Glycogen degradation
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Glycogen
Highly branched homopolymer of glucose
Present in all tissues
Where are the largest stores of glycogen?
Muscle and liver
Describe the structure of glycogen
a-1,4 chains
a-1,6 branches
Nonreducing ends
Glycogen phosphorylase
Phosphorolyzes glycogen a-1,4 linkages from the nonreducing ends
Creates glu-1-P
Dimer
Phosphorolysis
Addition of Pi to degrade a-1,4 linkages
Transferase
Shifts oligosaccharides away from branch point to increase accessibility to the phosphorylase
a-1,6 glucosidase
Hydrolyzes the branching point on glycogen
Releases FREE glucose (no Pi)
What is the ratio of glu-1-P to glucose produced for the glucosidase reaction?
12:1
Phosphoglucomutase
Converts glu-1-P to glu-6-P
Prepares glycogen derived glucose for glycolysis/use in cell
What is the mechanism for phosphoglucomutase (not liver)?
Ser114 is a Pi group carrier that adds to glu-1-P to create glu-1,6-P, then removes to create glu-6-P
What is the mechanism for phosphoglucomutase in the liver?
Ser114 is a Pi group carrier that adds to glu-1-P to create glu-1,6-BP, then removes to create glu-6-P
Glu-6-P is converted to glucose by glu-6-phosphatase to exit liver and enter bloodstream
How many glucoses can glycogen phosphorylase liberate from the molecule?
8
What enzyme regulates glycogen breakdown?
Glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase a
Active form
R state favored
Ser14 is phosphorylated
Glycogen phosphorylase b
Inactive form
T state favored
Ser14 dephosphorylated
What is the default state of liver glycogen phosphorylase?
a (active) form
Phosphorylated
R state
How is liver glycogen phosphorylase regulated?
Increased glucose concentration inhibits
Negative regulation
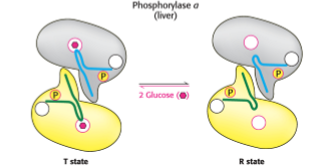
What is the default state of muscle glycogen phosphorylase?
b (inactive) form
T state
How is muscle glycogen phosphorylase regulated?
Increased AMP concentration activates
Positive regulation
What hormone(s) upregulate glycogen phosphorylase and how?
Glucagon, Epinephrine
These signaling pathways activate phosphorylase kinase which in turn activates glycogen phosphorylase
How is phosphorylase kinase activated?
Increased Ca2+ concentration
Phosphorylation
Calmodulin
Delta subunit of phosphorylase kinase
Calcium sensor
Aids in phosphorylase kinase activity
How is glycogen breakdown inhibited?
GTPase activity
Phosphodiesterase activity
Protein phosphatase 1 activity
What does GTPase do?
Inactivates G proteins
What does phosphodiesterase do?
Converts cAMP to AMP
No cAMP = no PKA stimulation
What does protein phosphatase 1 do?
Removes Pi from phosphorylase kinase and glycogen phosphorylase, leading to inactivation