BIOMI 2911 Practical
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Bacillus Characteristics
Rods/endospores; Catalase +; Not slimy (KOH); Gram +; No oxidase; Strict aerobes/facultative anaerobes; some ferment, some respires
Enteric Bacteria Characteristics
Rods; Catalase +; Slimy KOH; Gram -; Oxidase -; Facultative anaerobes; ferments
Pseudomonas Characteristics
Rods; Catalase +; Slimy KOH; Gram -; Oxidase -; Facultative anaerobes; doesn't ferment
LAB Characteristics
Rods/cocci; Catalase -; Not slimy (KOH); Gram +; No Oxidase; Aerotolerant anaerobes; ferments
Micrococcus Characteristics
Cocci (tetrads); Catalase +; Not slimy (KOH); Gram +; No Oxidase; Strict aerobe; doesn't ferment
Staphyloccocus Characteristics
Cocci (clusters); Catalase +; Not slimy (KOH); Gram +; No oxidase; Facultative anaerobe; Ferments
Preparing a Wet Mount
Pipette 10uL water (or broth culture) onto clean slide; use loop/pick to pick up cells from edge of colony; mix cells w/ water; place coverslip on slide
Wet Mount Microscopy
Turn on and set to 10X, focus on edge of the coverslip; rotate to 40X, rotate the condenser to Ph and slide the condenser to Ph2 (click!), refocus as needed; Kohler: close luminous field, use the condenser knob to sharpen the field of view, rotate silver pins to center, open field until edges are out of frame, focus as needed; slide condenser to Ph1 (click!), oil coverslip, rotate to 100X, focus and observe
MASS-E
Motility, arrangement, size, shape, endospores
Gram Stain Procedure
Prepare 2+ clean slides and draw 2 lines with wax crayon on them; use a loop to spread cells on slides, let sit for 10 min; heat fix with pin (3x); drop 1-2 drops crystal violet over cells, let sit for 60 sec then rinse with H2O; flood with iodine (mordant), let sit for 60 sec then rinse with H2O; drop EtOH one drop at a time for 5-10 sec, immediately rinse; stain with safranin, sit for 60 sec, then rinse. Dry with bibulous paper.
Gram Stain Microscopy
Start on 10x, focus on wax; rotate condenser and lens to 40x, focus; Kohler: close luminous field, use the condenser knob to sharpen the field of view, rotate silver pins to center, open field until edges are out of frame, focus as needed; add oil and switch to 100x lens and condenser, focus
CASS-G
Color, arrangement, size, shape, gram stain results
Streak Plate Method
Label agar side of plate; sterilize loop; when cooled (10+ sec), pick up bacteria with loop and spread over a small part of the plate; flame loop and cool, draw loop into loading zone 2-4 times then streak in 2nd sector; flame loop and cool, repeat with zone 2--> 3; flame loop and cool; draw loop into 3rd sector and streak 4th sector (zig zag)

Quick Test Protocol
Place drop of x solution on a clean glass slide; with a toothpick, place a small clump of cells in the solution; mix gently; wait for results
Catalase Test
Uses hydrogen peroxide bubbles indicated catalase was present; bubbles = catalase +
KOH Test
Confirms gram stain based on whether 3% KOH can lyse bacterial cell wall and release DNA; slimy = G-, not slimy = G+
Oxidase Test
Identifies bacteria that have cytochrome oxidase; ONLY DONE ON G- BACTERIA; do on blotting paper; red = oxidase +
Selective Media
Suppress growth of unwanted bacteria and encourage growth of desired microbes
Differential Media
Allows growth of several types of microbes and displays visible differences among those microbes
EMB Agar
Eosin Y and Methylene blue inhibit G+ growth, lactose indicates pH change based on lactose fermentation (metallic color = ferments lactose); selective and differential
MacConkey Agar
Selective (bile salts and crystal violet) for G- bacteria; differential (neutral red) based on Lac fermentation- turns purple
MRS Agar
Selective (acetate, tween 80, citrate) for G+ bacteria; enriches for LAB (anaerobic incubation)
Vitamin Free Minimum Medium (VFM)
No vitamins added, very few minerals in the plate- allows robust bacteria to grow (not fastidious)
E. Coli should grow, LAB shouldn't
PEA Agar
Selective for G+ bacteria (especially cocci) and inhibits most G- bacteria
MSA Agar
Mannitol Salt Agar- Both selective and differential; selects for salt-tolerant organisms and differentiates mannitol fermenters from non-mannitol fermenters (turns yellow if it ferments)
Staph. aureus grows and ferments, Micrococcus grows but doesn't ferment
Strict Aerobe
Requires O2 because they only make ATP via respiration
Purple, growth only at top, no cracks
Strict Anaerobe
Does not use O2 to make ATP, and O2 is lethal
Color change, growth only at the bottom
Facultative Anaerobe
Prefer to respire O2, but can ferment
Color change, growth concentrated at top but throughout
Aerotolerant Anaerobe
Can only ferment, but O2 is not lethal
Color change, evenly distributed growth with top 2mm relatively clear
What does a color change in a BCP shake indicate?
