Endocrine System
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What does the Endocrine System do?
It secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream to maintain homeostasis
Hormones
Chemical messengers that regulate many bodily functions. A specific hormone must bind to a specific receptor in order to create a response.
Endocrine cells are located in…
gland or gland like structure
Target cells in endocrine system are…
Specific cells that respond to hormones
The main endocrine organs are:
Pituitary gland - brain
Hypothalamus - brain
Thyroid gland - neck
Adrenal glands - on top of kidneys
Pineal gland - brain
Parathyroid glands - neck; posterior part of thyroid
Pancreas - abdomen
Organs with secondary endocrine functions:
heart
thymus
adipose tissue
digestive tract
kidneys
gonads
testes
ovaries
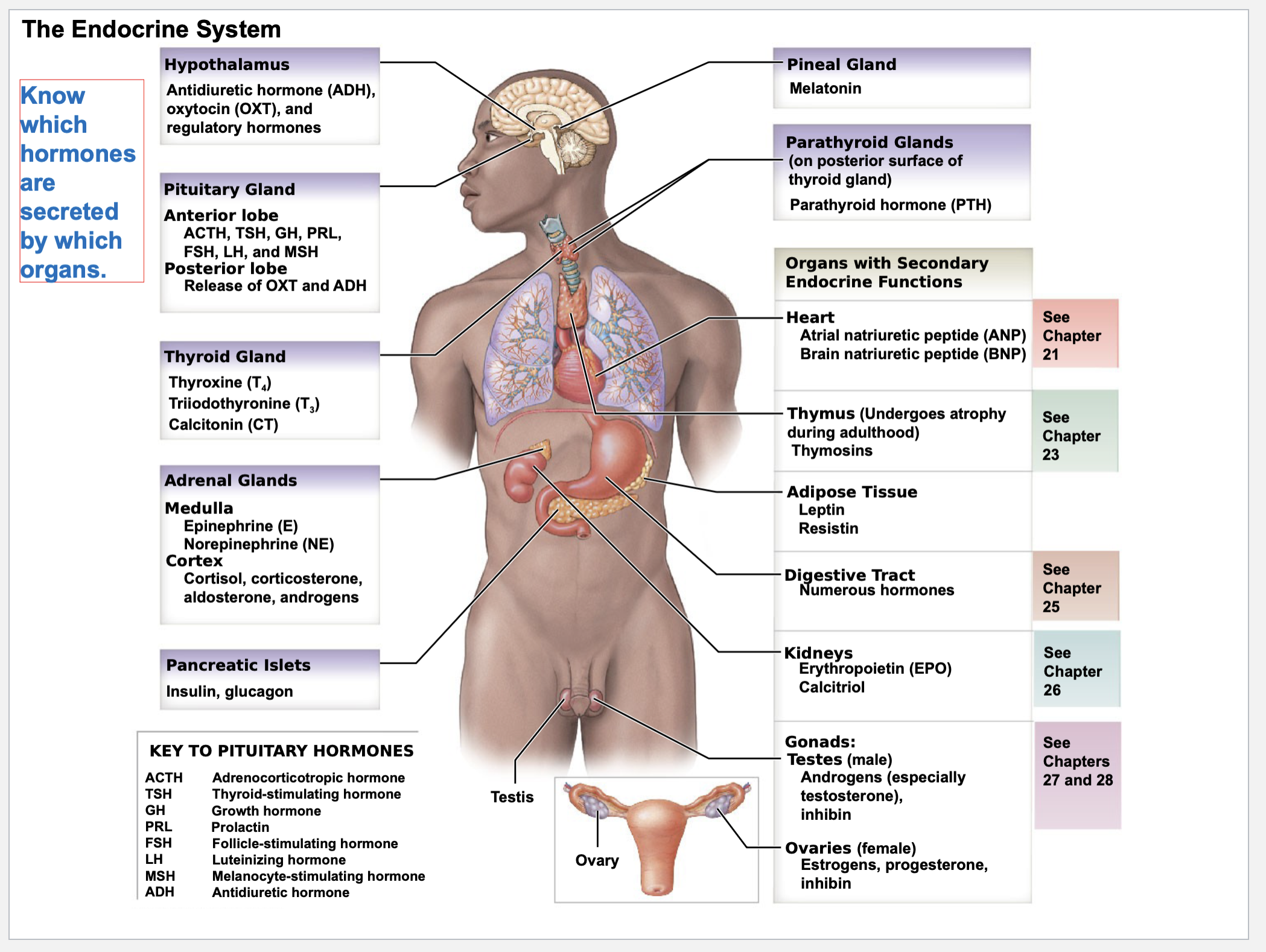
Hypothalamus secretes which hormones
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), oxytocin (OXT), and regulatory hormones
Pituitary Gland secretes …
from Anterior lobe (ACTH, TSH, GH, PRL, FSH, and MSH)
from Posterior lobe (Release of OXT and ADH)
Thyroid Gland secretes…
Thyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Calcitonin (CT)
Adrenal Glands secretes…
from Medulla
Epinephrine (E)
Norepinephrine (NE)
from Cortex
