Decoding genetic information
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What are mutations:
Changes in WHAT sequence (DNA and RNA)
Can be WHAT (WHAT) or not WHAT (WHAT)
Changes can be small (WHAT level) or large (WHAT)
Altered gene sequence can change the WHAT sequence of the polypeptide resulting in WHAT in the phenotypes
What are mutations:
Changes in NUCLEIC ACID sequence (DNA and RNA)
Can be INHERITED (GERMLINE) or NOT INHERITED (SOMATIC)
Changes can be small (GENE level) or large (CHROMOSOMAL)
Altered gene sequence can change the AMINO ACID sequence of the polypeptide resulting in VARIATION in the phenotypes

Effect on phenotypes can be
WHAT = WHAT
WHAT = WHAT
WHAT = WHAT
Effect on phenotypes can be
Harmless = neutral
Harmful = Deleterious
Beneficial = Advantageous

Spontaneous mutations are naturally-occurring mutations mainly caused by WHAT errors (1 mutation/1^10 bp of DNA replicated) and spontaneous WHAT
Include WHAT removed A/G bases and WHAT (losing a group (cytosine to uracil))
Spontaneous mutations are naturally-occurring mutations mainly caused by REPLICATIONS errors (1 mutation/1^10 bp of DNA replicated) and spontaneous LESIONS
Include DEPURINATION removed A/G bases and DEAMINATION (losing a group (cytosine to uracil))

Induced Mutations
Natural (environment) or artificial agents (mutagens) that cause mutations at a rate much higher than WHAT mutations
Induce mutations by replacing a WHAT, alter a base so it WHAT with another base, or WHAT a base where it can no longer pair with any base
Base analogs: mimic WHAT and incorporates into DNA (can cause mispairing during DNA replication); e.g. 5-bromouracil:thymine analog that can pair with A or G
Chemicals that alter base structure to cause WHAT (e.g. alkylating and intercalating agents-benzopyrene)
WHAT to bases (UV light-thymine dimers, aflatoxin B-apurinic sites)
Induced Mutations
Natural (environment) or artificial agents (mutagens) that cause mutations at a rate much higher than SPONTANEOUS mutations
Induce mutations by replacing a BASE, alter a base so it MISPAIRS with another base, or DAMAGE a base where it can no longer pair with any base
Base analogs: mimic BASES and incorporates into DNA (can cause mispairing during DNA replication); e.g. 5-bromouracil:thymine analog that can pair with A or G
Chemicals that alter base structure to cause MISPAIRING (e.g. alkylating and intercalating agents-benzopyrene)
DAMAGE to bases (UV light-thymine dimers, aflatoxin B-apurinic sites)

Germline mutation occur in WHAT, and therefore, are WHAT
Germline mutation occur in GAMETE FORMATION, and therefore, are HERITABLE
Example: sex-influenced trait – autosomal dominant trait
that is dependent on sex (males express the trait in
heterozygotes but females do not)
Somatic mutations:
Somatic mutations occurs in a WHAT cell (any cell that first experiences the mutation) and all sequential WHAT cells express the mutation
Somatic mutations are expressed as WHAT (size depends on time of mutation)
