phrm 82500: lecture 14: progestins
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
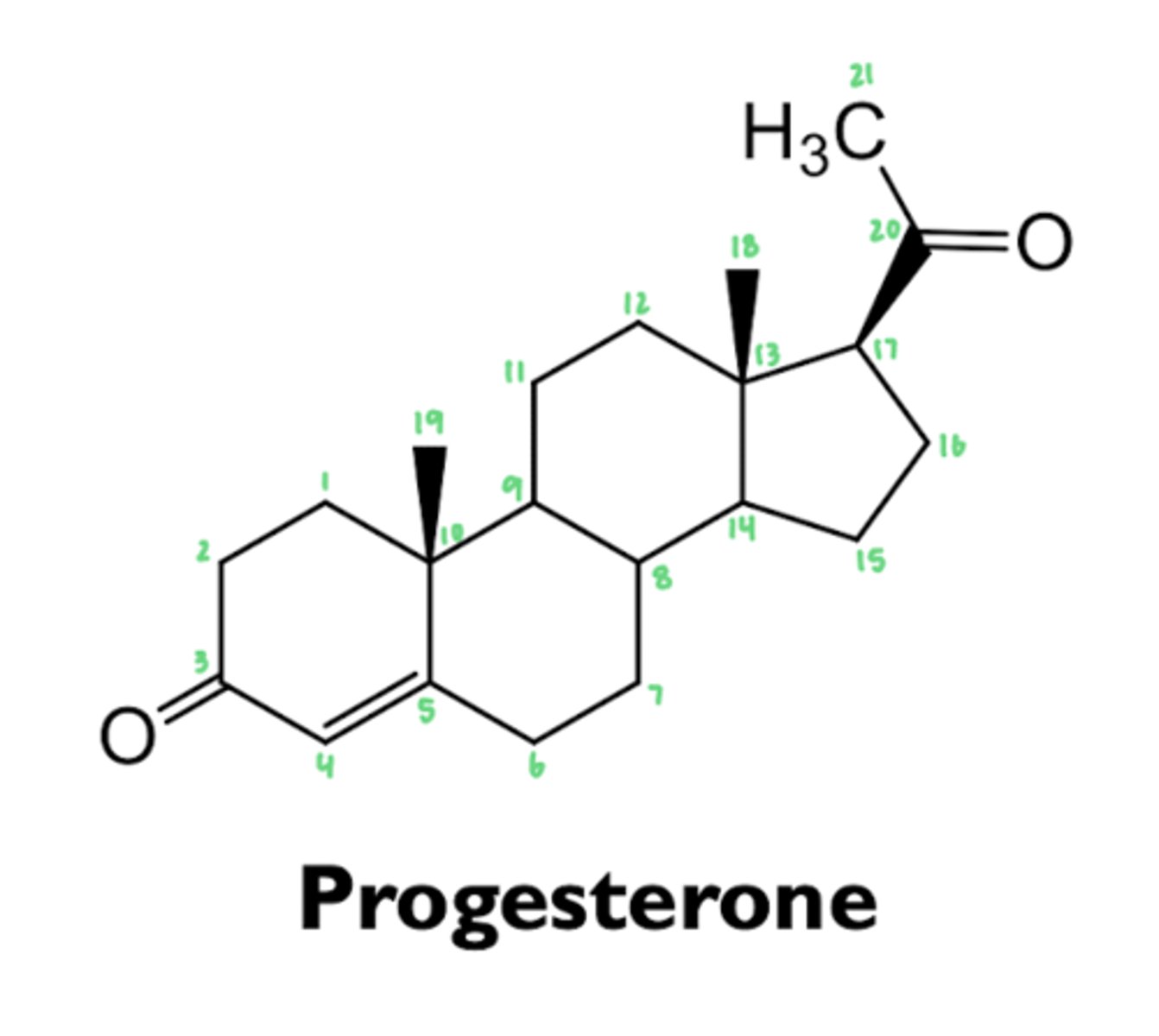
what is progesterone?
most important progestin in human
what does progesterone function as?
hormone
- also a precursor to estrogens, androgens, and corticosteroids
what does progesterone bind to?
progesterone receptor and alters rate of transcription
where is progesterone synthesized?
ovary, testis, and adrenal glands
- large quantity is synthesized by corpus luteum in ovary and luteal phase and by placenta during pregnancy
how is progesterone metabolized?
- rapidly absorbed following administration by any route
- half-life in plasma: ~5 min
- almost completely metabolized in one passage through liver
what is progesterone converted to during metabolism?
pregnanediol
- conjugated with glucuronic acid
where is progesterone excreted?
urine
what are the physiologic effects of progesterone?
- menstruation cycle
- metabolic effects
- interference with aldosterone
- depressant and hypnotic effects on the brain
how does progesterone contribute to the menstrual cycle?
causes maturation and secretory changes in endometrium following ovulation
how does progesterone contribute to metabolic effects?
- increases basal insulin levels and insulin response to glucose
- promotes glycogen storage in liver
how does progesterone interfere with aldosterone?
- competes with aldosterone for mineralocorticoid receptor
- causes a decrease in Na+ resorption, leading to increase of aldosterone secretion by adrenal cortex in pregnancy
what are the clinical uses of progesterone?
