Intro to Leg & Foot
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what forms the knee joint
femur articulating with tibia
lateral and medial femoral condyles articulate with what
lat and med tibial condyles forming knee joint
what does the patella articulate with
ONLY THE FEMUR- is a sesamoid bone
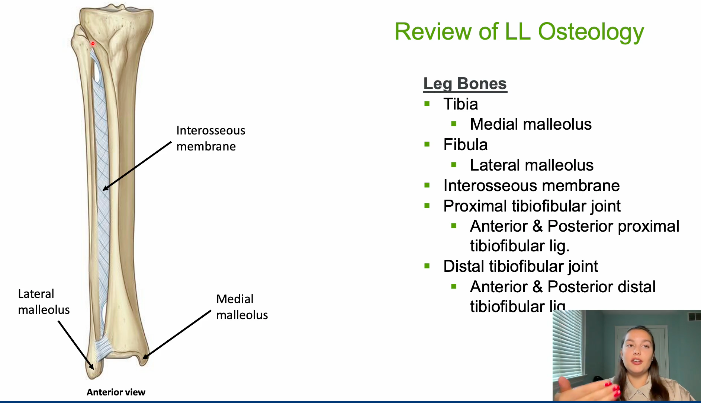
what holds tib and fib together
interosseous membrane
how does fibula articulate with tibia
distal and proximal tibiofibular joint
what is passive standing
regulating body against its weight and gravity
why doesnt passive standing require musch energy
hip & knee most stable in extension
maximum bone to bone contact
taut supporting ligaments
when foot is free what does it mean
(sitting) tibia moving relative to fixed femur
when foot is fixed what does it mean
standing (femur roating relative to tibia)
what is the screw home mechanism
in passive standing the femur rotates medially along the tibia resulting in articular surfaces locking
what muscle unlocks the knee
the popliteus muscle allowing us to go back into flexion
tibia inferiorly most medial aspect where rounds out called what
medial malleolus
on fibula, laterally follow inferiorly ends up at what
lateral malleolus
name ligaments on tib anf fib
ant & post proximal tibiofibular lig
ant and post distal tibiofibular ligament
leg compartments
intermuscular fossa, crural fossa. seperated by intermuscular septa
3 leg (crural) compartments
posterior compartment
superfical
deep
Anterior leg compartment
Lateral leg compartment
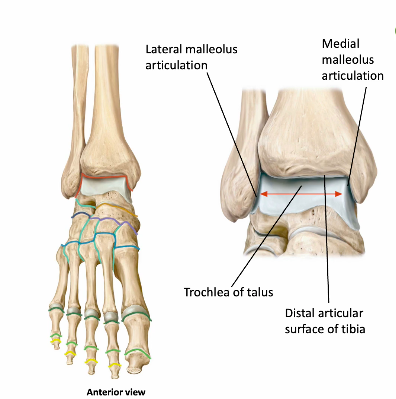
medial malleolous anf lateral malleolous articulate with 1 tarsal bone (talus) whats this joint called
ankle joint
actions happening at ankle joint
