spinal cord: structural and functional organization
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
vertebrae
bones that make up the vertebral column, which is a casing that protects the spinal cord
32
number of vertebrae bones that make up the vertebral column
cervical
7 bones make up this segment of the vertebral column
thoracic
12 bones that make up this segment of the vertebral column
lumbar
5 bones that make up this part of the vertebral column
sacral
5 fused bones that make up this part of the vertebral column

coccyx (1)
3 fused bones that make up this part of the vertebral column (1)
laminectomy
removal of the roof of the vertebral canal to expose the underlying spinal cord
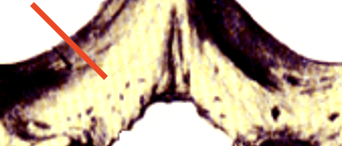
body
transverse process

spinous process
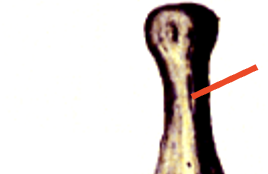
lamina
connect the transverse processes with the spinous process
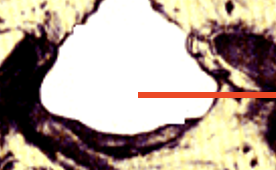
vertebral canal
spinal cord is located here
intervertebral foramen
joint between two vertebrae; site where nerves going out to muscles or carrying sensory information into spinal canal emerge
dorsal root ganglia