- hormonal contraception
- hormone replacement therapy in combination with estrogens
- endometriosis
- dysmenorrhea
- bleeding disorders
how does progesterone contribute to hormone replacement therapy in combination with estrogens?
prevents some adverse effects of estrogens
- uterine bleeding and endometrial carcinoma
how does progesterone contribute to endometriosis?
- growth of endometrial cells outside uterine cavity
- cells respond to hormonal changes and cause severe pain from inflammation during menstruation
- progestins suppress growth of endometrial cells
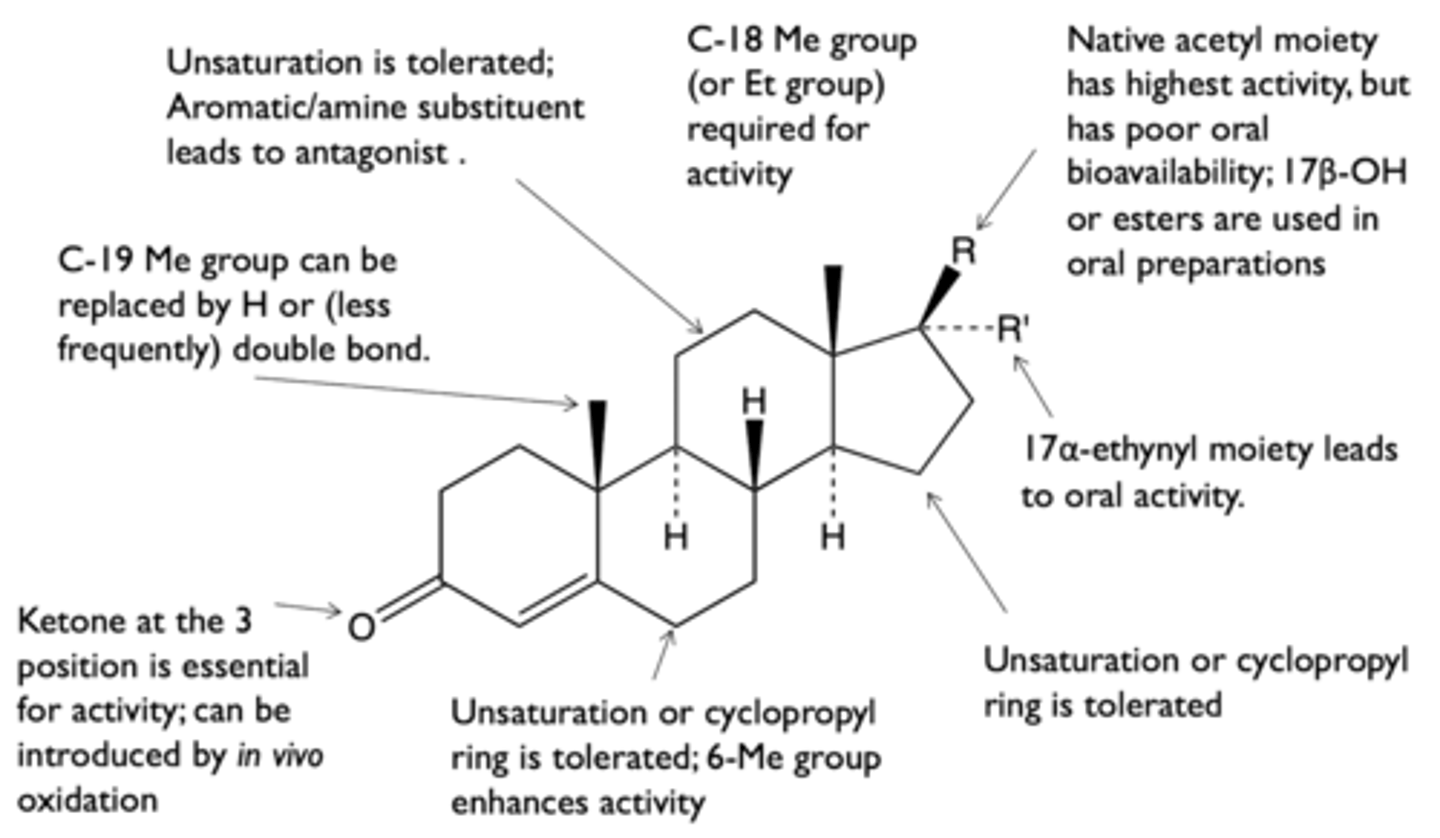
what is the structure-activity relationship of progestins?
what are the types of progestins?
- norethindrone
- ethynodiol diacetate
- levonogestrel
- norgestimate
- desogestrel
- drospirenone
- medroxyprogesterone acetate
what are the types of "19-nor, 17-ethynyl" steroids?
- norethindrone
- ethynodiol diacetate
what are the characteristics of "19-nor, 17-ethynyl" steroids?
oral contraceptives
- first generation progestins
- ester groups rapidly hydrolyzed in vivo
what are the effects of 19-methyl group on the activity of "19-nor, 17-ethynyl" steroids?
- 19-methyl group is not necessary for progestenic activity
- replacement of 19-methyl with H enhances activity
what are the effects of 17-ethynyl group on the activity of "19-nor, 17-ethynyl" steroids?
