3.4.3 genetic diversity -> mutations + meiosis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Define genetic diversity?
Number of different alleles in a population
Genetic diversity within a species can be caused by what?
Gene mutations
Meiosis → independent segregation of homologous chromosomes + crossing over)
Random fusion of gametes during fertilisation
Chromosome mutations
This genetic diversity is acted upon by natural selection, resulting in what?
In species becoming better adapted to their environment
What are gene mutations?
Changes in the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA → new alleles of genes are produced by mutations
Gene mutations occur ___ and might arise during….
spontaneously
DNA replication
The mutation rate is increased by what?
Mutagenic agent e.g X-rays, benzene, UV light
What can mutations result in + why?
Different amino acid sequence in the encoded polypeptide → due to altered base sequence coding for a different sequence of amino acids
Why don’t all mutations result in a change to the encoded amino acids?
Some only change one triplet code → may still code for the same amino acid due to degenerate nature of the genetic code
How do some mutations change all triplet codes?
They result in a frame shift → all bases move down/upstream from the mutation
What is substitution?
Replacement of one or more bases by one or more different bases
The substitution of a single base may result in what?
A new triplet coding for a different amino acid in the polypeptide chain → may result in a non functional protein
One different amino acid in polypeptide changes but functional protein is still produced
Same amino acid may e coded due to degeneracy of DNA code → polypeptide is unchanged
A stop codon → protein synthesis prematurely terminated
What is deletion?
Removal of one or more bases
What is the effect of deletion?
Results in a frame shift → alteration in all base triplets from point of mutation
Sequence of amino acids is altered from point of mutation → protein formed is nearly always non-functional
What is addition?
Adding of one or more bases
What does addition result in?
Frame shift → sequence of amino acids is altered from point of addition + protein formed may be non-functional
What is duplication + what does it result in?
Where one or more bases is repeated → frame shift - alteration in base triplets from point of addition
What is inversion?
Where a sequence of bases is reversed → multiple amino acids could be affected + may result in non-functional protein
What is translocation?
Where a sequence of bases is moved from one location in the DNA molecule to another part of the genome
A gene can exist in different forms called…
alleles → code for different types of the same characteristic
If the base sequence of a gene that codes for an enzyme is altered, what effect does this have on the enzyme?
Change in amino acid sequence may affect position of H/ionic/disulfide bonds which results in a different tertiary structure
Change in tertiary structure may alter shape of active site → no longer complementary to substrate + ES complexes don’t form - reaction isn’t catalysed
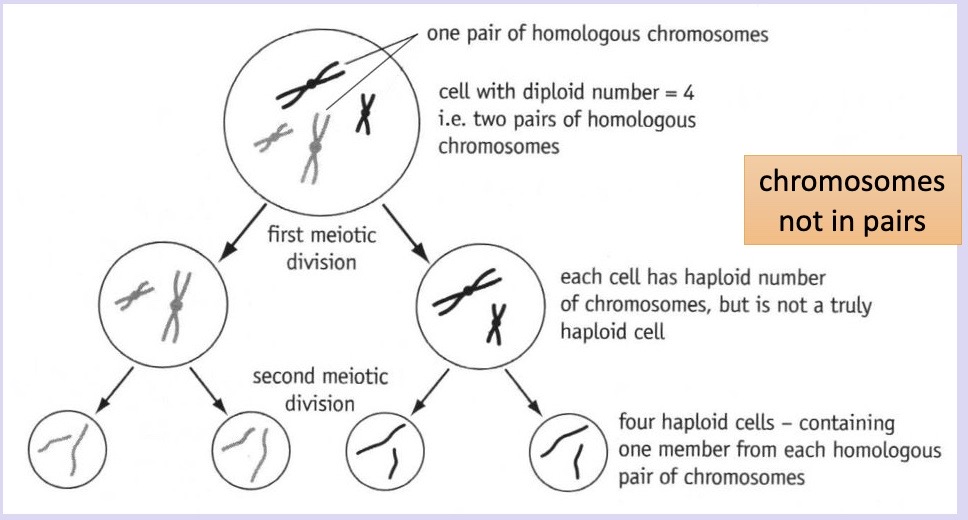
What is meiosis?
A type of nuclear division that produces cells that are genetically different
Single cell divides twice but DNA replication only occurs once
4 cells are produced that are varied + possess half the number of chromosomes (haploid) of original cell
Where is meiosis important?
In the production of haploid gametes → result in the diploid number being restored when gametes fuse at fertilisation to produce a zygote
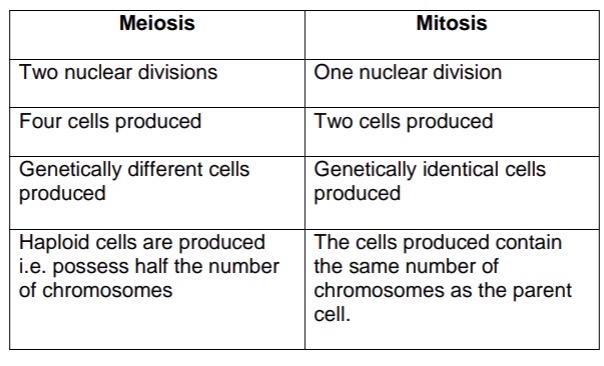
Compare mitosis + meiosis
How to spot where meiosis takes place in a cell life cycle?
When the diploid number (2n) halves to the haploid number (n)
What is the process of meiosis?
During late interphase → DNA replication, build up of ATP, protein synthesis + replication of cell organelles
Meiosis I + meiosis II occur
Results in 4 haploid genetically different daughter cells
What is separated in each meiosis division?
Members of each homologous pair → results in 2 haploid daughter cells with 2 copies of each chromatid
Chromatids of each chromosome → results in 4 haploid daughter cells with one copy of each chromatid
What 2 processes in meiosis produce genetically different cells?
Independent segregation of homologous chromosomes
Genetic recombination by crossing over within homologous chromosomes
Explain independent segregation
During first meiotic division (metaphase), homologous chromosomes pair together, lining up opposite each other on the spindle + then separate (anaphase) so one member from each pair enters gamete
The pairing + segregation of 2 members of a pair is completely independent from the separation of another pair → chromosomes randomly associate within a gamete + so contains varied combination of maternal + paternal chromosomes / alleles
How to work out the number of possible combination of paternal + maternal chromosomes from a known number of homologous pairs?
2 to the power of no. homologous pairs
When does crossing over occur?
During prophase of the first meiotic division
What happens during crossing over?
2 members of each homologous pair lie side by side forming a bivalent
Chromatids of homologous chromosomes intertwine → break + equivalent portions are exchanged → results in exchange of alleles of the same genes + produces new combinations of alleles - recombinants
Called genetic recombination
Chromosomes then separate
What is a chiasma?
The place where crossing over occurs
Why is the number of recombinants formed is relatively low?
Crossing over is relatively rare