Peripheral nervous system
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
parts of the PNS
stomatic (voluntary) nervous: sensory and motor
automatic (involuntary) nervous: sympathetic and parasympathetic
What does the somatic nervous system do?
Contains sensory/afferent neurons: detect stimuli
contains motor/efferent neurons: signal from cns to muscles for movement
controls bones, muscles, skin
movement that a person can control
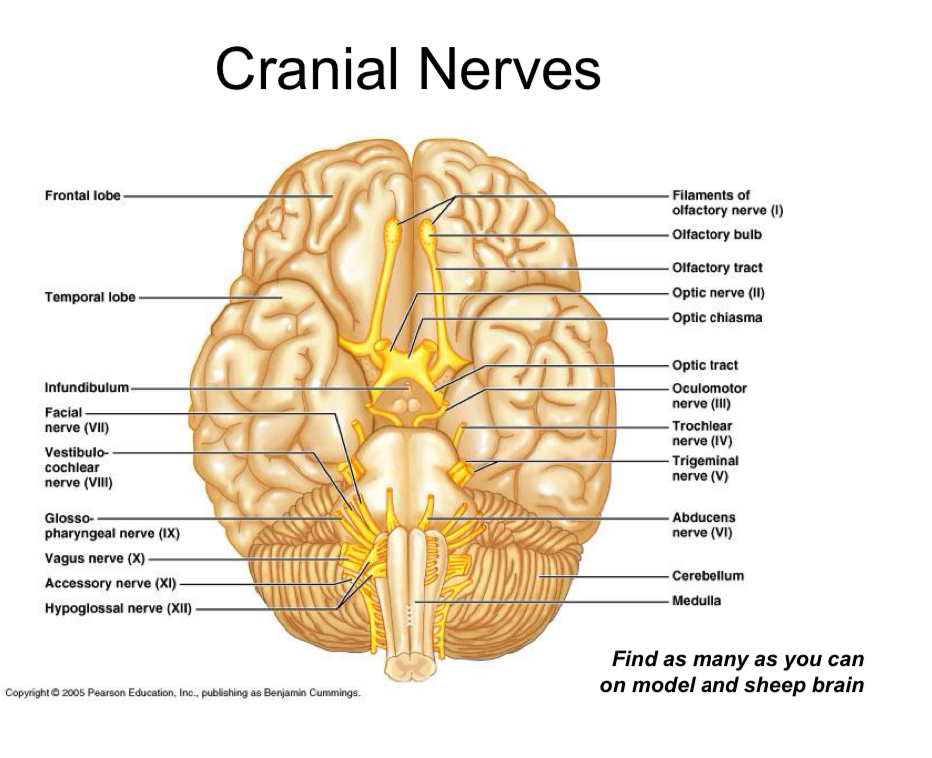
How many nerves in the somatic nervous system
12 pairs of cranial nerves (brain)
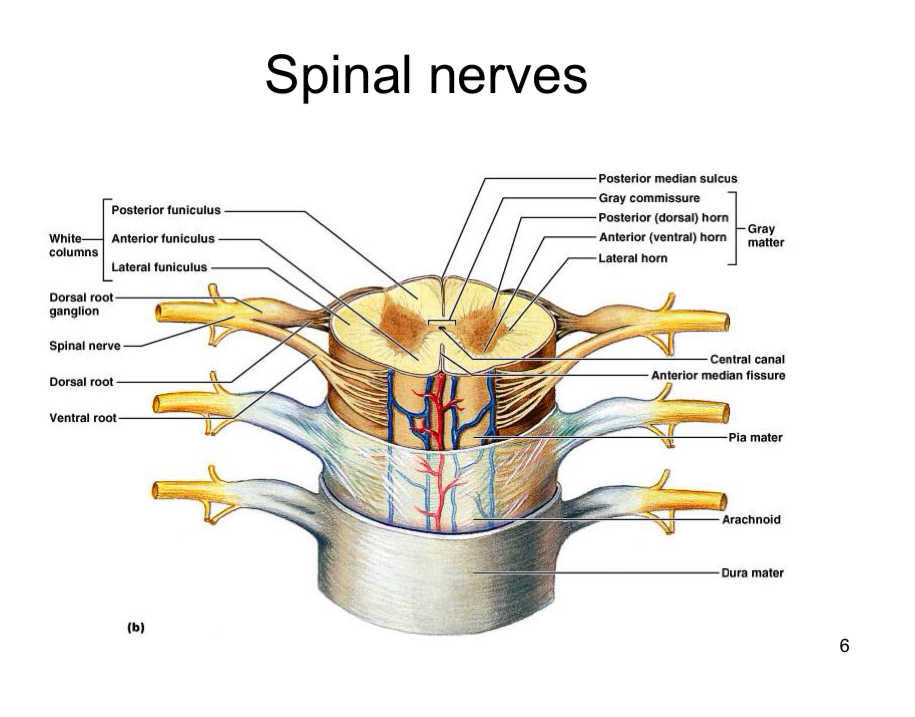
31 pairs of spinal nerves
Pairs because two sides of body, hemispheres of brain, spinal cord
Cranial nerves and nerve damage
cannot be repaired
Causes loss of certain functions
Somatic nervous system is also known as
voluntary nervous system
How come cranial nerves attach to brain stem?