- 17-ethynyl group increases oral bioavailability
- replacement of 17-acetyl with OH increases oral bioavailability
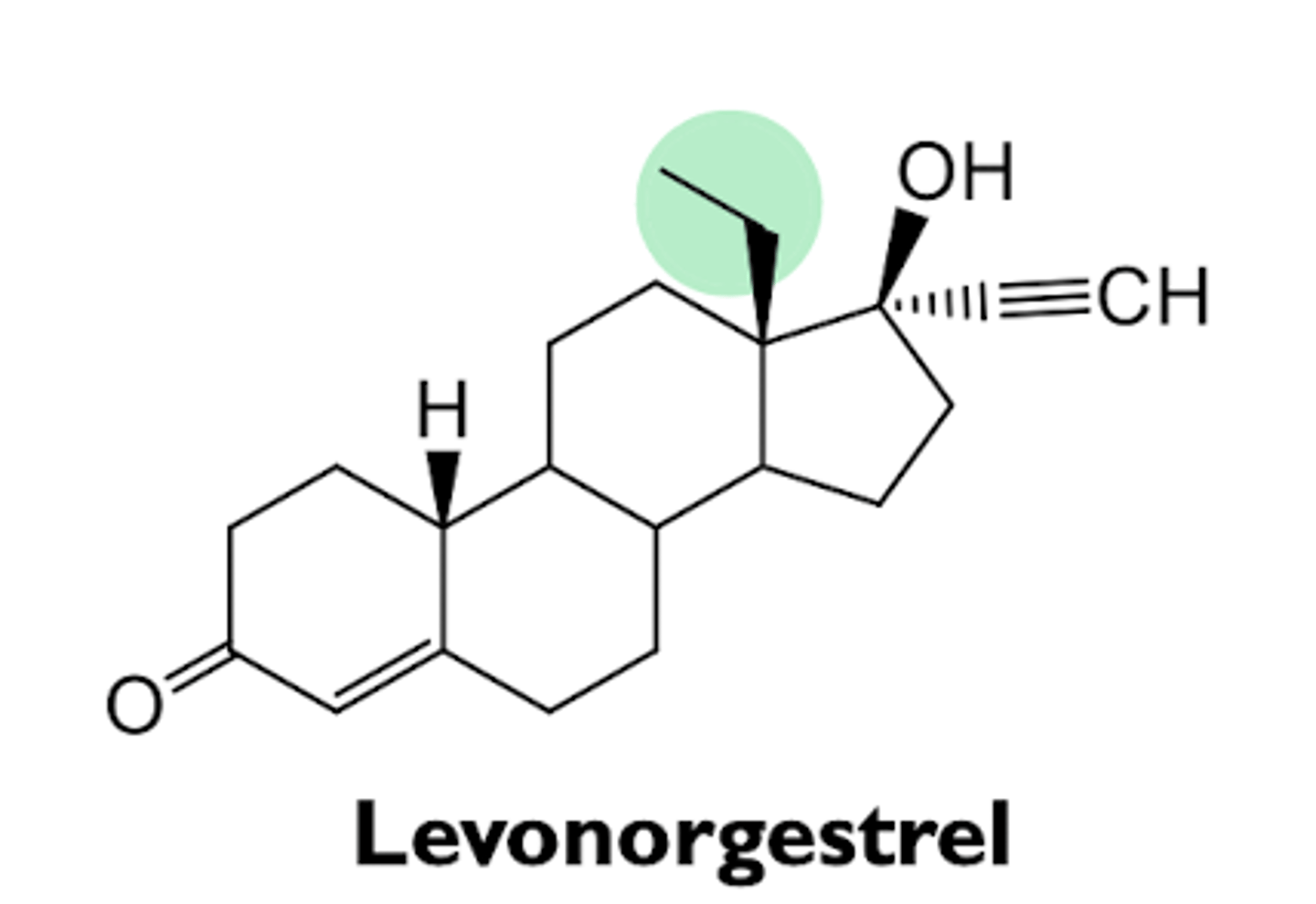
what are the characteristics of levonorgestrel?
