Male Reproductive System
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
____ produce male gamete and male sex hormones
testicles (gonads)
how many testicles (gonads) are there?
two (inguinal canal)
failure of one testicle (gonad) to descend is called ___
failure of both to descend is called ____
monorchid, cryptorchid
_____ produce testosterone but no sperm bull will mate, but usually will not settle a cow
retained testicles
an intact adult male HORSE is called ___
stallion
a castrated male HORSE is called ___
gelding
an intact adult male OX is called ___
bull
a castrated male OX is called ___
steer
an intact adult male PIG is called ___
boar
a castrated male PIG is called ___
barrow
an intact adult male SHEEP is called ___
ram
a castrated male SHEEP is called ___
wether
an intact adult male GOAT is called ___
buck (billy)
a castrated male GOAT is called ___
Wether
an intact adult male CHICKEN is called ___
rooster
a castrated male CHICKEN is called ___
capon
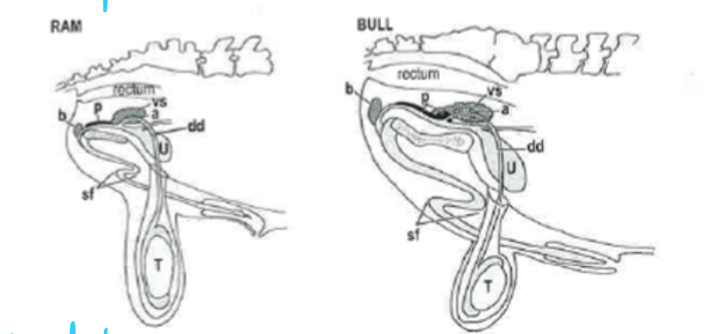
Which species has pendulous testes?
ram and bull
Which species has non-pendulous testes?
boar and stallion
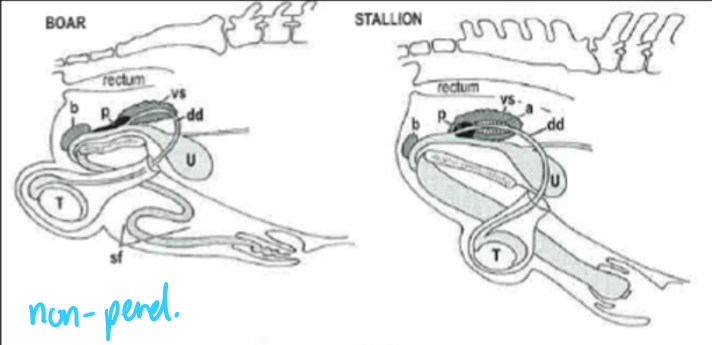
pendulous versus non-pendulous testes is related to ____ (absent in stallion)
sigmoid flexure
the ___ is absent in stallions
sigmoid flexure
Irrespective of difference (pendulous or non-pendulous), the male repro tract has the same basic tubes and physiology… produce and deliver ___
spermatozoa
____ contains the testes
scrotum
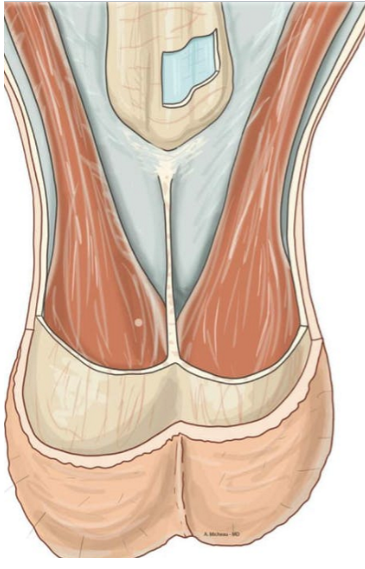
the scrotum regulates the ___ of the testes for sperm production
temperature
____ occurs at a temperature below core body temperature
spermatogenesis
