3.1 Biological molecules
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are monosaccharides?
One unit of carbohydrate (a monomer)
Examples of monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose
Characteristics of monosaccharides
Sweet tasting Soluble General formula (CH₂O)ₙ where n is a number from 3 to 7
Anabolic Reaction
Building polymers
Catabolic reaction
Breaking down polymers
Types of reactions
Hydrolysis
Condensation
Hydrolysis reaction
Using water to break apart cells (separate polymers). Water is added
Condensation reaction
Anabolic- building polymers, where water leaves the reaction
2 types of glucose
alpha- glucose
beta- glucose
Alpha- glucose diagram
H is ABOVE carbon 1
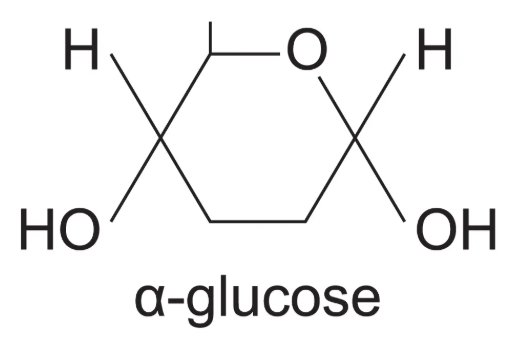
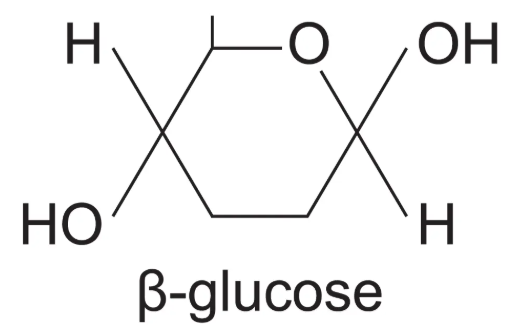
Beta- glucose diagram
H is BELOW carbon 1
Isomers definition and examples
Compounds with the same formula but different arrangement alpha and beta glucose
Hydroxyl group
OH
Carbonyl group
C=O
Disaccharides e.g
glucose + glucose = maltose
glucose + fructose = sucrose
glucose + galactose = lactose
Reducing sugars definition and example
Can donate electrons to reduce another chemical e.g disaccharides
Reducing sugar test
Benedict's solution, heat in warm water bath
Results: Blue- non-reducing sugar. Green- traces of reducing sugar. Orange- moderate levels. Brick red- high levels + insoluble red ppt of copper (I) oxide formed
Positive result shown because the benedict's solution gained electrons from the reducing sugar
Non-reducing sugar e.g
Sucrose
Polysaccharides characteristic and uses
Large so insoluble
Uses: Starch and glycogen- storage, but are broken down when monosaccharides have been broken down (used up). Cellulose- structural support in plants
What are starch and cellulose formed from?
Starch- alpha glucose Cellulose- beta glucose
How are cellulose molecules adapted?
They have long and straight chains which become linked together by many hydrogen bonds to form fibrils. This provides strength to cell walls
How are starch molecules adapted for function in plant cells?
Function= storage They are large, so insoluble, and the large molecules cannot leave the cell. They are also compact so can store lots with minimal space
What joins only saccharides together?
Glycosidic bonds (covalent bond, condensation reaction)