4.4 Earth's Atmosphere; 4.5 Global Wind Patterns; 4.7 Solar Radiation seasons; 4.8 Earth's Geography and Climate; 4.9 El Nino and La Nina
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Atmosphere
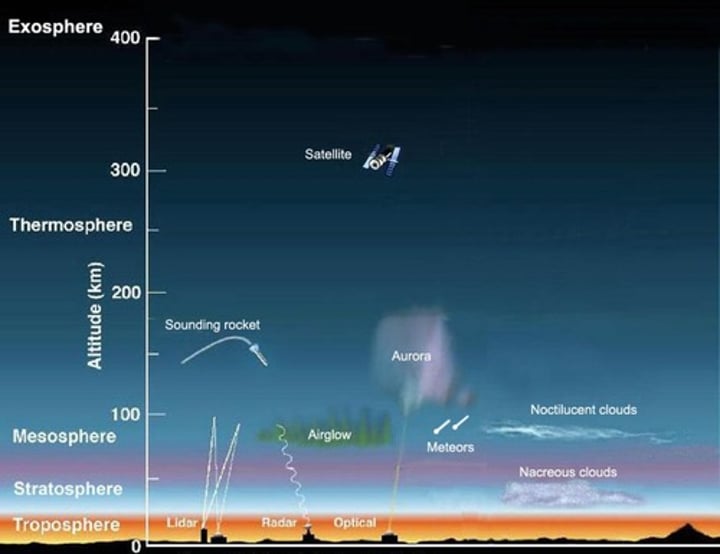
Thin layer of gases surround the earth. It includes the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere.
Troposphere
0-17 km above Earth's surface, site of weather, organisms, contains most atmospheric water vapor. (temperature decreases with increasing altitude, pressure decreases) densest layer of Earth's atmosphere

Stratosphere
16 to 60 km, Ozone held here, absorbs UV radiation. less dense due to pressure from layers above.

Ozone
A form of oxygen that has three oxygen atoms in each molecule instead of the usual two.
Mesosphere
middle; the region of the earth's atmosphere above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere, between about 30 and 50 miles (50 and 80 km) in altitude.

thermosphere (ionosphere)
the upper layer of the atmosphere, above 50 miles (80 km) from the Earth's surface. It is extremely hot due to absorption of radiation by gases. (northern lights)
Exosphere
The outer layer of the thermosphere, extending outward into space.

Air Properties
warm air rises, holds more moisture
rising air expands and cools
cold air cant hold h20 vapor
after cooling and expanding, air sinks
Altitude
height above sea level
atmospheric pressure
the pressure exerted by atoms and molecules in the atmosphere surrounding Earth, resulting from collisions of these particles with objects
Latitude
is a measurement on a globe or map of location north or south of the Equator
Longitude
known as lines of meridians; runs in a north and south direction; measurement distance east or west of the prime meridian
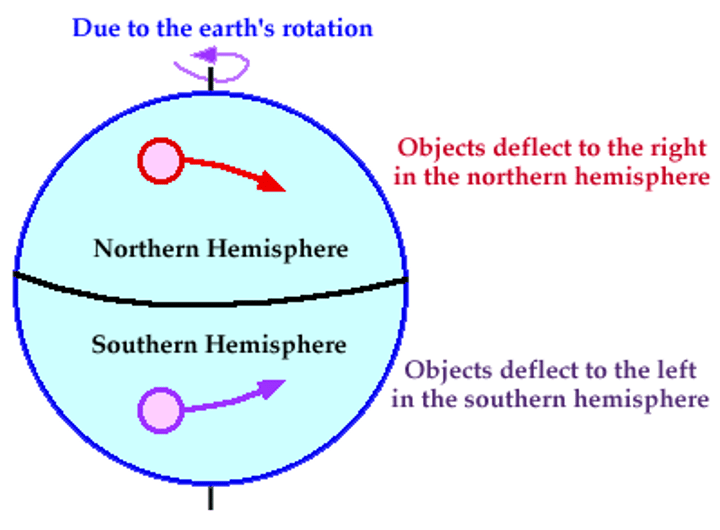
Coriolis Effect
the apparent deflection of north-south air currents to a partly east-west direction, caused by faster spin of the regions near the equator than of regions near the poles as a result of earth's rotation
Solar Intensity
amount of solar energy an area receives. Often measured in a Solar radiation unit.
