Bonding, Molecular Structure, and Lewis Structures in Chemistry
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the center of an atom called and what does it contain?
The center of an atom is called the nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons.
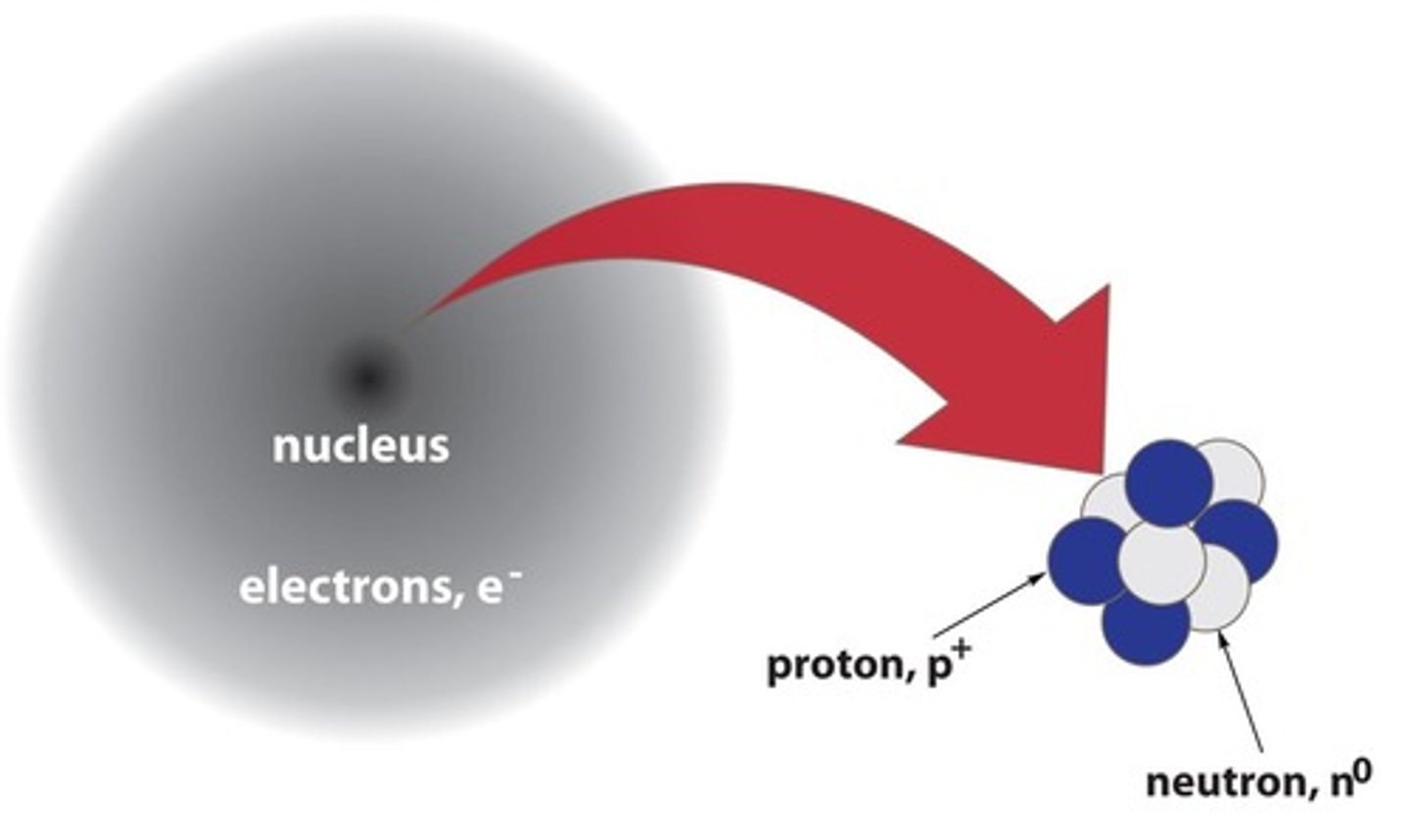
How are electrons characterized in relation to the volume of an atom?
Electrons are very tiny but occupy most of the atom's volume.
What is the significance of the atomic number in the Periodic Table?
