AICE ENVIRONEMENTAL: UNIT 1
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Country classification, sustainability, water cycle, Atmosphere, ecosystems (Unit 1.2-1.6)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What is the GNI of low income countries that puts them in that category? Give an example
The countries with a GNI per capita of $1,145 or less.
Example: Chad, and Ethiopia.
What is the GNI of lower middle income countries that puts them in that category? Give an example
Countries with a GNI per capita of $1,146-$4,515
Example: Cuba
What is the GNI of higher middle income countries that puts them in that category? Give an example
Countries with a GNI per capita of $4,516-$14,005
Example: Mexico and Iraq
What is the GNI of high income countries that puts them in that category? Give an example
Countries with a GNI per capita above $14,005
Example: Germany and USA
What is GNI?
GNI, or Gross National Income, (per capita) is a measure of the total income of a country, divided by the number of people in that country.
What factors make a High Income Country?
Good, clean, water supply
stable government
Able to buy raw materials and then process it, into a more expensive product.
import costs less than export
Good trade
What factors make a low income country?
Income inequality
Climate change
Government conflict
Lack of access to basic healthcare
poor basic infrastructure
What is sustainability?
(Cambridge definition) Ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs.
When you use a resource from the environment such that it is replenished at the same rate you use it.
What are some renewable sources that need to be protected? What can communities do to conserve ecosystems and maintain the equilibrium?
Light, air, soil energy, atmosphere, forests, are all renewable sources that need to be protected.
Communities have to develop judicious land-use practices for both conserving the ecosystems, and enhance local economies as they maintain the equilibrium in the environment.
What was the Brandt line?
A line that divided the planet into the rich North, and poor South- However the world has changed a lot in the last 20 years, and is now too simplistic (outdated)
Example: China and India are no longer seen as poor countries.
What are the 14 rules of sustainability?
Save energy—> Reduce carbon Emission
Eat less meat
Use reusable alternatives—> less plastic pollution
Go paperless
Use renewable energy—> electronic cars
Recycle and Reuse
Grow your own fruit and vegetables
Donate unused items
Save Water
Buy fair trade products
Drive less
Don’t waste food
Wear sustainable clothing
Use eco-friendly, cleaning products
How does water change states?
By adding or removing heat energy.
Add Energy: think energy in
Remove Energy: think energy exits
Where does the energy come from?
This process is driven by the sun and it’s energy
What is the water cycle?
The continuous movement of water into the air, onto land, and back in the air, over and over again
What is condensation?
Water vapor in the air gets cold and changes back into liquid, forming clouds
What is precipitation?
Solid or liquid water that falls from the air to the surface.
Rain, Snow, sleet and hail
What is interception?
Part of the rainfall that is intercepted by the earth’s surface and which subsequently evaporates. The earth’s surface includes anything that becomes wet after a rainfall event and dry soon after.
What is Infiltration?
Process by which precipitation or water soaks into subsurface soils and moves into rocks through cracks and spore spaces.
Occurs in the upper layer of the ground, but may also continue further downwards into the water table
The ____ you are from a body of water, more absorption, the ____you are to a body of water the more the _____ there is.
The further you are from a body of water, more absorption.
The closer you are to a body of water, the more the surface runoff there is
What is transpiration?
The process by which plants lose water from their leaves.
Gives evaporation a bit of a hand in getting water vapor back in the air
What is surface runoff?
Water that flows across land and collects in rivers , streams and eventually the ocean.
What is Groundwater flow?
Water located within the rocks below the earth’s surface.
What is through-flow?
Moves diagonally, downslope of water through the soil
What is evaporation?
The sun heats up liquid water and turns it into water vapor (gas)
What percentage of the hydrosphere is the ocean?
97.2%
What percentage of the hydrosphere is the Non ocean components?
2.8%
What percentage of non ocean components is made up by saline lakes and inland seas?
0.008%
What percentage of non ocean components is made up by soil moisture?
0.005%
What percentage of non ocean components is made up by stream channels?
0.0001%
What percentage of non ocean components is made up by the atmosphere?
0.001%
What percentage of non ocean components is made up by groundwater?
0.62%
What percentage of non ocean components is made up by glaciers?
2.15%
list 5 characteristics of the water cycle
Recycles the earths fixed supply of water
Water remains chemically unchanged
Changes physical state (by freezing and boiling)
powered by solar energy and gravity
Works if we do not overload water systems with slowly degrading wastes or withdraw water from underground supplies faster than it is replenished.
