Studying Human Evolution and Evidence
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
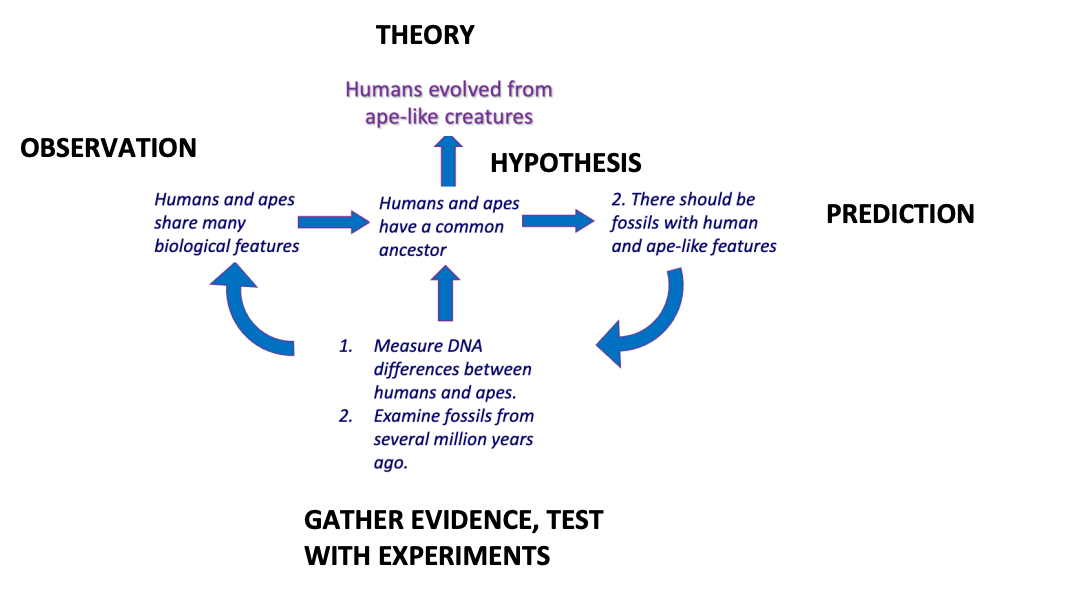
How do you study human evolution?
Always start with an observation
Hypothesis
Prediction
Gather evidence, test with experiments (statistical analysis)
Create theory
What are the forms of primary evidence?
Anatomy (fossil and comparative anatomy)
Artefacts (stone/bone tools, site patterning)
Genetics/molecular evidence (proteins and enzymes, chromosomes, comparative genetics and ancient DNA, DNA (nuclear, mtDNA, Y chromosome))
What are the limitations of primary evidence?
Time depth for some lines of evidence like history
How do fossils form?
Phase 1: death
Phase 2: deposition
Phase 3: perimineralisation (replacement of the original organic tissues with minerals from the surrounding rock)
Phase 4: exposure
How are fossils dated?
Relative dating and numerical dating
What is relative dating?
A method of determining the order in which geologic events occurred, specifically establishing whether one rock or event is older or younger than another
Comparison to other similar material of know age
Palaeomagnetism: changes in Earth’s magnetic field
What is numerical dating?
A method of determining the age of Earth materials by assigning a specific number of years to an event or interval of time in Earth's history
Isotope analysis (decay other time): potassium-argon, argon-argon, carbon-14 (or radiocarbon), and uranium series
Thermo-luminescence: amount of electrons trapped inside
Molecular clock: DNA-based, mutation over time
What are recent developments in the field?
New discoveries keep changing our understanding and new technologies allows old evidence to be re-analysed