, glial cells, unmyelinated
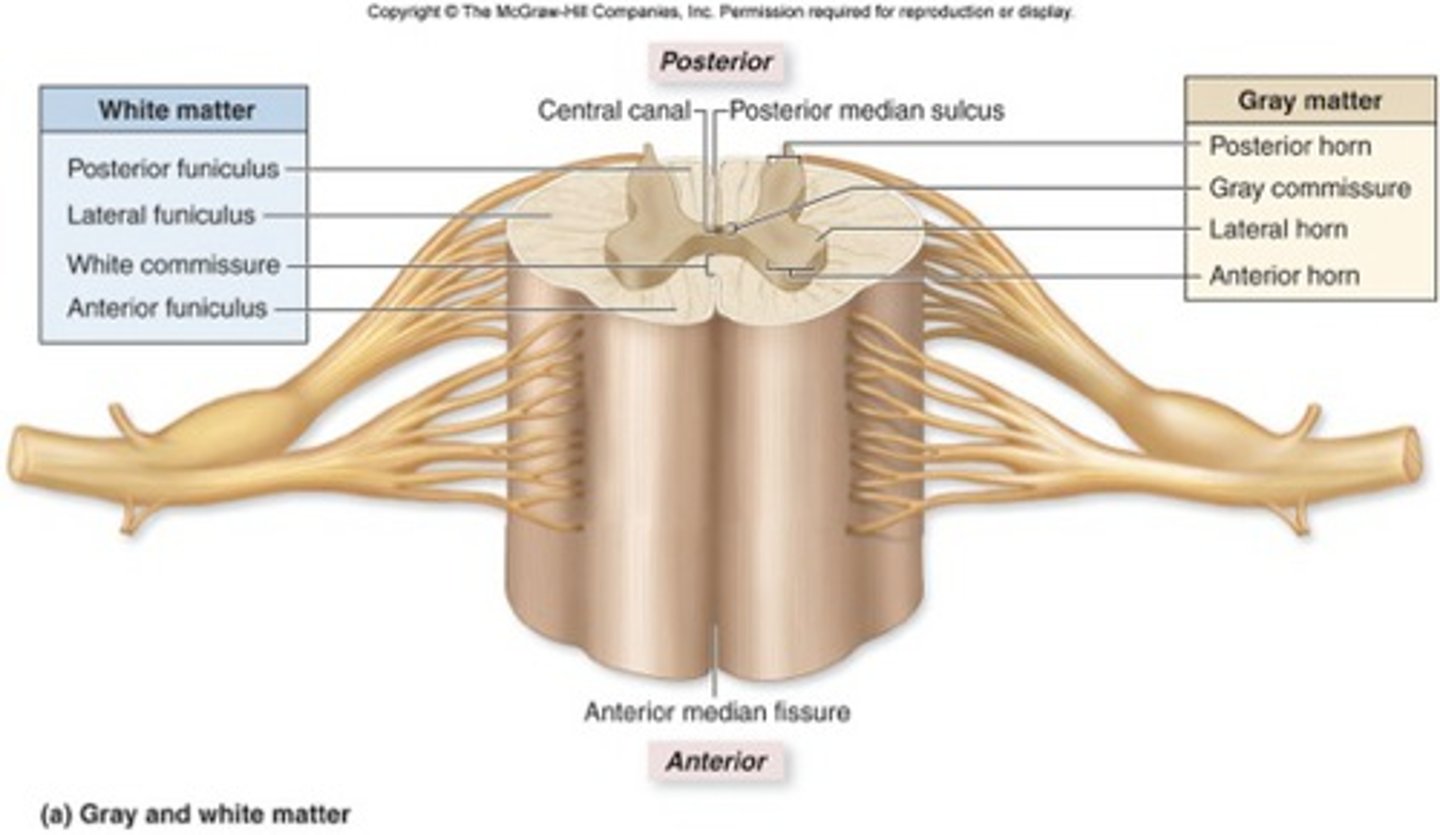
Gray Matter subdivided:
-Anterior horns: somas of somatic motor neurons
-Lateral horns: somas of autonomic motor neurons (T1-L2)
-Posterior horns: axons of sensory N., body of interneurons
-Gray commissure: communication of unmyelinated
White Matter of spinal cord
Outer layer
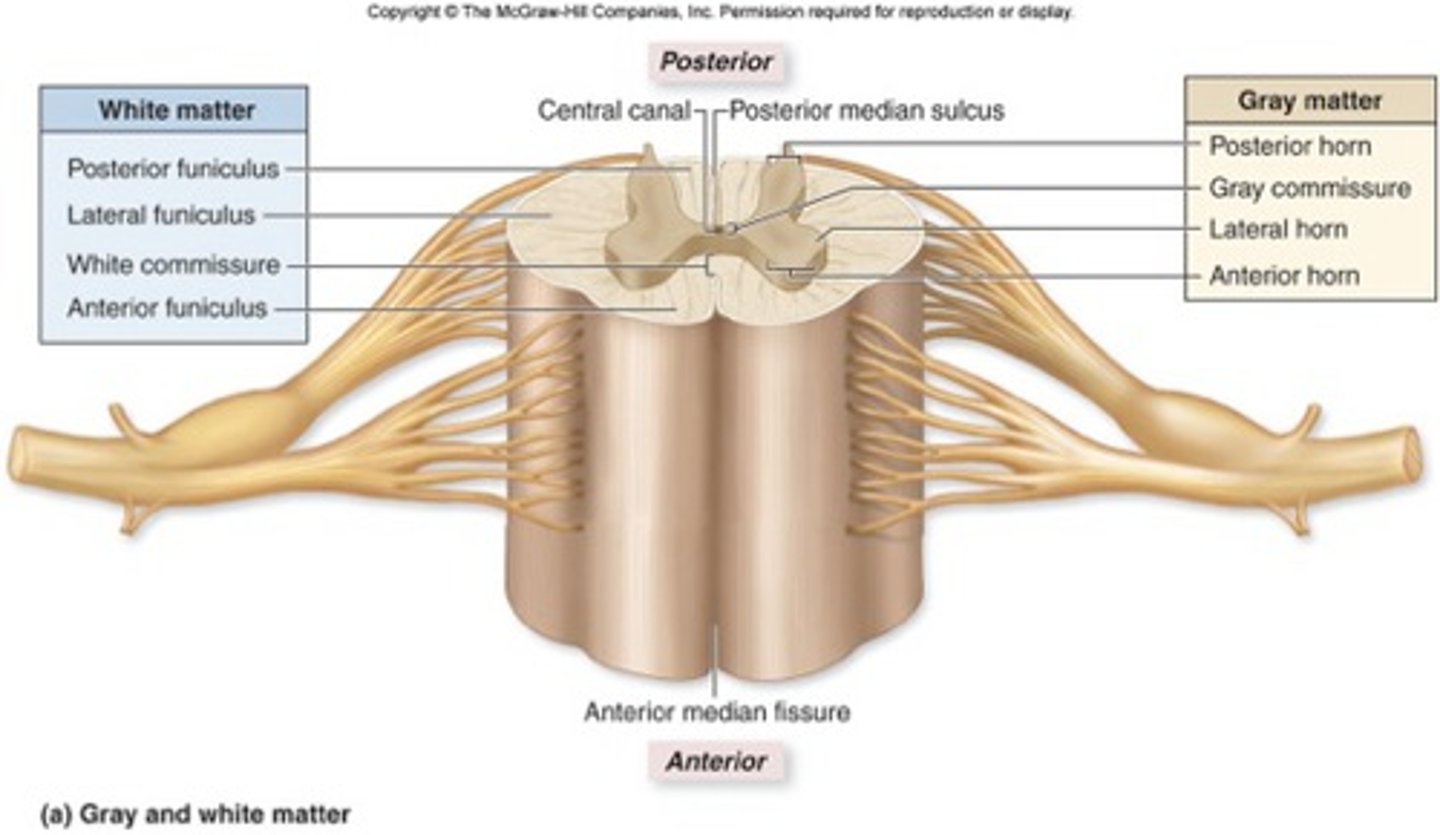
Three regions of white matter
-Posterior funiculus
-Lateral funiculus
-Anterior funiculus
Spinal Nerves characteristics:
- 31 pairs of nerves
-Motor and sensory axons
-Wrapping: Endoneurium, Perineurium, Epineurium
Rootlets(2):
-Multiple anterior rootlets: ONLY motor axons, arise from anterior cell bodies and lateral horns of spinal cord, anterior root
-Multiple posterior rootlets: ONLY sensory axons, arise poster root ganglion (attached to posterior root)
*both unites at intervertebral foramen to become a Spinal Nerve
How are nerves numbered?