Cortisol, corticosterone, aldosterone, androgens
Pancreatic Islets secretes…
Insulin, glucagon
Pineal Gland secretes…
Melatonin
Parathyroid Glands (on posterior surface of thyroid gland) secretes…
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Hypothalamus is the key endocrine organ that serves as the …
link between the neural and endocrine systems
Hypothalamus integrates neural and endocrine activities via 3 mechanisms …
Acts as an endocrine organ
secretes regulatory hormones
contains automatic nervous system centers
Heart secretes…
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
Thymus (undergoes atrophy during adulthood) secretes …
Thymosins
Adipose Tissue secretes…
Leptin, Resistin
Digestive tract secretes…
Numerous hormones
Kidneys secrete…
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Calcitriol
Gonads secrete…
Testes (males)
Androgens (esp testosterone), inhibin
Ovaries (females)
estrogens, progesterone, inhibit
Preganglionic neurons start in the
hypothalamus synapse on the adrenal medulla
Hypothalamus produces
oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH). These hormones travel thru hypothalamic neurons (their axons). Eventually, oxytocin and ADH are released by the posterior part of the pituitary gland.
Anterior Lobe of Pituitary Gland consists of 5 diff cell types:
Thyrotropes — thyroid gland
Corticotropes — adrenal cortex
Gonadotropes — reproductive organs
lactotropes — mammary glands
Somatotropes — growth of the body
Posterior pituitary gland is also known as:
Neurohypophysis
Anterior pituitary gland is also known as
adenohypophysis
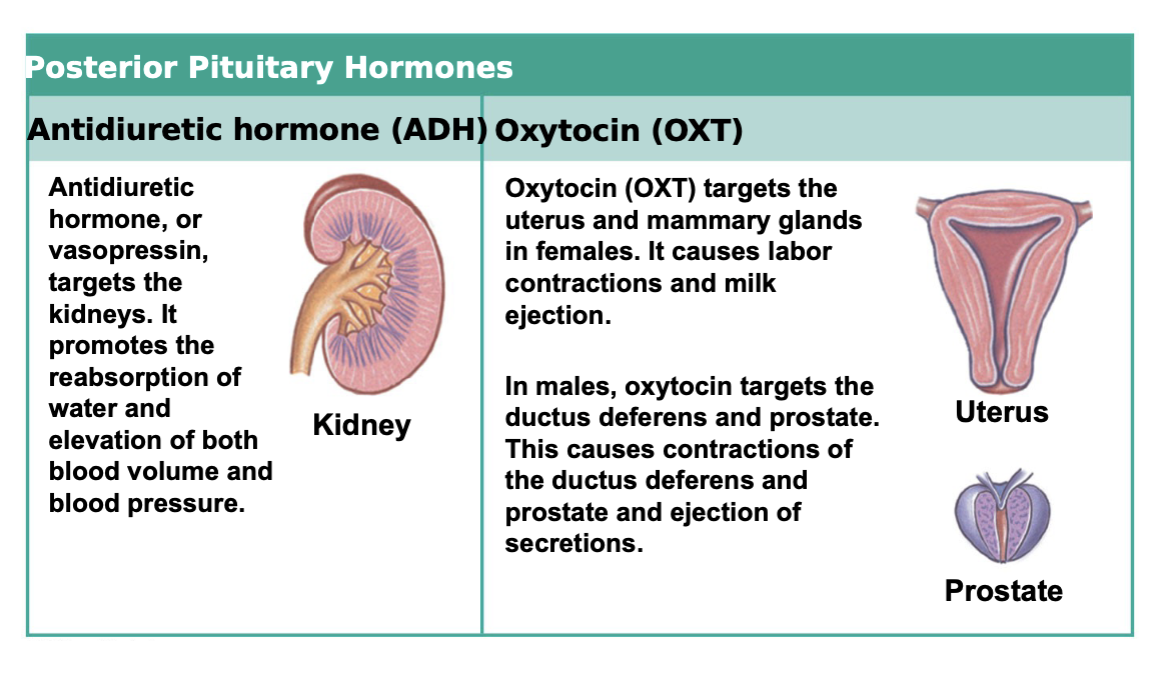
Main organs released by posterior pituitary gland are:
Oxytocin and ADH
ADH targets what organ and what does it do
Kidneys; it works to reabsorb water (water retention). By reabsorbing water, we can increase blood volume and blood pressure
Oxytocin targets what
mammary glands and uterus in females. This causes milk ejection in the mammary gland; it causes uterine wall contraction. In males, oxytocin acts on the prostate gland and ductus deferens. This leads to contractions of both of these structures
Where is the thyroid gland in the body
It sits in the inferior neck just in front of the trachea. It secretes T3 and T4 —- these hormones influence metabolism in the body.
Calcitonin is also releases by thyroid. It works on lower blood calcium levels.
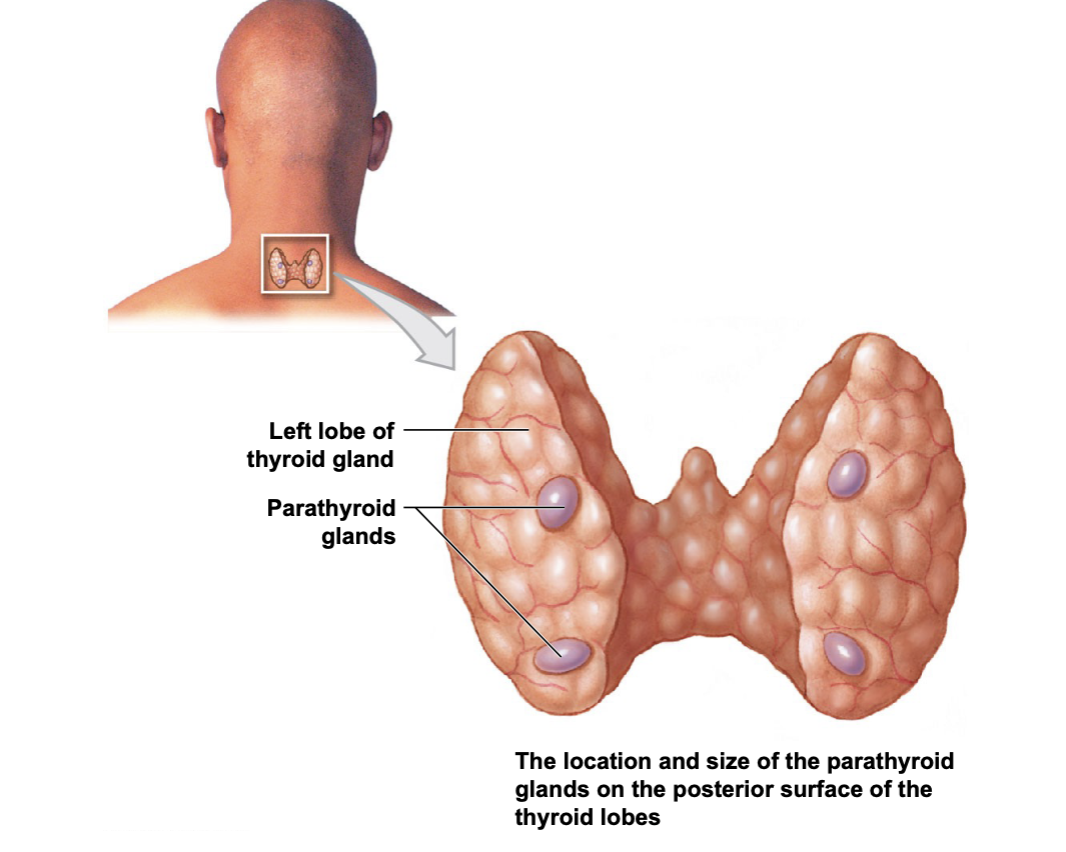
Where are parathyroid glands in the body
They lie on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. there are 4 nodules. Parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone which works to increase blood calcium levels