____ is the smooth muscle layer that lies beneath the scrotal skin
tunica dartos muscle
(tunica dartos muscle) ____ detect temperature
sensory neurons
tunica dartos muscle pushes the testes closer toward the body for ___ or relaxes to ___ the testes away from the body
warmth, cool
(tunica dartos muscle) ____ muscle allows for sustained contractions
smooth
____ also regulates the temperature of the testes for sperm production
spermatic cord
spermatogenesis occurs at a temperature ____
below core body temperature
____ is located along the spermatic cord and attaches to testis. Also helps regulate the temperature of testes
cremaster muscle

contraction of the cremaster muscle aids in ___ to the testis and increases/decreases cooling efficiency
blood flow
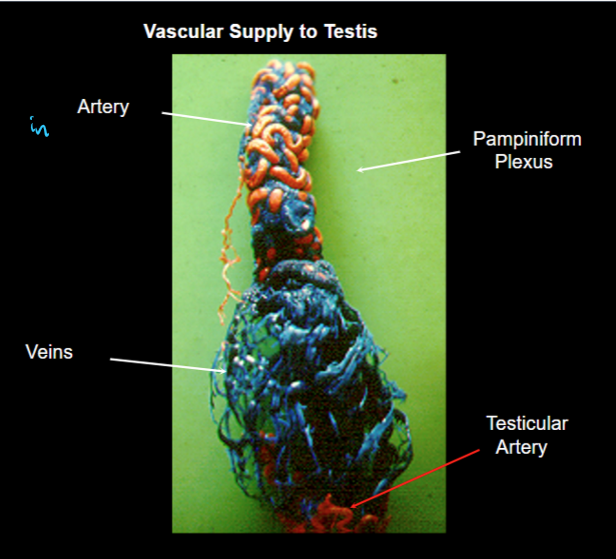
____ counter-current heat exchange causes a cooling of arterial blood supply; single Artery surrounded by a network of veins (increased surface area)
pampiniform plexus

____ is on the surface of the testis and in rams the temperature decrease 4 CELSIUS before entering testis
convoluted testicular artery
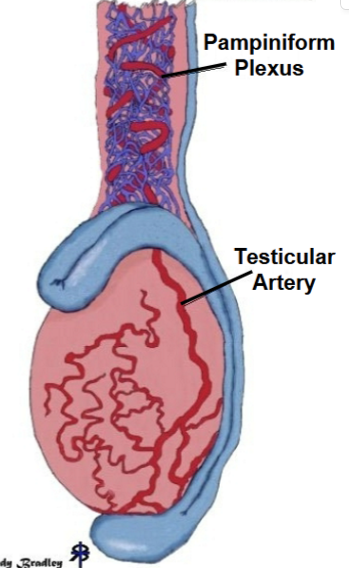
scrotum, testis, and spermatic cord are all involved in ____
thermoregulation
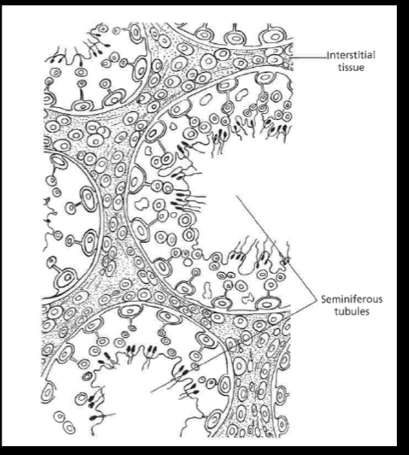
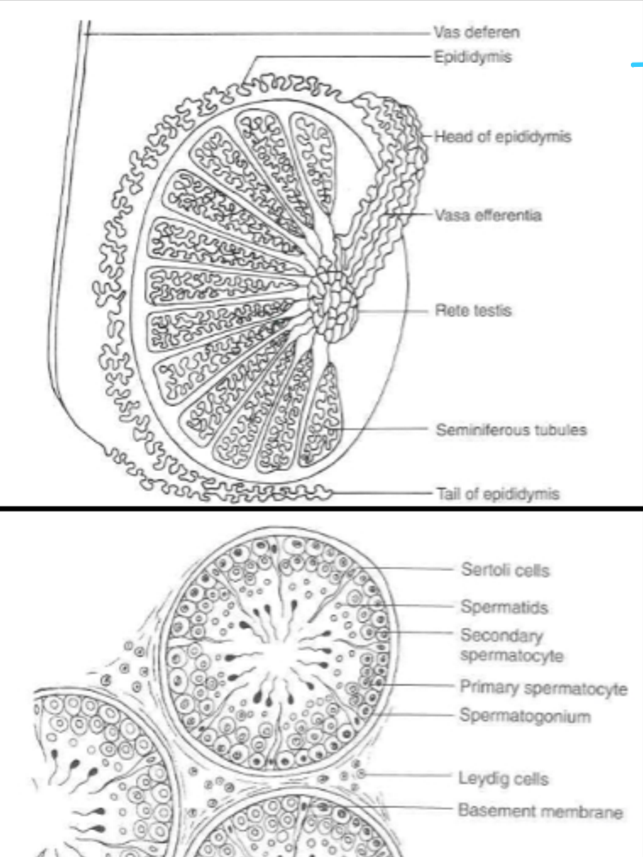
**____ are the functional unit of the testis
seminiferous tubules
____ is the site of spermatogenesis
testis
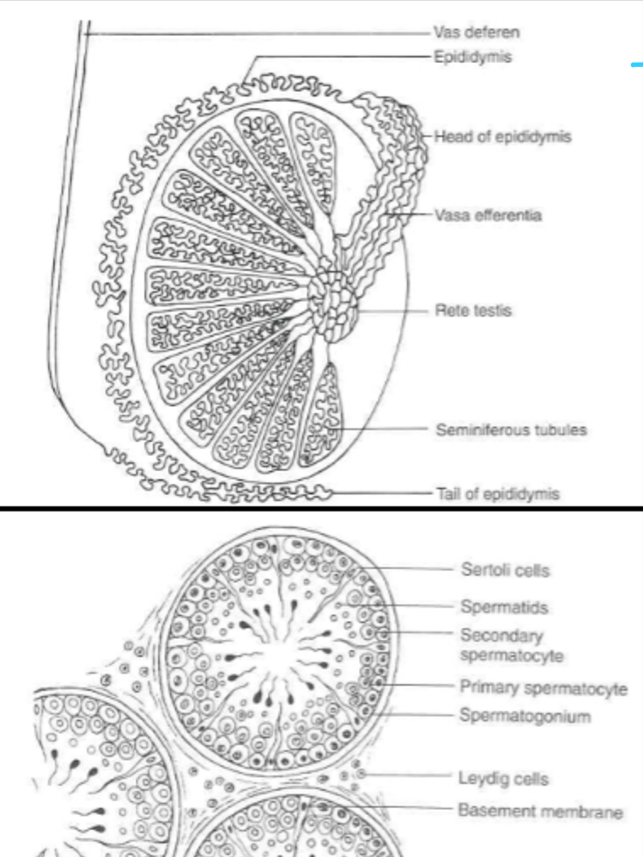
(testis) tubules contain ___ (which nurse the developing spermatozoa)
Sertoli cells
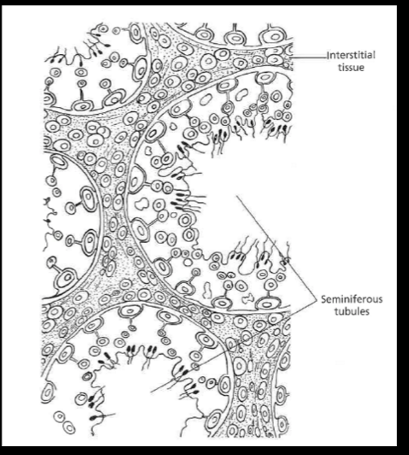
(testis) interstitial space contains ___ (which produce testosterone)
Leydig cells

Leydig cells produce ___
testosterone
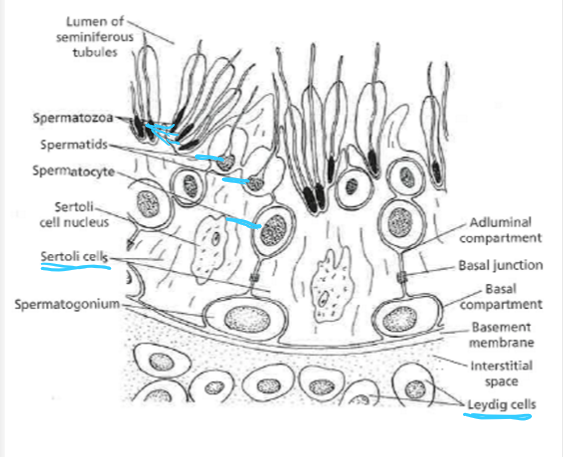
What are the phases of sperm?