By location of their EXIT intervertebral foramen
What is a Plexuses?
it is a large anterior branches of spinal nerves that interlace to form networks.
Major Nerve Plexuses:
-Cervical
-Brachial
-Lumbar
-Sacral
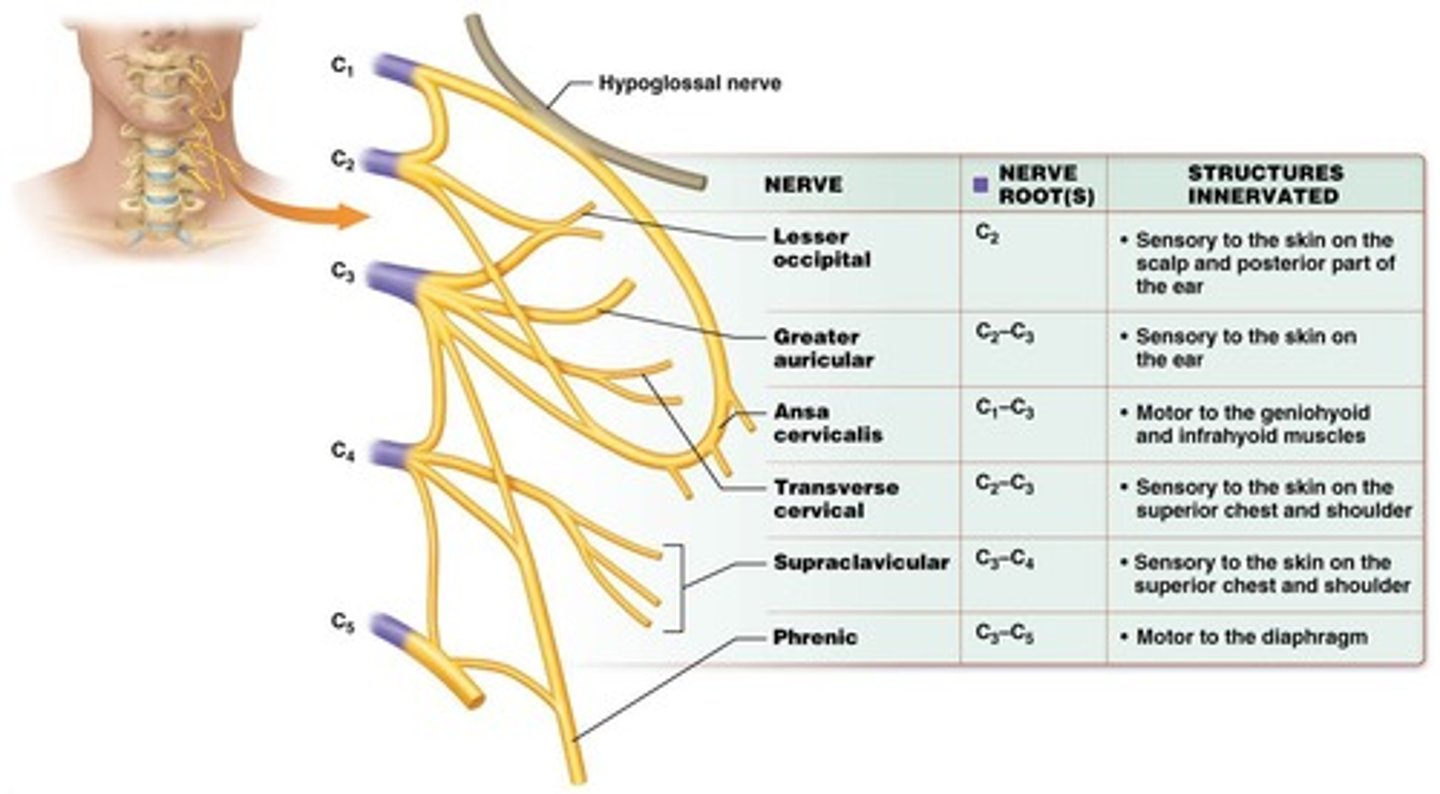
Cervical plexuses
-Formed by anterior rami SN C1-C4
-Innervate anterior neck, skin on neck, some head/shoulders
-Phrenic nerve primarily from C4 through thoracic cavity to innervate diaphragm
Brachial plexuses
-Formed by anterior rami SN C5-T1