Cancer tumors are an example of somatic mutations
Somatic mutations:
Somatic mutations occurs in a PROGENITOR cell (any cell that first experiences the mutation) and all sequential DAUGHTER cells express the mutation
Somatic mutations are expressed as SECTORS (size depends on time of mutation)
Cancer tumors are an example of somatic mutations

Point mutation
A change at a SINGLE BASE on the DNA
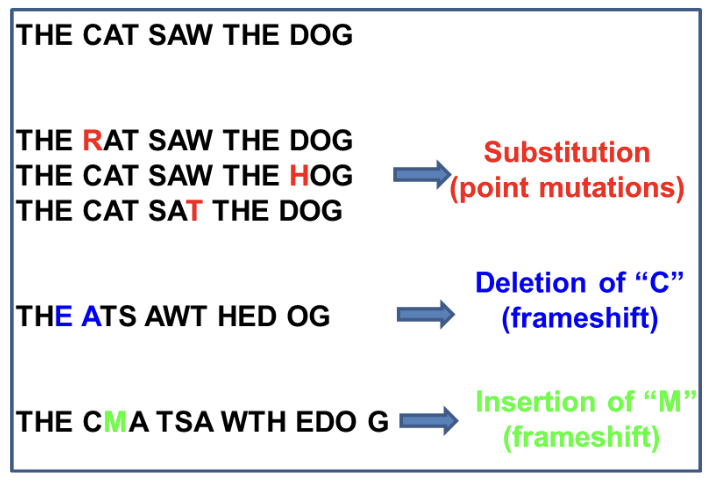
What are all the point mutations:
WHAT
What are the frameshift mutations
WHAT
WHAT
What are all the point mutations:
Base substitution
What are the frameshift mutations
Insertion
Deletion
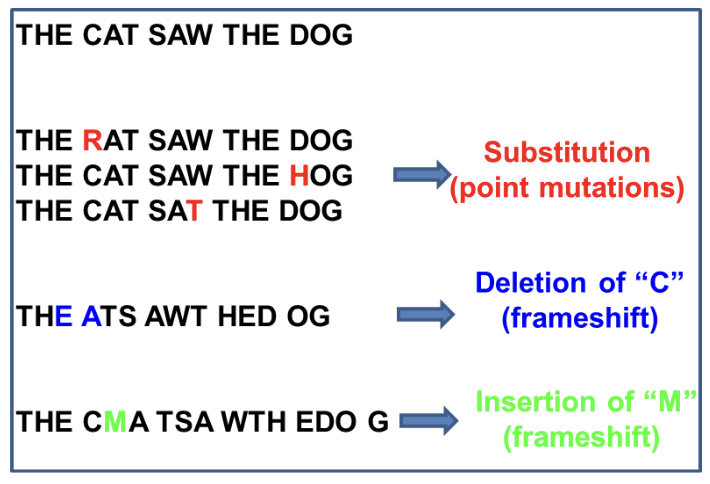
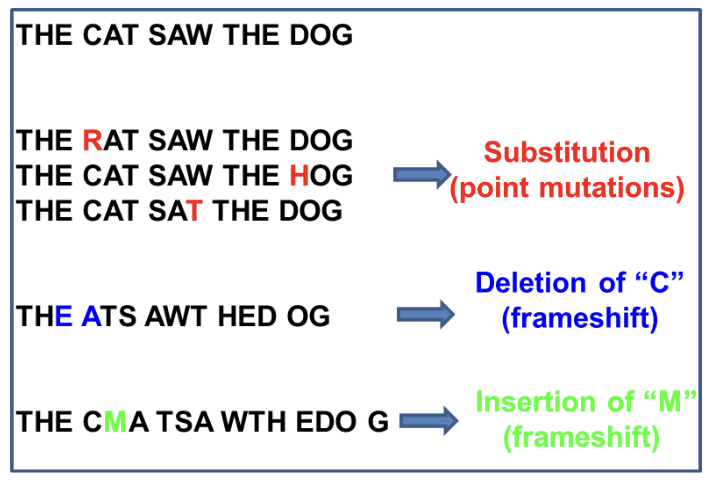
Base substitution
Original nucleotide becomes a different nucleotide
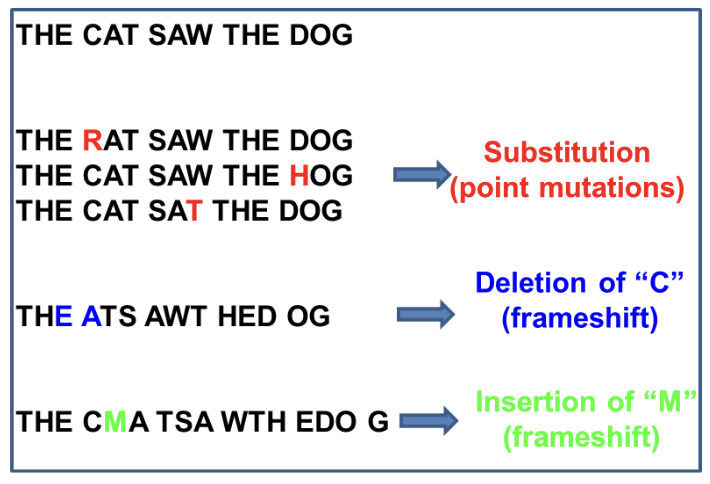
Insertion
A nucleotide is ADDED to the double helix
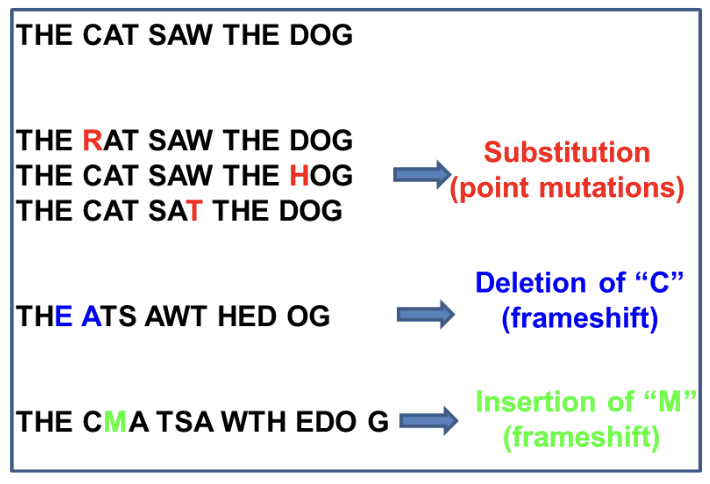
Deletion
A nucleotide is REMOVED from the double helix
Point mutation
Base substitution
Insertion
Deletion
These mutations all occur on WHAT DNA strand
Point mutation
Base substitution
Insertion
Deletion
These mutations all occur on BOTH DNA strand
Types of base substitutions
WHAT
WHAT
Types of base substitutions
Transitions
Transversions
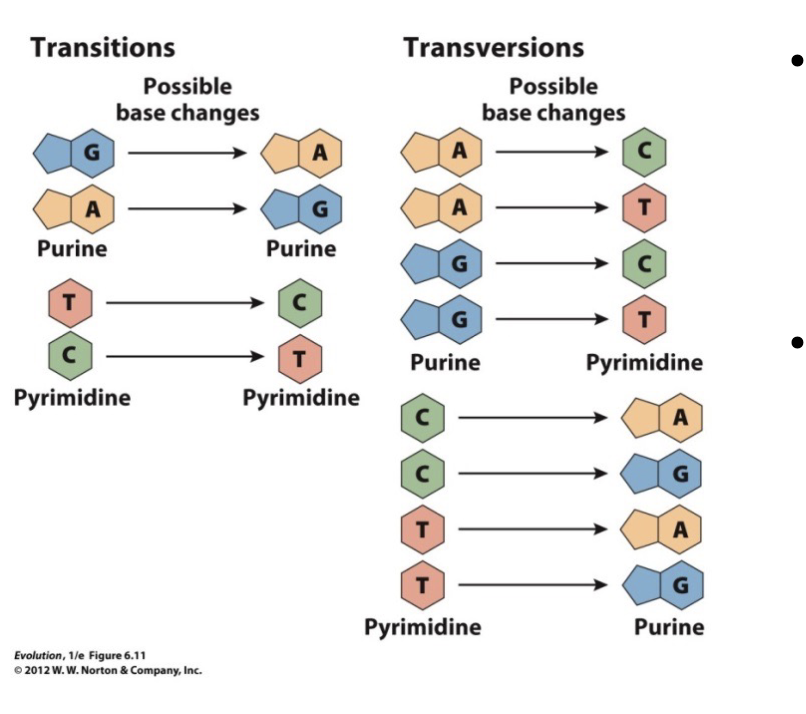
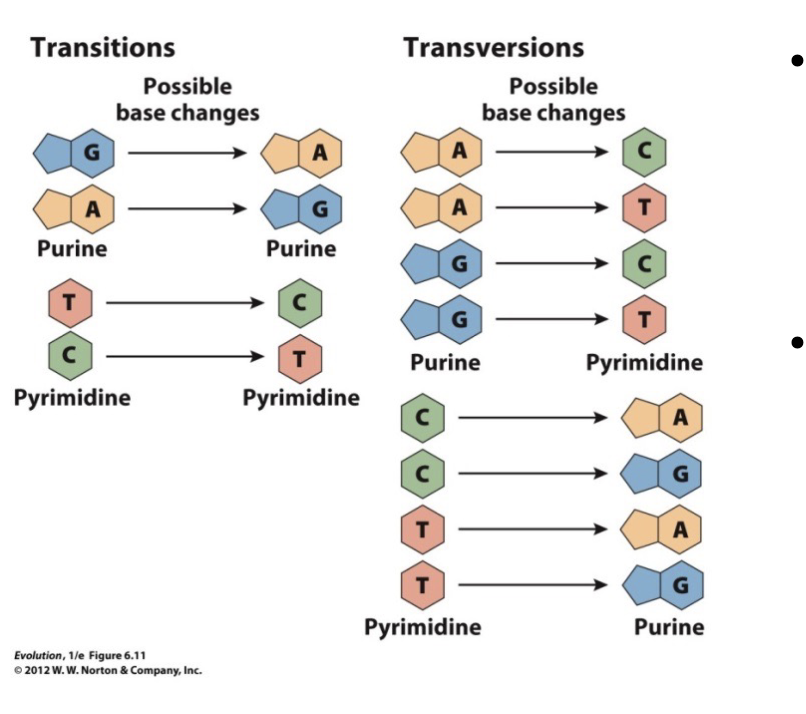
Transition
A purine is swapped for a purine or a pyrimidine for a pyrimidine
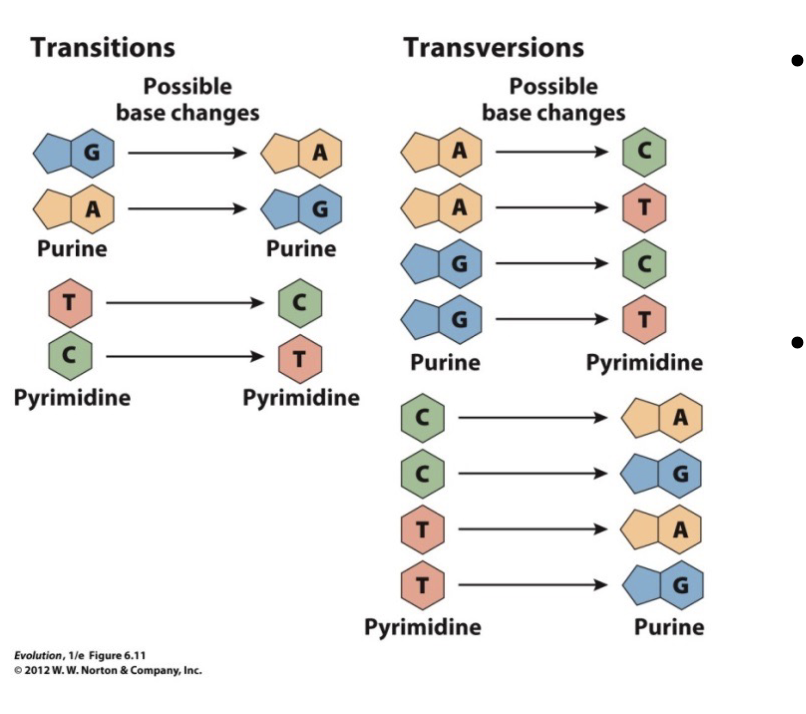
Transversions
A purine to a pyrimidine or a pyrimidine to a purine
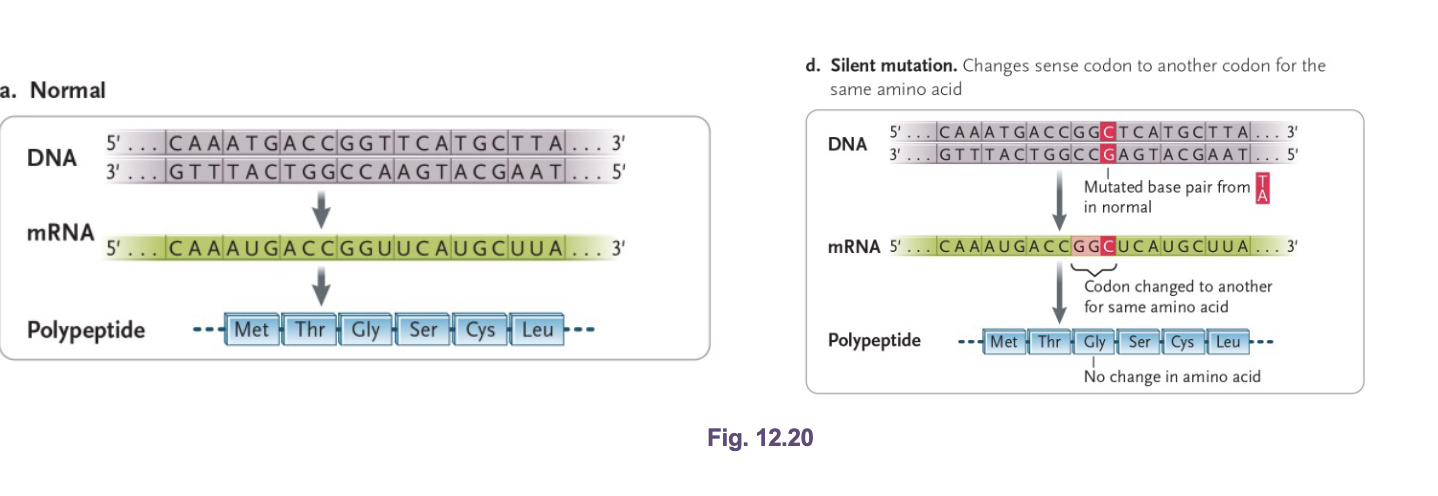
Silent (synonymous) mutation
Codon change does NOT change the amino acid due to degeneracy of the genetic code
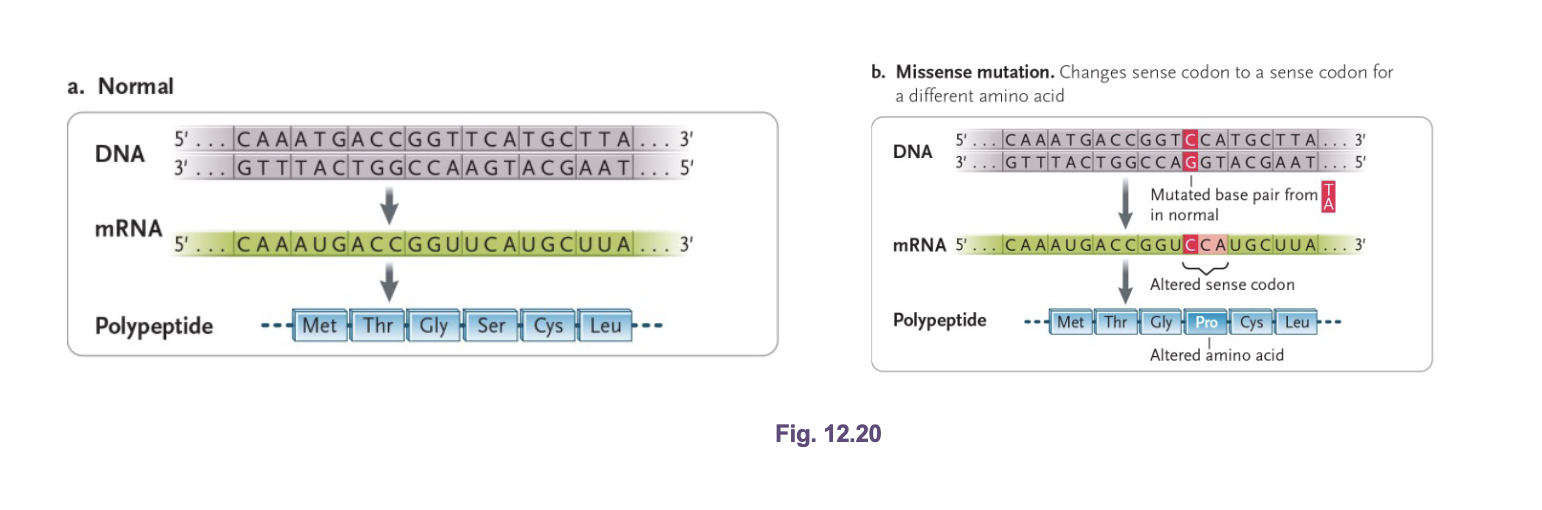
Missense (non-synonymous) mutations
Codon change causes a CHANGE in the amino acid sequence
Nonsense mutations
Sense codon is changed to a nonsense (STOP) codon, resulting in a TRUNCATED polypeptide
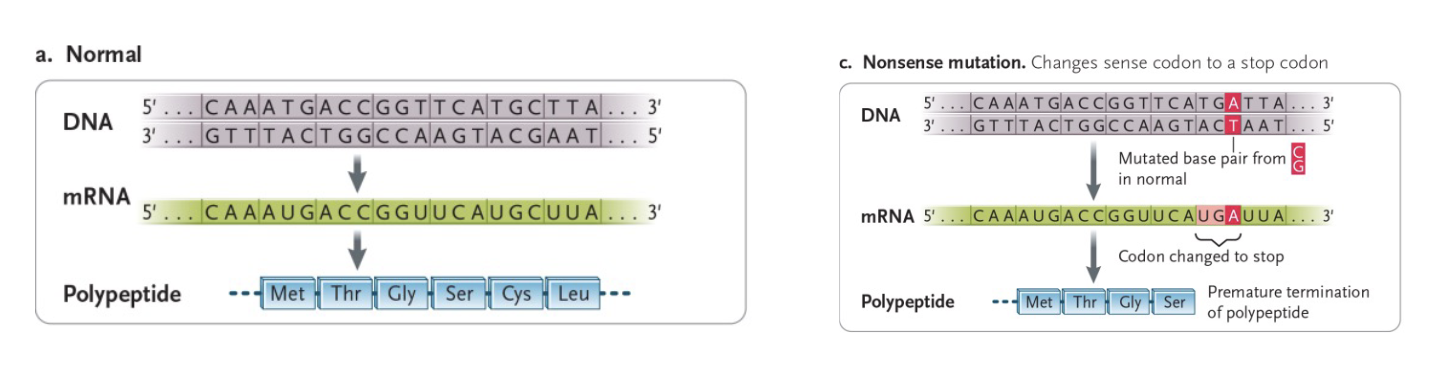
Nonsense mutations
Missense (non-synonymous) mutations
Silent (synonymous) mutation
These are all WHAT mutations
Nonsense mutations
Missense (non-synonymous) mutations
Silent (synonymous) mutation
These are all BASE PAIR mutations
Frameshift mutation
Changes the reading frame of the mRNA due to INSERTION or DELETION of nucleotides
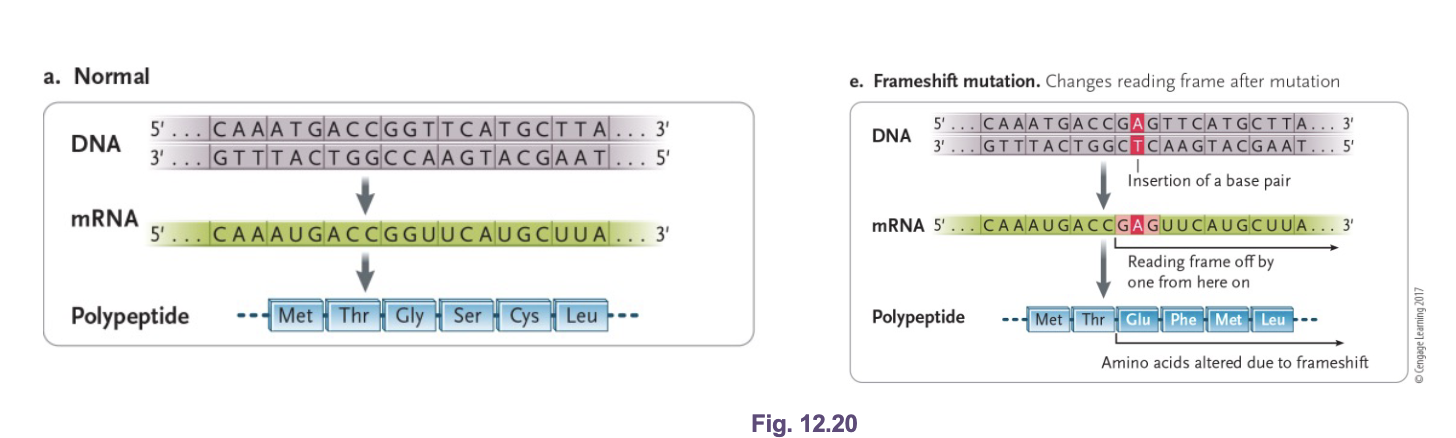
Sickle cell anemia:
A base substitution point mutation in the WHAT gene
The WHAT results in a WHAT mutation that changes the 6th amino acid from glutamic acid (Glu) to valine (Val)
In low oxygen environments, the beta subunit causes hemoglobin molecules to polymerize into WHAT that alter the shape of WHAT
Leads to deficient gas exchange, clogged arteries (pain), circulatory problems, higher risk of heart attack and stroke
Sickle cell anemia:
A base substitution point mutation in the BETA HEMOGLOBIN gene
The TRANSVERSION results in a MISSENSE mutation that changes the 6th amino acid from glutamic acid (Glu) to valine (Val)