spermatocyte → spermatids → spermatozoa
testis delivers sperm to ____ which then drains into the efferent ducts
rete testis
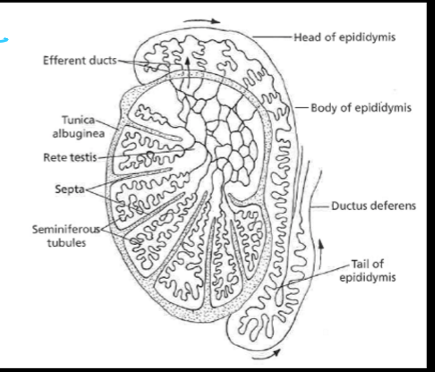
testis delivers sperm to rete testis which then drains into the ___
efferent ducts
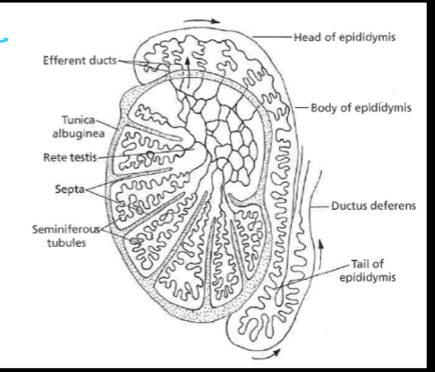
____ then coalesce into a single epididymal duct
efferent ducts
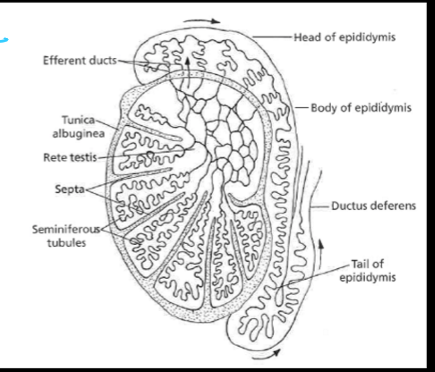
____ is a duct located on the outside of the testes and is composed of three parts (head, body, and tail)
epididymis
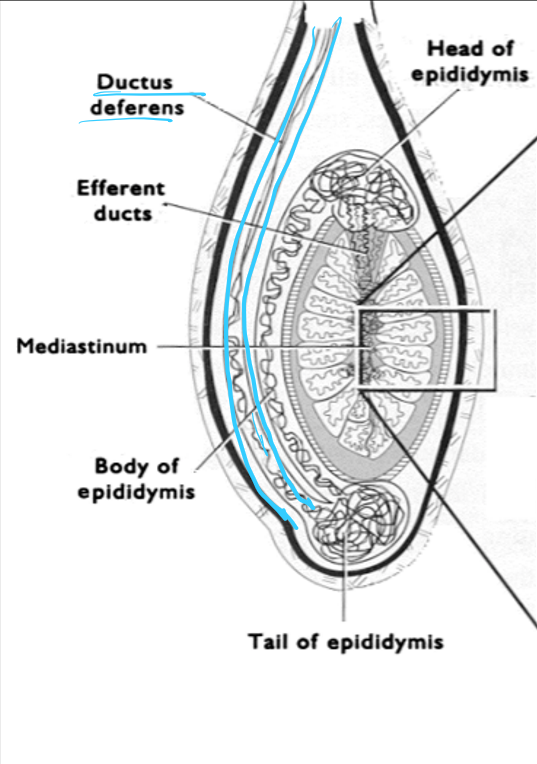
What are the functions of the epididymis?
concentrate sperm
store sperm
transport sperm
site of store maturation
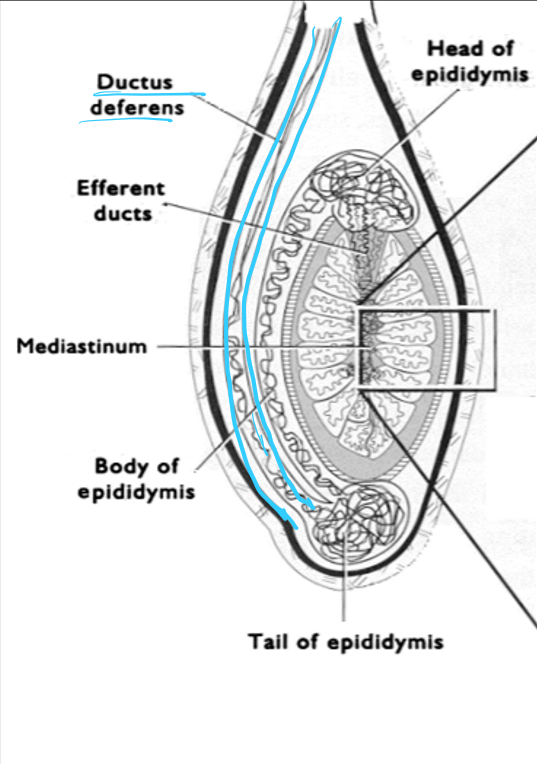
epididymis is the site of sperm maturation; this process from the start of spermatogenesis to maturity takes ____ depending on species
40-60 days
____ is a duct which connects epididymis to urethra of the penis
ductus (vas) deferens

ductus (vas) deferens transports sperm at the time of ___
ejaculation
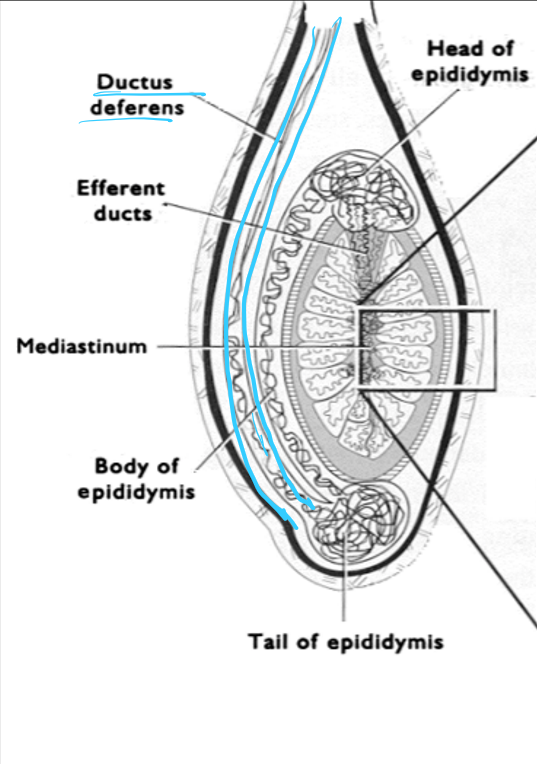
the ductus (vas) deferens is ___ to sterilize the male (vasectomy)
cut
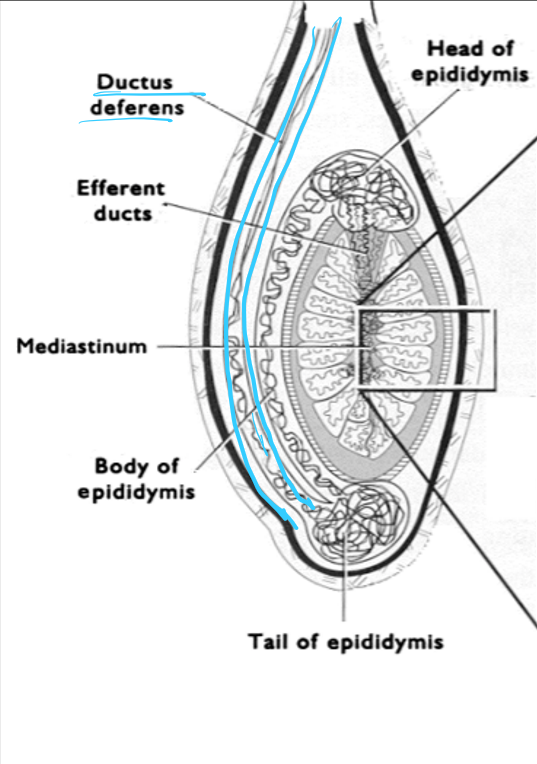
vasectomy vs castration (google answer)
vasectomy = reversible, prevents ejaculation by cutting small piece of vas deferens
Castration = irreversible, removal of entire testicles