-C5-T1 the roots for brachial plexus
-Innervate left/right for upper limbs and pectoral girdle
Root of Brachial Plexus:
Unites to form:
-Superior trunk (nerves C5-C6)
-Middle trunk (nerve C7)
-Inferior trunk (nerves C8-T1)
*each divided to anterior/posterior division
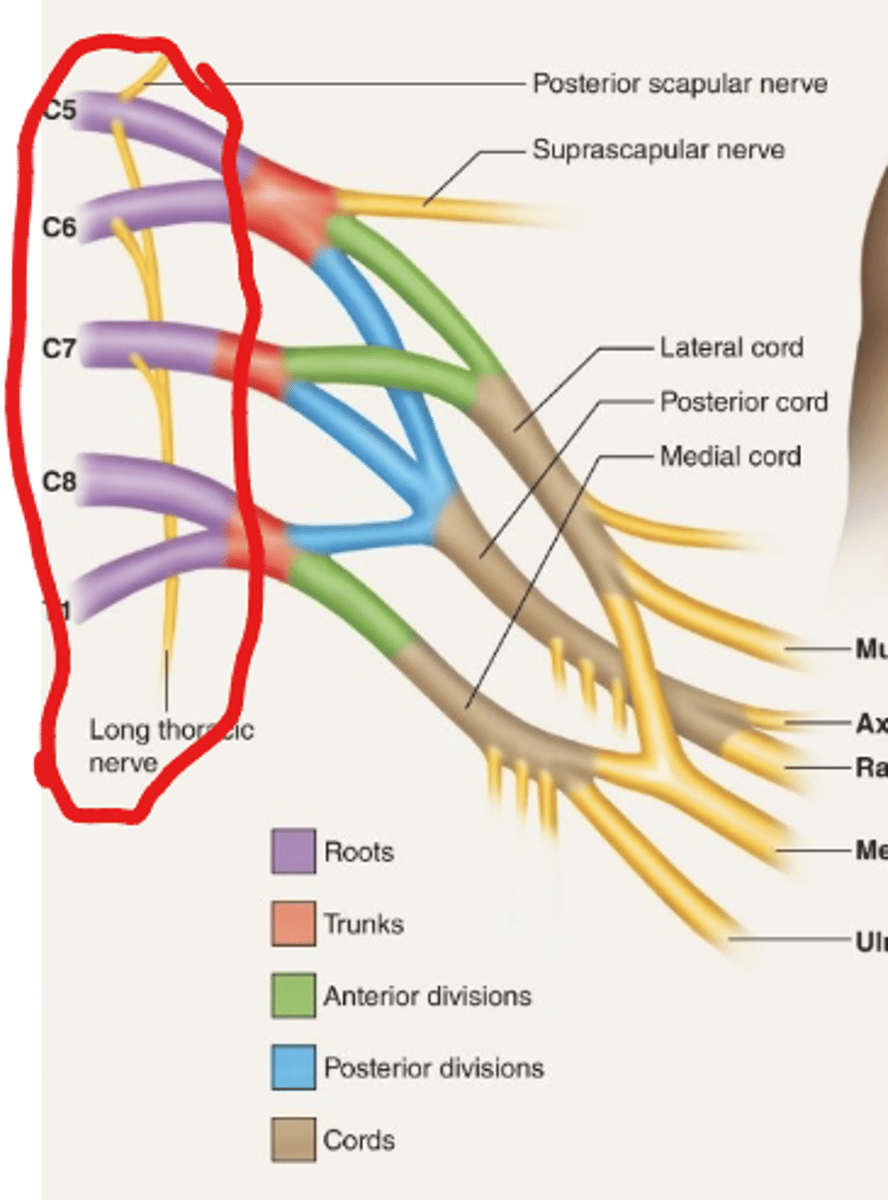
The three cords from anterior-posterior division (brachial plexuses)
1.Posterior cord
2.Medial cord
3.Lateral cord
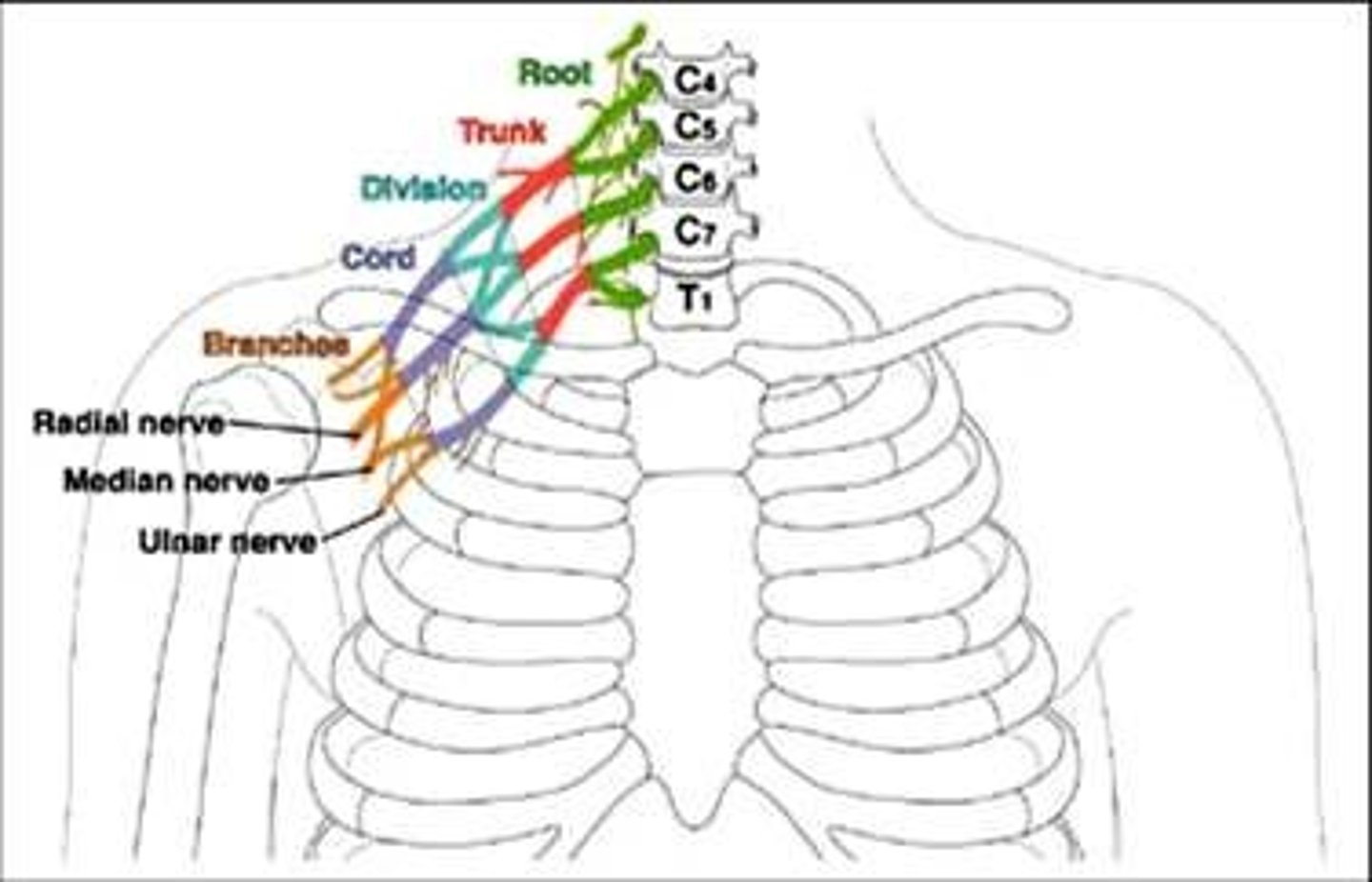
Five terminal branches from three roots (brachial Plexuses)