- 2nd generation progestin
- levo isomer of norgestrel, which is a racemic mixture
- only levo form is active
- high oral bioavailability
- used in intrauterine devices (IUDs)
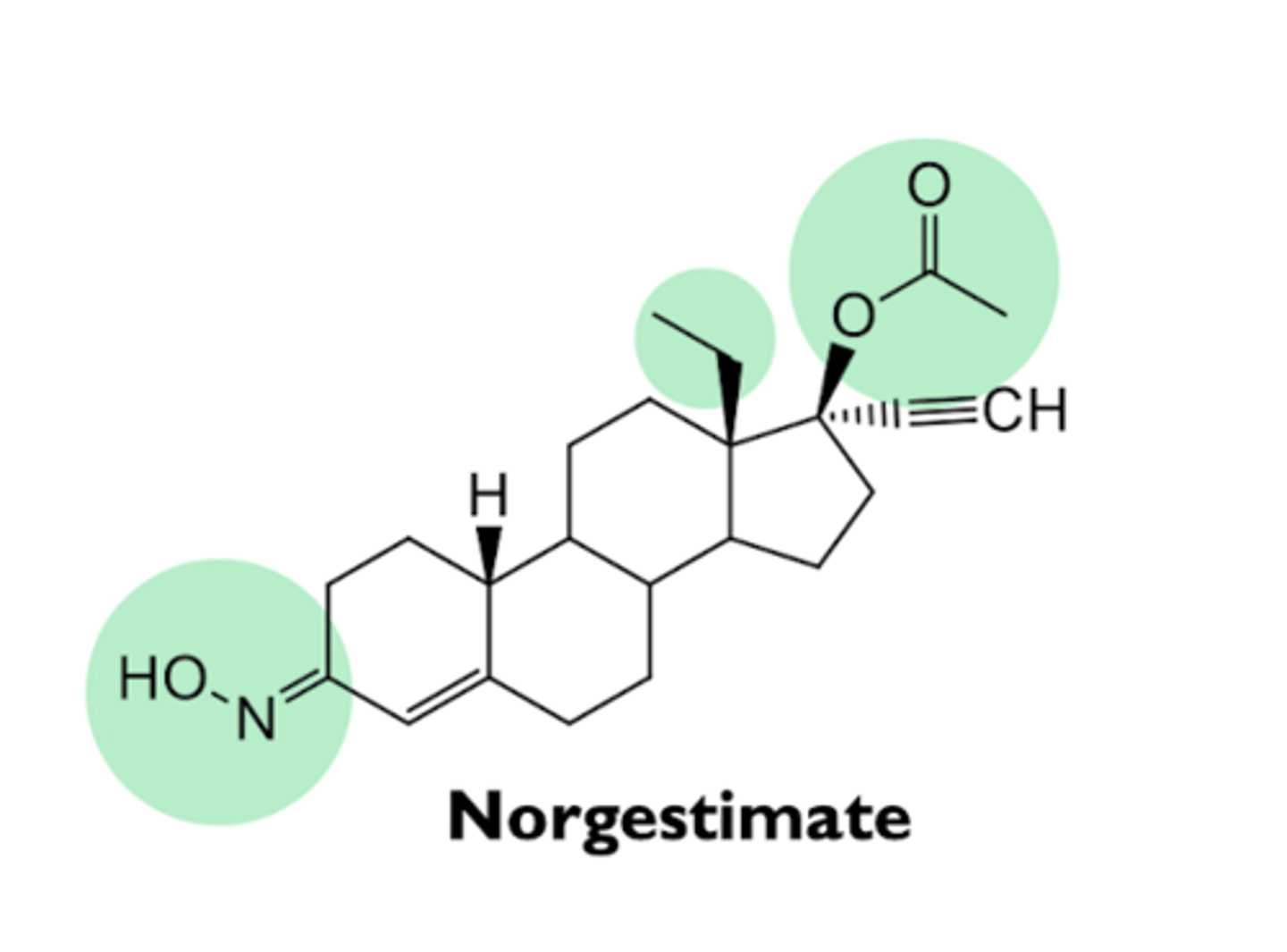
what are the characteristics of norgestimate?
- prodrug
- converted to levonorgestrel oxime and then to levonorgestrel in vivo
what are the characteristics of desogestrel?