Distribution of water across the earth is often described as _____
Interacting water compartments
Water may reside briefly in _____ or stay there for _____.
one compartment, or stay there for eons
The length of time water typically spends in a compartment is called_____
The residence time
The average residence time of water in the ocean is about _____ years before the water ______ and enters the ________
about 3,000 years before the water evaporates and enters the hydrologic cycle
Major water compartment example: Rivers and streams (characteristic)
Precipitation that does not evaporate or infiltrate into the ground runs off the surface, back towards the sea
Major water compartment example: Wetlands (characteristic)
lush plant growth stabilizes soil and holds surface run-off allowing more aquifer infiltration.
Disturbances reduce natural water absorbing capacity, resulting in floods and erosion in wet periods, and less water flow the rest of the year.
Give examples of running water
Rivers, streams, drainage basins
Streams
Any channelized flow of water
Rivers
A stream that has at least one tributary
Drainage basins (watershed)
Land area that contributes to a river system
All energy from the Earth’s surface comes from the?
Sun
What is the atmosphere?
Region of space occupied by the gases above the lithosphere, extending to space.
How does the atmosphere protect us?
The atmosphere protects us from intense energy from the sun (UV) and stores the oxygen we need.
What is the atmosphere made up of? And what is the percentage of each component?
Nitrogen: 78%
Oxygen: 21%
Water vapor: 0 to 4% ( Depends on region: Snow/Clouds/Rain)
Carbon Dioxide: 0.37% (needed to keep Earth from being ice cold, and is “plant food”)
Argon: 0.93%
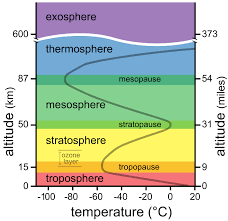
What is the atmosphere classified into?
The Troposphere
The Stratosphere
The Mesosphere
The thermosphere
Which is the lowest layer and how far does it extend from the Earth’s surface?
The lowest layer is the Troposphere and it extends up to 10Km from the Earth’s crust
In which layer of the atmosphere does weather occur?
The troposphere
Does the troposphere contain any gases or water vapor? Is yes, what percentage?
Yes, this layer contains 99% of the water vapor and 75% of the atmospheric gases
Give a brief description of the temperature that can be found in the Troposphere
Temperature cools about 6.5 degrees celcius/Km of altitude
Most of this layer’s heat is from the Earth itself
Gets cooler as you go higher up
Density of air particles decrease with altitude
What layer comes after the Troposphere? and how far does it extend?
The Stratosphere comes after the Troposphere
It extends from 10Km to about 50Km above the Earth’s surface
The stratosphere is a major home of high levels of gas called _____
Ozone
What is the ozone layer, and what does it do?
The ozone layer is made up of 3 atom molecules that protect the Earth from the sun’s harmful Ultraviolet radiation
it absorbs harmful rays from the sun
Pollutants called Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCS) are destroying the ozone
Give a brief description of the temperature that can be found in the Stratosphere
Temperatures get warmer as you increase in this layer
Density of air particles increase with altitude
Ozone may make this layer warm
What comes after the Stratosphere? how far does it extend?
The mesosphere comes after the Stratosphere
it extends from the top of the Stratosphere to about 85Km above Earth
What burns in the Mesosphere?
Meteorites and Rock fragments burn in this layer
Give a brief description of the temperature that can be found in the Mesosphere
Coldest layer with little ozone
Temperatures decrease with altitude
Density of air particles decrease with altitude
What layer is also called the “Ionosphere”?
The Thermosphere is also called the Ionosphere
How far does the Thermosphere extend?
It is the thickest layer of the atmosphere and is found between 85Km to 500Km above Earth’s surface
Which layer in the atmosphere contains auroras?
The Thermosphere
Give a brief description of the temperature that can be found in the Thermosphere
Very high temperatures
very little air particles
Warmed as it filters out x-rays and gamma rays from the sun
In between each atmospheric layer is the?
The pause
What is the pause?
The pause is found between each layer in the atmosphere
It is a transition layer between the two atmospheric layers
Tropopause, Stratopause, and Mesopause
The sun emits ____ radiation because it is _______ _______ and has a lot of ______ to give off.
The sun emits shortwave radiation because it is extremely hot and has a lot of energy to give off.
Once in the atmosphere _____ on the surface absorb ____ ______.
Once in the atmosphere clouds on the surface absorb solar energy.
The Earth emits _____ radiation because it is ______ than the sun and has ____ ______ available to give off.