1. Axillary nerve
2. Median nerve
3. Musculocutaneous nerve
4. Radial nerve
5. Ulnar nerve
Lumbar plexuses
-Formed from the anterior rami SN L1-L4
-Posterior division Femoral nerve (main)
-Anterior division Obturator nerve (main)
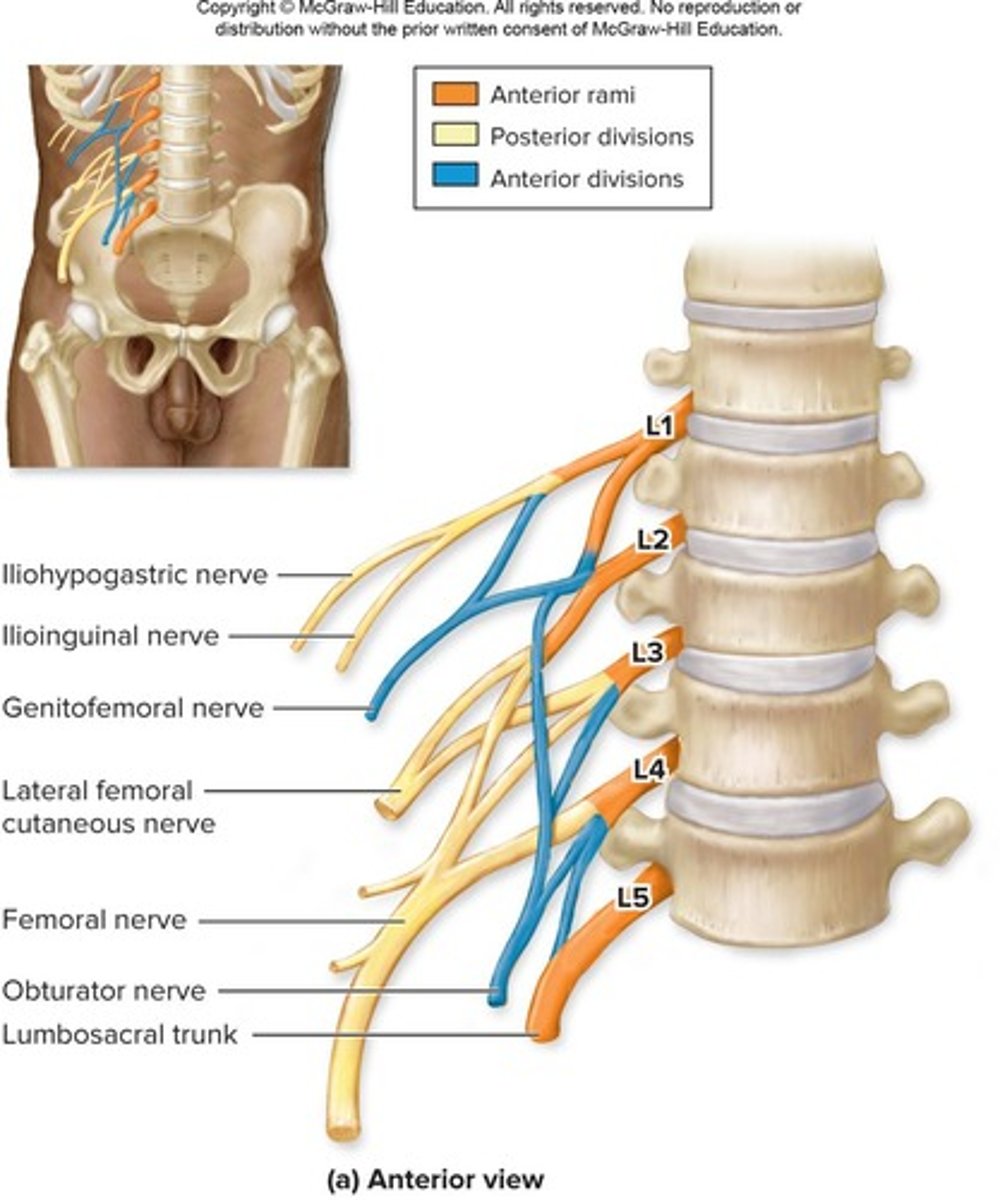
Sacral plexuses
-Formed from anterior rami SN L4-S4
-Sciatic nerve largest and longest in body
-Anterior/Posterior division
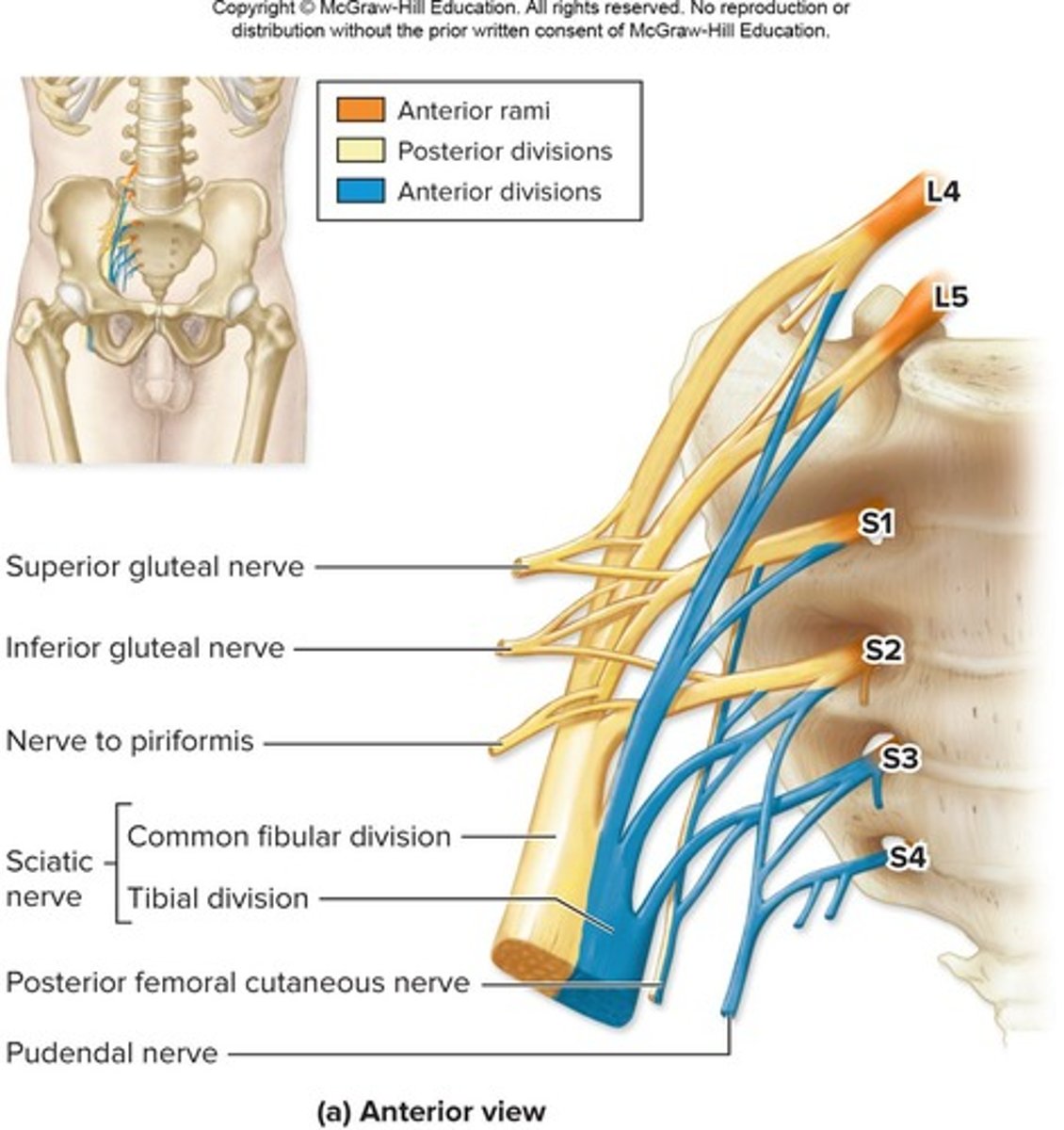
Divisions (sciatic) of sacral plexuses
-Tibial nerve
-Common fibular nerve (deep/superficial part)
What is a Dermatome?
an area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
Damaged dermatome examples:
Anesthesia- specific spinal nerve damage
Shingles- rash and blisters
Reflex Properties:
-Require stimulus
-Rapid response
-Preprogramed response
-Involuntary response
What is a Reflex Arc?
The neutral circuit of a reflex
Reflex Arc five steps:
1. receptor
2. sensory neuron
3. integration center
4. motor neuron
5. effector
Components of reflex arc:
-Ipsilateral
-Contralateral
-Monosynaptic (sometimes)
-Polysynaptic (sometimes)
Withdrawal Reflex
-Polysynaptic reflex arc
- initiated by painful stimulus
Stretch Reflex
-Monosynaptic reflex arc
-Receptors called (muscle spindles)
Tendon Reflex
-Golgi tendon organs (stretch receptors in a tendon)
-Respond to increased tension within tendons so muscle relaxes
-Protects muscles and tendon
What reflex testing can shows
-Hypoactive: response is diminished or absent
-Hyperactive: response is abnormally strong