contain neuronal cell bodies that are involved in carrying sensory information from the periphery to the spinal cord

spinal nerve
the dorsal and ventral roots unite to form this, which continous out to the periphery - contain both sensory and motor information
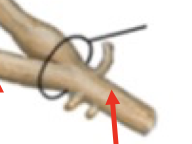
dorsal horn

dorsal rootlets
dorsal root
transmit sensory information from the periphery to the CNS

ventral horn

ventral rootlets

ventral root
carry motor information from the CNS to the periphery

meninges
membrane that surrounds the central nervous system; composed of three layers
dura mater
arachnoid
pia mater
layers of meninges (first - outermost; last - innermost)
dura mater
tough mother; thick/dense membrane of the meninges
arachnoid
the middle layer of the meninges, the outersurface attaches to the dura mater, its characteristic meshwork extends to pia mater
pia mater
tender mother; adheres to all surfaces of the CNS
subarachnoid space
located between the arachnoid and pia mater; contains the cerebrospinal fluid
coccyx
where all three layers of the meninges terminate
2nd lumbar vertebrae
where the spinal cord ends in an adult; level of the spinal cord is not the same as their adjacent vertebral level
embryo 8 weeks
all three layers of meninges anchored to coccyx
spinal cord extends from base of skull to coccyx
nerves leave the spinal cord through adjacent intervertebral foramen
embryo 24 weeks
all three layers of meninges anchored to coccyx
spinal cord extends from base of skull to S-1 (sacral-1)
nerves still leave through the same foramne as E-8weeks, however they have stretch to reach out
birth
all three layers of meninges anchored to coccyx
spinal cord extends from skull to lumbar-3
nerves leave through the same foramen as E-8weeks, they stretch to reach it
adult
all 3 layers of meninges anchored to coccyx
spinal cord extends from skull to L-2
nerves leave through the same foramen as E-8weeks, they stretch to reach it
filum terminale
fine filament that extends inferiorly from the distal end of the spinal cord; it is made up of pia-mater (non-neural tissue) - extends from conus medullaris
cerebrospinal fluid
located in the subarachnoid space between arachnoid and pia mater - forms a reservoir below the distal end of the spinal cord