- 3rd generation progestin
- prodrug
- rapidly metabolized to etonogestrel
- high oral bioavailability
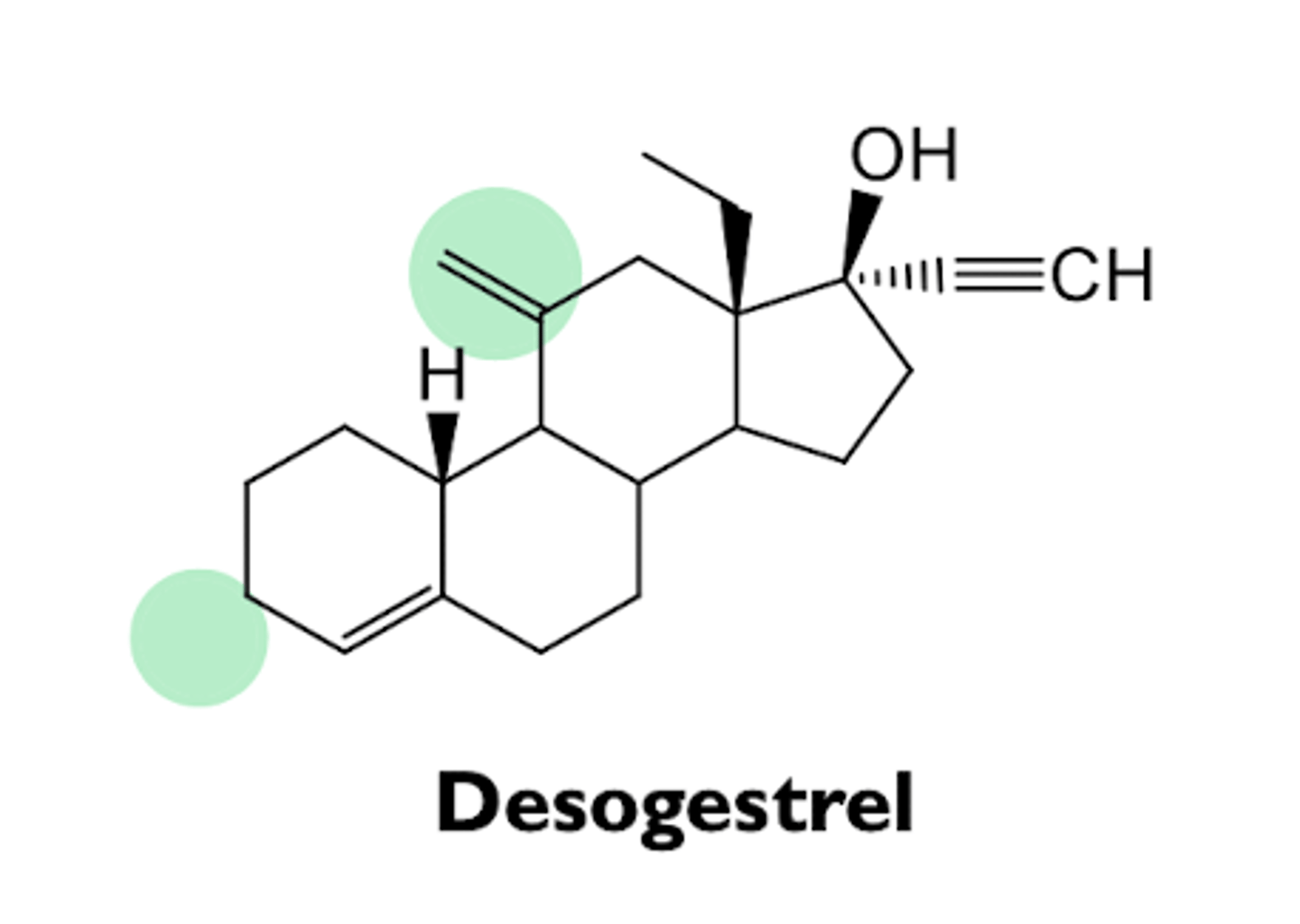
what are the characteristics of etonogestrel?
- active form of desogestrel
- structurally analogous to levonorgestrel
- used in subdermal implant of vaginal ring
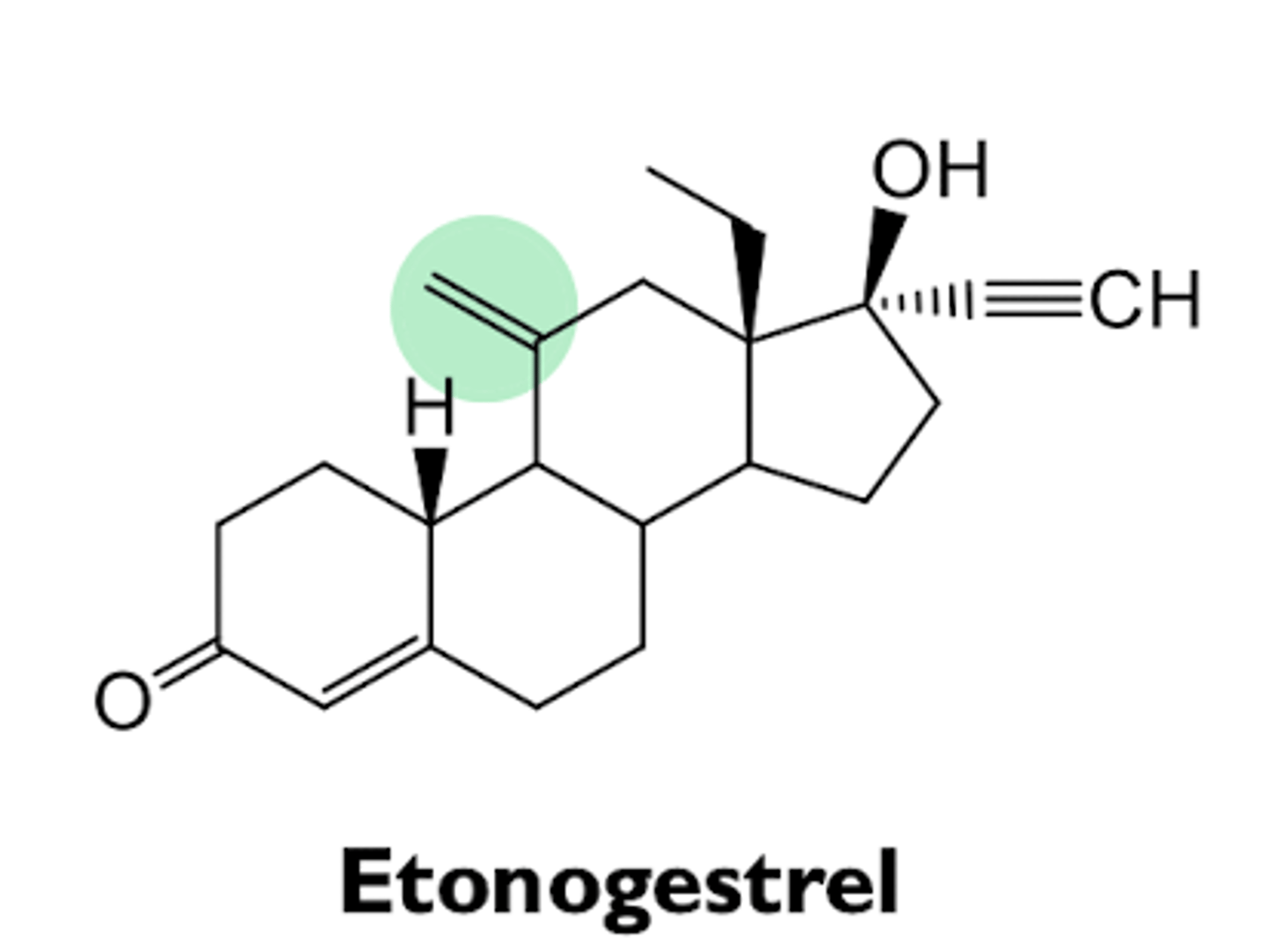
what are the characteristics of drospirenone?
