6. Chest pain
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the differential diagnoses with chest pain
Cardiac
(AMI, pericarditis, aortic dissection, cardiac tamponade, arrhythmias)
Pulmonary
(PE, tension pneumothorax, pneumonia)
GI
(GERD, peptic ulcer disease, hiatal hernia, achalasia)
Chest wall
(costochondritis, herpes zoster, TB, rib contusion)
Psychological
(panic attack, anxiety)
What are life threatening causes of chest pain
AMI
Pulmonary embolism
Aortic dissection
Tension pneumothorax
Cardiac tamponade
Esophageal rupture
When should you do a more narrow differential diagnosis
When life threatening causes are ruled out by- patient history, examination, rapid diagnosis
What are the symptoms of chest pain (red flags)
Sudden onset
Exertional chest pain
Substernal or left-sided pain
Radiation to the left arm, jaw, neck and/or back
What are the qualities of chest pain (red fllags)
crushing
pressure
teating
ripping
What are the associated symptoms (red flags)
dyspnoea
excessive sweating
nausea
vomiting
What are the signs accompanying chest pain (red flags)
Vital sign abnormalities (e.g. hypoxia, hypotension)
Pulsus paradoxus (decrease in systolic BP during inspiration)
Difference of >20mmHg in systolic BP between arms
Chest wall crepitus
Distant heart sounds
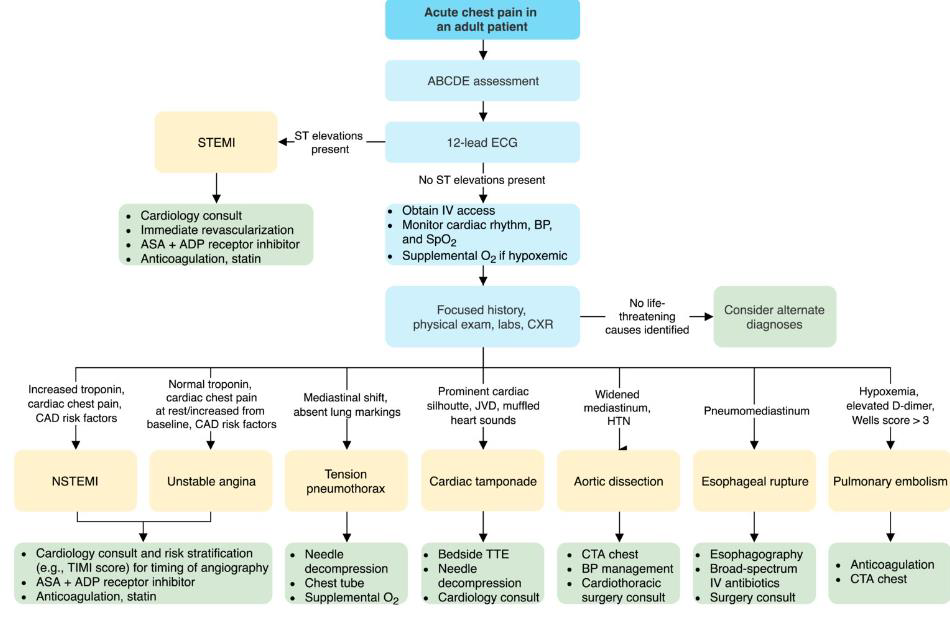
How do you approach CP in all patients
ABCDE approach
(airway, breathing, circulation, disability, exposure)
12-lead ECG
(ST elevations or no ST elevations)
Routine diagnostic studies
(e.g. troponin, CXR)
Identify and treat the underlying cause
How do you approach CP if red flags are present
in high risk of critical causes of chest pain
Perform point of care US (e.g. eFAST)
Begin time-sensitive management (e.g. activate cath lab for STEMI)
Obtain definitive imaging (e.g. CTA chest for TAA)
How do you approach CP if red flags are absent
low risk of critical causes of chest pain
Use risk stratification tools, e.g.:
HEART score for ACS risk stratification
Wells score for PE
What is the diagnostic process of chest pain
What are the pulmonary causes of chest pain
PE
tension PTX
spontaneous PTX
asthma exacerbation
COPD exacerbation
pleural effusion
Describe PE
Clinical features:
Pleuritic chest pain
Acute onset dyspnea, hypoxemia
Cough, hemoptysis
Unilateral leg swelling or history of DVT
Hypotension, shock (if massive PE)
Diagnostic findings:
Labs: elevated D-dimer, troponin, BNP
ECG: normal sinus rhythm, sinus tachycardia, signs of RV strain
CT angiography: pulmonary artery filling defect
V/Q scintigraphy: perfusion-ventilation mismatch
Clinical calculators: Wells score, PERC rule, PESI
Describe tension pneumothorax
Clinical features:
Severe, sharp chest pain
Dyspnea, hypoxemia
History of trauma
Hyperresonance on percussion, decreased breath sounds, tracheal deviation
Tachycardia, hypotension
Diagnostic findings:
Clinical diagnosis