In low oxygen environments, the beta subunit causes hemoglobin molecules to polymerize into LONG FIBERS that alter the shape of RBCs
Leads to deficient gas exchange, clogged arteries (pain), circulatory problems, higher risk of heart attack and stroke
What are large scale chromosomal mutations
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
What are large scale chromosomal mutations
Deletion
Duplication/Amplification
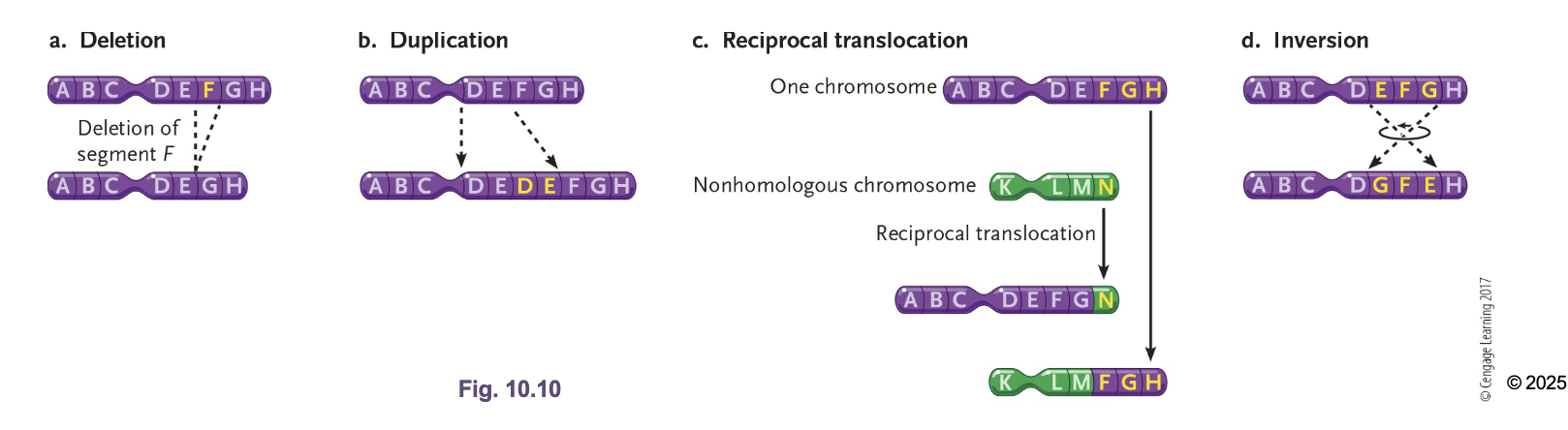
Translocations
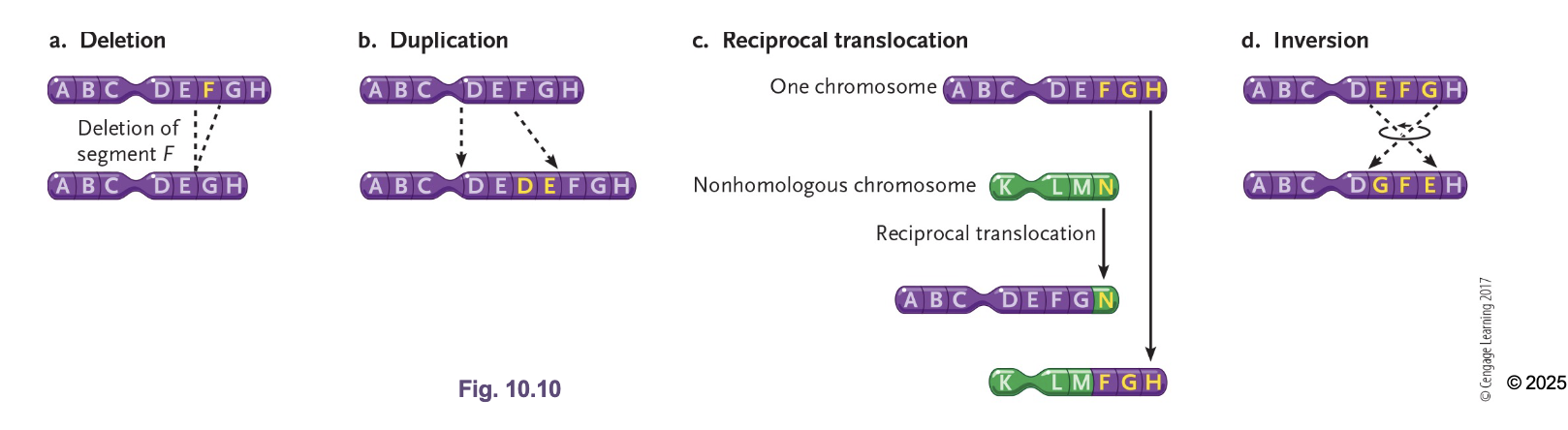
Inversions
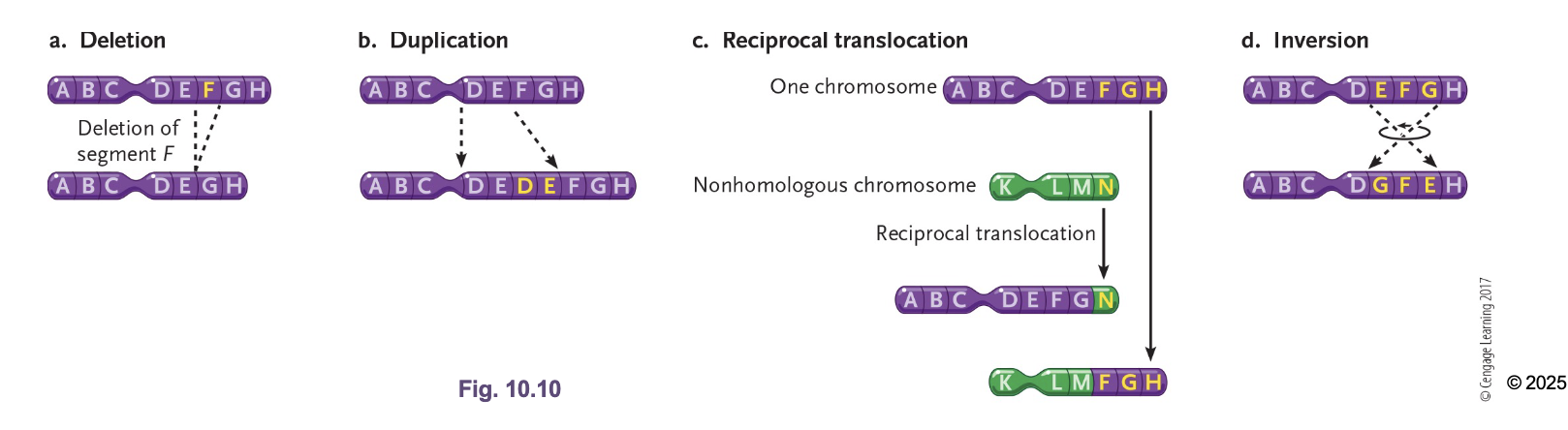
Deletion
Loss of GENES
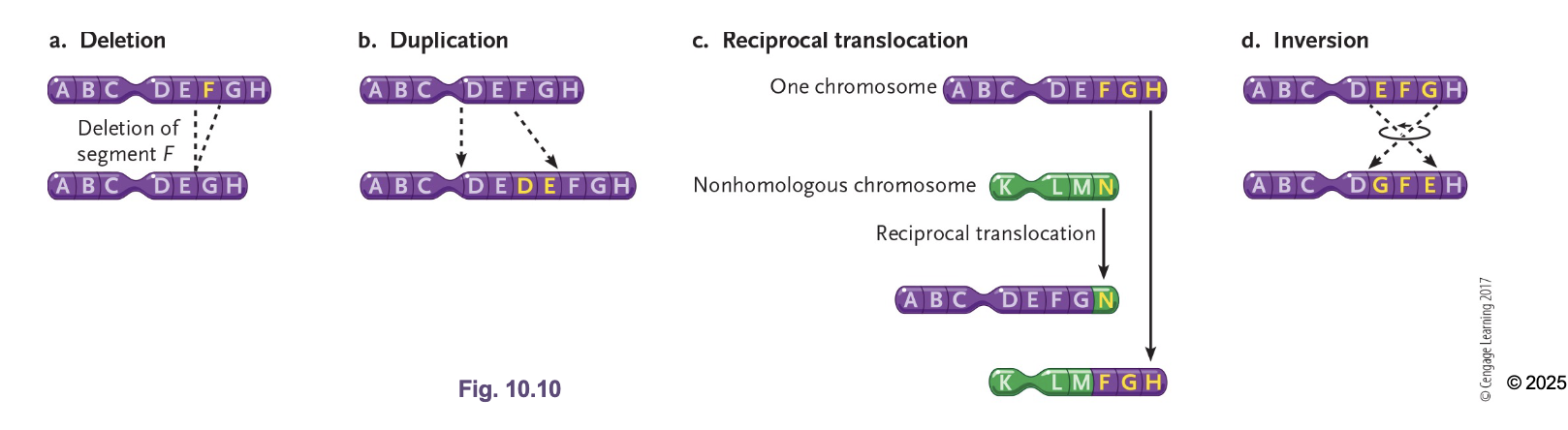
Duplication/Amplification
Increasing dosage of genes (Main way to evolution)
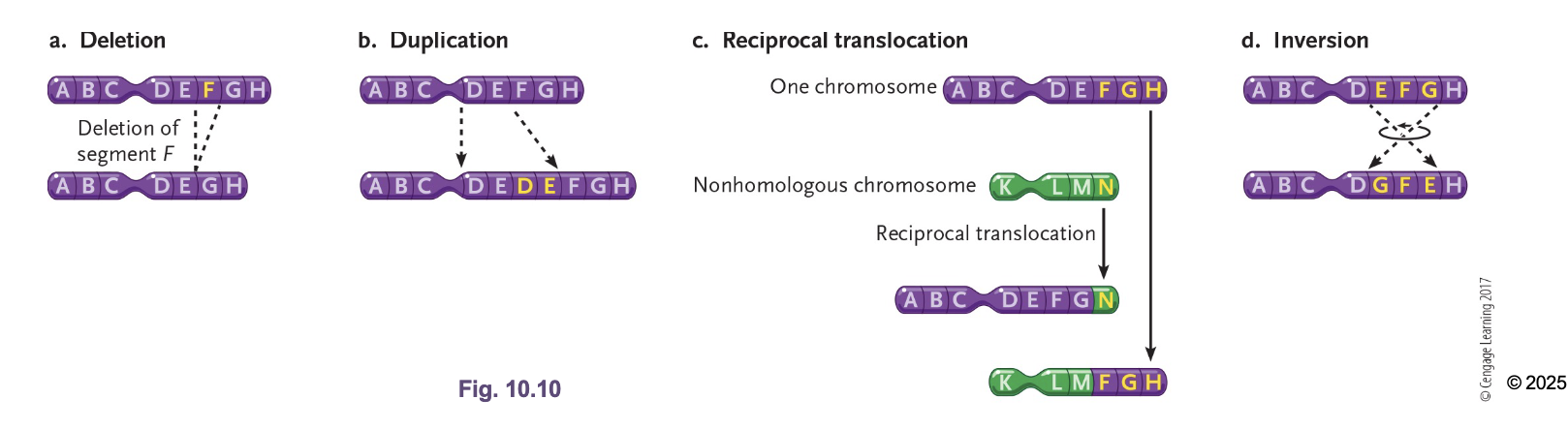
Translocations
Interchange of genetic parts from NON-HOMOLOGOUS chromosomes (not crossing over)
Inversions
Reversing orientation of a segment of the chromosome
Allele
One of many different forms of a GENE (sequence variations) which can cause DIFFERENT PHENOTYPES
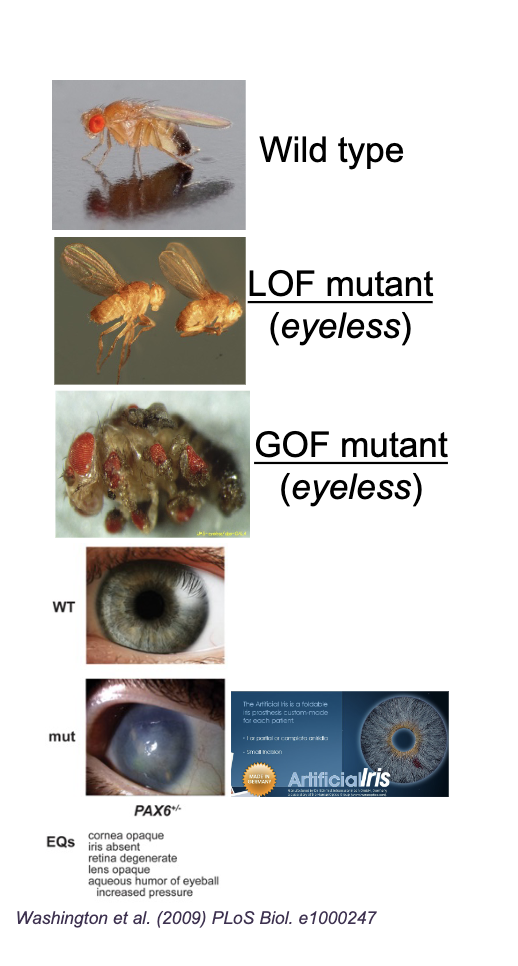
Wildtype allele
“Normal” form of the gene found in nature or the standard laboratory strain of a model organism
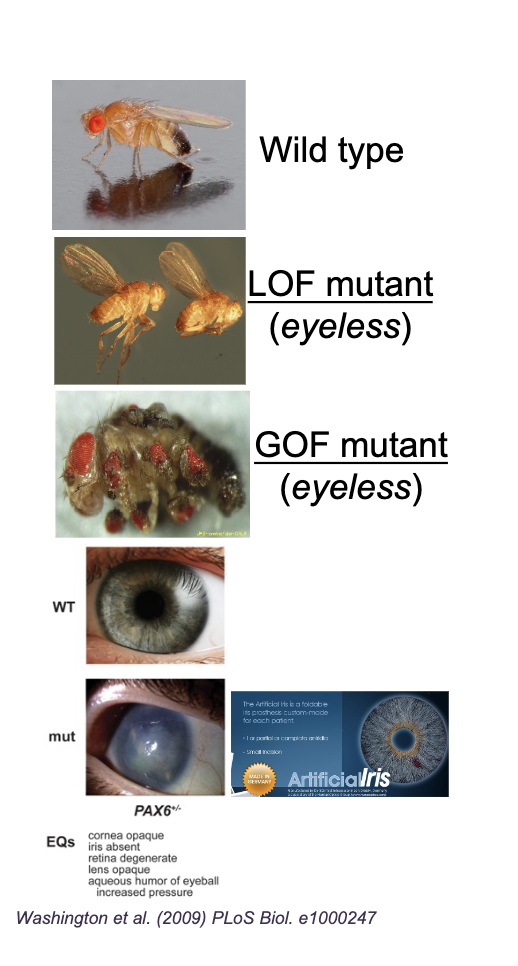
Gain of function
Mutations that ENHANCE gene function/expression
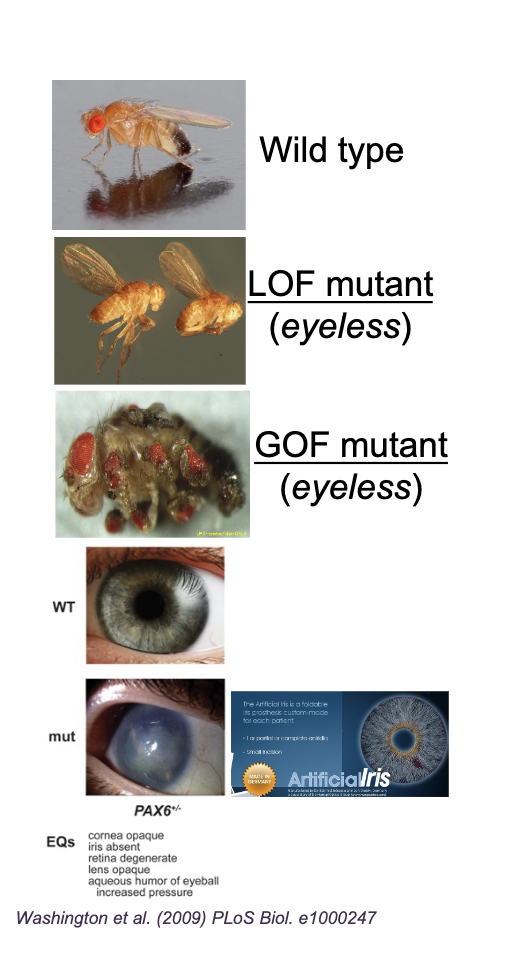
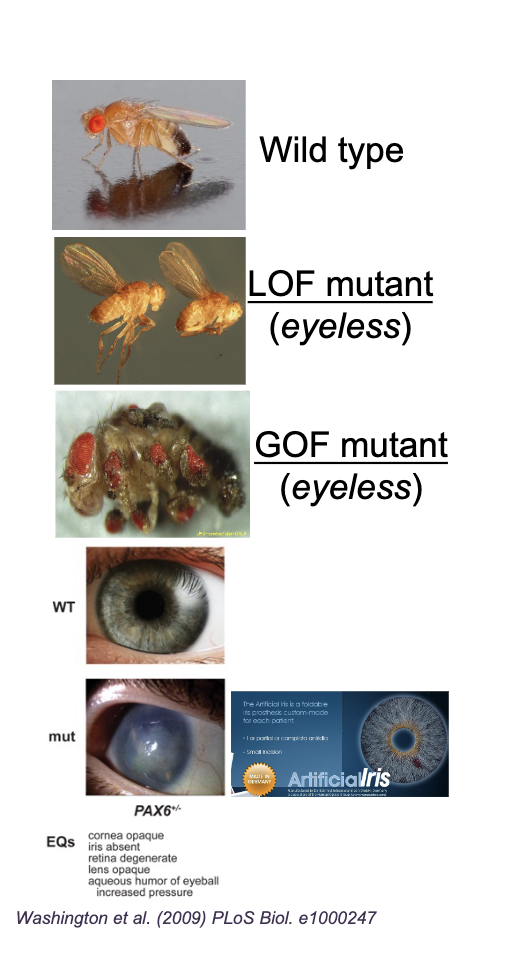
Loss of function
Mutations that REDUCE/ELIMINATE gene function/expression
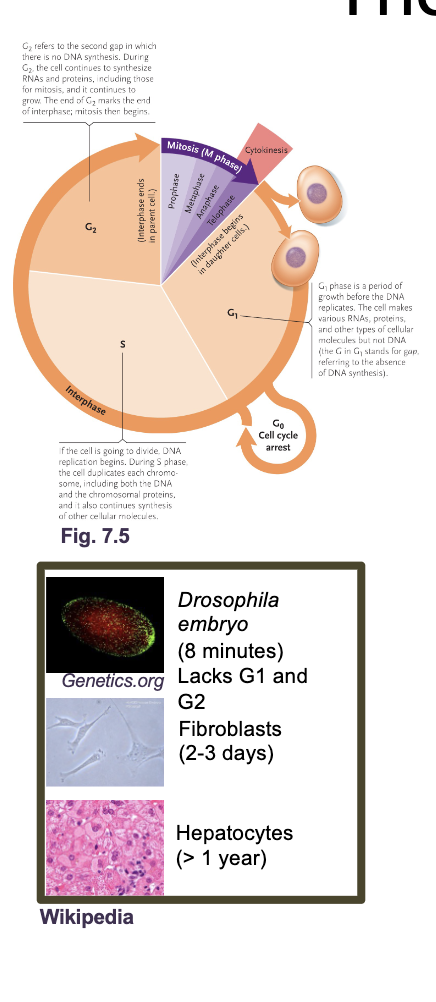
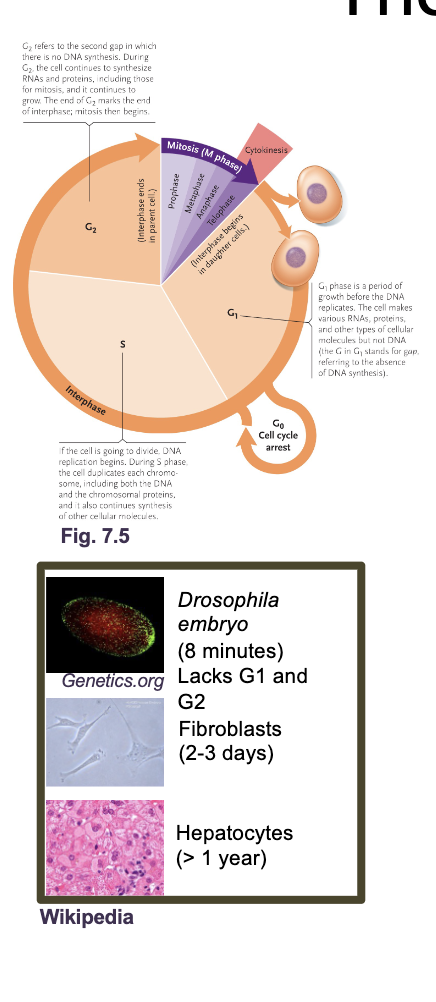
The eukaryotic cell cycle
The cell cycle is an ordered set of processes by which one cell WHAT and WHAT into two WHAT cells
The eukaryotic cell cycle
The cell cycle is an ordered set of processes by which one cell GROWS and DIVIDES into two DAUGHTER cells
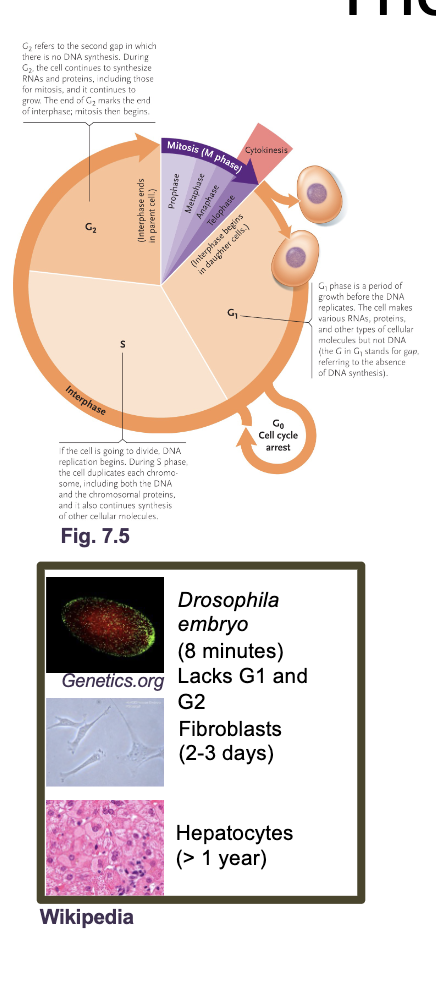
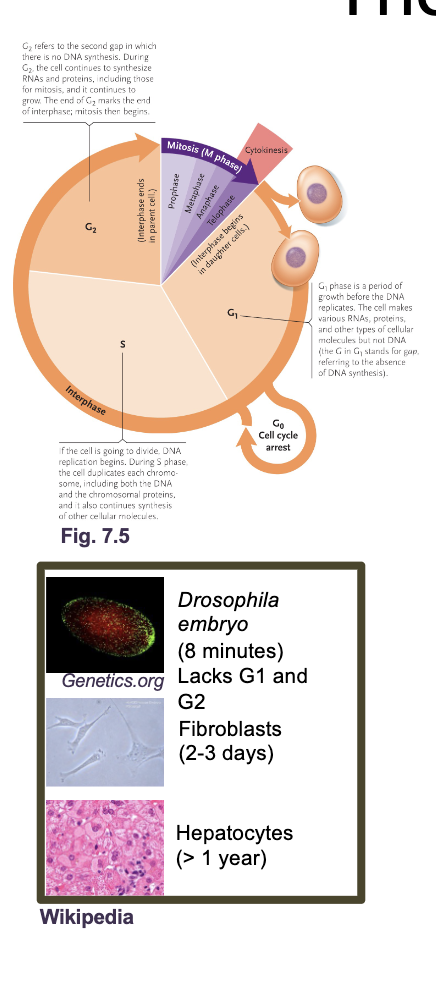
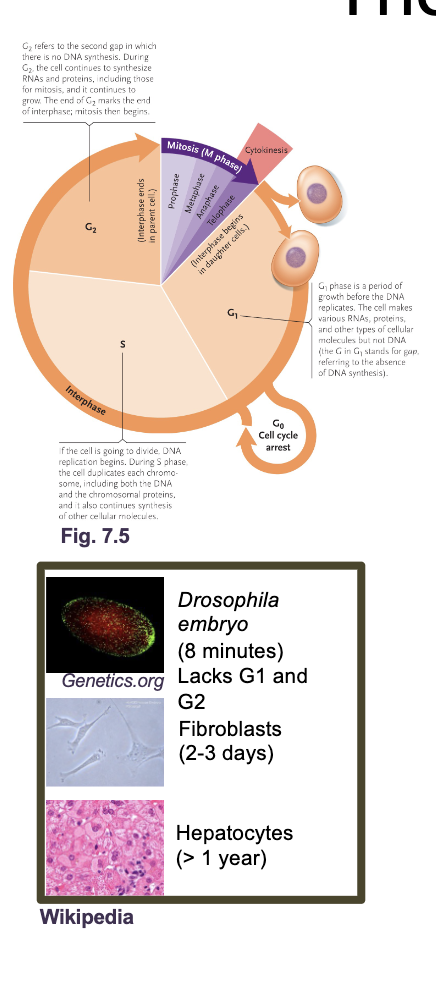
The eukaryotic cell cycle
Need to fully replicate WHAT and WHAT and properly segregate them to WHAT cells
The eukaryotic cell cycle
Need to fully replicate DNA and ORGANELLES and properly segregate them to DAUGHTER cells
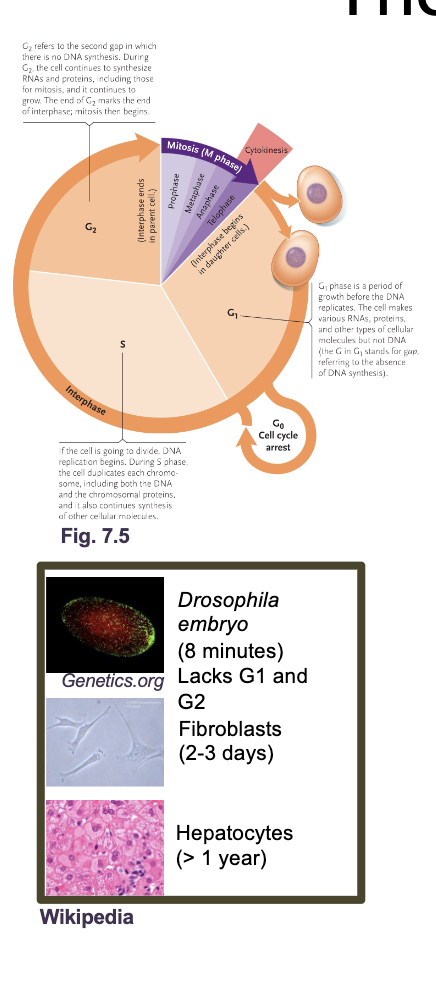
The eukaryotic cell cycle what all occurs
G1 and G2 (Gap and growth phase)
S phase
M phase (mitosis)
Cytokinesis
G0 phase

The eukaryotic cell cycle
G1 and G2 (growth and gap phase): WHAT
The eukaryotic cell cycle
G1 and G2 (growth and gap phase): Synthesis of PROTEINS, RNA, metabolites, other than DNA
The eukaryotic cell cycle
S phase: WHAT
The eukaryotic cell cycle
S phase: DNA replication
The eukaryotic cell cycle
M phase: WHAT
The eukaryotic cell cycle
M phase: NUCLEAR division
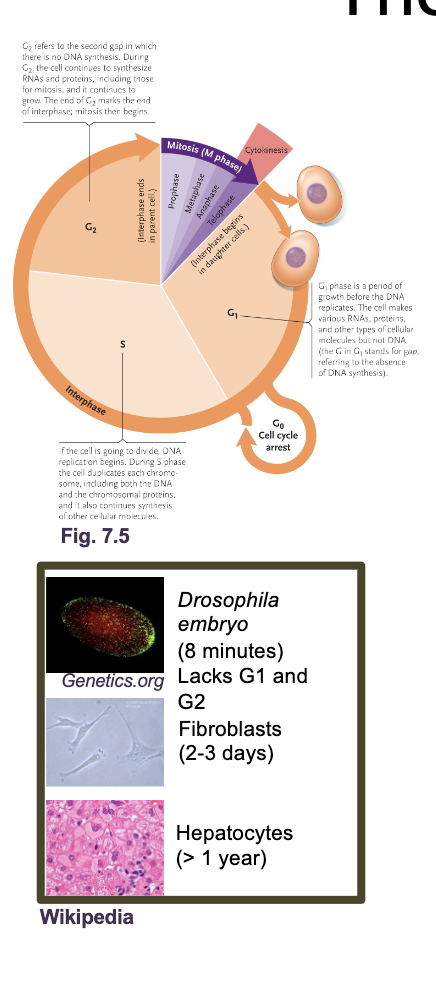
The eukaryotic cell cycle
Cytokinesis: WHAT
The eukaryotic cell cycle
Cytokinesis: CELL division
The eukaryotic cell cycle
G0: WHAT
The eukaryotic cell cycle
G0: Resting phase or quiescence (doesn’t under go mitosis again or under goes in very slowly)
The eukaryotic cell cycle