The Earth emits Longwave radiation because it is cooler than the sun and has lesser energy available to give off.
What is the Greenhouse effect?
It is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When the sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gasses include?
Water vapor
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Nitrous Oxide
Ozone
Some artificial chemicals such as Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
How do greenhouse gases maintain the Earth’s temperature?
Absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth.
This process maintains the Earth’s temperature at around 33 degrees celcius.
Warmer than it would be otherwise, allowing life to exist on earth.
How do greenhouse gases add heat to the atmopshere?
Greenhouse gases absorb certain wavelengths of longwave radiation, preventing the thermal radiation from reaching space, adding heat to the atmosphere.
Explain the Greenhouse effect
Step 1: Solar radiation reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, some of which is reflected back into space.
Step 2: Rest of the sun’s energy is absorbed by the land, and the oceans, heating the earth
Step 3: Heat radiates from Earth towards space
Step 4: Some of this heat is trapped by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm enough to sustain life
Step 5: Human activity such as burning fossil fuels, agriculture, and land clearing are increasing the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere
Step 6: This traps extra heat, and causes the Earth’s temperature to rise
What are ecosystems?
The self-sustaining structural and functional interaction between living and non-living components.
What are the 8 components of an ecosystem?
Solar radiation
moisture
habitat
communities (plant & animal)
soil organisms
minerals
nutrients
disturbances
What is a population?
A group of organisms of the same kind living in the same place
What is a community?
All the population that live in an ecosystem at the same time form a community
All members of a community live in the same ecosystem but they do not all live in the same part of the ecosystem.
What is a habitat?
Place where plants and animals live
A place where they can meet their needs
Animals get food, water, and shelter
What is a natural ecosystem?
Ecosystems like ponds, lakes, oceans, forests, grasslands, deserts etc.
Self regulating without much direct human interference or manipulation
What are the two types of natural ecosystems?
Terrestrial ecosystem
Aquatic ecosystem
What is the aquatic ecosystem divided into?
Lentic: Stagnant water (like lakes, ponds)
Lotic: Flowing water (like rivers, oceans)
What is an artificial ecosystem?
A crop land, garden, aquarium, park, kitchen
What is a desert ecosystem?
Very dry ecosystems
Desert plants and animals can survive with very little water
What are grassland ecosystems?
Dry, often flat areas of land that are hot in the summer, and cold in the winter
They get more rain and snow than deserts but less than most other ecosystems
What is a forest ecosystem?
Ecosystem in which many trees can grow
What are saltwater ecosystems?
Oceans
Oceans cover about one-third of the earth’s surface, so there are more saltwater ecosystems than any other.
What are freshwater ecosystems?
Rivers, ponds, lakes, and streams have fresh water
Lakes and rivers are closely tied:
Some lakes are the source for other rivers
some rivers end in lakes
Since both rivers and lakes are freshwater, and flow in and out of each other, they share similar characteristics, and many species reside in both habitats
All ecosystems have what two factors?
Abiotic factors
Biotic factors
What are abiotic factors?
Water, air, soil, sunlight, and minerals
What are biotic factors?
living or once living organisms in the ecosystem.
Obtained from the biosphere and are capable of reproduction.
Plants, animals, birds, fungi
What are the abiotic components of an ecosystem?
Sunlight, temperature, precipitation, water, or moisture, soil
What are the biotic components of an ecosystem?
Primary producers, Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores, and Detritivores
What function do the producers play in an ecosystem?
The producers, green plants, fix radiant energy with the help of minerals, taken from their edaphic, or aerial environment and build up complex organic matter
This is their food.
So, with the help of solar energy, they convert the chemical energy of the food to kinetic energy and finally heat energy.
chemical energy —> kinetic energy—> heat energy
How do animals and plants transfer energy?
The animals eat up the plants and other animals as food.
So, the energy is transferred through food to animals
How does elements/energy return from where they were taken?
When plants and animals die, the decomposers act on their dead bodies and decompose them into simple materials, like carbon dioxide, water, minerals, which go back to the air, water bodies, and soil they were taken from.
What are autotrophs?
Producers
get energy from the sun
What are heterotrophs?
Consumers
What is the equation for photosynthesis? (chemical equation)
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
The same _____ atoms are used ____ on earth
The same carbon atoms are used repeatedly on earth
the carbon atoms cycle between the _______, ______, ________, and ______
the carbon atoms cycle between the lithosphere, Biosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere
called carbon cycle