CXR: absent lung markings, tracheal deviation, pneumomediastinum
Describe sponteneous PTX
Clinical features:
sudden, sharp unilateral chest pain
Acute dyspnea, hypoxemia
Hyperresonance on percussion, decreased breath sounds on the affected side
Crepitus
History of lung disease or trauma
Diagnostic findings:
Inspiratory CXR: increased lucency, displaced lung markings, subcutaneous emphysema
POCUS: absent lung sliding on eFAST
Describe pneumonia
Clinical features:
Fever, chills
Cough, dyspnea
Hypoxemia, crackles
Diagnostic findings:
Labs: leukocytosis, elevated ESR/CRP and procalcitonin
Positive sputum culture
CXR: consolidation, pleural effusion
CT chest: hyperdense consolidation
Describe asthma exacerbation
Clinical features:
Dyspnea, cough
Tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxemia
Diffuse wheezing
Decreased or absent breath sounds
Increased work of breathing
Diagnostic findings:
Peak expiratory flow: decreased from predicted or personal best
ABG: ↓pH, ↑PaCO2, ↓PaO2 ( → respiratory acidosis)
Describe COPD exacerbation
Clinical features:
Dyspnea, cough
Purulent sputum#
Tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxemia
Diffuse wheezing, decreased breath sounds
Signs of imminent respiratory arrest: confusion, absent breath sounds, bradycardia
Diagnostic findings:
ABG: ↓pH, ↑PaCO2, ↓PaO2 ( → respiratory acidosis)
Labs: ↑CRP, ↑procalcitonin (if underlying bacterial infection)
CXR: hyperinflated lungs: signs of pneumonia, pneumothorax and/or pleural effusion
Describe pleural effusion
Clinical features:
Unilateral, pleuritic chest pain
Dyspnea
Dry, nonproductive cough
Dullness to percussion, decreased breath sounds, decreased tactile fremitus
Pleural friction rub
Diagnostic findings:
CXR: homogenous opacity with blunting of the costophrenic angle
POCUS: hypoechoic space between the parietal and visceral pleura
What are CV causes of chest pain
STEMI
NSTEMI
aortiic dissection
cardiac tamponade
pericarditis
HF exacerbation
What are the characteristics of N/STEMI
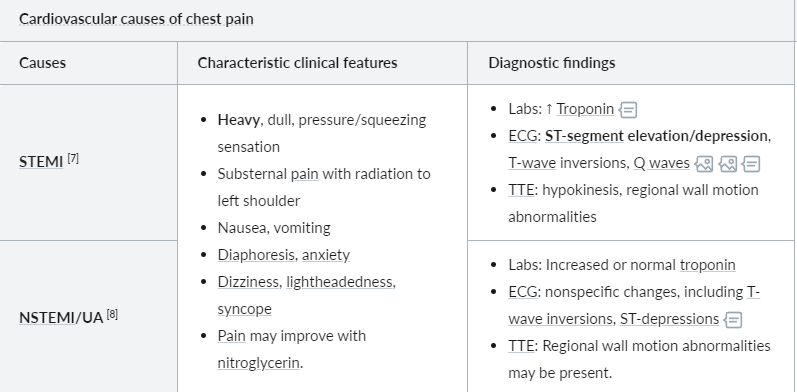
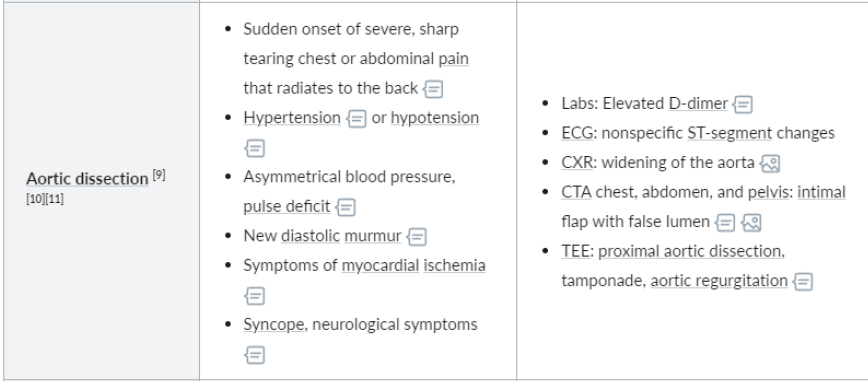
What are the characteristics of aortic dissection
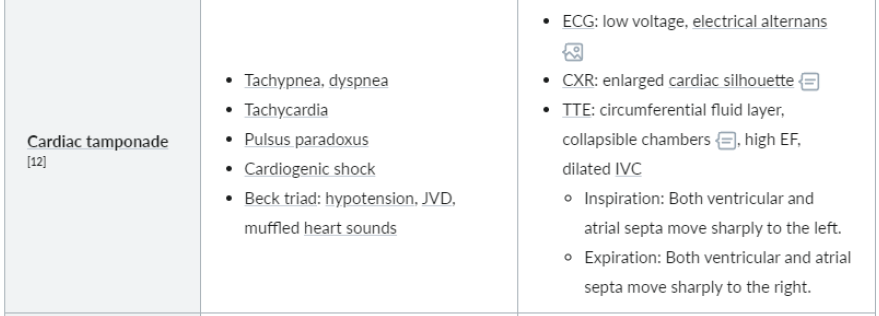
What are the characteristics of cardiac tamponade
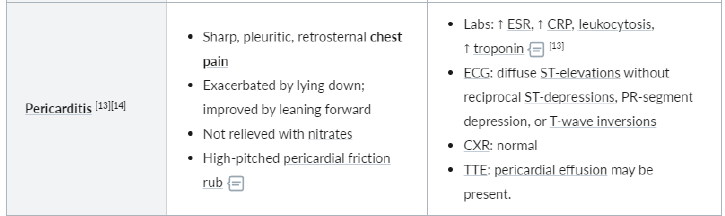
What are the characteristics of pericarditis
What are the characteristics of HF exacerbation

What are the GI causes of chest pain
esophageal perforation
GERD and erosive erophagitis
Gastritis
peptic ulcer disease
acute pancreatitis
esophageal hypermotility
What are the characteristics of oesophageal perforation

What are the characteristics of GERD and erosive oesphagitis

What are the characteristics of gastritis

What are the characteristics of peptic ulcer disease

What are the characteristics of acute pancreatitis

What are the characteristics of oesophageal hypermotility disorders