Most adult human cells are in WHAT either permanently (WHAT or WHAT cells) or semi permanently (WHAT cells reenter G1 during injury)
The eukaryotic cell cycle
Most adult human cells are in G0 either permanently (MUSCLE or NERVE cells) or semi permanently (LIVER cells reenter G1 during injury)
Regulation of eukaryotic cell cycle
Progression of the cell cycle depends upon activation of a WHAT bound to its regulatory WHAT subunit in each phase of the cell cycle
Checkpoints WHAT the cell cycle to allow completion of the event of each phase before proceeding to the next phase
Regulation of eukaryotic cell cycle
Progression of the cell cycle depends upon activation of a CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE (CDK) bound to its regulatory CYCLIN subunit in each phase of the cell cycle
Checkpoints DELAY the cell cycle to allow completion of the event of each phase before proceeding to the next phase
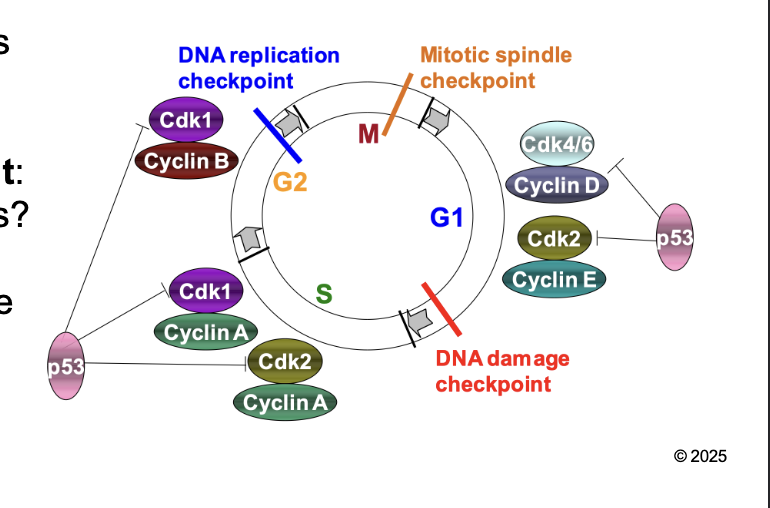
What are the the check point to regulation of eukaryotic cell cycle
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
What are the the check point to regulation of eukaryotic cell cycle
DNA damage (G1/S) checkpoint
DNA replication (G2/M) checkpoint
Mitotic spindle (M) checkpoint
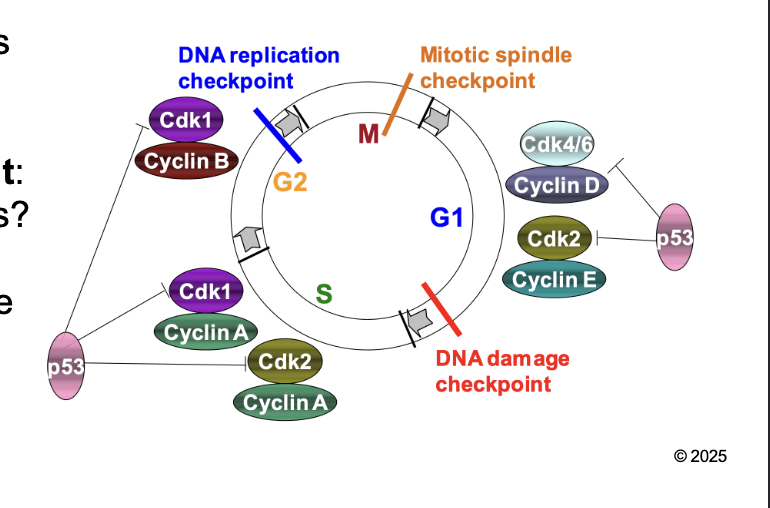
DNA damage (G1/S) checkpoint: WHAT
DNA damage (G1/S) checkpoint: Is DNA okay for REPLICATION
DNA replication (G2/M) checkpoint: WHAT
DNA replication (G2/M) checkpoint: Is DNA fully replicated before mitosis

Mitotic spindle (M) checkpoint: WHAT
Mitotic spindle (M) checkpoint: Are CHROMOSOMES aligned properly in metaphase
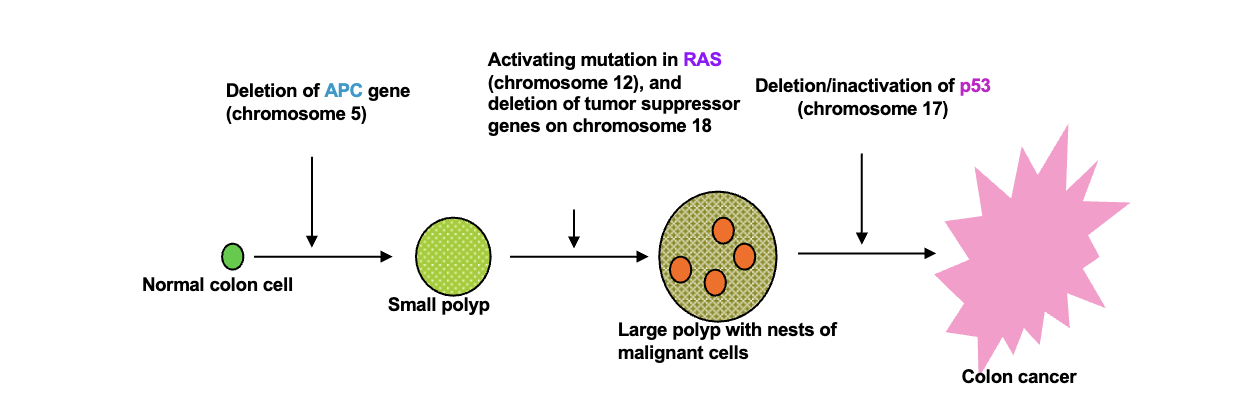
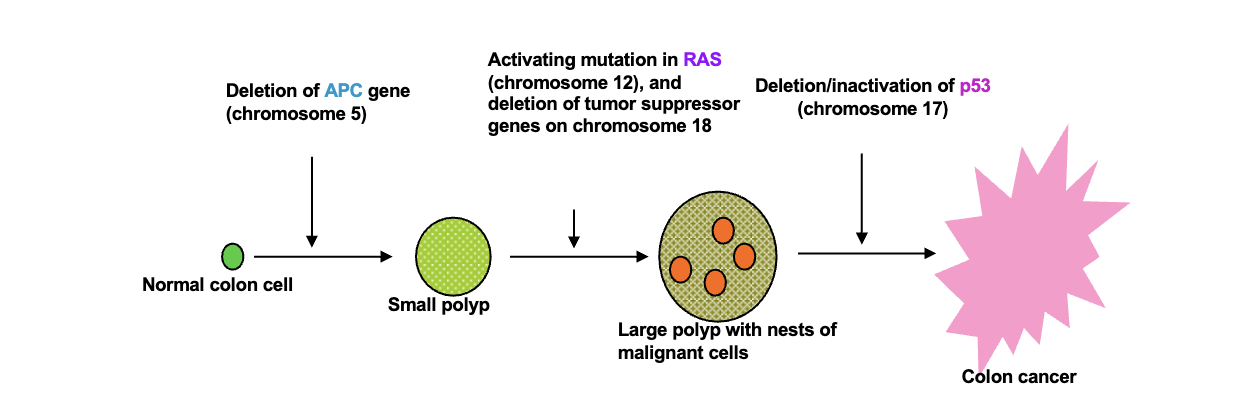
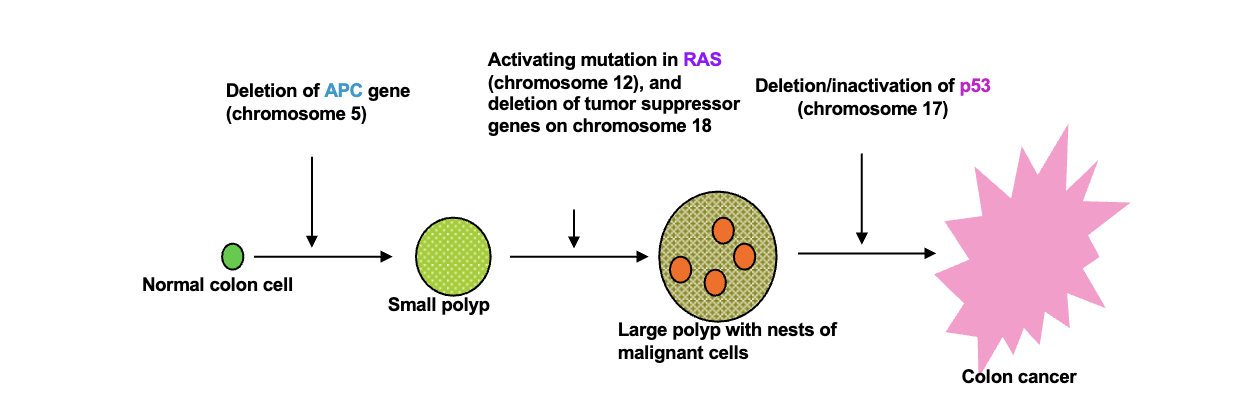
Cancer = WHAT
Cancer = Uncontrolled cell division
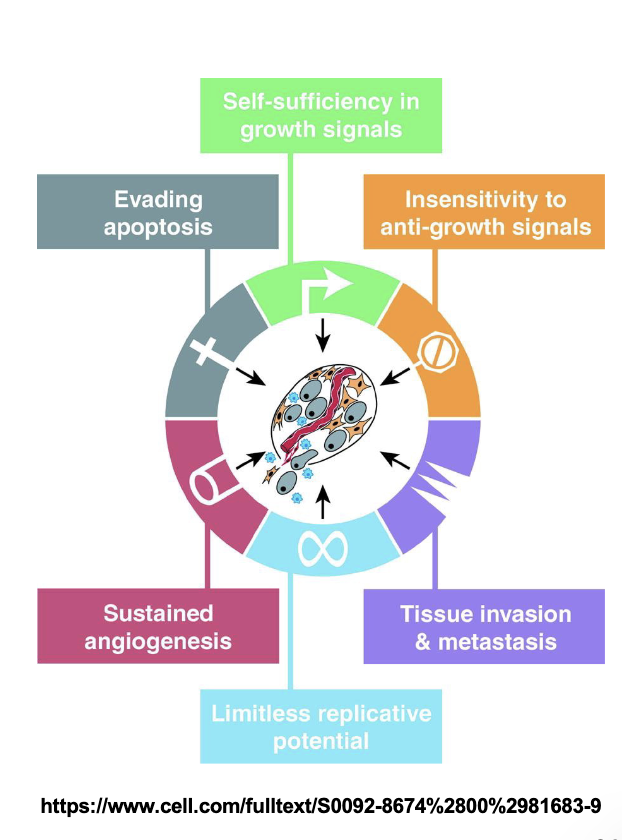
Cancer is WHAT growth caused by WHAT cell division and is caused by altered WHAT of multiple genes due to WHAT (polygenic disease)
→ Cells don’t go in the WHAT
→ cancer = when cell division isn’t WHAT
→ Gain of function = WHAT
→ Loss of function = WHAT
Cancer is MALIGNANT growth caused by UNCONTROLLED cell division and is caused by altered EXPRESSION of multiple genes due to MUTATIONS (polygenic disease)
→ Cells don’t go in the CHECKPOINT
→ cancer = when cell division isn’t REGULATED
→ Gain of function = GO signal
→ Loss of function = Broken breaks
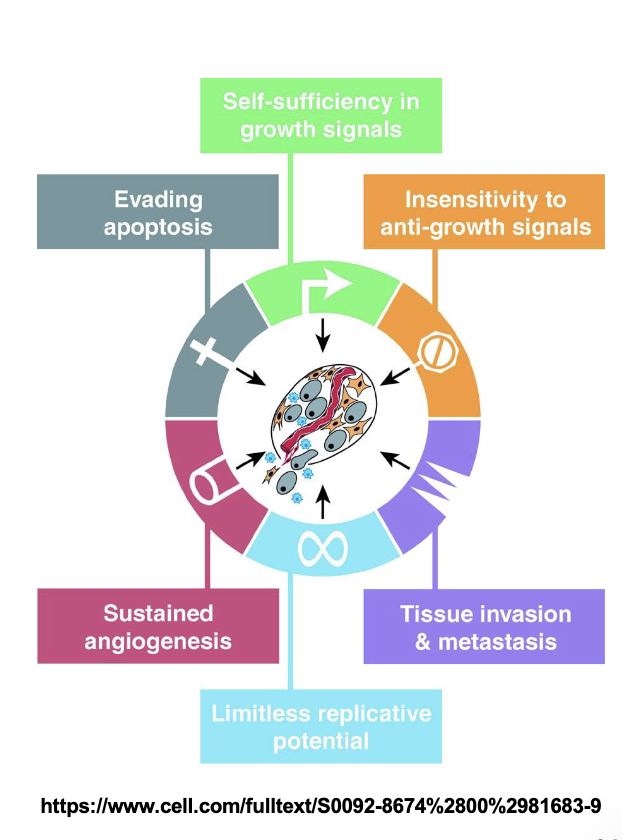
Which mutated genes are implicated in cancer:
WHAT
WHAT
About 50% of tumors have an inactive WHAT gene and cyclin WHAT and WHAT are often highly expressed in WHAT cancer carcinomas
Each cancer is cause by different WHAT - Difficult to find universal cure
Which mutated genes are implicated in cancer:
Oncogenes (Go)
Tumor supressor genes (breaks)
About 50% of tumors have an inactive p53 gene and cyclin D and E are often highly expressed in BREAST cancer carcinomas
Each cancer is cause by different GENE MUTATIONS - Difficult to find universal cure
Which mutated genes are implicated in cancer:
Oncogenes = WHAT regulators of the cell cycle (gain-of-function) including WHAT (gene amplification), WHAT alleles (insensitive to inhibition)
Which mutated genes are implicated in cancer:
Oncogenes = POSITIVE regulators of the cell cycle (gain-of-function) including CYCLIN D/E (gene amplification), cdk4 alleles (insensitive to inhibition)
Which mutated genes are implicated in cancer:
Tumor supressor genes: WHAT regulators of the cell cycle ( loss of function) including WHAT genes WHAT and WHAT
Which mutated genes are implicated in cancer:
Tumor supressor genes: NEGATIVE regulators of the cell cycle (loss of function) including CHECKPOINT genes p53 and RB
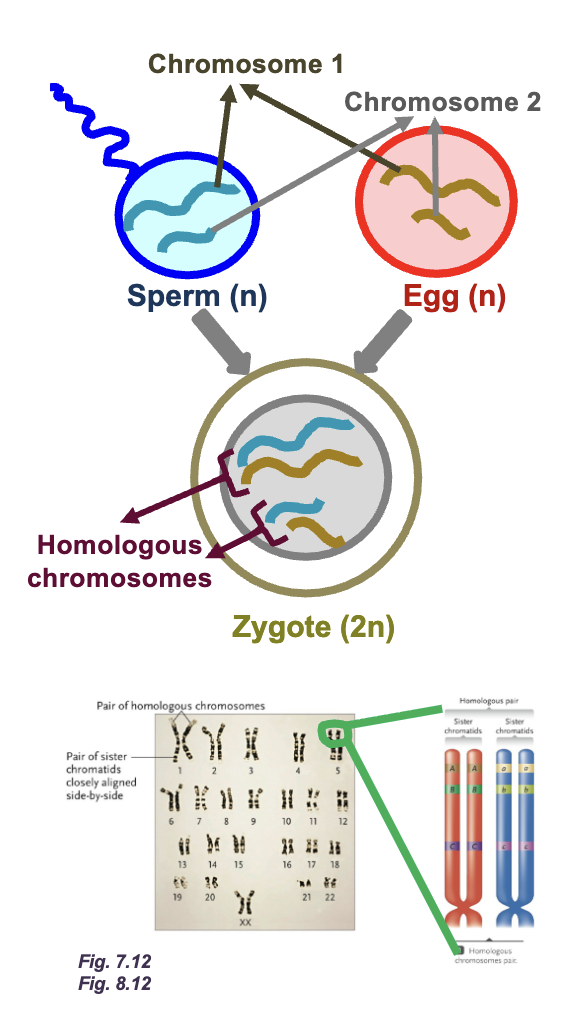
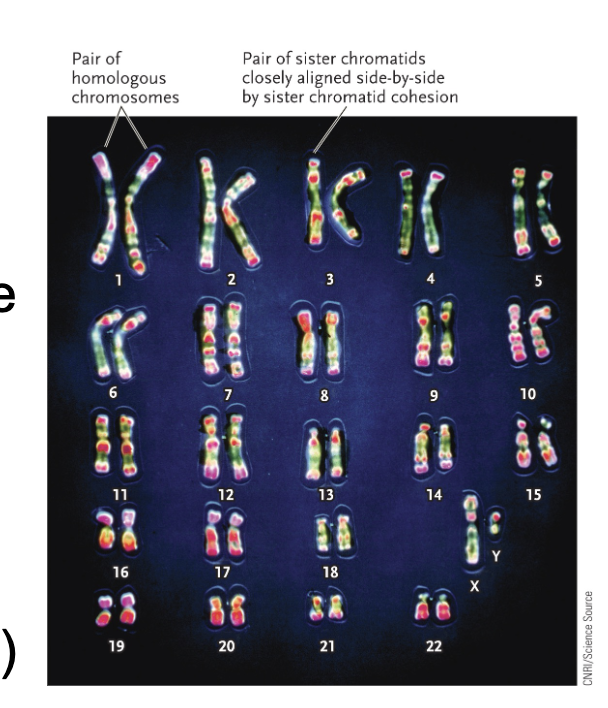
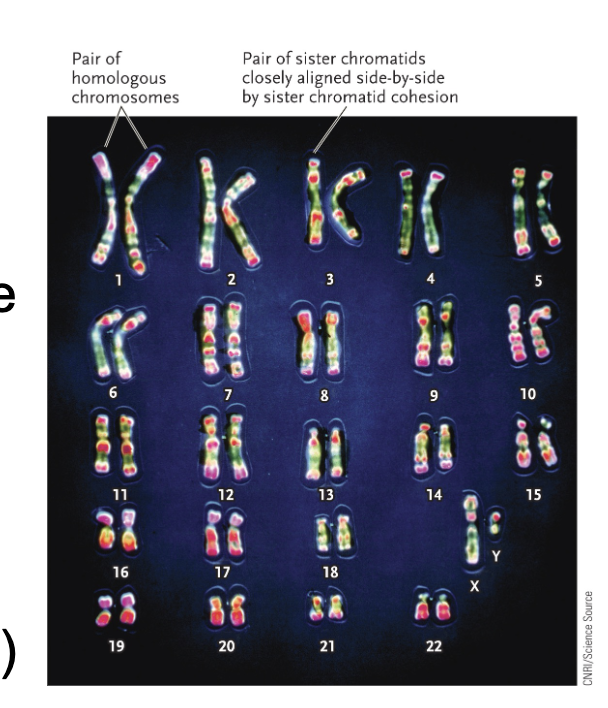
Homologous chromosomes:
Parental pair of WHAT molecules
The number and order of WHAT are the same between homologous chromosomes but WHAT can be different
2n = WHAT number of DNA molecules
n = WHAT number of DNA molecules
Homologous chromosomes:
Parental pair of DNA molecules
The number and order of GENES are the same between homologous chromosomes but ALLELES can be different
2n = DIPLOID number of DNA molecules
n = HAPLOID number of DNA molecules
DNA replication (S phase)
Each DNA molecule is replicated WHAT
Following replication, each DNA molecules exists as a pair of WHAT that are attached at the WHAT
DNA replication (S phase)
Each DNA molecule is replicated INDEPENDENTLY
Following replication, each DNA molecules exists as a pair of SISTER CHROMATIDS that are attached at the CENTROMERE
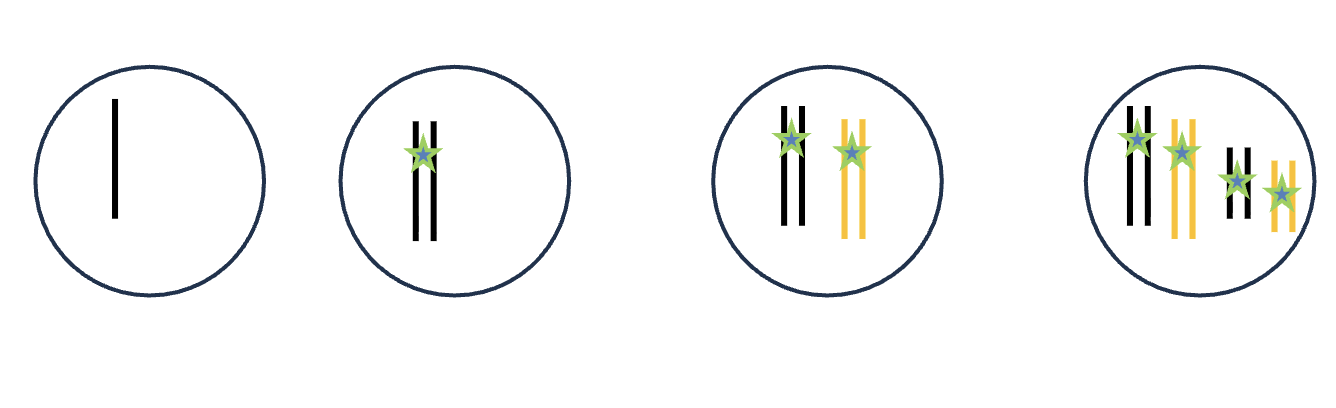
DNA replication (S phase)
HOW MANY DNA molecules
HOW MANY Homologous pairs
HOW MANY Chromatid
HOW MANY Sister chromatids
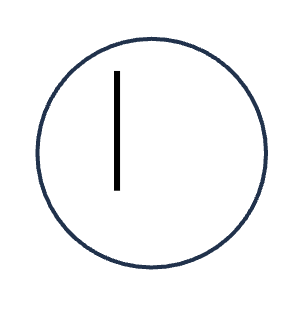
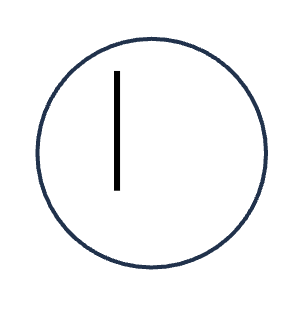
DNA replication (S phase)
1 DNA molecules
0 Homologous pairs
1 Chromatid
0 Sister chromatids
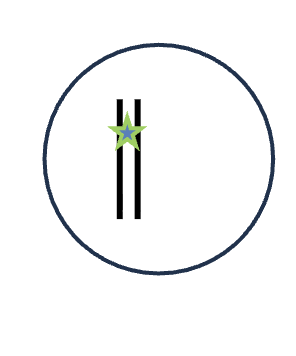
DNA replication (S phase)
HOW MANY DNA molecules
HOW MANY Homologous pairs
HOW MANY Chromatid
HOW MANY Sister chromatids
DNA replication (S phase)
1 DNA molecules
0 Homologous pairs
2 Chromatid
1 Sister chromatids
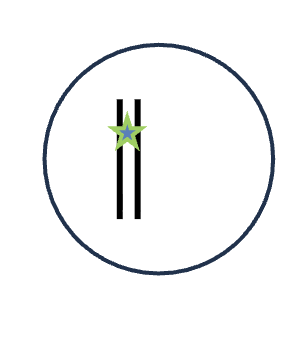
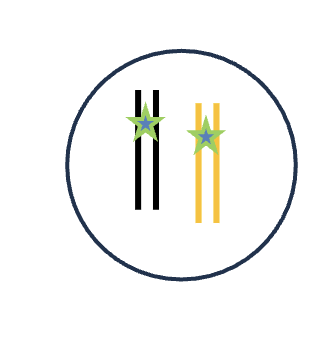
DNA replication (S phase)
HOW MANY DNA molecules
HOW MANY Homologous pairs
HOW MANY Chromatid
HOW MANY Sister chromatids
DNA replication (S phase)
2 DNA molecules
1 Homologous pairs
4 Chromatid
2 Sister chromatids
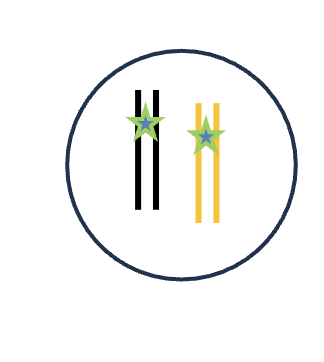
DNA replication (S phase)
HOW MANY DNA molecules
HOW MANY Homologous pairs
HOW MANY Chromatid
HOW MANY Sister chromatids
DNA replication (S phase)
4 DNA molecules
2 Homologous pairs
8 Chromatid
4 Sister chromatids

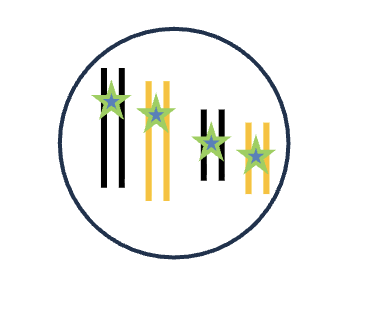
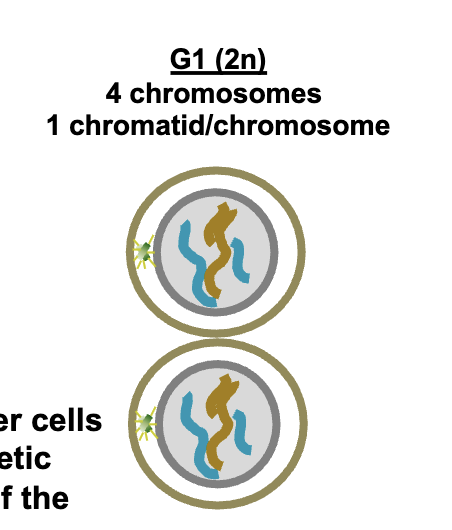
G1 (2n)
HOW MANY chromosomes (DNA molecules)
HOW MANY chromatid/chromosomes (per each)
G1 (2n)
4 chromosomes (DNA molecules)
1 chromatid/chromosomes

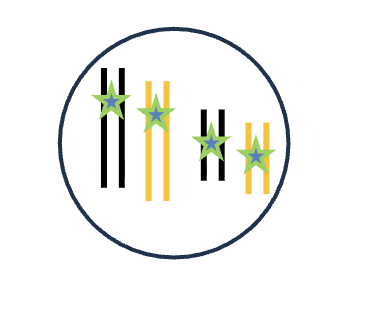
G2 (2n)