Many cranial nerves have nuclei in the Brain stem allowing them to attach to the brain stem
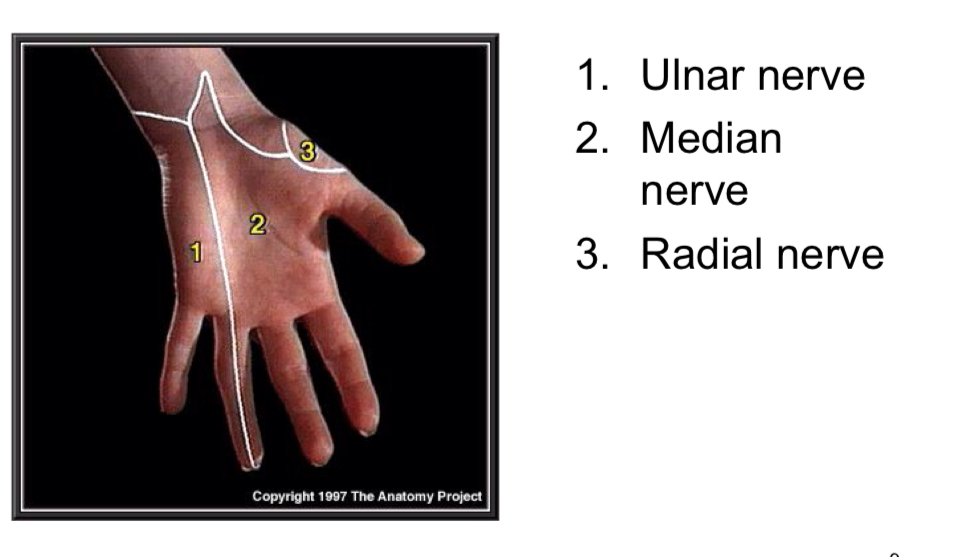
Sensitivity and nerves
how sensitive an area of your body is reflects how many nerves present
place that are more sensitive have more nerves
Back has less nerves than palm
Palm has 3 nerves: ulnar, median and radial nerve
Autonomic nervous system
regulates glands, blood vessels, internal organs
Process that occur without conscious control; unaware
Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic
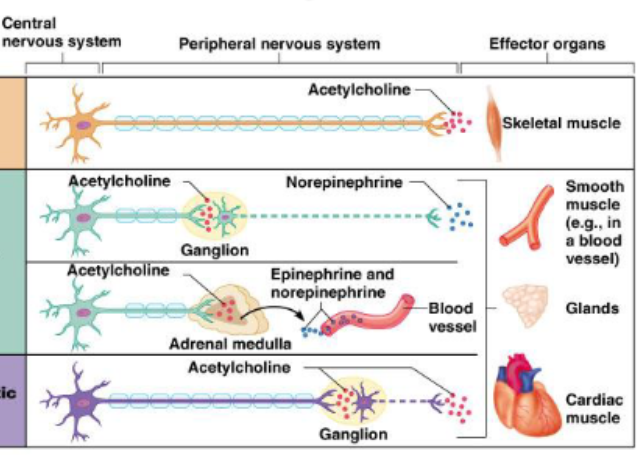
Skeletal muscles are in
Somatic nervous system
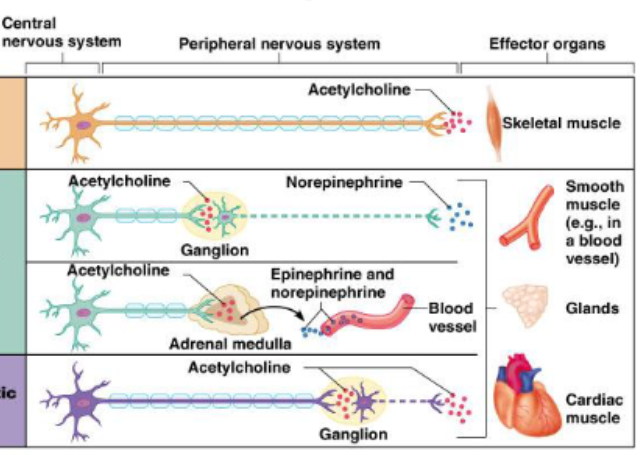
Smooth muscle and glands
Autonomic nervous system: sympathetic division
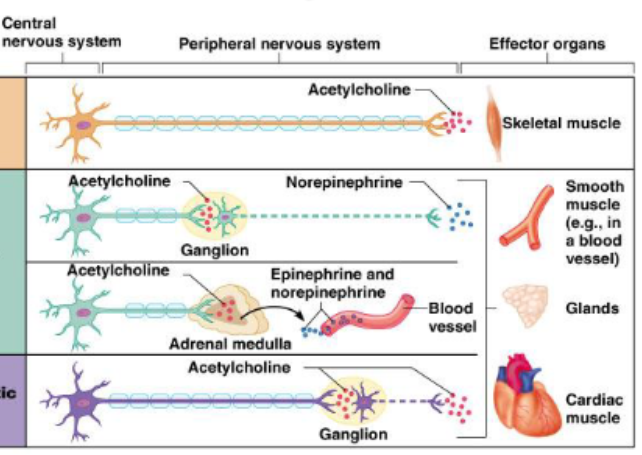
Cardiac muscle
Autonomic nervous system: parasympathetic division
What is autonomic nervous system also called?
