BIOL CHAP 39- Neurons and Synapses
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Neural signaling
How a neuron communicates; response to stimulus
reception
detection of stimulus by sensory neurons; see ball coming at you
input
integration
brain processes sensory neurons and decides what to do
processing
response
signals sent to muscles by brain about what to do
action
cell body
houses nucleus
eukaryotic
genes transcribed here
protiens made here
Nerve fibers
dendrites and axons
dendrites
receive information
sends info to the cell body
less than 1 mm
call dendritic tree or dendritic arbor
axon hillock
start of the action potential
axon
take signal to axon terminal
surrounded by myelin sheath
axon terminal
send signal to other neurons or muscles by sending signal to effector
effector
nerves, cell, glands or muscles that respond to signals from axon terminal
interneurons
Axon has axon terminals that sprout out
used for neuron-to-neuron communication
terminal less than 1 mm
Projection Neurons
Used for long distance communication
Axon terminals are longer than 1 mm
gilia cells
Provide support to neurons
can multiply and replace dead cells
loss of gliia regulation = brain tumor
types of gilia cells
Astrocytes cover blood vessels. CNS
Oligodendrocytes make myelin. CNS
Schwann cells- make myelin. PNS
Synapse
after the axon terminal, the period where neurons make connections to effector
presynaptic cell
cell or neuron that sends signal
post synaptic cell
effector that receives signal
Chemical synapse
Presynaptic and postsynaptic cells are separated by a gap. Neurotransmitters in axon terminal go from pre to post to transmit a signal
synaptic cleft
in chemical synapse, 25 nm gap between pre and post synaptic cells
Electrical Synapse
Pre and post-synaptic cells touch and gap junctions allow ion signals to flow to post synaptic cell
exocytosis
Only for a chemical synapse. vesicle and membrane fuse to let neurotransmitters bind to receptors in post synaptic cell. After binding, ion channels open or close

chemical synapse
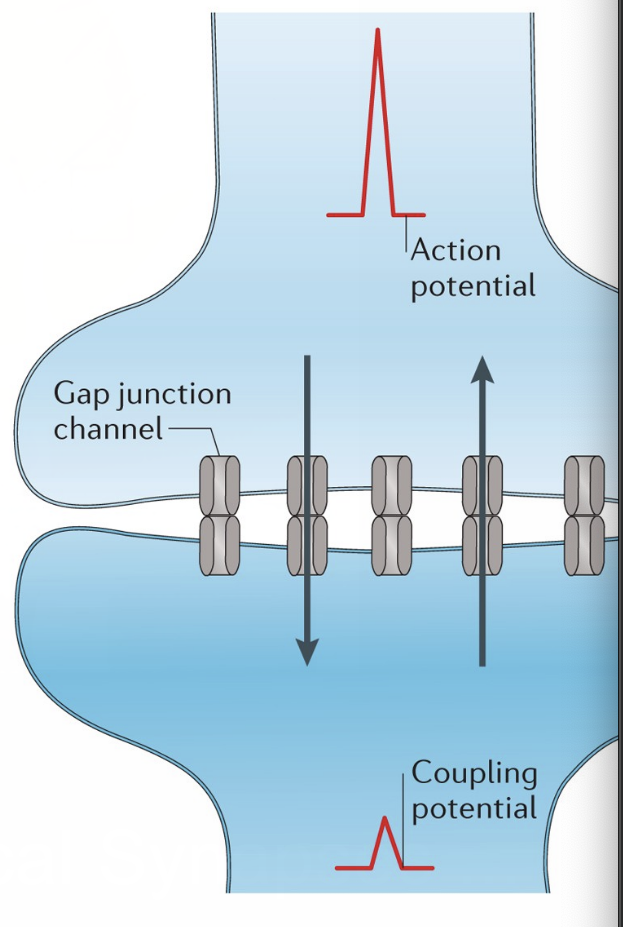
Electrical synapse
cytosol
A jelly-like substance in a cell made of cations and anions
Animals have more anions in cytosol
lots of K+
cytoplasm
everything in cell besides nucleus
cytosol and organells
membrane potential
electrical change inside the cell vs outside the cell
ICF is more negative bc K+ leaves the cell
ECF is more positive
An action potential leads to ICF depolarization; ECF stays the same
Charge measured in mV
equilibrium membrane potential is -98 mV
ICF
intracellular fluid
made of water, ions and protiens
includes all fluid inside cell as well as cytosol
Lots of Na+
ECF
Fluid outside the cell
includes blood plasma, lymph and intercellular fluid (Middle ground fluid in between tissue kida)
Main ions are NA+ and CL-
leak ion channels
Ion channels that are always open so ions can pass thru
gated ion channels
channels that can close to regulate which ions come thru
How do small organic molecules (like amino acids) cross the membran
With carrier proteins, but this is slower than channels
How does a carrier protein work
carrier proteins are attached to the plasma membrane. On the outside of the cell they bind to non-lipid things and then change shape and push thing inside cell
Na+/K+ pump
Helps to keep sodium and potassium levels different inside and outside of cell.