HOW MANY chromosomes (DNA molecules)
HOW MANY chromatid/chromosomes
G2 (2n)
4 chromosomes (DNA molecules)
2 chromatid/chromosomes (per each)
Between G1 and G2
Between G1 and G2
DNA REPLICATION
chromosomes are not VISIBLE
CENTRIOLE duplication
MITOCHONDRIA duplication
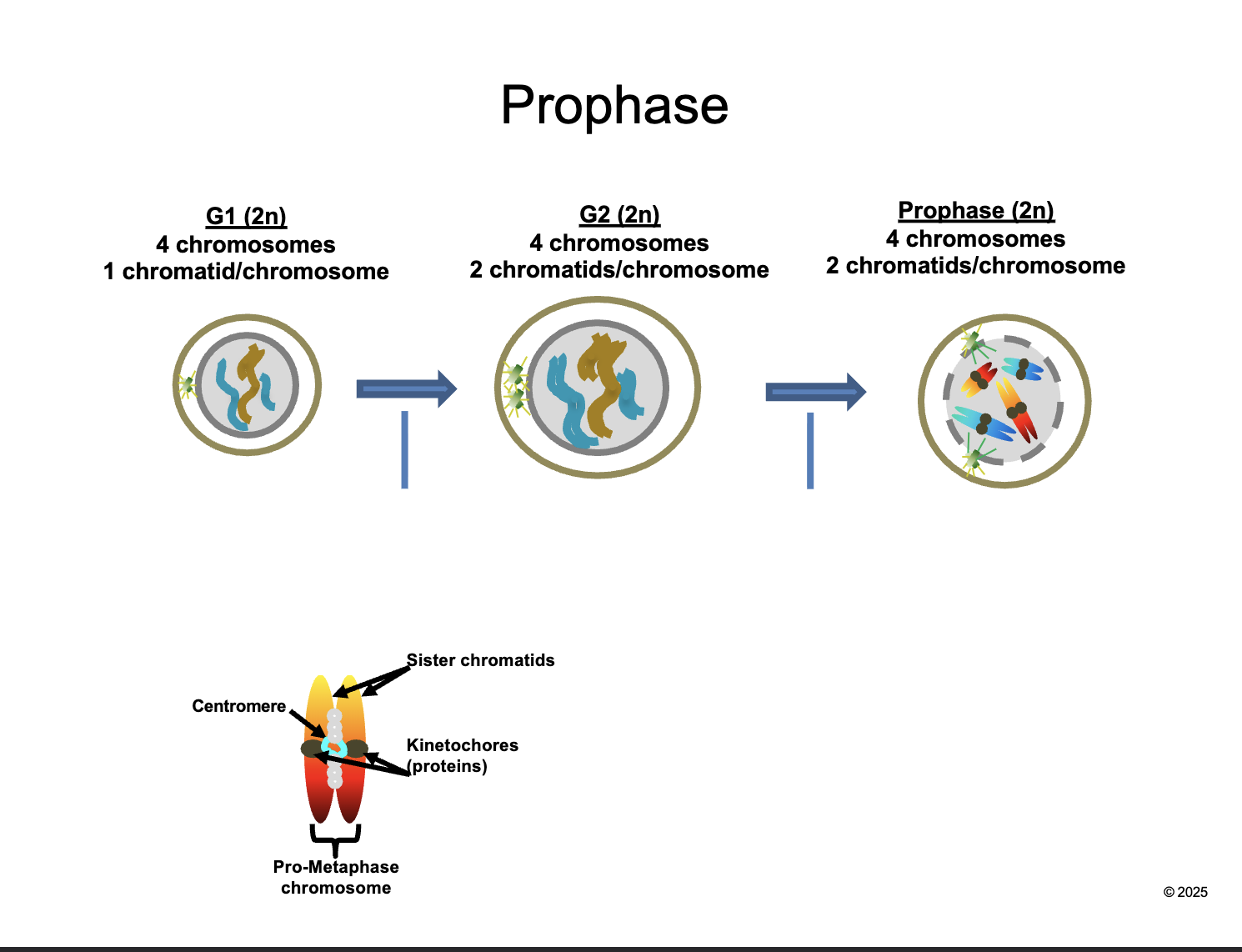

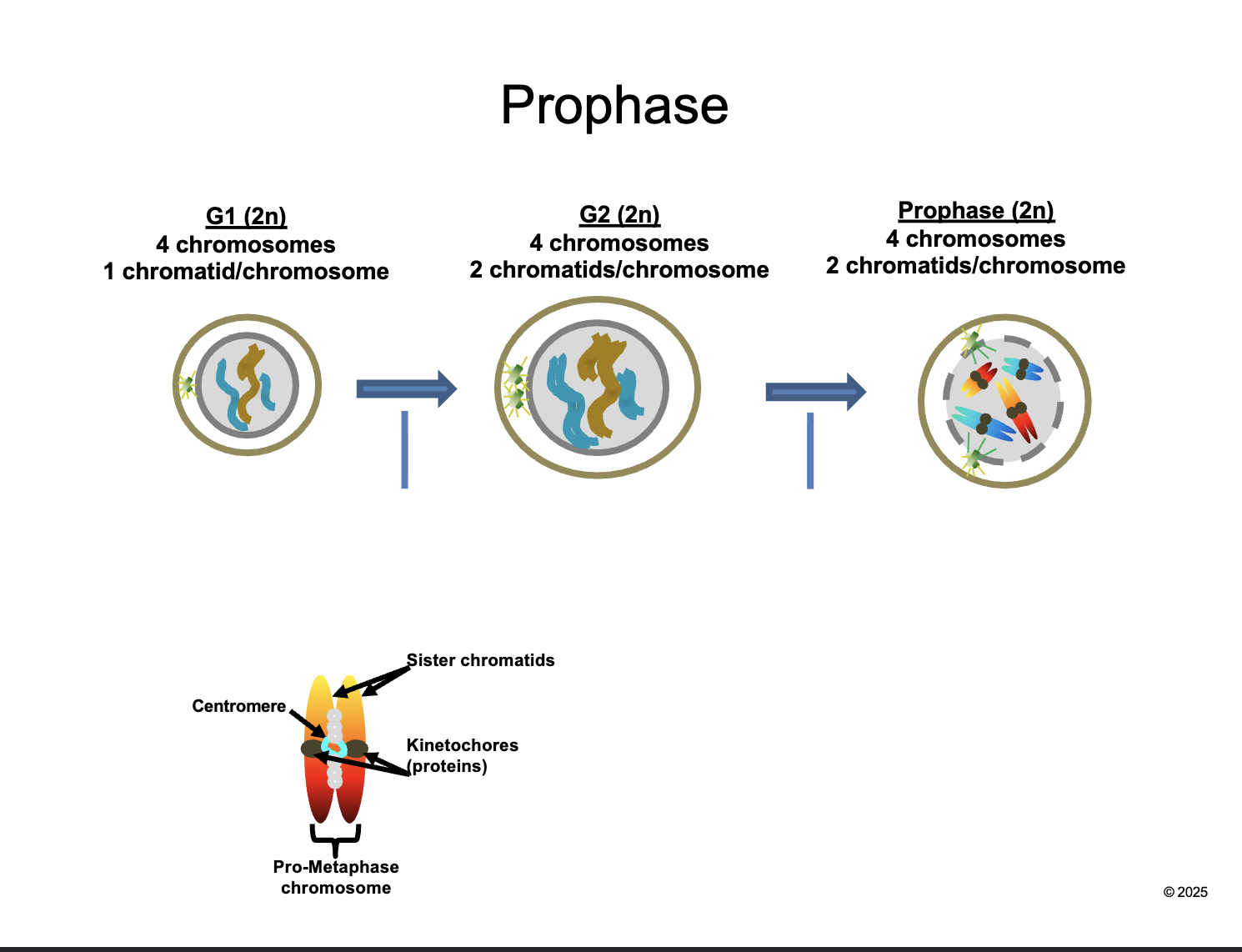
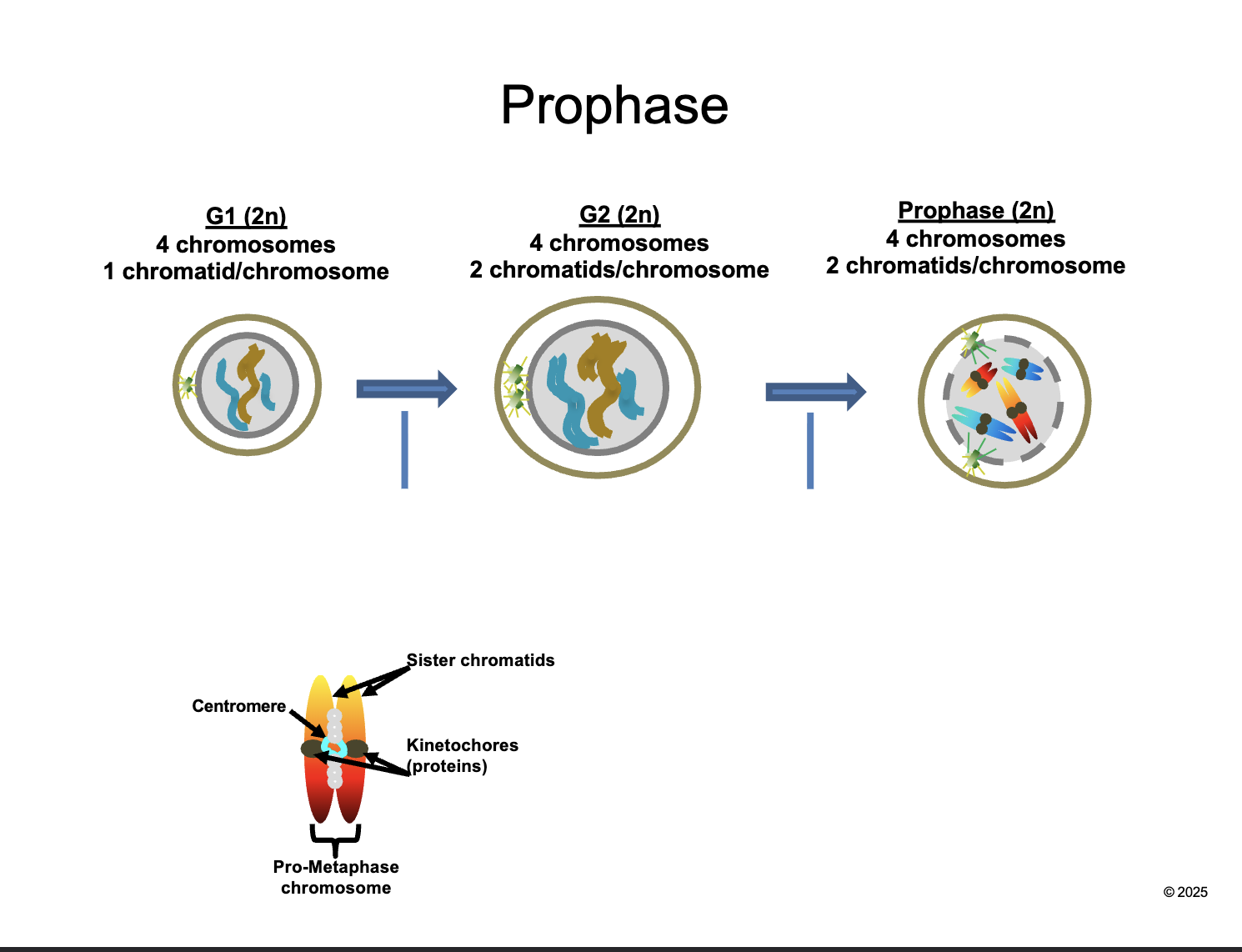
Prophase (2n)
HOW MANY chromosomes
HOW MANY chromatids/chromosomes
Prophase (2n)
4 chromosomes
2 chromatids/chromosomes
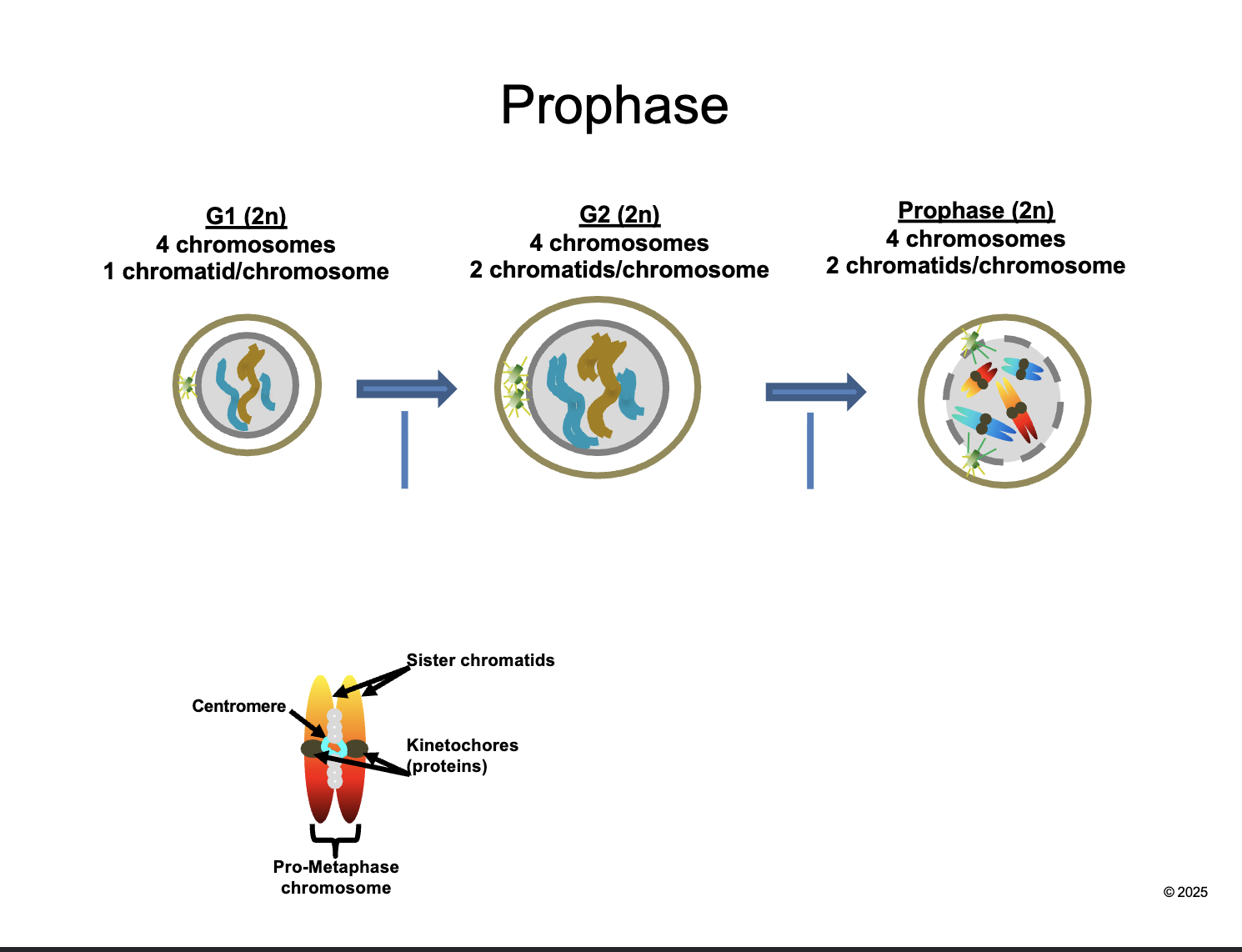
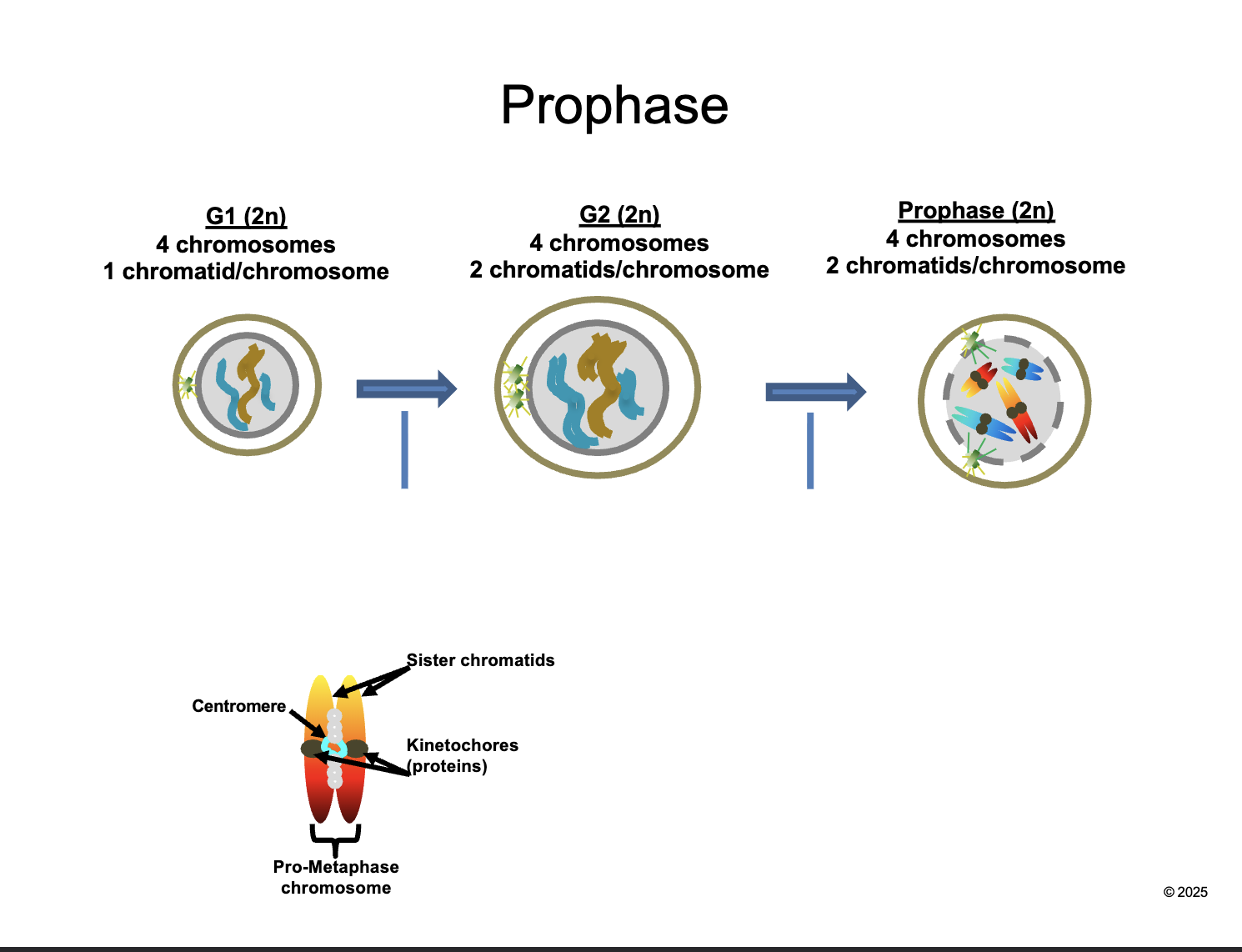
Between G2 and prophase
Between G2 and prophase
Chromosomes CONDENSE and become VISIBLE
CENTROSOMES move apart and form MITOTIC SPINDLES
NUCLEAR ENVELOPE breaks down
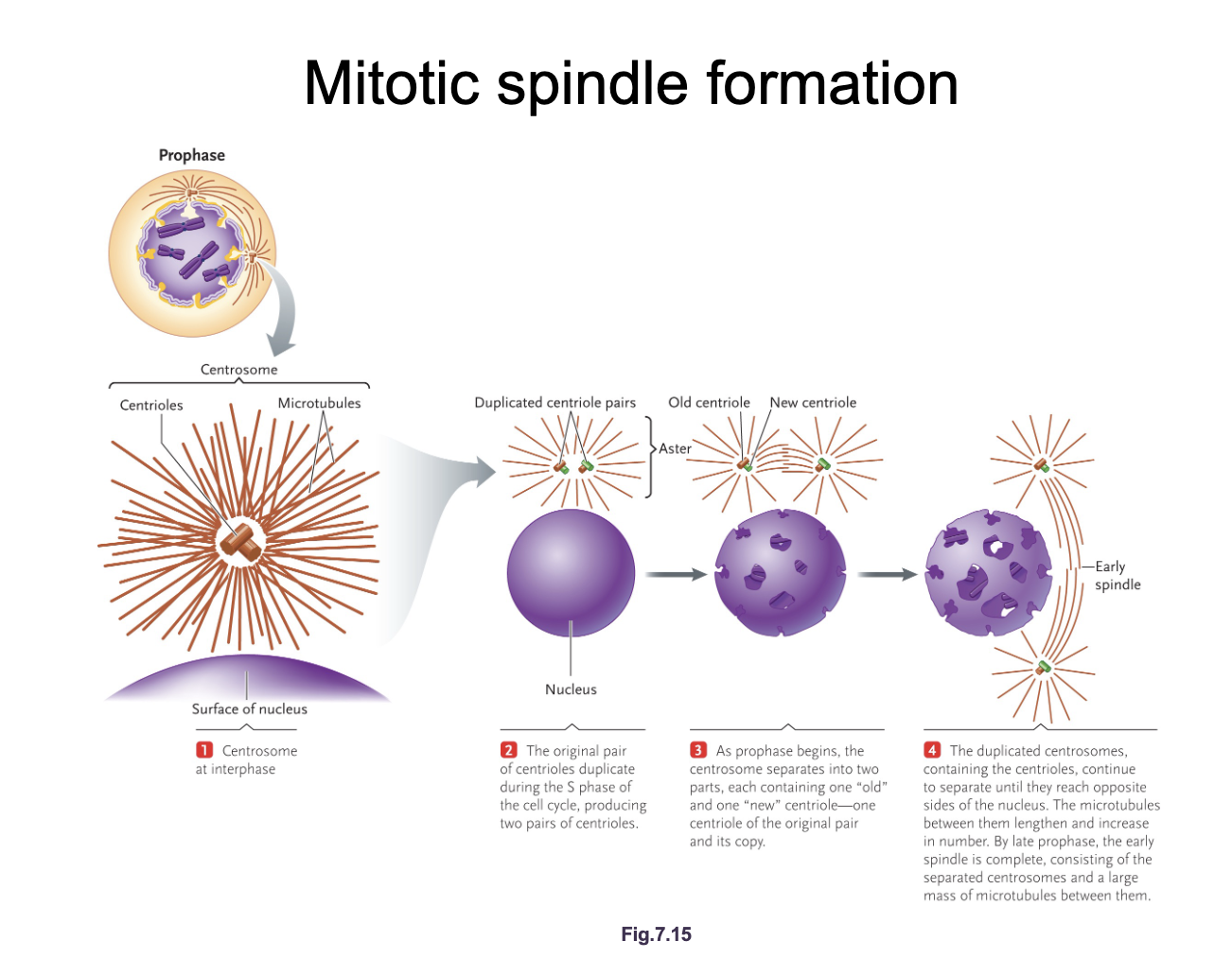
Mitotic spindle formation diagram
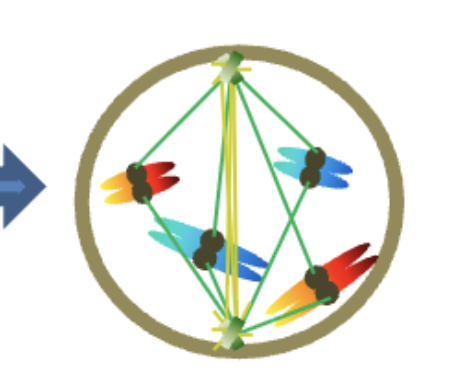
Prometaphase (2n)
HOW MANY chromosomes
HOW MANY chromatids/chromosomes
Prometaphase (2n)
4 chromosomes
2 chromatids/chromosomes
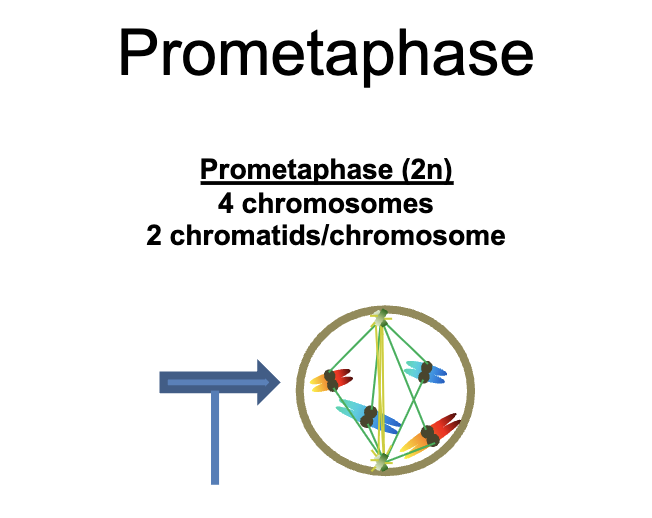
Prometaphase
Centrosomes reach opposite WHAT
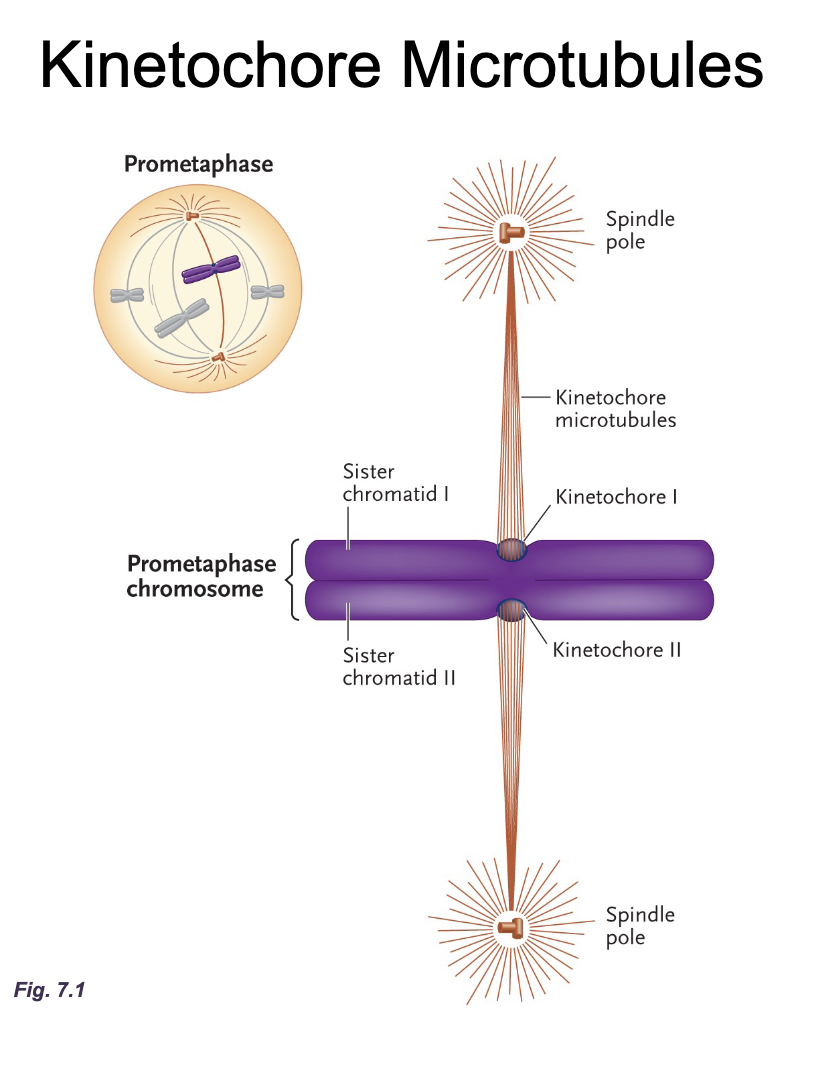
WHAT microtubules attach to each other
WHAT microtubules attach to WHAT proteins at the WHAT
Sister chromatids are connected to WHAT
Chromosomes start migrating to WHAT
Prometaphase
Centrosomes reach opposite POLES
NON-KINETOCHORE microtubules attach to each other
KINETOCHORE (SPINDLE) microtubules attach to KINETOCHORE proteins at the CENTROMERES
Sister chromatids are connected to OPPOSITE POLES
Chromosomes start migrating to EQUATOR

Kinetochore microtubules diagram

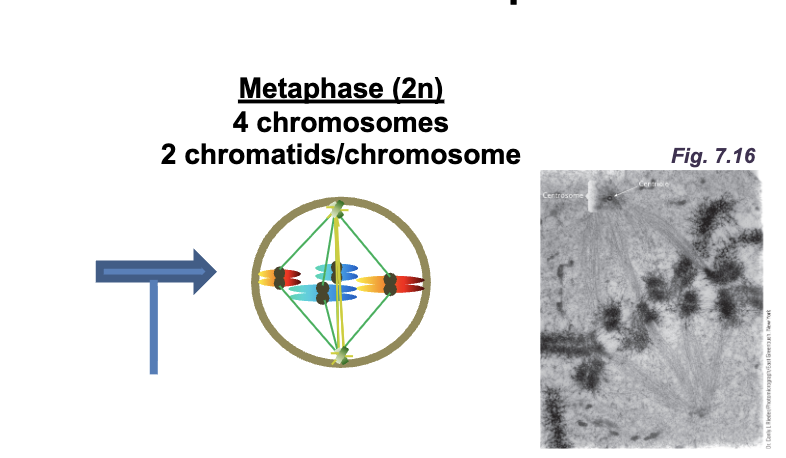
Metaphase (2n)
HOW MANY chromosomes
HOW MANY chromatids/chromosomes
Metaphase (2n)
4 chromosomes
2 chromatids/chromosomes
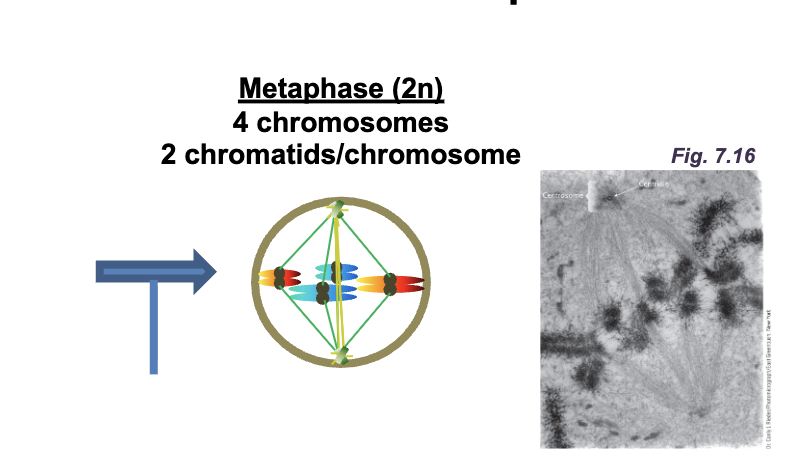
Metaphase
All DNA molecules are aligned at the WHAT (WHAT plate)
Sister chromatids are attached to WHAT
Metaphase
All DNA molecules are aligned at the EQUATOR (METAPHASE plate)
Sister chromatids are attached to OPPOSITE POLES
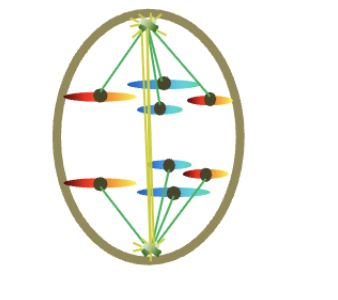
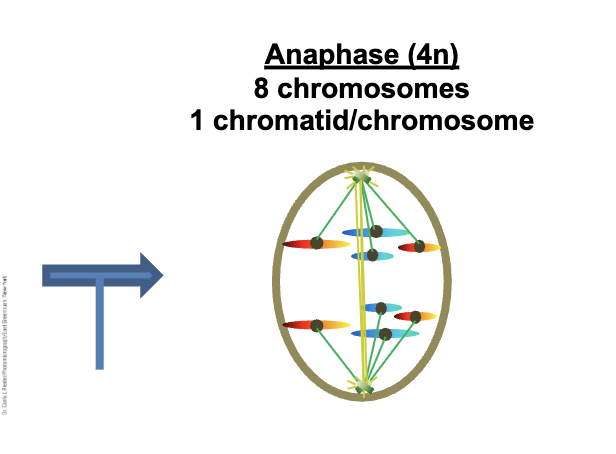
Anaphase (4n)
HOW MANY chromosomes
HOW MANY chromatids/chromosomes (per DNA molecule)
Anaphase (4n)
8 chromosomes
1 chromatids/chromosomes (per DNA molecule)
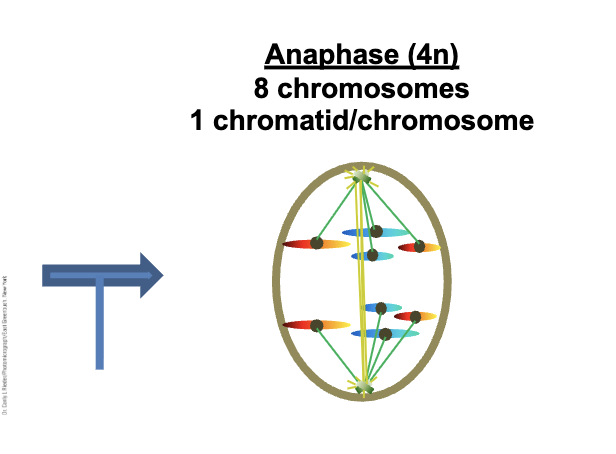
Anaphase (4n)
Sister chromatids are WHAT
Chromatids are now WHAT DNA molecules (chromosomes)
Cell is WHAT
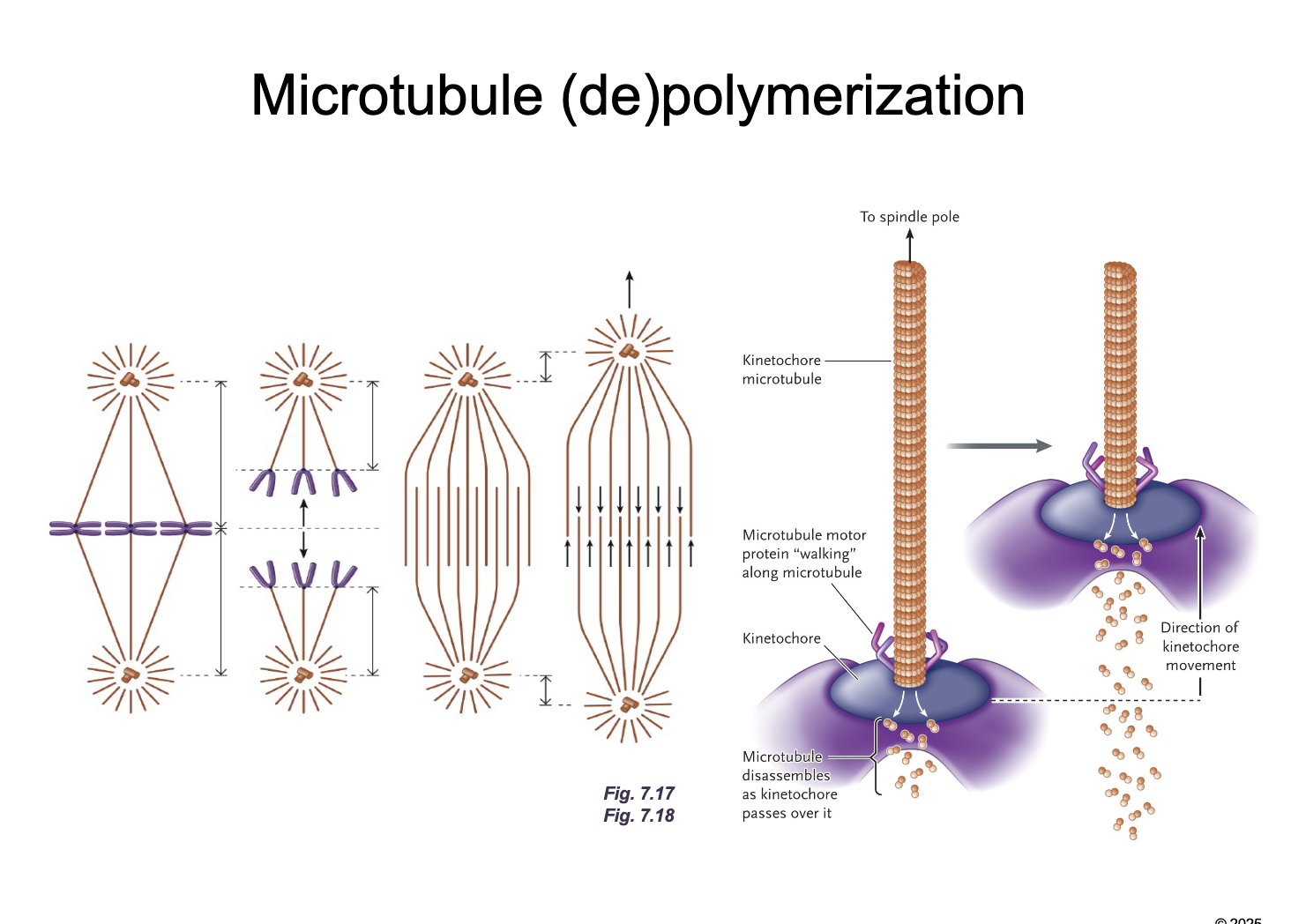
Kinetochore microtubules WHAT (WHAT)
Non-kinetochore microtubules WHAT
Anaphase (4n)
Sister chromatids are SEPARATE
Chromatids are now INDEPENDENT DNA molecules (chromosomes)
Cell is TETRAPLOID
Kinetochore microtubules DEPOLYMIZE (SHORTEN)
Non-kinetochore microtubules LENGTHEN
Microtubules (de)polymerization diagram
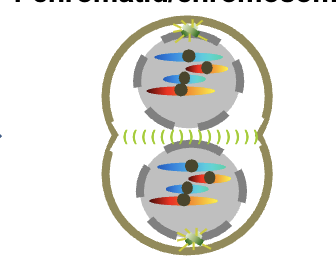
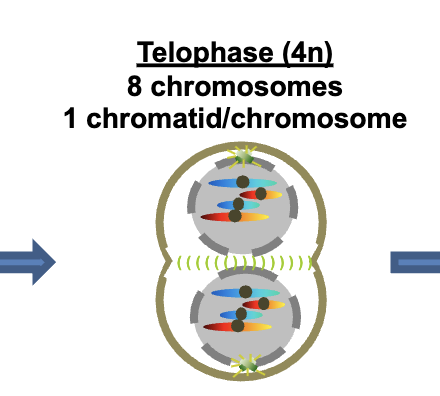
Telophase 4n
HOW MANY chromosomes
HOW MANY chromatid/chromosomes per DNA molecule
Telophase 4n
8 chromosomes
1 chromatid/chromosomes per DNA molecule