The Periodic Table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
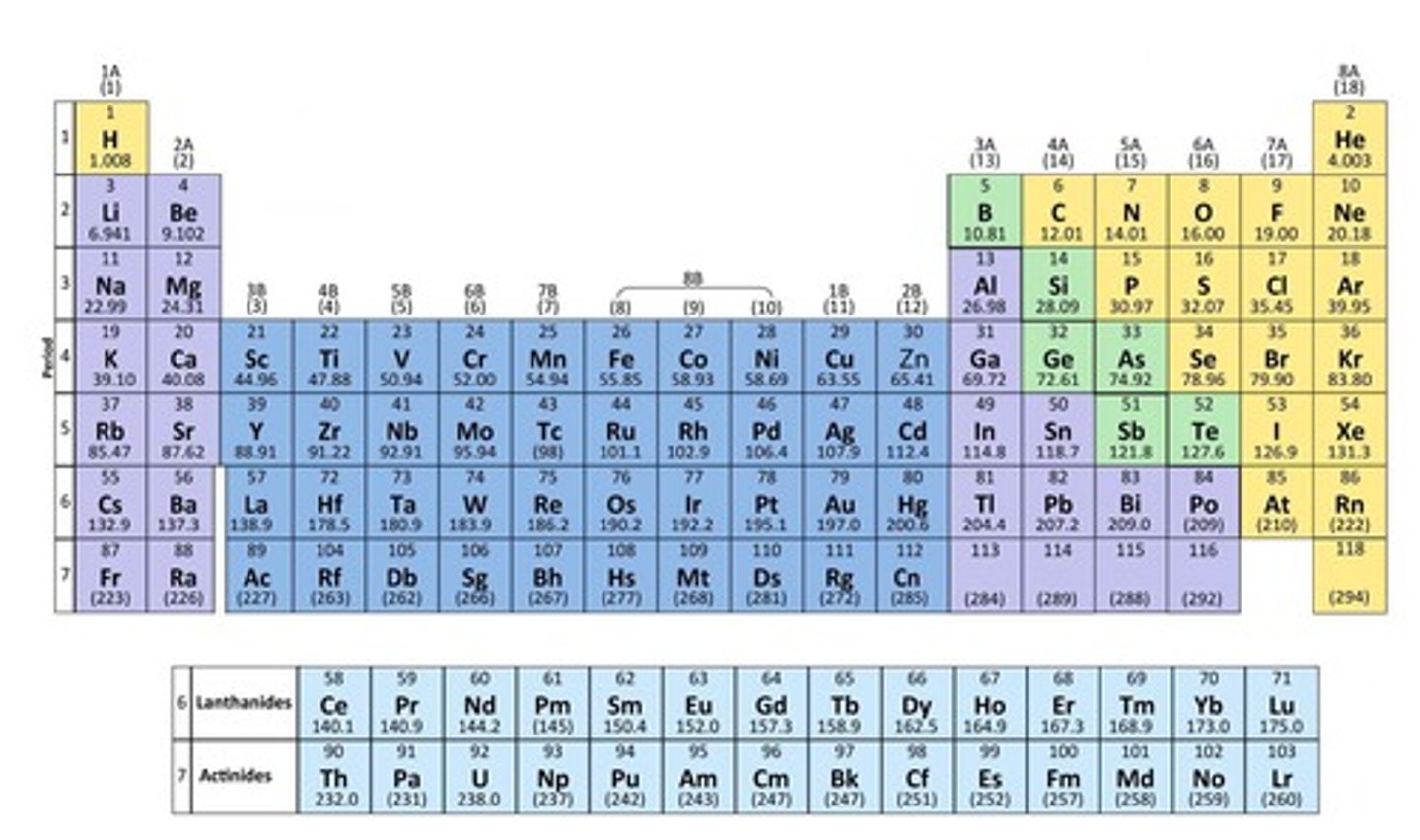
What is the relationship between protons and electrons in a neutral atom?
In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons.
What are valence electrons and how are they determined for main group elements?
Valence electrons are those in the highest occupied energy level, and for main group elements, the group number equals the number of valence electrons.
What is the octet rule?
The octet rule states that atoms strive for a full valence shell octet to attain stability.
What is the difference between ionic, metallic, and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals; metallic bonds involve a sea of electrons among metals; covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between non-metals.