dorsiflexion & plantar flexion
shape of distal crural region articulating with talus creates what kind of joint
mortis joint
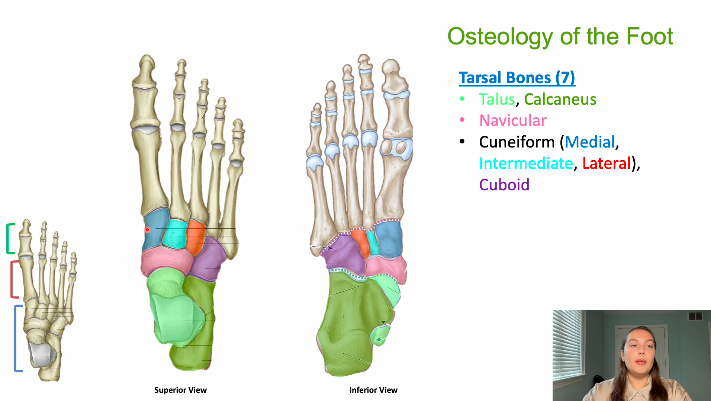
how many tarsal bones do we have, name them
7
talus
calcaneus
navicular
cuneiform (medial, intermediate, lateral), cuboid
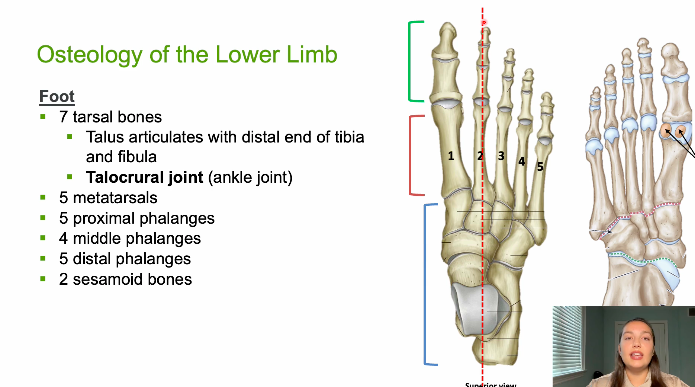
how many metatarsals do we have
5
how many phalanges do we have
5 proximal
4 middle phalanges
5 distal phalanges
2 sesamoid bones
name joints in the foot
metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP JOINT)
proximal interphalangeal joints (PIP JOINT)
Distal interphalangeal joints (DIP JOINT)
actions of talocrural joint
dorsiflexion & plantar flexion
at the subtalar joint what happens
talus to calcaneus
inversion
eversion
two views of the foot
toe flexion
plantar muscles
toe extension
dorsal muscles
tendons of what muscles can be found in foot
the leg muscles
what are intrinsic foot muscles
originate and insert into the foot only
name the arches of the foot
medial longtitudinal arch
lateral longtitudinal arch
transverse arch
transfer weight
absorb shock
increase flexibility
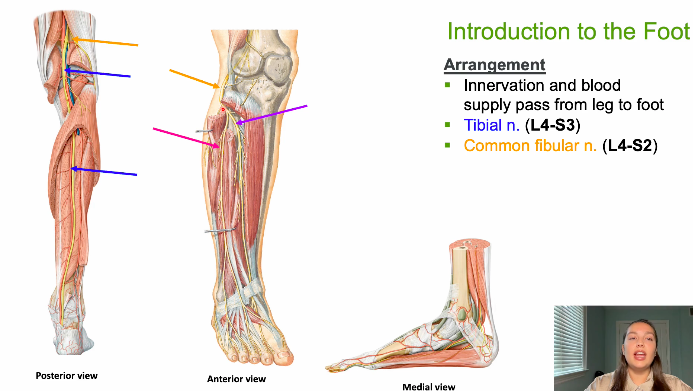
arrangement of innervation and blood supply of leg originally come from where
thigh-leg- foot
coming from popliteal artery and vein becomes what when enters into posterior leg and bifracates
posterior tibial artery
fibular artery
anterior tibial artery
ATA pierces through interosseous membrane to travel along anterior surface of interrosseous membranne
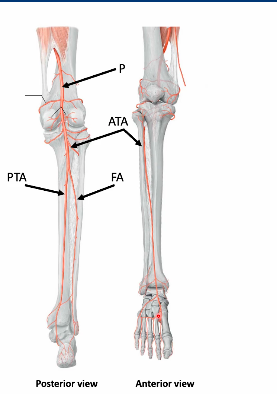
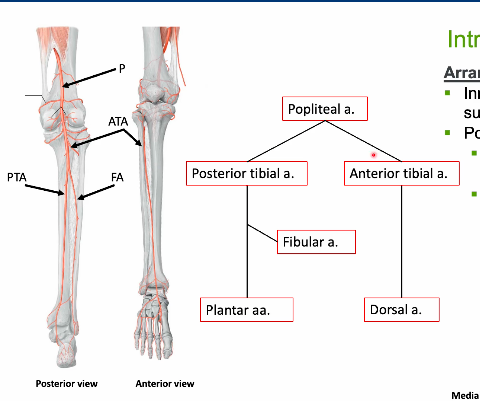
what nerves are descending into popliteal fossa
tibial n (L4-S3)
common fib nerve (L4-S2)
superficial fib n
deep fib n