G1 2n
HOW MANY chromosomes
HOW MANY chromatid/chromosomes per DNA molecule
G1 2n
4 chromosomes
1 chromatid/chromosomes per DNA molecule
From anaphase to telophase
Chromosomes cluster at OPPOSITE poles and DECONDENSE
Nuclear envelope REFORMS
Cytokinesis (division of the cell) beings by FURROWING
From telophase to G1
Two daughter cells taht are GENETIC DUPLICATES of the parental strand
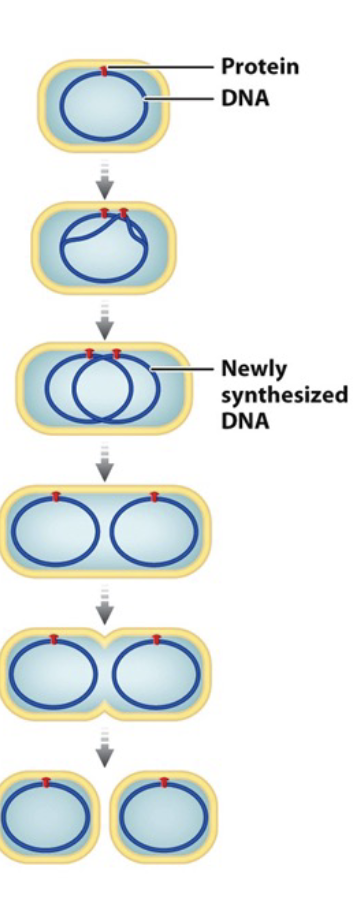
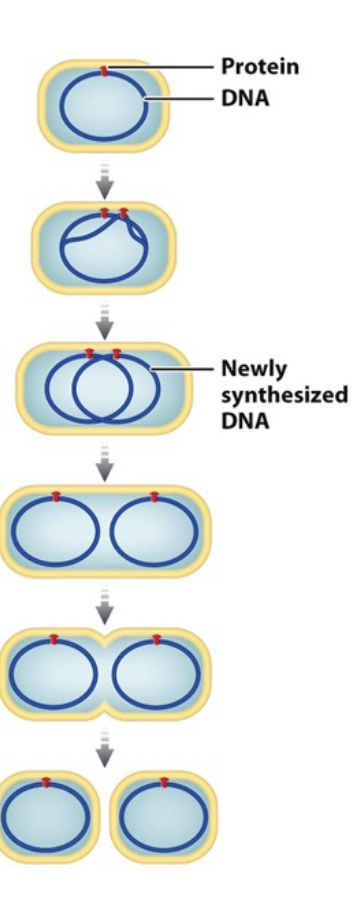
Cell cycle in prokaryotes (binary fission)
Replication beings at the WHAT
Bacterial chromosome (template and daughter) is attached to the WHAT
Cell WHAT and bacterial chromosomes WHAT
Inward growth of plasma membrane and partition assembly of new WHAT, WHAT replicated DNA
Produces WHAT
Effective because only HOW MANY chromosomes
WHAT evolved from this process
Cell cycle in prokaryotes (binary fission)
Replication beings at the ORI
Bacterial chromosome (template and daughter) is attached to the INNER MEMBRANE
Cell ELONGATES and bacterial chromosomes SEPARATE
Inward growth of plasma membrane and partition assembly of new CELL WALL, DIVIDING replicated DNA
Produces TWO DAUGHTER CELLS
Effective because only 1 chromosomes
MITOSIS evolved from this process
Our germ cells contain HOW MANY chromosomes
We have HOW MANY pairs of homologous chromosomes
Our germ cells contain 46 chromosomes
We have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
Reproduction must maintain the WHAT number of chromosomes, so gamete formation separates the WHAT pairs
Results in WHAT
Reproduction must maintain the DIPLOID number of chromosomes, so gamete formation separates the HOMOLOGOUS pairs
Results in HAPLOID sperm/ova
WHAT (WHAT) restores the diploid number in the zygote in a “new” combination of WHAT
FERTILIZATION (SYNGAMY) restores the diploid number in the zygote in a “new” combination of ALLELES
Interphase
Germ cells follow a modified cell cycle
- WHAT, WHAT, WHAT, WHAT*
S phase
- All WHAT DNA molecules are WHAT
- Each DNA molecule exists as a pair of WHAT
M phase
- First cellular division
- Generates WHAT
- Each DNA molecule exists as a pair of WHAT
- Second cellular division
- Generates WHAT
- Each with a WHAT copy of each DNA molecule
Interphase
Germ cells follow a modified cell cycle
- G1, S, G2, M*
S phase
- All 46 DNA molecules are REPLICATED
- Each DNA molecule exists as a pair of SISTER CHROMATIDS
M phase
- First cellular division
- Generates HAPLOID CELLS
- Each DNA molecule exists as a pair of SISTER CHROMATIDS
- Second cellular division
- Generates HAPLOID GAMETES
- Each with a SINGLE copy of each DNA molecule
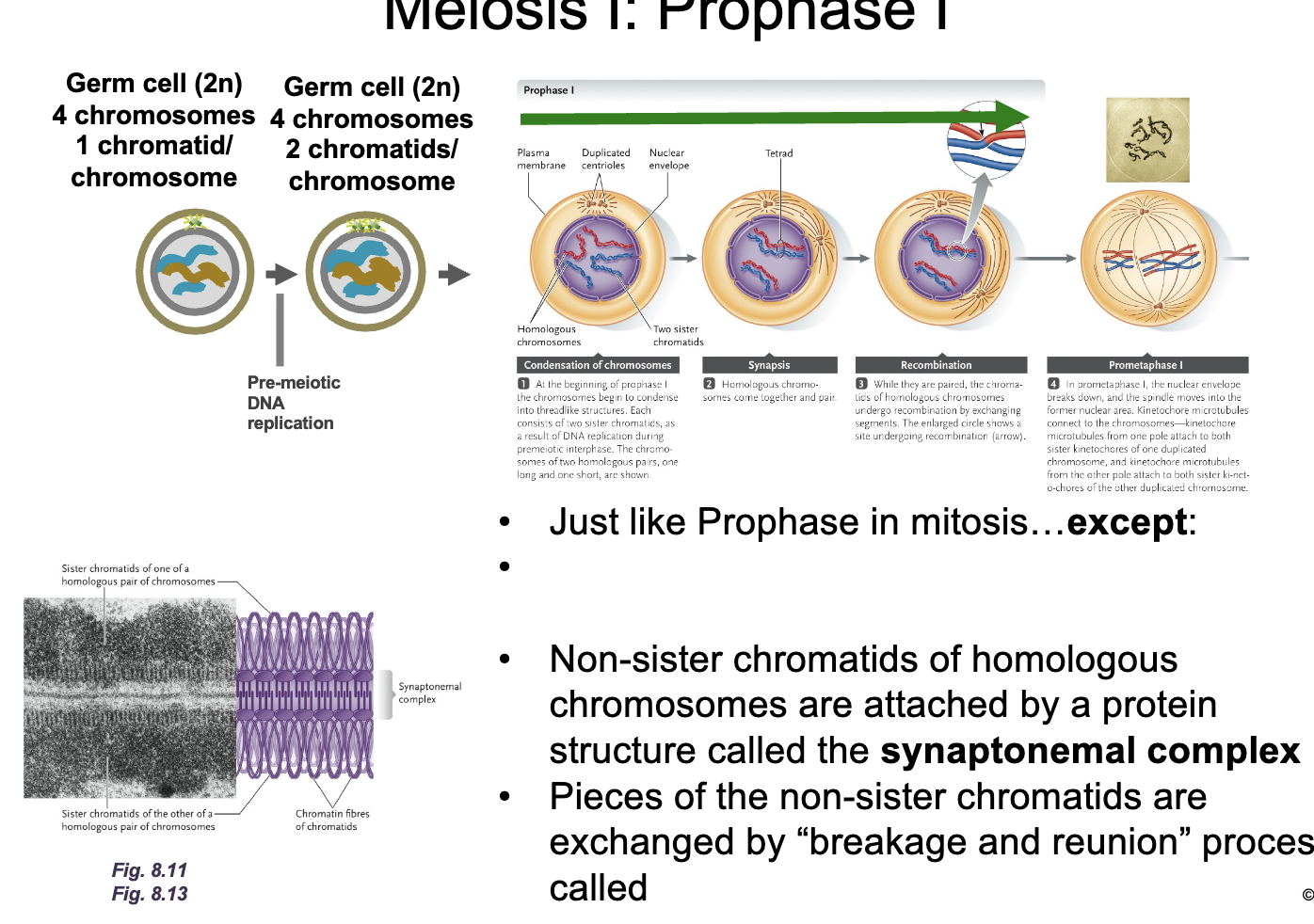
Meiosis 1: Prophase 1
Just like prophase in mitosis except WHAT
Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes are attached by a protein structure called the WHAT
Pieces of the WHAT are exchanged by “breakage and reunion” process called WHAT
Meiosis 1: Prophase 1