(male anatomy) picture of common urogenital system
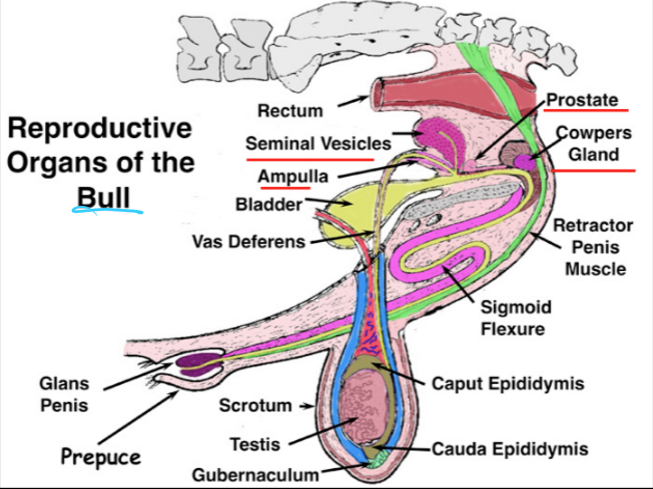
a common urogenital system contains:
four accessory sex glands (ampullae, vesicular glands, prostate glands, and bulbourethral/Cowper’s gland)
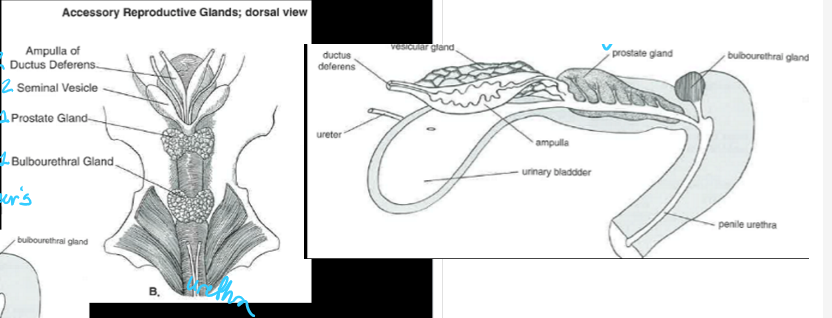
the secretions from the four accessory sex glands of the common urogenital system constitute ___% of the volume of ejaculate
50-90
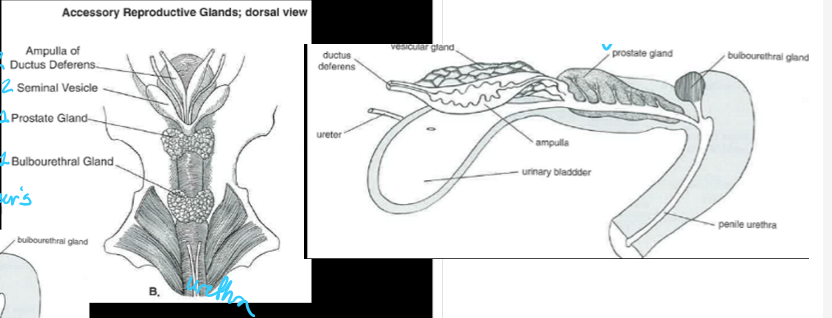
(accessory sex glands - asg) ___ are glandular enlargements associated with the terminal parts of the ductus deferens
ampullae
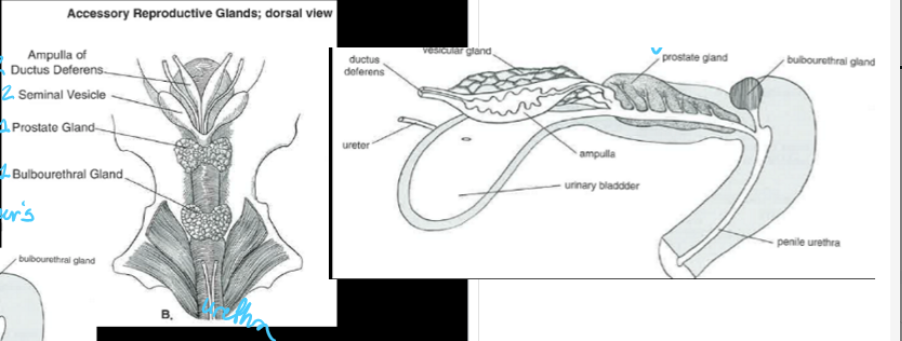
the ampullae is well developed in the ___, ___, and ___, but is absent in the ___
stallion, bull, ram
boar
the ampulla adds ___ to ejaculate
volume
____ are paired glands that enter dorsocranial to the pelvic urethra
vesicular glands (seminal vesicles)
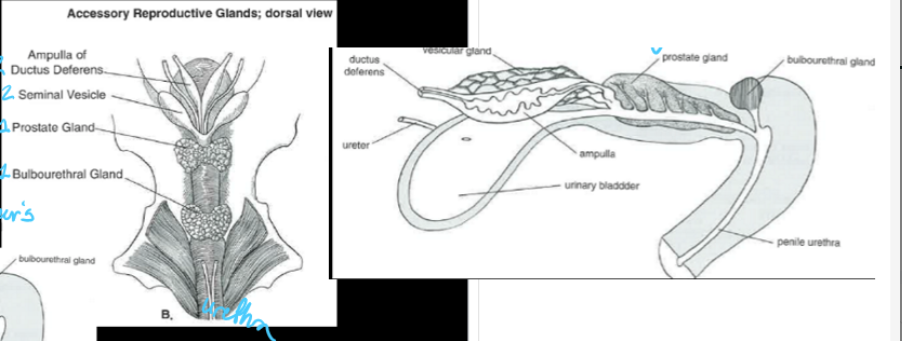
the vesicular glands (seminal vesicles) supply ___ for the sperm following ejaculation and deposition into the female reproductive tract
nutrients
the vesicular glands (seminal vesicles) include ____ (energy), ___ (buffers), and ____ that activate the sperm
carbohydrates, ions, enzymes
the vesicular glands (seminal vesicles) contribute a large portion of ejaculate volume in ___ and ___
stallions and boars
What is the ejaculate volume and concentration rank of: rams?