3 Na+ out of cell
2 K+ inside of cell
Uses about half of brains ATP
without pump, neurons cant send electrical signals
ionic driving force
chemical vs electrical force
when will K+ stop leaving the cell/ when will cell have charge of 0 mV and how
it will stop when ICF and EFC are balanced. this can happen because K+ will leave until K= wants to come back because it attracts to more negative, or the ICF.
equilibrium potential
electrical energy needed to balance out chemical energy (electrical energy needed to balance the K+ that left)
threshold potential
-50 mV
depolarization
Na+ ions rush in, caused by Na+ gates opening. after reaching threshold, ICF becomes positive in less than 1mS
repolarization
After reaching about 30 mV, K+ leaves or Cl- comes in and goes to hyper polarization, or less than -70
Refractory Period
Reaction potential can’t be generated for a few milliseconds. Starts at the peak of the action potential. The cell can’t be restimulated. The threshold required for another action potential is higher than normal. 1-4 mS for 1 action potential cycle. makes sure action potential is 1-way movment
all-or-nothing principle
Action potential is produced only if the threshold is met. if its 1 above or even 100 threshold, action potential size is same
explain action potential from start to finish
starts at axon hillock. The resting potential is -70 mV. Stimulus makes Na+ channels open and depolarization happens. reaches about 30 mV, then repolarization happens, or K+ leaves cell, or Cl- comes in. The refractory period happens, then back to resting potential.
Hyperpolarization
goes below to about -80 mV
voltage-gated ion channels
open/ close in response to changes in membrane potential
found on axon hillock and axon
depolarization-activated ion channels
activated after depolariation, and its the K+ channels opening tso K+ can leave.
Reflexes
Does not require brain to process
Involuntary
respond to stimuli faster than voluntary movment
Propagation/ how action potential propagates
Moving or spreading
Action potential propagates down the axon bc positive charges influence axon segments to make an action potential, helping action potential travel down the axon
frequency of action potentials
More action potentials cause more neurotransmitters to be released at the synapse (10 above threshold produces more frequency than 1 above threshold)
anesthetics effects
Procaine and lidocaine bind to Na+ channels and block their ability to let ions flow. Sensory nerves in this region can’t send pain signals fully. Tetrodotoxin also blocks Na+ channels, leading to muscle paralysis or death.
what is ganglion
neuron chunks in PNS
Nuceli
Neuron chunks in CNS. Found in gray matter or brain
inside of cell membrane is charged
negatively
what is resting potential range
-40 to -90 mV. average is -70
membrane potential
separation of positive and negative charges across the plasma membrane
Neuronal membrane doing nothing is called
polarized
what is an action potential
a neuron sending electrical signal causing membrane potential change
why is refractory period important
so action potential doesnt reverse direction along axon
action potential is considered as an
all or nothing principle
what happens to magnitude of action potential as propagates
remains the same
the intensity of a stimulus is reflected in
frequency. greater stimulus is more AP per second
myelin
speed up in axon