Just like prophase in mitosis except HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES synapse to form TETRADS
Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes are attached by a protein structure called the SYNAPTONEMAL COMPLEX
Pieces of the NON-SISTER CHROMATIDS are exchanged by “breakage and reunion” process called HOMOLOGOUS RECOMBINATION
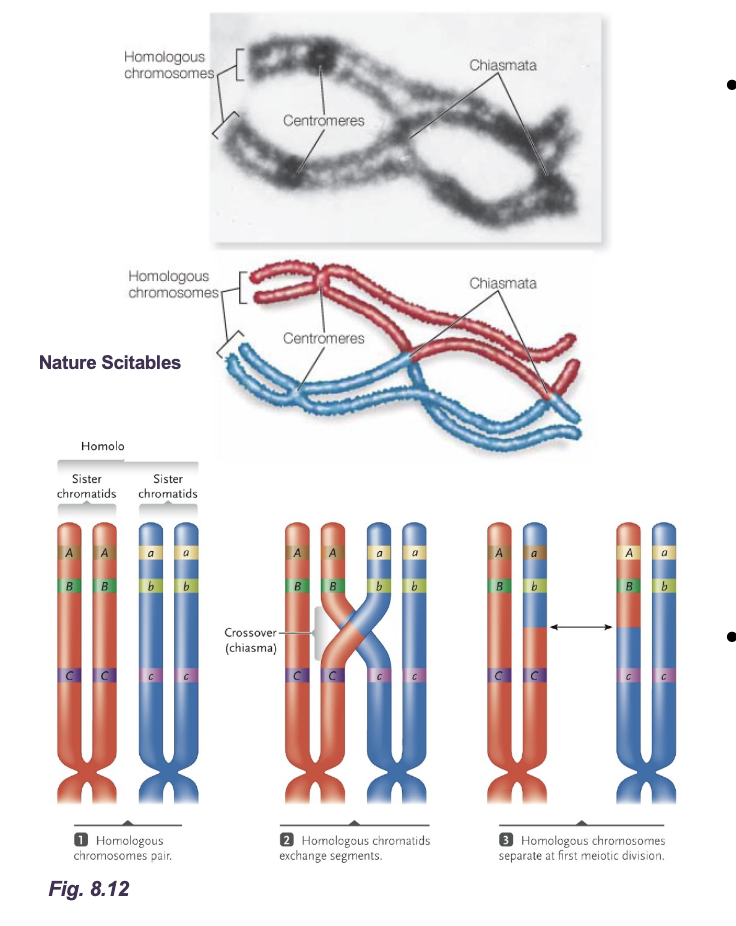
Recombination in eukaryotes (swapping only the alleles)
Homologous chromosomes align with each other during WHAT and exchange of sections of WHAT occur by WHAT
Precise breakages of each strand
Equal exchange of WHAT material
Repair of breakage after WHAT exchange
Genetic exchange can involve large sections of the homologous chromosomes creating new chromatids with various of 100’s of genes/alleles
Recombination in eukaryotes (swapping only the alleles)
Homologous chromosomes align with each other during PROPHASE 1 and exchange of sections of NON-SISTER CHROMATIDS occur by CROSSING-OVER
Precise breakages of each strand
Equal exchange of CHROMATID material
Repair of breakage after GENETIC exchange
Genetic exchange can involve large sections of the homologous chromosomes creating new chromatids with various of 100’s of genes/alleles
Meiosis 1: Reductional division
During Metaphase 1, WHAT are aligned at the WHAT facing opposite poles
Genetic diversity in gametes is increased due to WHAT
The homologous chromosomes are separated during WHAT
Therefor, after meiosis 1, the chromosome number is WHAT, but there are HOW MANY chromatids/chromosomes
Unlike mitosis (and meiosis 2) the sister chromatids are not WHAT
The sister chromatids are no longer WHAT due to WHAT
Meiosis 1: Reductional division
During Metaphase 1, HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES are aligned at the EQUATOR facing opposite poles
Genetic diversity in gametes is increased due to INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT
The homologous chromosomes are separated during ANAPHASE 1
Therefor, after meiosis 1, the chromosome number is HAPLOID, but there are TWO chromatids/chromosomes
Unlike mitosis (and meiosis 2) the sister chromatids are not SEPARATED
The sister chromatids are no longer IDENTICAL due to CROSSING OVER
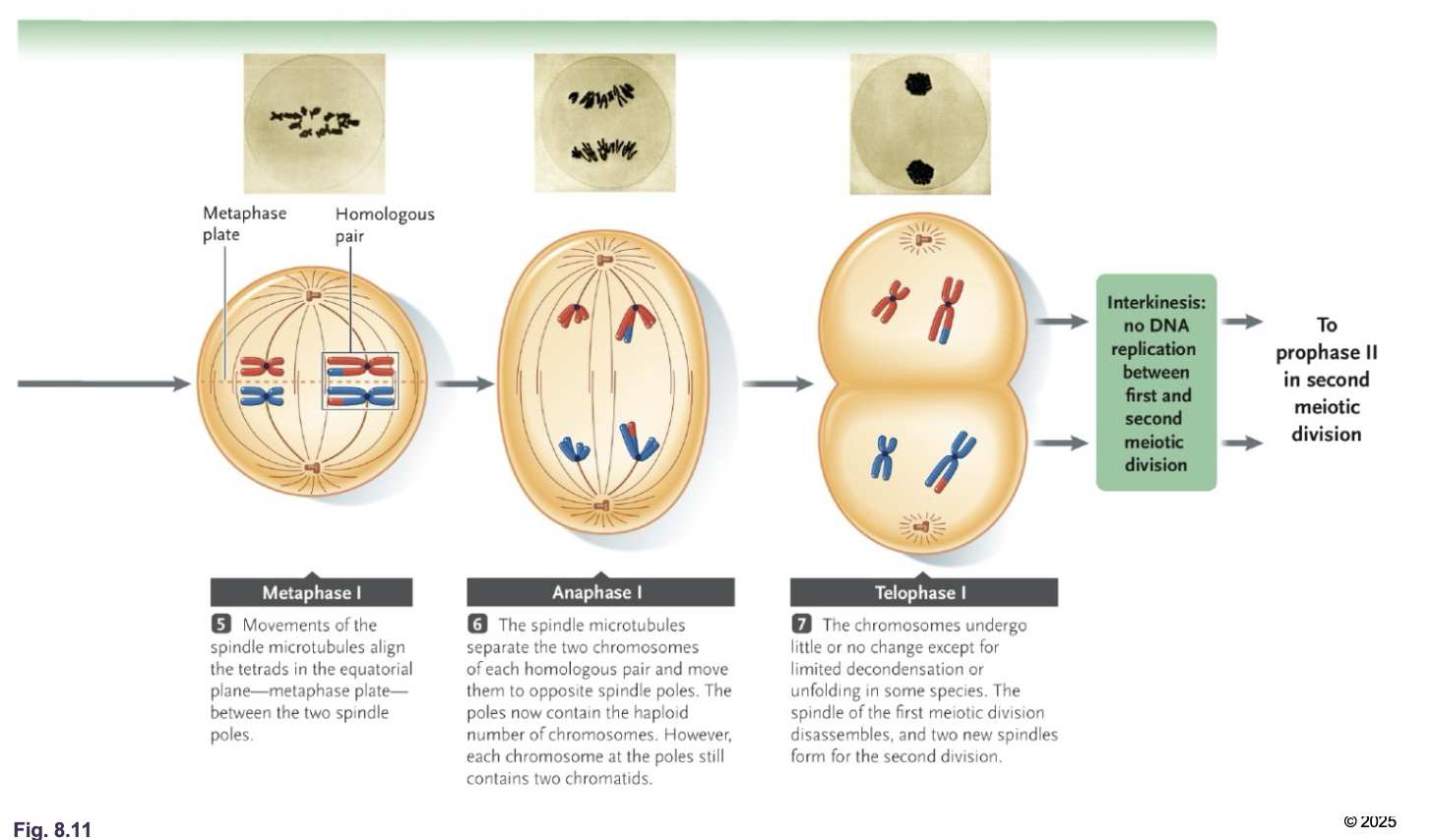
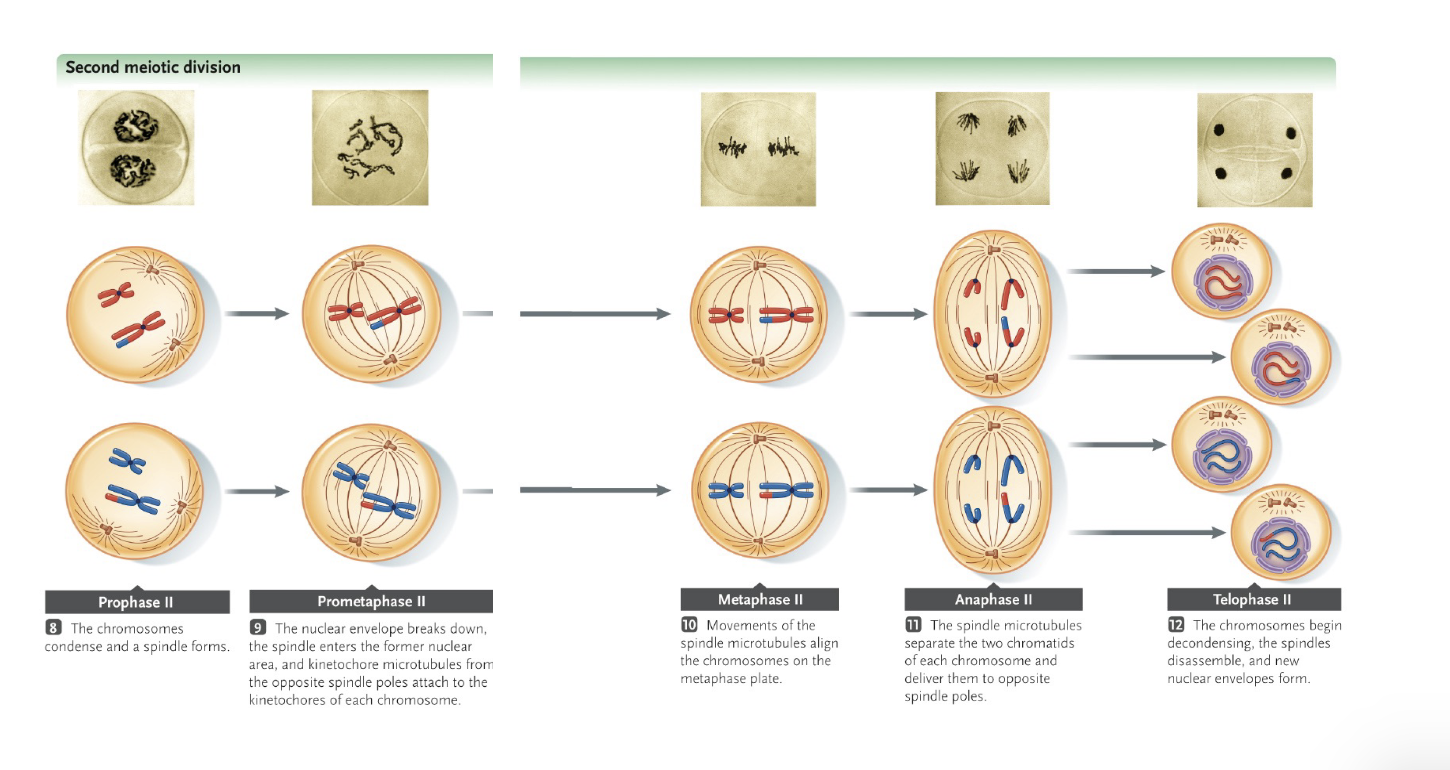
Meiosis 2
No WHAT happens between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
The process of meiosis 2 and mitosis is otherwise similar
Sister chromatids are separated during WHAT
At the end of meiosis 2, HOW MANY gametes are produced with a WHAT number of chromosomes (one chromatid/chromosome) that are not WHAT due to WHAT and WHAT
Meiosis 2
No DNA REPLICATION happens between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
The process of meiosis 2 and mitosis is otherwise similar
Sister chromatids are separated during ANAPHASE 2
At the end of meiosis 2, 4 gametes are produced with a HAPLOID number of chromosomes (one chromatid/chromosome) that are not IDENTICAL due to CROSSING OVER and RANDOM ASSORTMENT