0.5-2.0
1
What is the ejaculate volume and concentration rank of: bulls?
3-10
2
What is the ejaculate volume and concentration rank of: stallions?
40-100
3
What is the ejaculate volume and concentration rank of: boars?
150-250
4
What is the ejaculate volume and concentration rank of: man?
2-6
5
____ is the organ of copulation
penis proper
____ is the duct through the penis that carries sperm and urine
urethra
The ____ is a muscular organ characterized especially by its spongy, erectile tissue that fills with blood under considerable pressure during periods of sexual arousal
Penis Proper
____ is erectile tissue that fills with blood
corpora cavernosa
____ contains dense collagenous tissue (firm when not erect; ruminants and swine)
fibroelastic penis type
____ blood sinusoids predominate over connective tissue, flaccid when not erect (stallion)
musculocavernous penis
____ is attached to the sacral vertebra and relaxes during sexual excitement
retractor penis muscle

____ is the terminal portion of the penis
glans penis

____ glans penis tapers to the end
bull
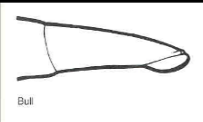
____ glans penis is filiform (tubular) appendage; helps deposit semen in the anterior vagina
ram
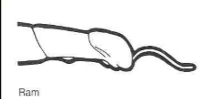