- 4th generation progestin
- relatively weak progestogenic activity (10% of levonorgestrel)
- antimineralocorticoid activity
- negates side effects of ethynyl estradiol in combination therapy
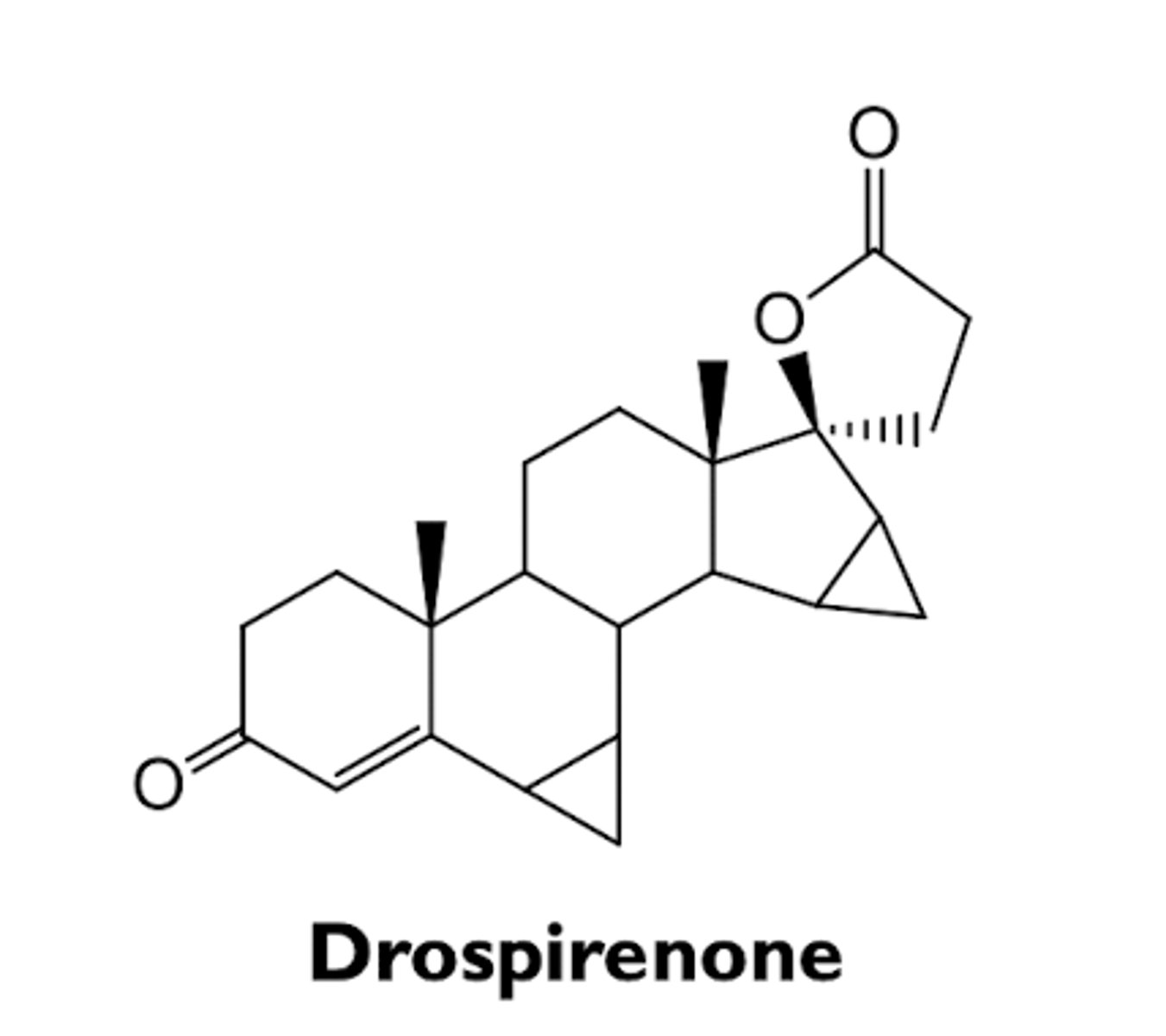
what are the characteristics of medroxyprogesterone acetate?