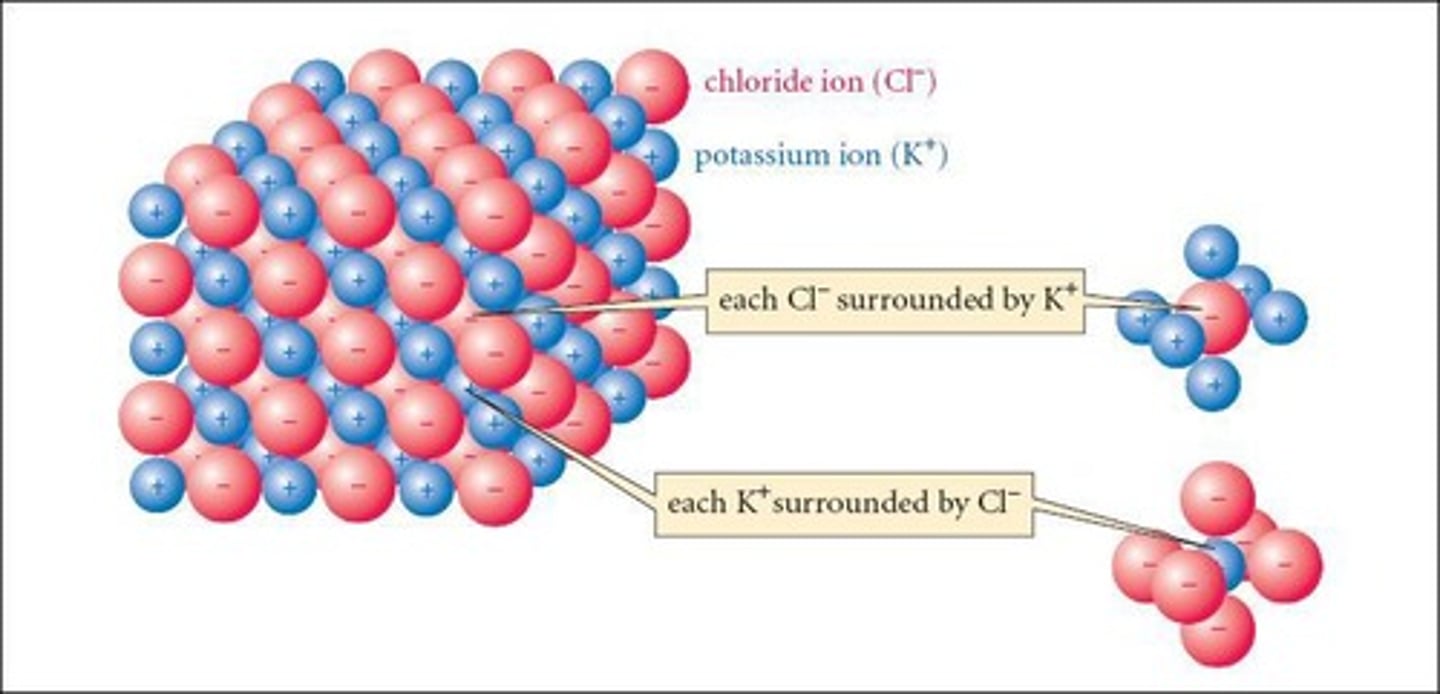
What factors affect covalent bond length?
Covalent bond length is affected by the attraction between nuclei and shared electrons, as well as repulsions between nuclei and electrons.
How is bond length related to bond energy?
As bond length decreases, bond energy increases due to maximized nucleus-electron attractions and minimized nucleus-nucleus and electron-electron repulsions.
What is a Lewis dot symbol and its purpose?
A Lewis dot symbol shows the valence electrons of an element and can be used to predict bonding behavior.
What is the preferred bonding pattern for oxygen in a Lewis structure?
The preferred bonding pattern for neutral oxygen is to form 2 bonds and have 2 lone pairs.
How is formal charge calculated in a Lewis structure?
Formal charge is calculated as the number of 'owned' electrons minus the number of valence electrons of the unbonded atom.
What does a formal charge of zero indicate?
A formal charge of zero indicates that an atom is bonding according to its preferred bonding pattern.
What is the process for drawing a Lewis structure?
To draw a Lewis structure, count valence electrons, construct a skeleton with the lowest group number atom in the center, draw single bonds, and use multiple bonds if necessary to fill octets.
What is the significance of the electronegativity difference (ΔEN) in bond types?
The ΔEN helps determine bond type: a higher difference indicates ionic bonds, while a smaller difference indicates covalent bonds.
What is the electron sea model?
The electron sea model describes metallic bonds where electrons are delocalized and shared among a lattice of metal cations.