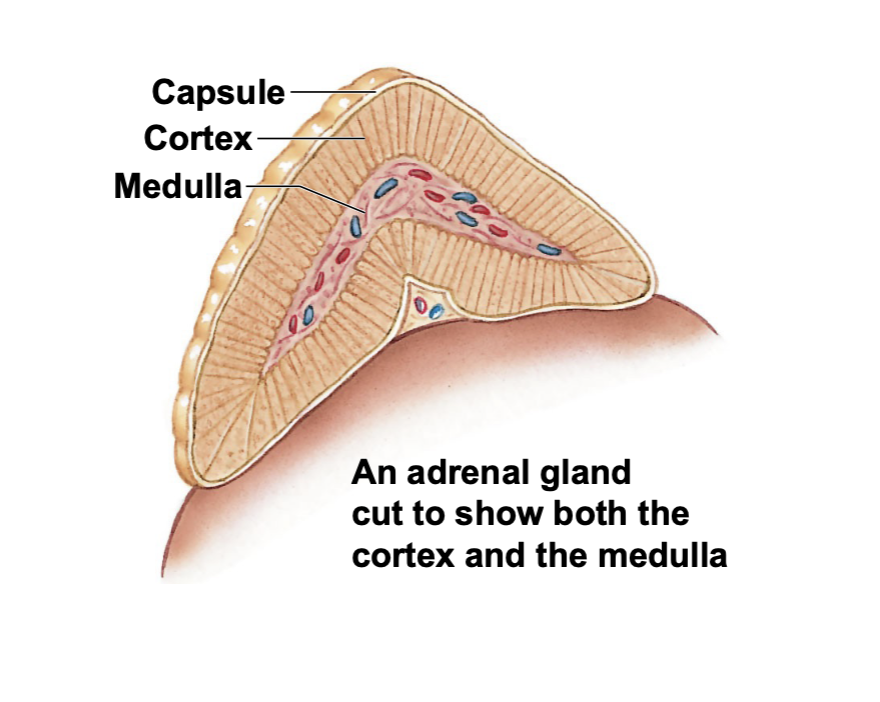
Where are adrenal glands
They sit on top of the kidneys. They have a pyramidal shape and sit on the superior surface of ur kidneys
Adrenal gland has 2 main parts:
adrenal cortex (outer portion)
Adrenal medulla (inner portion)
Adrenal medulla secretes
norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline)
Adrenal cortex secretes several major hormones including:
cortisol (works to increase blood sugar so that we have E to respond to internal and external stress)
Aldosterone (this hormone helps promote water retention to increase blood volume and blood pressure)
The androgens (these are sex hormones; this includes estrogen and testosterone)
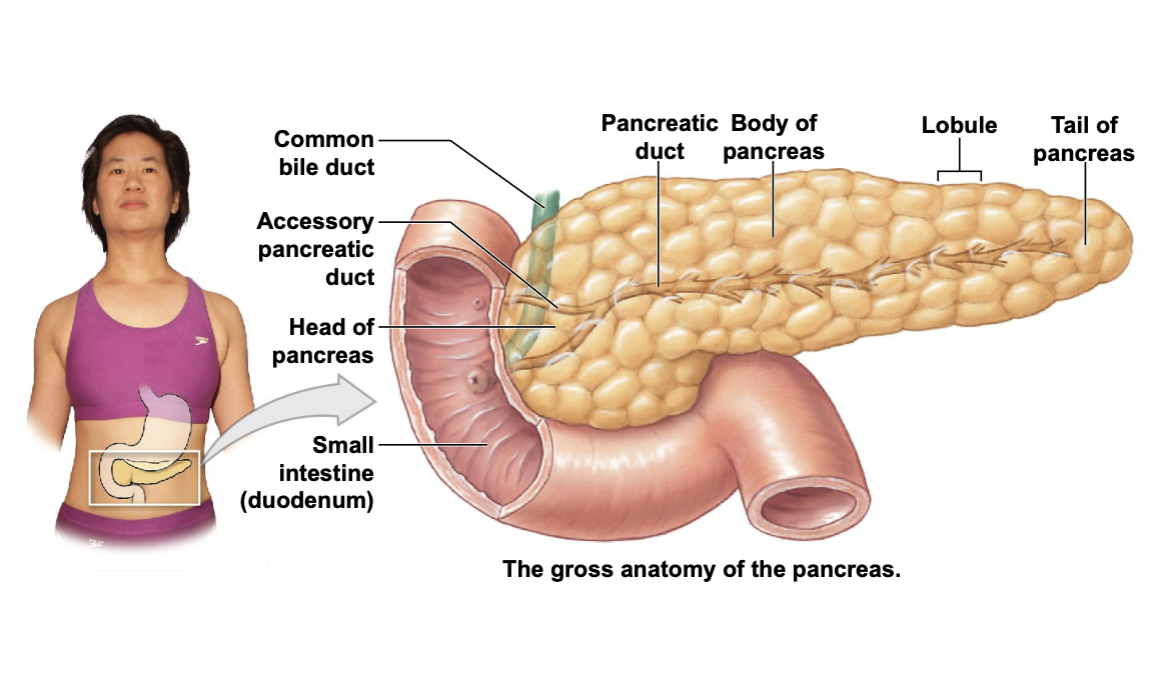
where are pancreas located
in the abdomen. It sits behind (posterior) to the stomach.
Function of pancreas
it functions as both exocrine and endocrine gland.
Endocrine portion relies on bloodstream to move the hormones made by pancreas. The exocrine portion relies on the ducts within the pancreas to move its produce, mainly digestive enzymes.
Appearance of pancreas
The head of pancreas is tucked into the “U” shaped curve of the duodenum of the small intestine
Main hormones made by the pancreas are
glucagon and insulin.
glucagon works to increase blood sugar levels
insulin works to decrease blood sugar levels
Kidneys also work as …
secondary endocrine organs.
The kidney can secrete renin. Renin stimulates a series of steps that ultimately lead to production/release of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex. In this instance, renin is working to increase sodium and water retention.
Kidneys play a role in
regulating blood calcium levels. Whenever we have low blood calcium levels in the body, we need an
active form of vitamin D to stimulate our digestive tract to absorb more dietary calcium. In order for this to happen vitamin D needs to be converted from an inactive form into an active form. Our kidney cells perform this activation step. However, we need to keep in mind that the inactive form of vitamin D must be created from something. Exposure to sunlight plays a vital role here. An initial hormone is converted into the inactive vitamin D by sunlight. Go through the steps listed in the lecture slides.
The ultimate goal for all these steps is to increase blood calcium
Our kidneys release a hormone called
Erythropoietin (EPO) whenever we need to increase blood oxygen levels. EPO stimulates creation of more red blood cells so that we can carry more O2 in the body.