- 1st generation progestin
- used for depot injection as a long-acting progesterone-only contraceptive
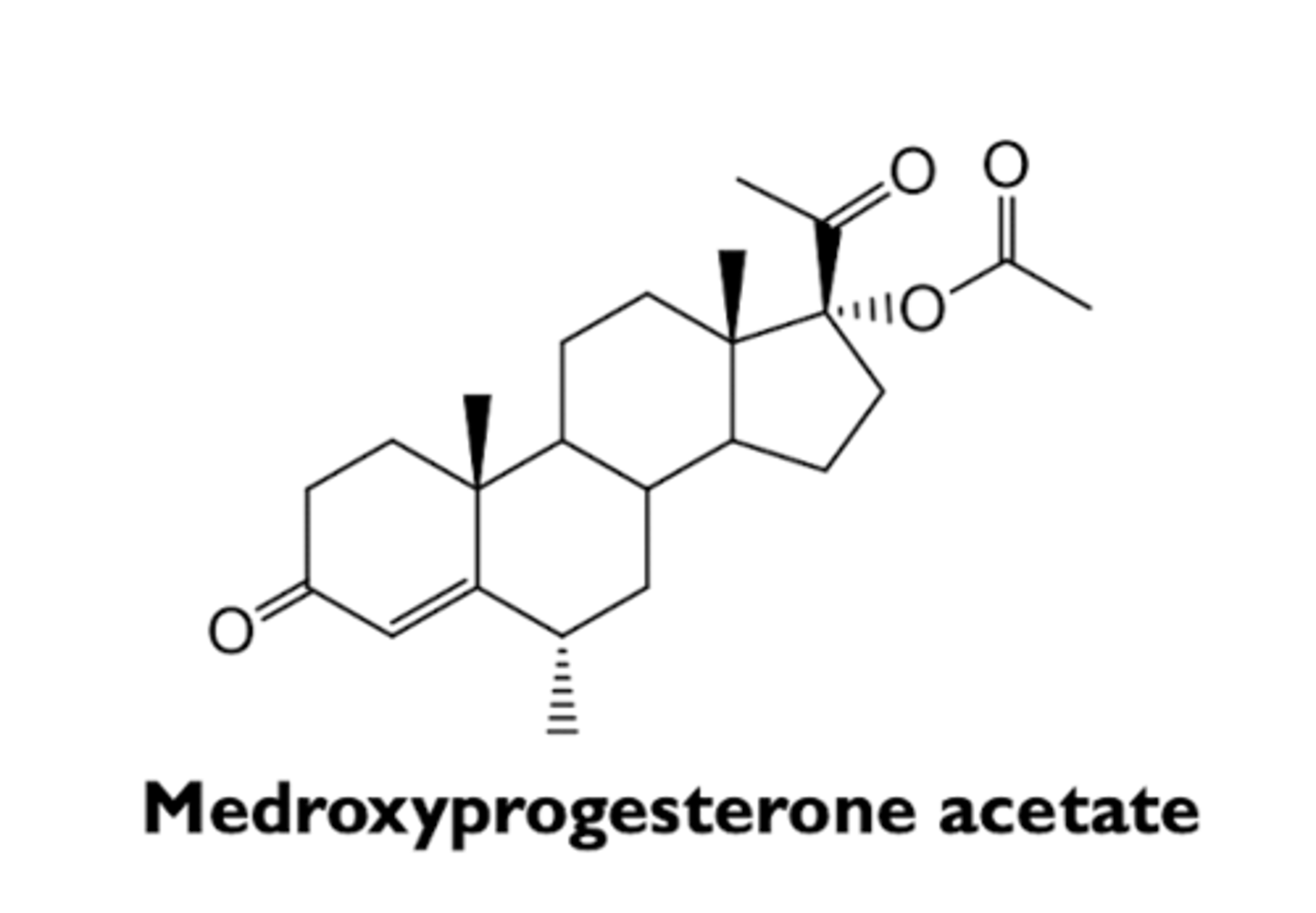
what are the hormonal activities of progestins?