lumbar puncture
carried out to collect samples of CSF for testing or for injection of anesthesia into CSF for spinal block
needle inserted below L3 to avoid contact with SC
conus medullaris
tapered distal end of the spinal cord
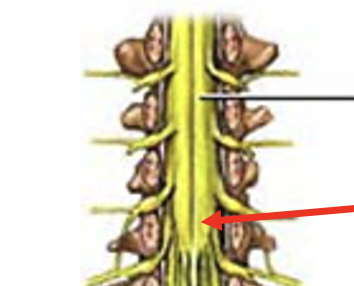
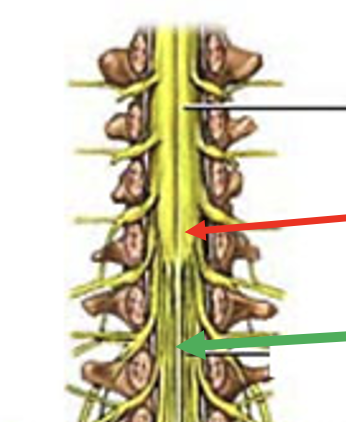
cauda equina
made up for ventral and dorsal roots arising from the spinal cord and descending to their respective intervertebral foramen to exit at lower lumbar and sacral levels
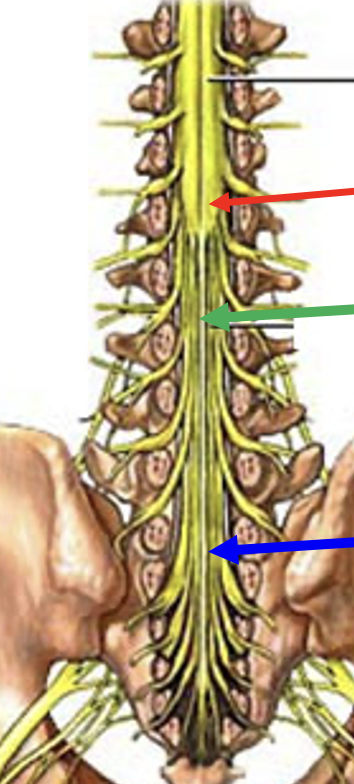
cauda equina syndrome
caused by tumor or rupture of intervertral disk that encroaches on cauda equina in vertebral canal
treated with surgical decompression to avoid permanent damage
saddle numbness
nissl stain
label endoplasmic reticulum in cell bodies
fiber stain
labels myelin on axons
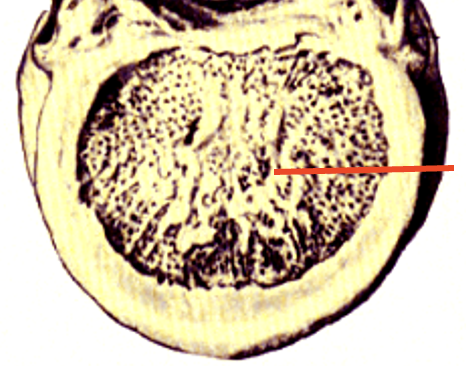
butterfly
center of the spinal cord; contains neurons and glia (grey matter)
grey matter
primarily made up of neurons (cell bodies)
white matter
primarily made up of myelinated axons
intermediate gray area
located between the dorsal and ventral horn; primarily used by autonomic nervous system