____ glans penis is spiral; deposits semen in the cervix
boar

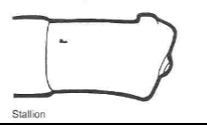
____ glans penis has a bloated end; butts up against the cervix where semen is deposited
stallion
____ is the sperm producing units of the testes and make up approximately 90% of the testes mass
seminiferous tubules
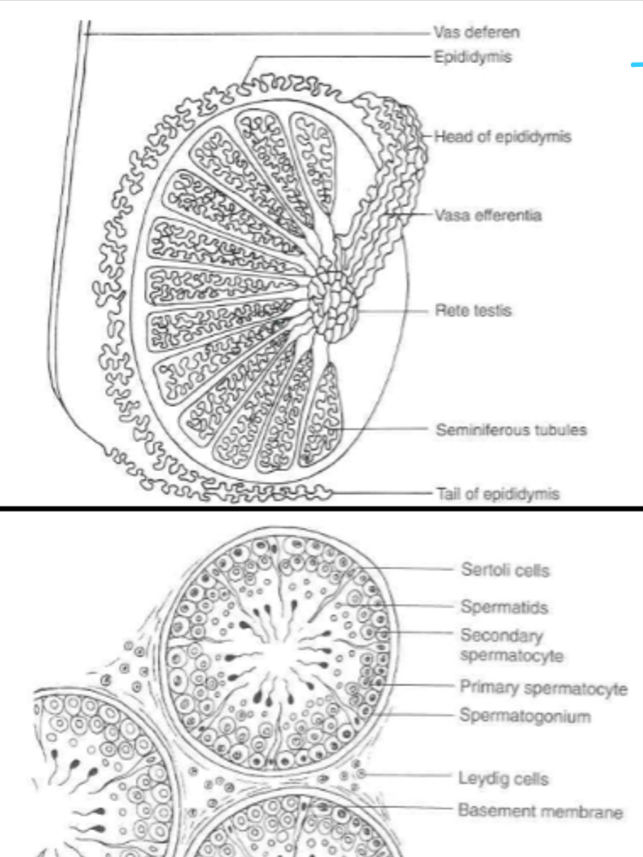
Spermatogenesis occurs within the ____ of these long, coiled structures (seminiferous tubules)
lumen

____ provide nourishment for the developing sperm located Within the seminiferous tubules which contain androgen-binding protein
Sertoli cells
_____ produce testosterone and are located Between the seminiferous tubules
Leydig or interstitial cells
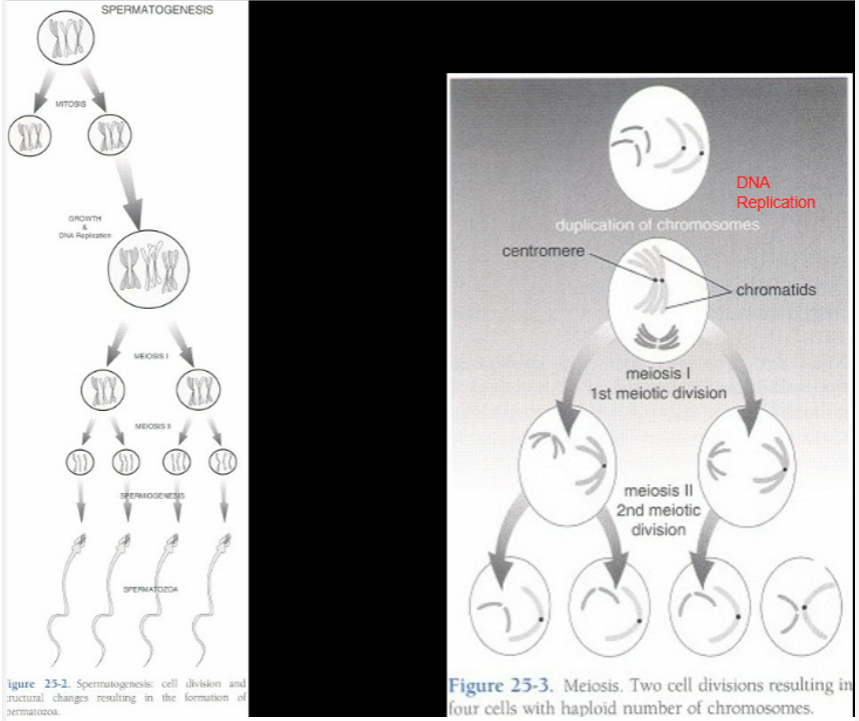
spermatocytogenesis is several ____ (non-reductional division)
mitotic cell divisions
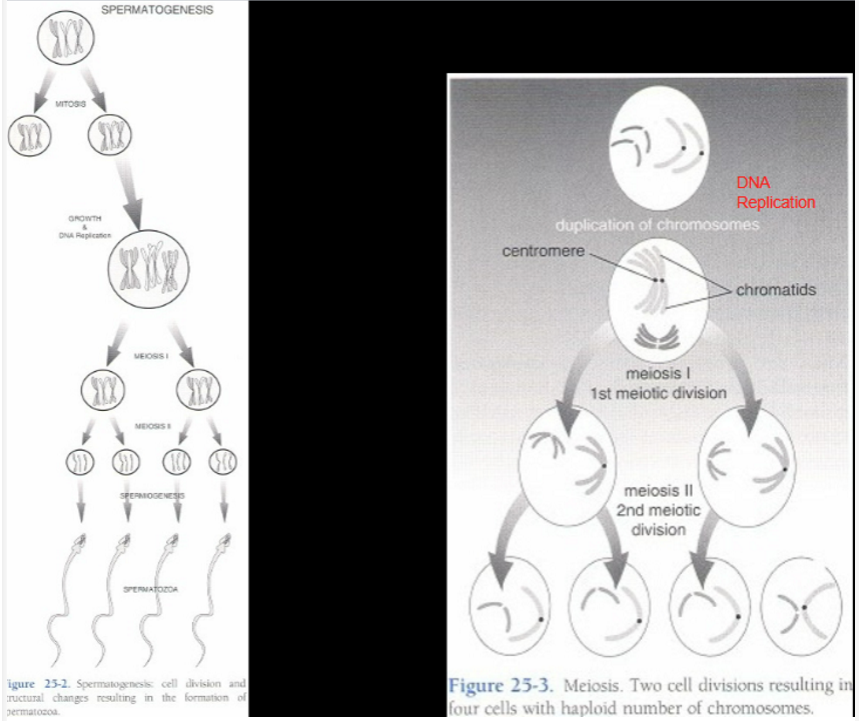
What happens to chromosomes in meiotic cell divisions (reductional)?
reduced from diploid to haploid
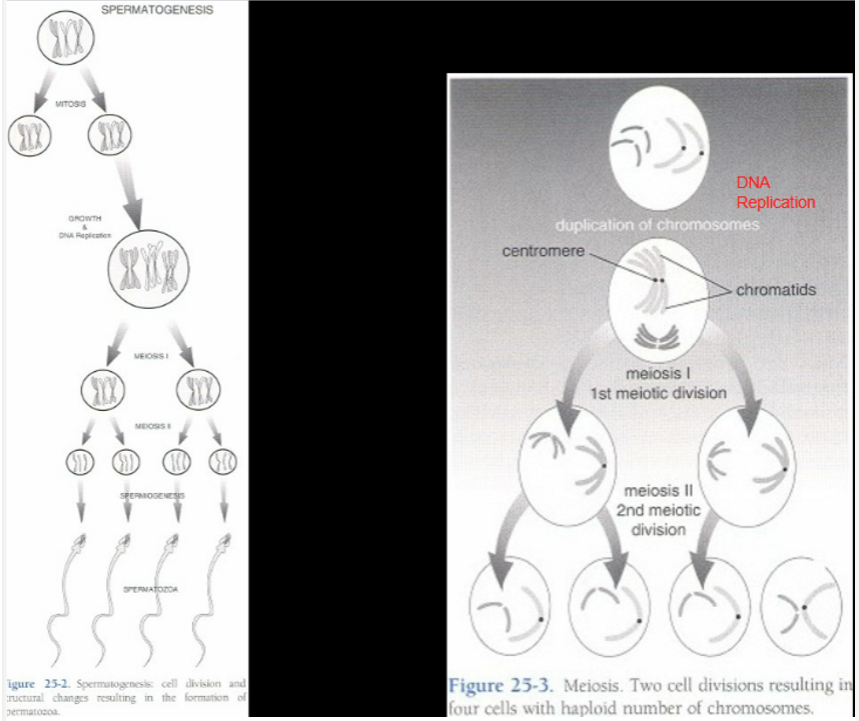
What happens in the first meiotic cell division (reductional)?
two identical diploid cells form
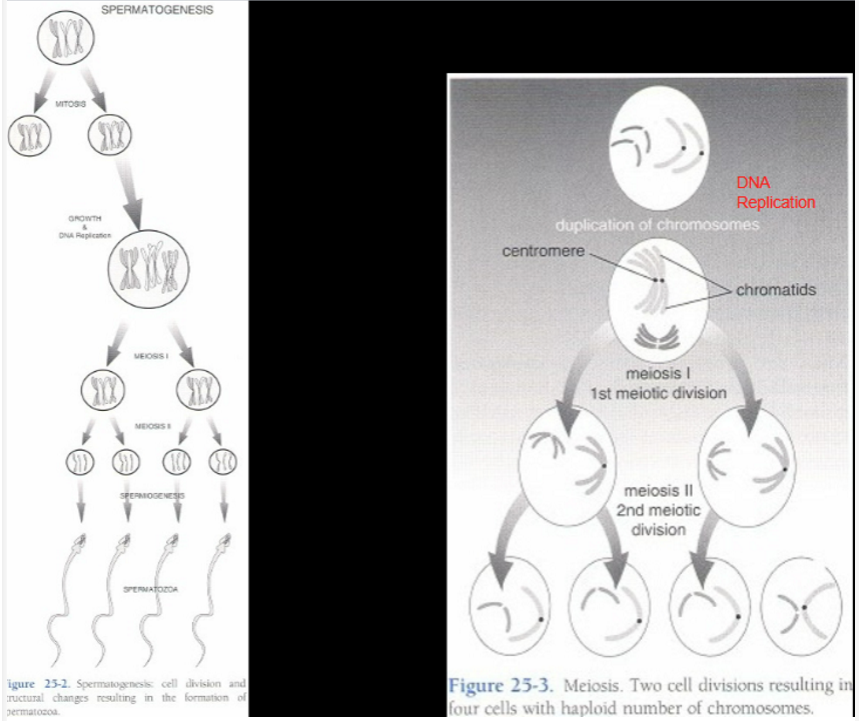
What happens in the second meiotic cell division (reductional)?