High Pressure Circulation
contains air that descends because it is cools; It spreads outward as it nears the ground; It brings fair weather
Low Pressure Circulation
warm air rises and draws air inward toward the center of low pressure. Rising air expands and cools. It brings clouds and precipitation
wind
The horizontal movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of lower pressure; created by uneven heating and cooling of Earth's gasses and the Earth's rotational spin.
Hadley Cells
one of a pair of cells of convective circulation between the equator and 30 degrees north and south latitude that influence global climate patterns
Ferral cell
defines air flow between the subtropical high and sub-polar low
Polar Cell
Cells of air circulation occurring between 60 degrees north and south and each pole.
Westerlies winds
prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude.
Easterlies (Trade Winds)
permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region (between 30°N and 30°S latitudes). The trade winds blow predominantly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase.
oscillation
movement back and forth at a regular speed
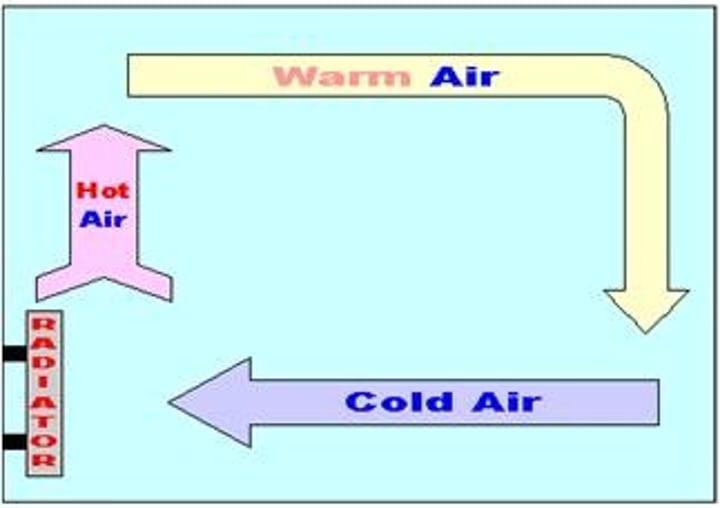
Convection
Process by which, in a fluid being heated, the warmer part of the mass will rise and the cooler portions will sink.
Conduction
Form of heat transfer where heat energy is directly transferred between molecules through molecular collisions or direct contact.
Radiation
Energy that is radiated or transmitted in the form of rays or waves or particles.

Latent Heat
energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state (phase) that occurs without changing its temperature.