Involuntary nervous system
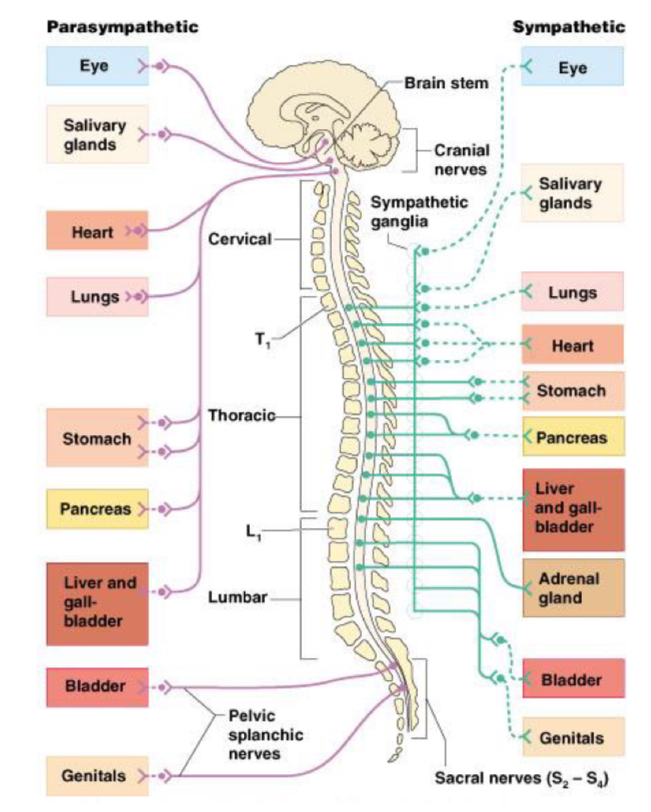
Anatomy of autonomic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous farther off spinal cord
allow for impulses to certain organs for rest and digest
Sympathetic nervous closest to spinal cord
allow for quick impulses to multiple organs, needed for fight or flight
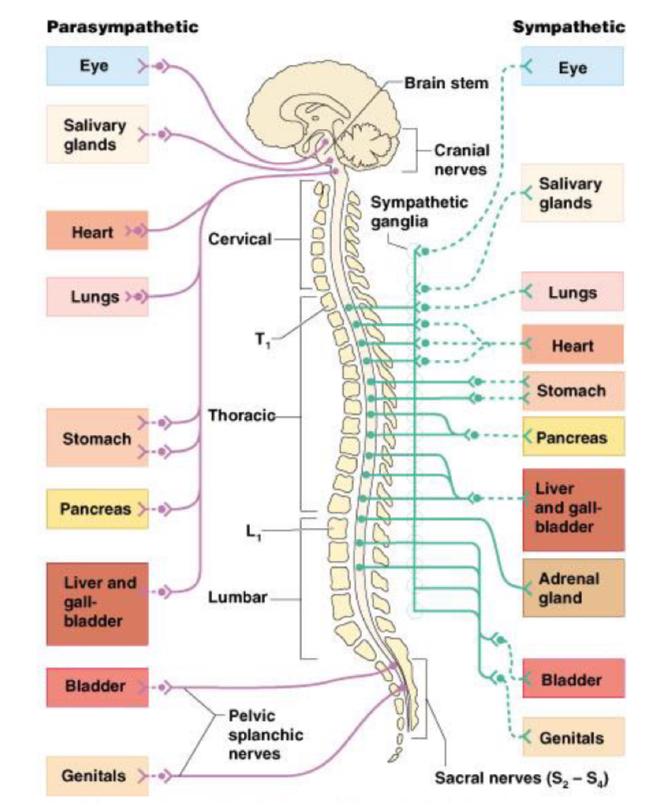
Sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
Stress response
Response to unusual stimuli by increase overall activities
activated during e division: exercise, excitement, emergency, and embarrassment
Works against parasympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Rest and digest: Body rests and recovers
conserves energy
Maintains daily necessary body function
Acetylcholine is released: regulates bp, heart rate, digestion, etc.