- frequently have hormonal activities other than progestonic effects due to their interaction with other steroid receptors
- minimizing androgenic and antiestrogenic activities are desirable
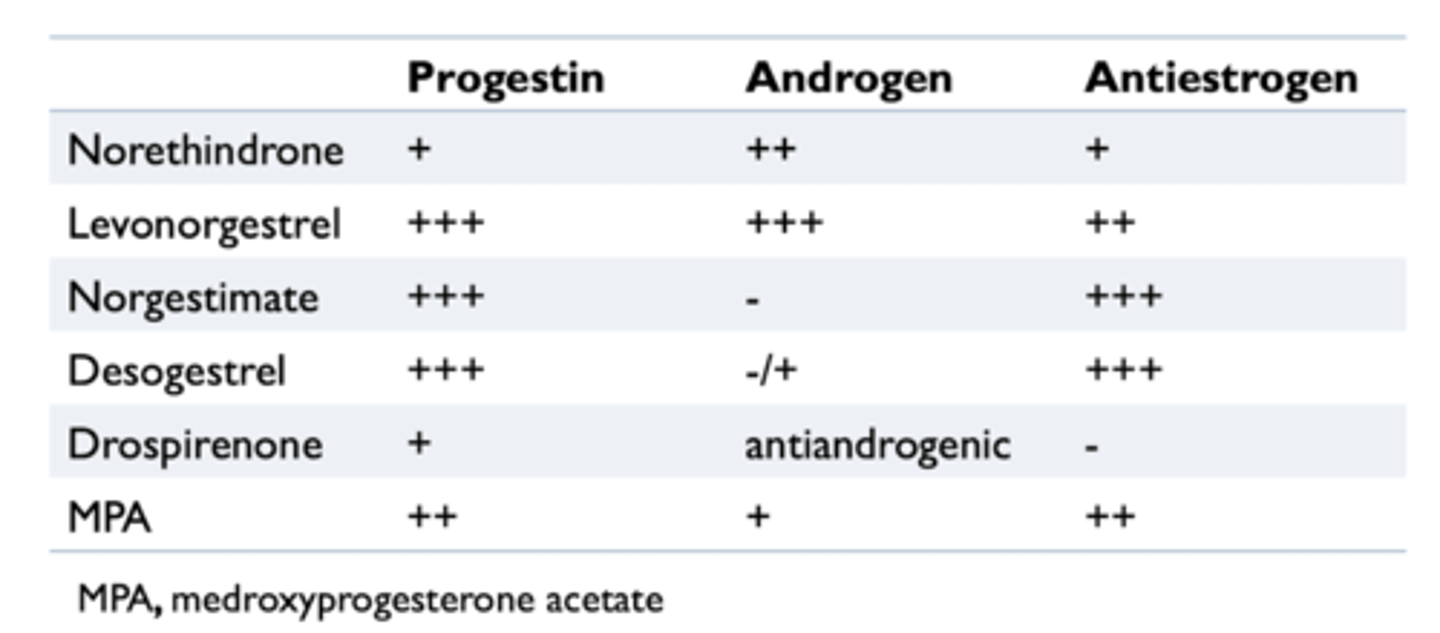
what are the types of hormonal contraceptions?
- combination of estrogens and progestins
- continuous progestin therapy with estrogen
what are the characteristics of combinations of estrogens and progestins?
- typically 21 days on active compounds and 7 days on placebo (withdrawal bleeding)
- monophasic, biphasic, or triphasic according to dose variation
how are hormonal contraceptives delivered?
- mostly oral administration
- implantable, IUD, or depot injection
how do oral contraceptives inhibit ovulation?
- combinations of estrogens and progestins selectively inhibit pituitary function
- progestin-only contraceptives do not always inhibit ovulation
what are the effects of oral contraceptives on the ovary?
- suppression of ovarian function
- when discontinued, a majority of patients return to the normal cycle in 1-2 months
what are the effects of oral contraceptives on the uterus?
change in the cervical mucus and in uterine endometrium
- decrease in likelihood of conception and implantation
what are the effects of oral contraceptives on the breast?
combinations only
- stimulation of breasts (enlargement)
- suppression of lactation
what are the mild adverse effects of oral contraceptives?
- nausea, hypertension, edema, breast fullness due to estrogens
- increased appetite, fatigue, breast regression due to progestins
what are the moderate adverse effects of oral contraceptives?
- irregularities in menstruation (breakthrough bleeding) (more common in progestin-only contraceptives)
- weight gain, acne, hirsutism (more common with the combinations containing androgen-like progestins
- amenorrhea
what are the severe adverse effects of oral contraceptives?
- venous thromboembolic disease due to estrogens
- myocardial infarction due to androgenic activity of progestins
- can be dangerous in women over 35 who smoke
what are the drug interactions of oral contraceptives with other steroids?
oral contraceptives may increase the blood levels of other steroids by interfering their metabolism
- ex. glucocorticoids
what are the drug interactions of oral contraceptives with anticonvulsants?
phenytoin
- induces drug-metabolizing enzymes in the liver
what are the drug interactions of oral contraceptives with antibiotics?
rifampin
- induces drug metabolizing enzymes in liver
- increases rate of metabolism of many other drugs
tetracyclines
- suppresses gut flora that participate in enterohepatic recycling
what are the characteristics of emergency contraceptives?
- postcoital ("morning after") contraception
- effective 99% of the time when treatment is begun in 72 hours
- similar to oral contraceptives, but with much higher doses
what are the side effects of emergency contraceptives?
nausea, vomiting
- more common in combinations
what are the types of emergency contraceptives?
- selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM)
- progesterone antagonist
- atypical
what is an example of a selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM)?
ulipristal acetate
what are the characteristics of ulipristal acetate?
- selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM)
- used as an emergency contraceptive
- can be effective up to 5 days after unprotected sex
- side effects include nausea and abdominal pain
what is an example of a progesterone antagonist?
mifepritsone
what are the characteristics of mifepristone?
- RU-486
- progesterone antagonist
- abortifacient
how is mifepristone used as an abortifacient?
used in combination with misoprostol (PGE1 derivative, oral prostaglandin) up to 70 days
what are the side effects of mifepristone?
- nausea, vomiting
- bleeding (5%) (requires intervention and administered only by physicians)
what are the characteristics of danazol?
- weak androgen, weak progestin, and antiestrogen
- effective for endometriosis
how is danazol effective for endometriosis?
- inhibits the surges of LH and FSH and suppress ovarian function
- causes atrophy of endometrium
what are the adverse effects of danazol?
- mostly from weak androgenic activity
- weight gain, decreased breast size, acne, oily skin, hirsutism
what are the contraindications of danazol?
- hepatic dysfunction
- pregnancy and breast-feeding