two identical haploid cells form (two contain Y chromo, two contain X chromo)
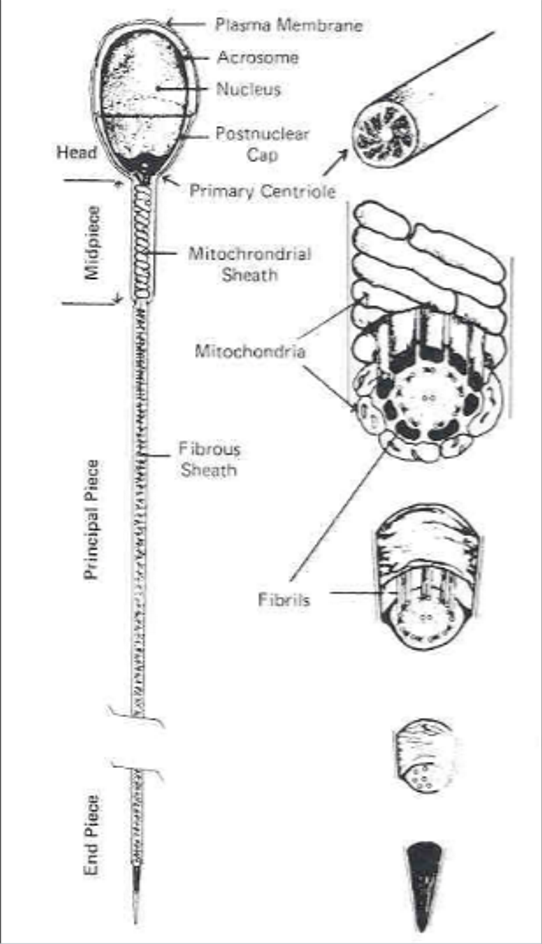
(sperm cell) ___ contains genetic material (chromatin) and enzymes (in the acrosome) necessary for fertilization
head
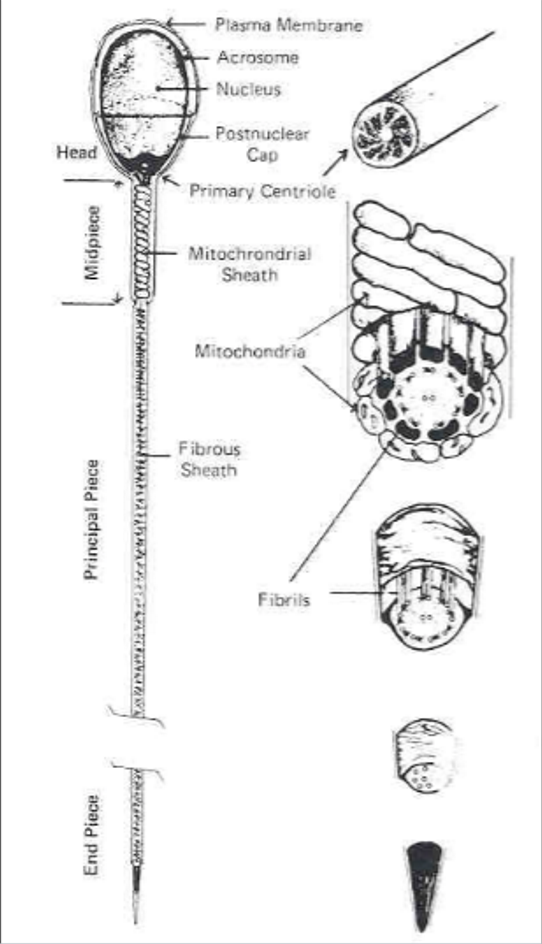
(sperm cell) ___ attaches the head to the midpiece
neck
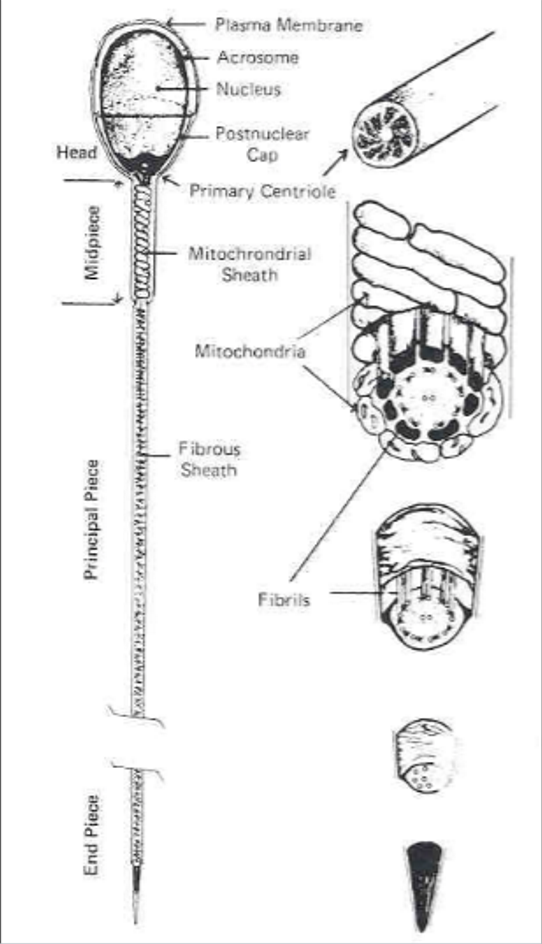
(sperm cell) ___ produces energy for the sperm
midpiece
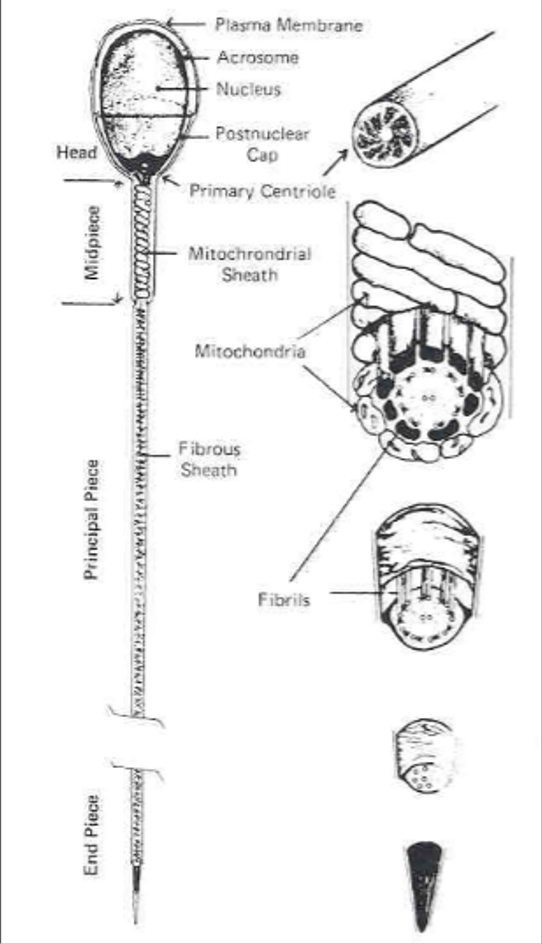
___ propels sperm cell
tail
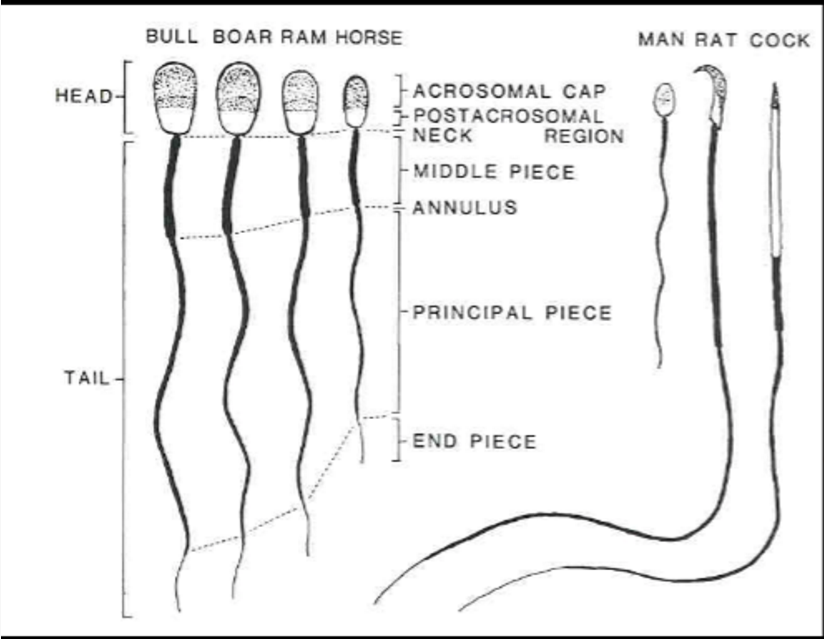
____ has more cylindrical sperm than bull, boar, or ram
Horse
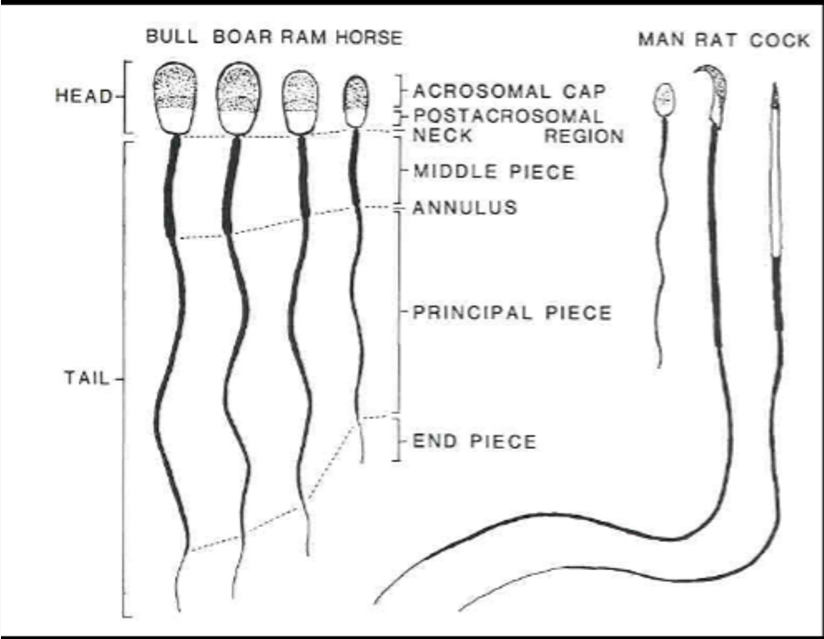
____ sperm head looks like an inverted egg or neckpiece
man
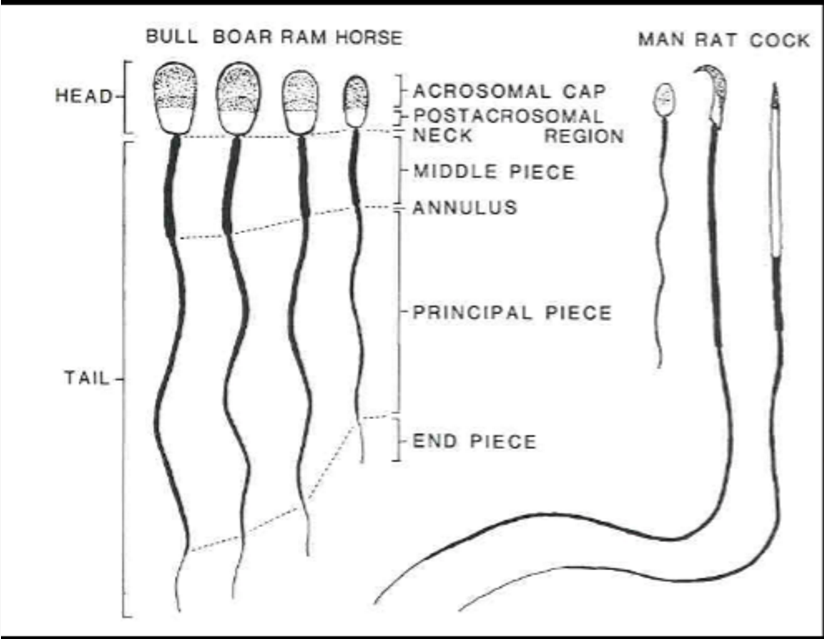
____ has bent or turned sperm
rat

____ has very straight, long and slender sperm
cock
____ located within the brain is an integrator of most of the brain’s activities
hypothalamus
hypothalamus produces a peptide called ___ which controls the release of two hormones from the anterior pituitary gland called gonadotropin hormones (FSH and LH)
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
hypothalamus produces a peptide called gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) which controls the release of two hormones from the ____ called gonadotropin hormones (FSH and LH)
anterior pituitary
hypothalamus produces a peptide called gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) which controls the release of two hormones from the anterior pituitary gland called ____
gonadotropin hormones (FSH and LH)
stimulation by GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH to be released from the anterior pituitary into the ___, which then go to the gonads where they stimulate specific functions
blood
stimulation by GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH to be released from the anterior pituitary into the blood, which then go to the ____ where they stimulate specific functions
gonads