Opposes sympathetic
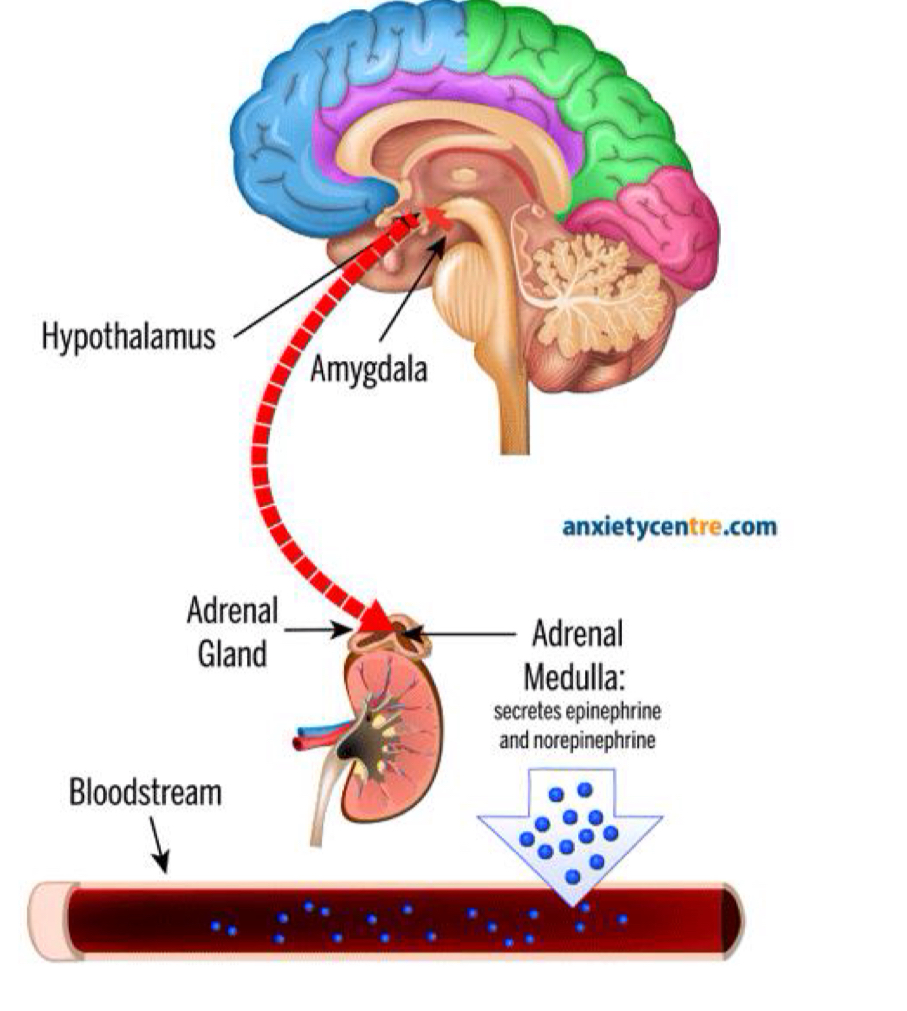
Sympathetic and adrenaline release
hypothalamus signals adrenal glands via sympathetic nervous system
Produces adrenaline
Adrenaline (epinephrine) and norepinephrine are released into bloodstream
Causes fight or flight response
Sympathetic vs parasympathetic: pupil, saliva, bop, breathing, digestion, glucose, adrenaline, excretory
sympathetic: dilates pupil to let more light in, inhibits saliva (dry mouth), increases heartbeat, increases breathing, liver releases glucose for more energy production, adrenaline produced, relaxes excretory system
Parasympathetic: pupils become smaller, saliva flows, slows heartbeat, breathing is slowed, digestion is stimulated, bile is released, contracts bladder
sensory, motor and interneurons, pns or cns?
sensory: pns, carry impulse from stimuli to cns
motor: pns, carry impulse from cns to muscles
interneurons: pns