Acid production during fermentation- pH drops
What do cracks in a BCP shake indicate?
Gas is produced during fermentation
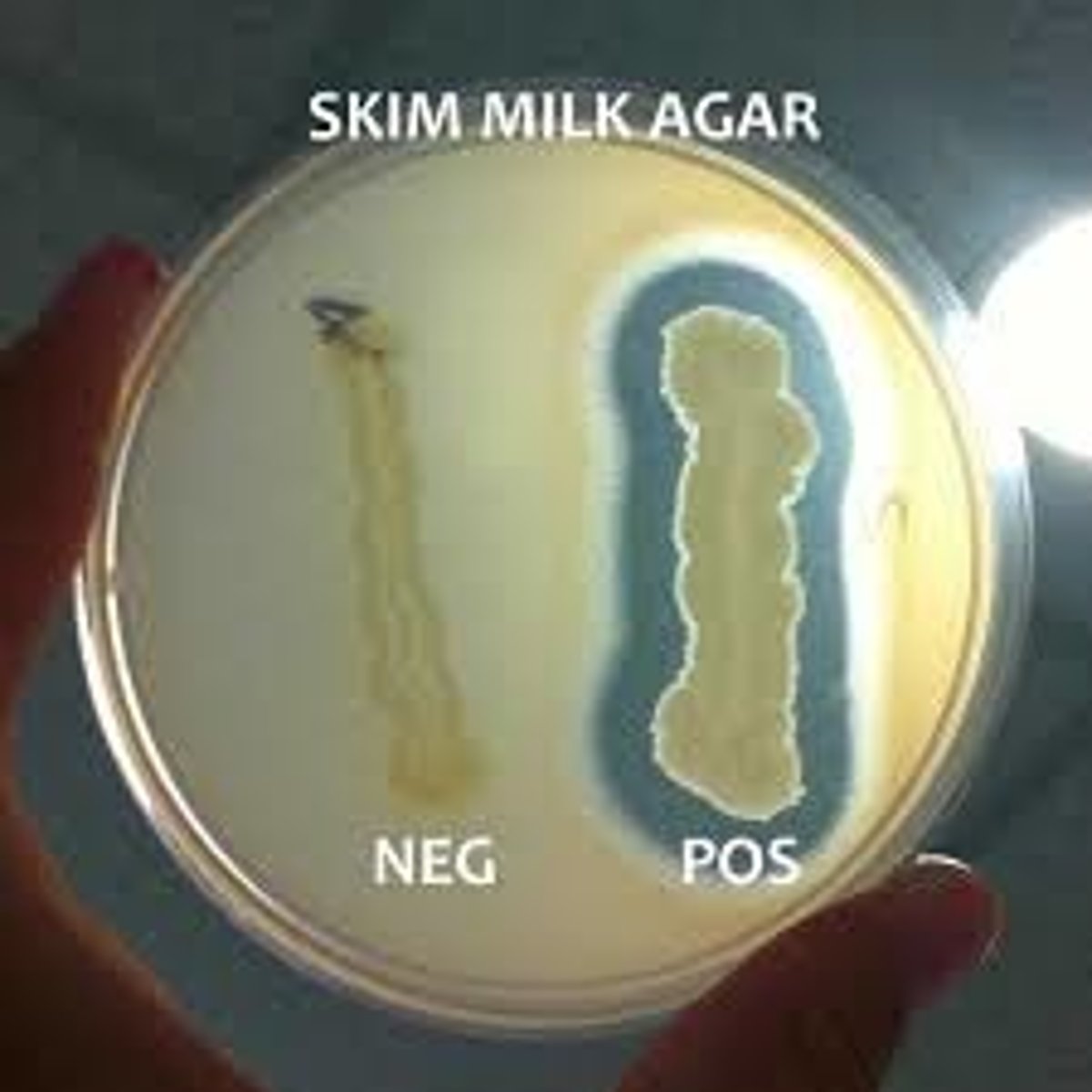
Caseinase (Protease) Test
Add Casein (substrate) to the media, spot inoculate Bacillus, and incubate; degradation can be directly visualized as clearing around bacterial growth.