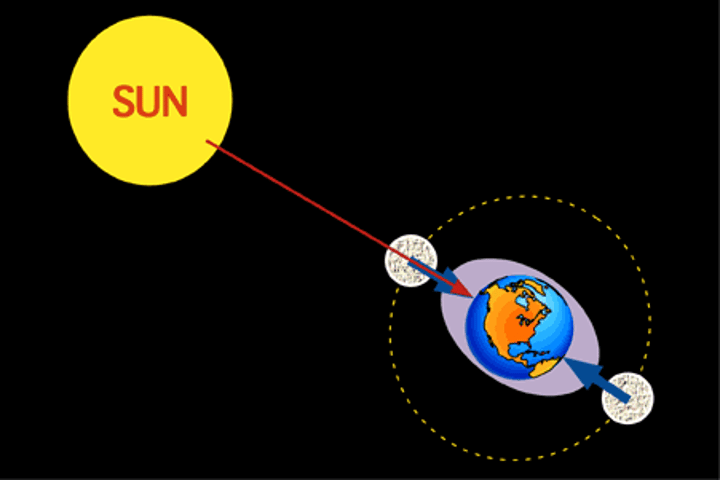
Earth's tilt
23.5 degrees
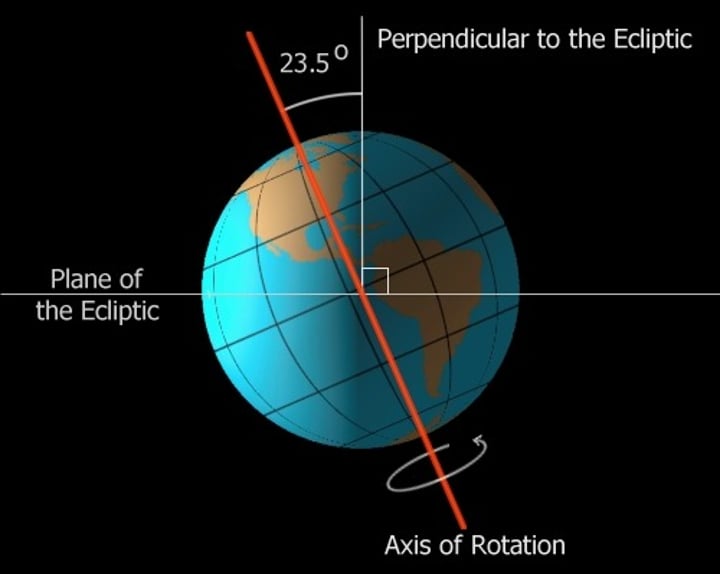
Season
Generated by Earth's rotation around the sun, combined with its axial tilt, allows for different seasons: summer, winter, fall, and spring. Depending on the region, different amounts of solar energy strike the Earth at various times of the year. The equator gets the most, and the poles the least. Distance from the equator and the intensity of solar radiation have a direct effect on seasonal changes.
Solar radiation unit
of measurement is 1 langley, which is equal to 1 calorie per square centimeter of the Earth's surface Solar radiation is also stored in materials like water and soil. Solar radiation is highest at the equator.
Insolation
incoming solar radiation
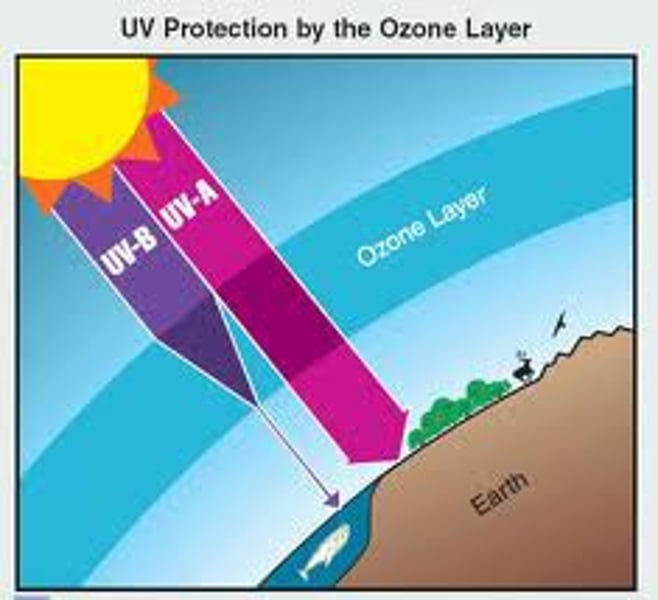
Ultraviolet Radiation (UV Rays)
-Short, more dangerous wavelength.
-Causes sunburn and eventually skin cancer.
-Many are filtered out by ozone.