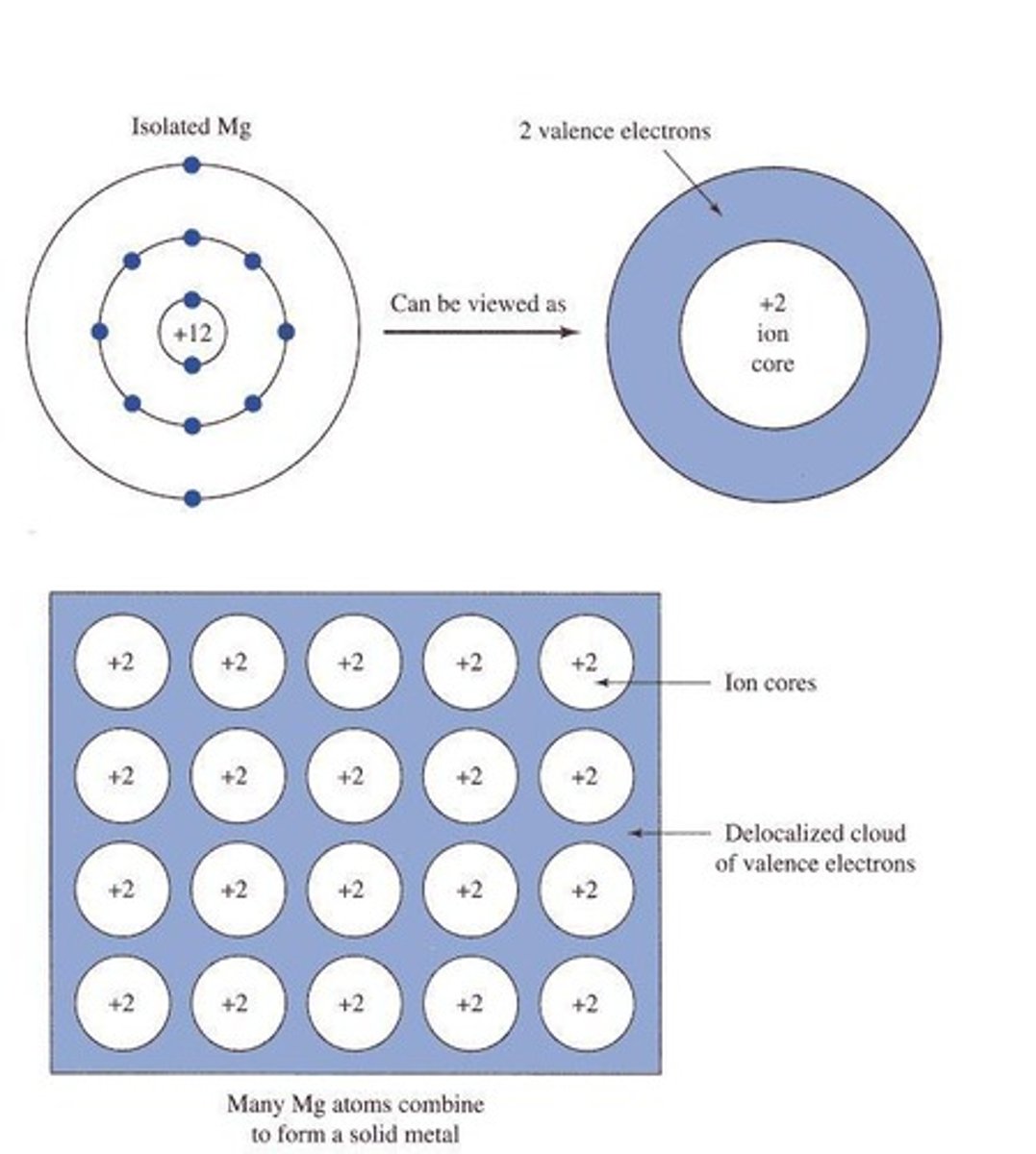
How do covalent bonds behave during phase changes?
Covalent bonds do not break during phase changes.
What is the role of lone pairs in Lewis structures?
Lone pairs in Lewis structures represent nonbonded electrons that can affect bonding and formal charge.
What is the relationship between bond length and van der Waals distance?
The distance between the nuclei of covalently bonded atoms is less than the van der Waals distance between nonbonded atoms.
How are multiple bonds used in Lewis structures?
Multiple bonds are used in Lewis structures to fill octets when single bonds are insufficient.
What is the significance of the central atom in a molecular formula?
The central atom in a molecular formula is usually the one with the lowest electronegativity or the lowest group number, and hydrogen is never a central atom.
What is the importance of assigning formal charges in Lewis structures?
Assigning formal charges helps identify the most stable structure and whether atoms are bonding according to their preferred patterns.