tract
a bundle of axons arising from a specific area and having the same function; connect two CNS regions
ascending tract
project from the spinal cord to the brain
descending tract
project from the brain to the spinal cord
fasiculus
a bundle of anatomically defined fibers that serve a common function (aka tract)
funiculus
an area containing multiple tracts
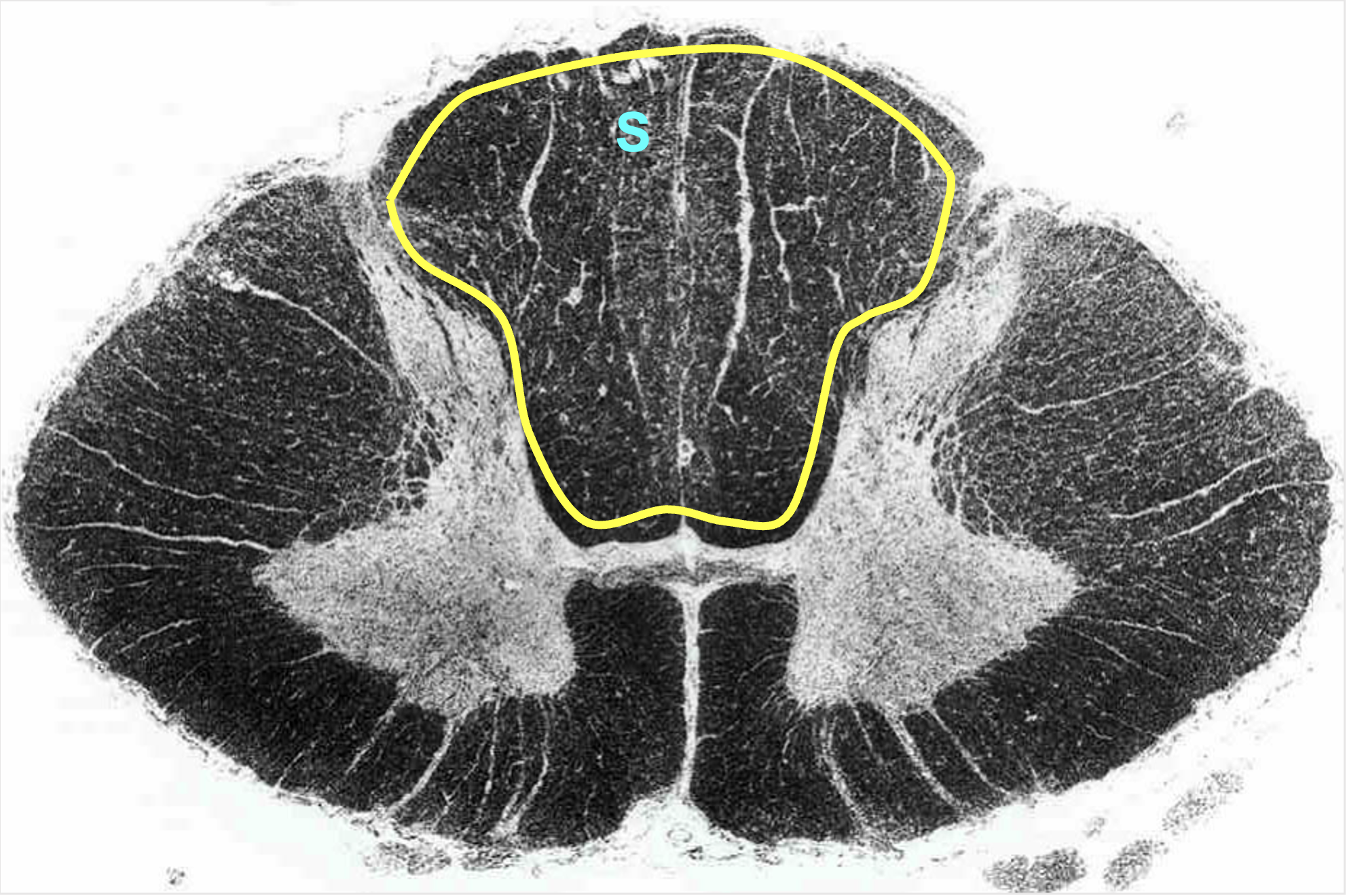
dorsal column/funiculus
white matter located in between dorsal horns; contain multiple tracts
sensory information (ascending)
contains large diameter processes of dorsal root ganglia
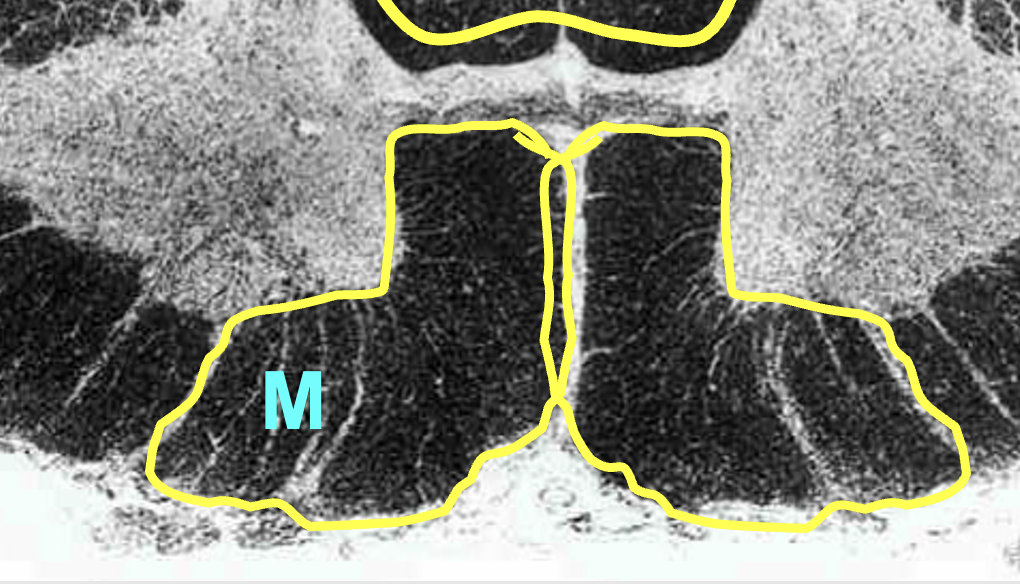
ventral column/funiculus
white matter located between two ventral horns; contain multiple tracts
motor informsation (descending)
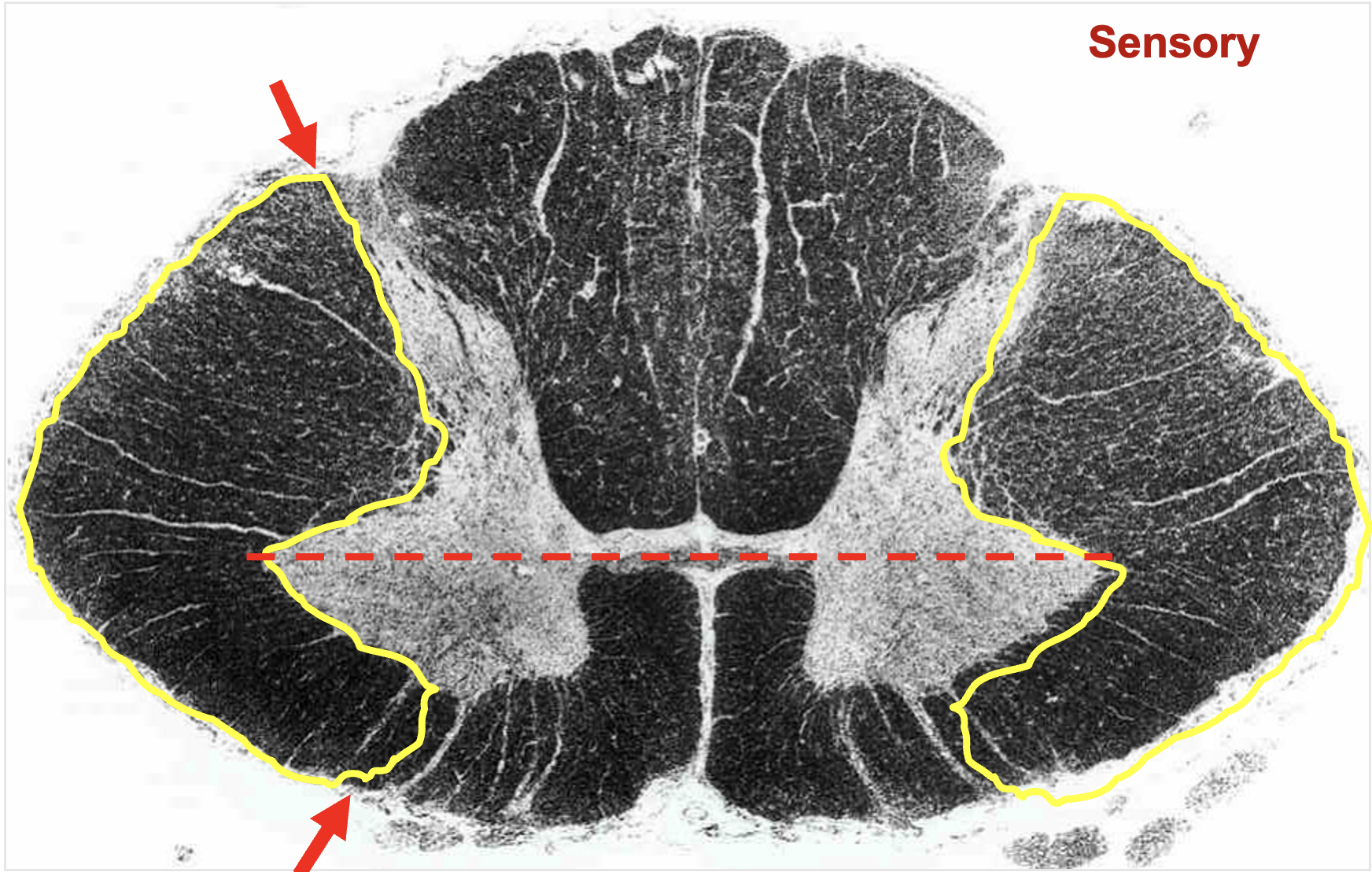
lateral funiculus
between lateral edge of dorsal and ventral horns; contains multple tracts
sensory and motor tracts
ascending and descending tracts
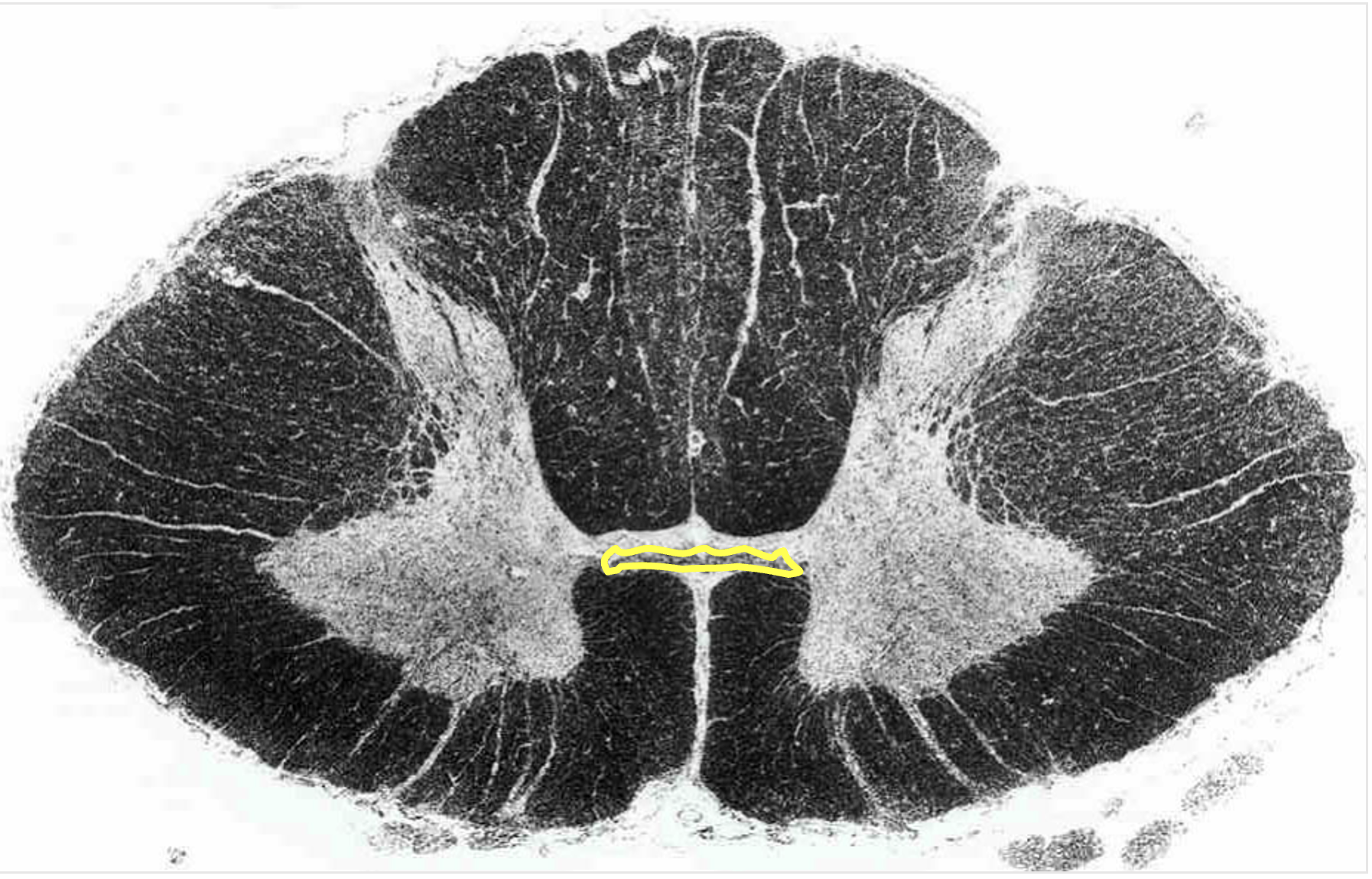
anterior white commissure
located dorsal to the anterior median fissure
contains axons from one side of spinal cord to another