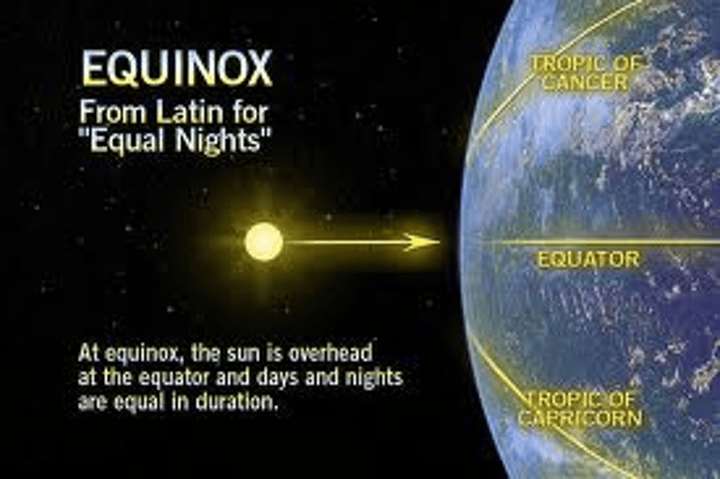
Equinox (Spring/Fall)
A day when both day and night are the same length
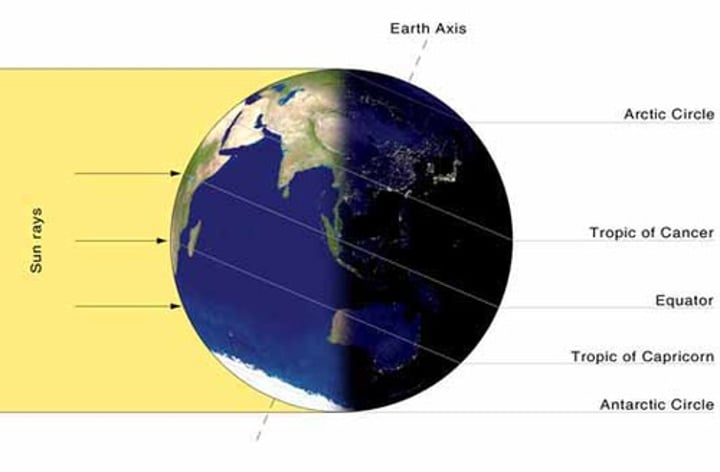
Solstice
either of the two times in the year, the summer solstice and the winter solstice, when the sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky at noon, marked by the longest and shortest days.
Tides
the regular rise and fall of the ocean's surface influenced by the moon's gravity pulling on earth
weather
the current meteorological conditions: temperature, wind, clouds, and precipitation
climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
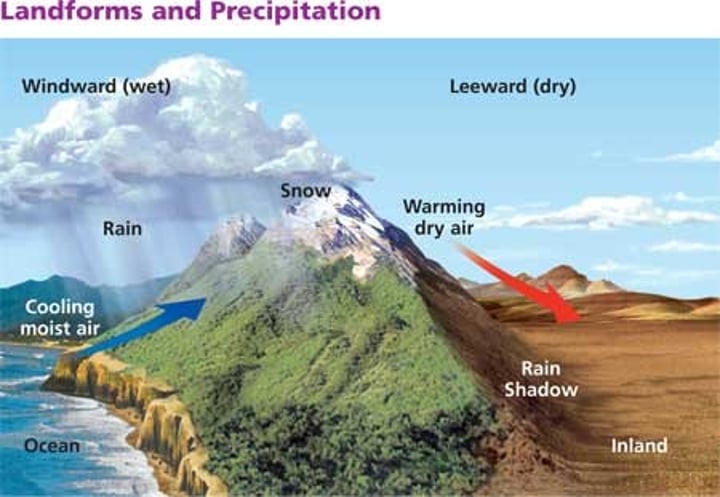
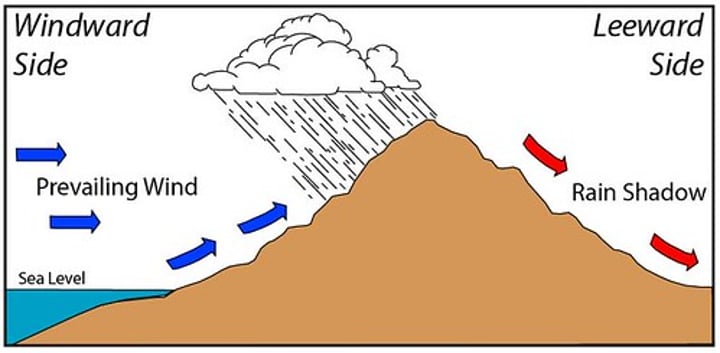
Leeward
The side of a mountain range that faces away from the oncoming wind. Often resulting in less precipitation
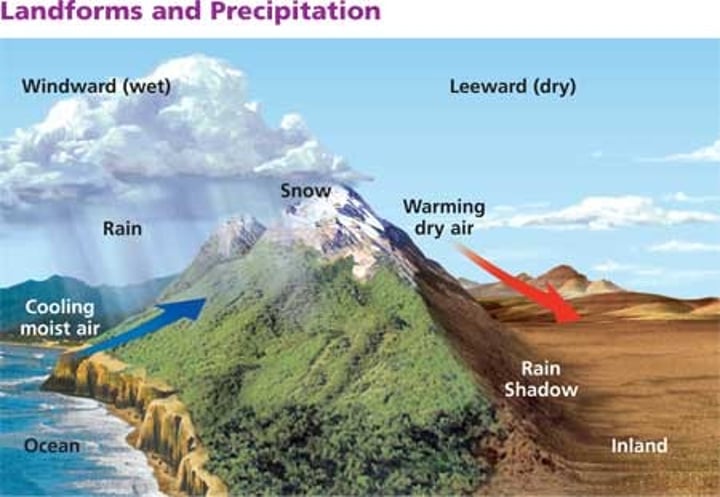
windward side
side of the mountain where rain and other weather are expected
Ocean Temperature