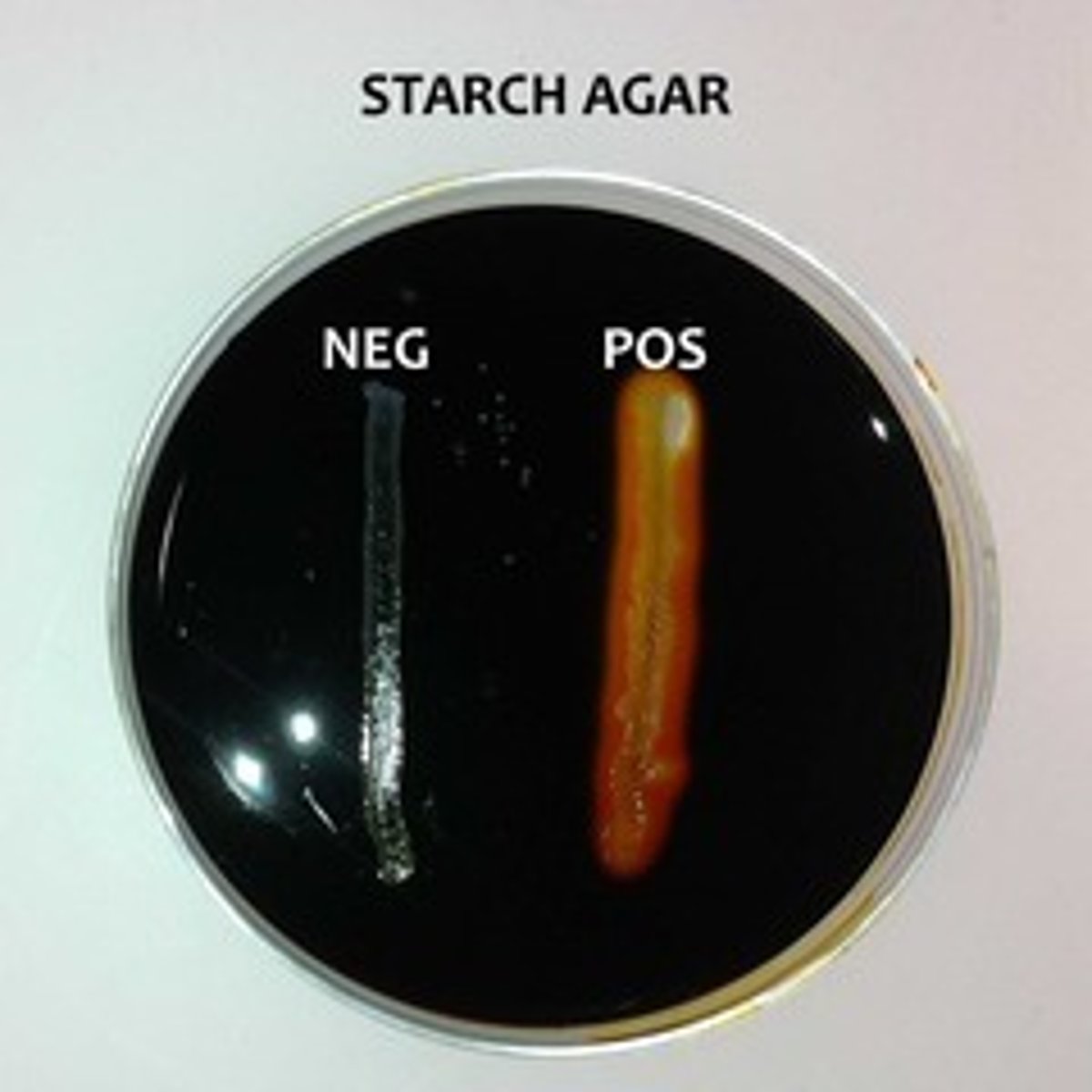
Amylase Test
Add Starch (substrate) to the media, spot inoculate Bacillus, and incubate; add iodine (indicator; binds to starch
forming dark brownish color) to visualize
clearing.