this factor is affected by the amount of solar energy an area receives and by the movement of water; influences weather
rain shadow effect
Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side.
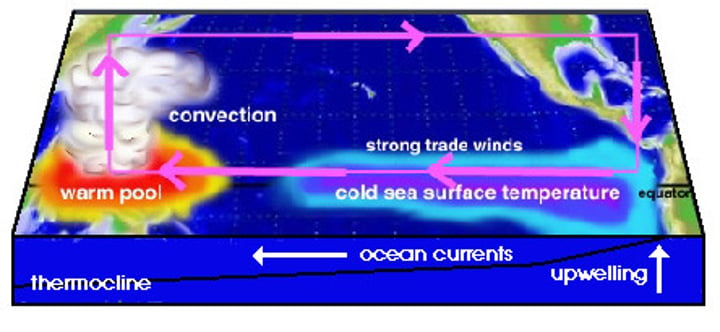
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
is the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature (SST) of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean. El Niño is accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific. El Niño phases are known to last close to four years, however, records demonstrate that the cycles have lasted between two and seven years. During the development of El Niño, rainfall develops between September-November. The cool phase of ENSO is La Niña, with SSTs in the eastern Pacific below average, and air pressure high in the eastern Pacific and low in the western Pacific.
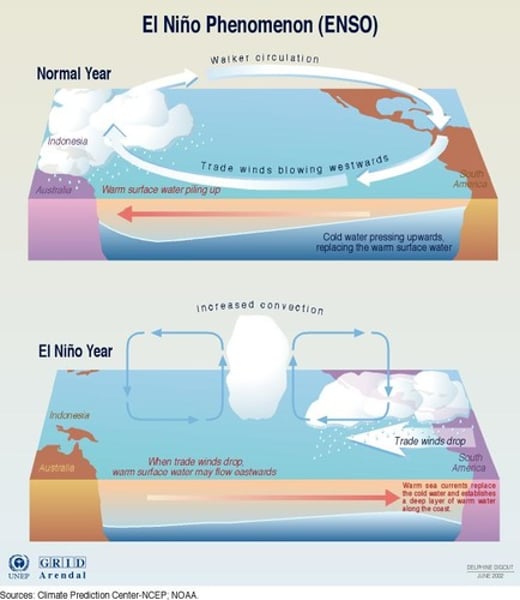
La Nina Effect
a change in the eastern Pacific Ocean in which the surface water temperature becomes unusually cool