Anatomy and Physiology of the Adrenal Glands
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Adrenal Glands
Also known as suprarenal glands, endocrine organs.
ACTH
Hormone from anterior pituitary controlling adrenal glands.
Gerota's fascia
Connective tissue enclosing the adrenal glands.
Adrenal Cortex
Outer layer of adrenal glands, secretes steroids.
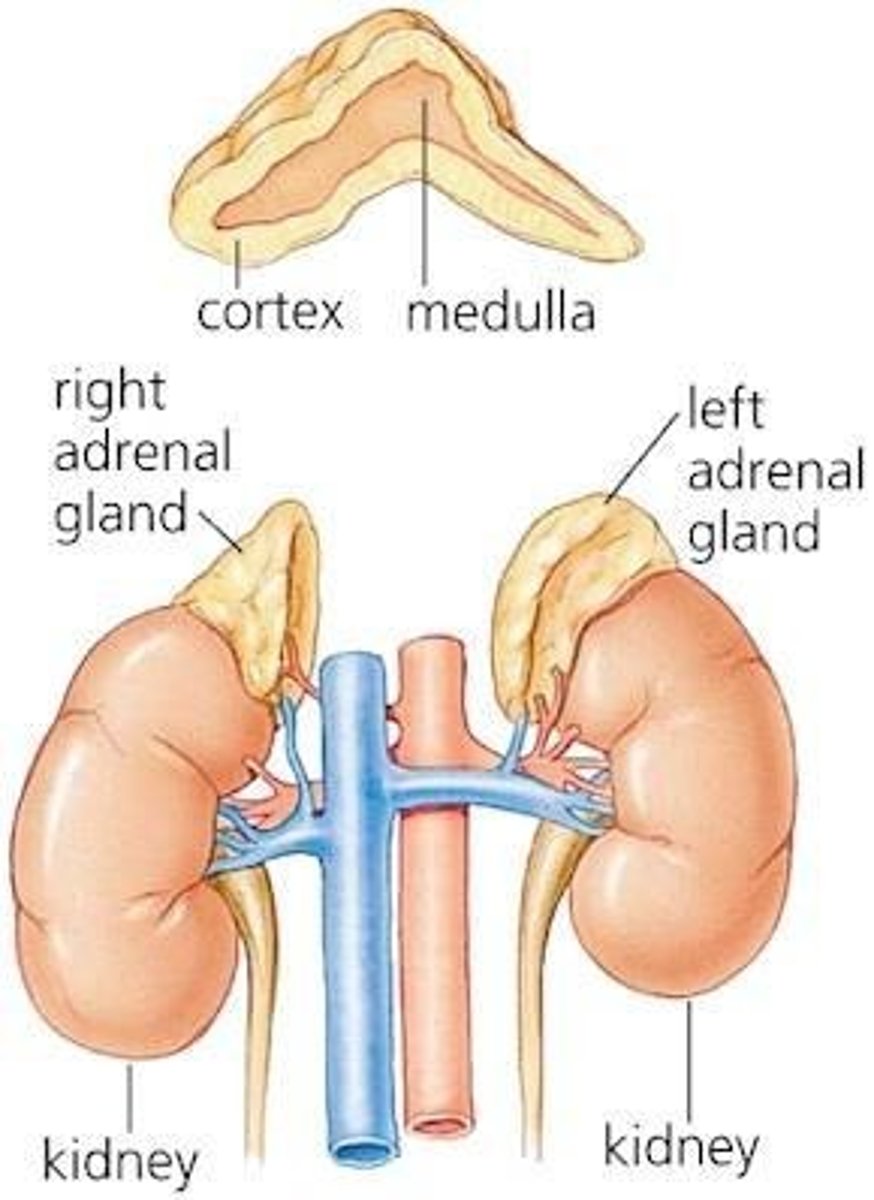
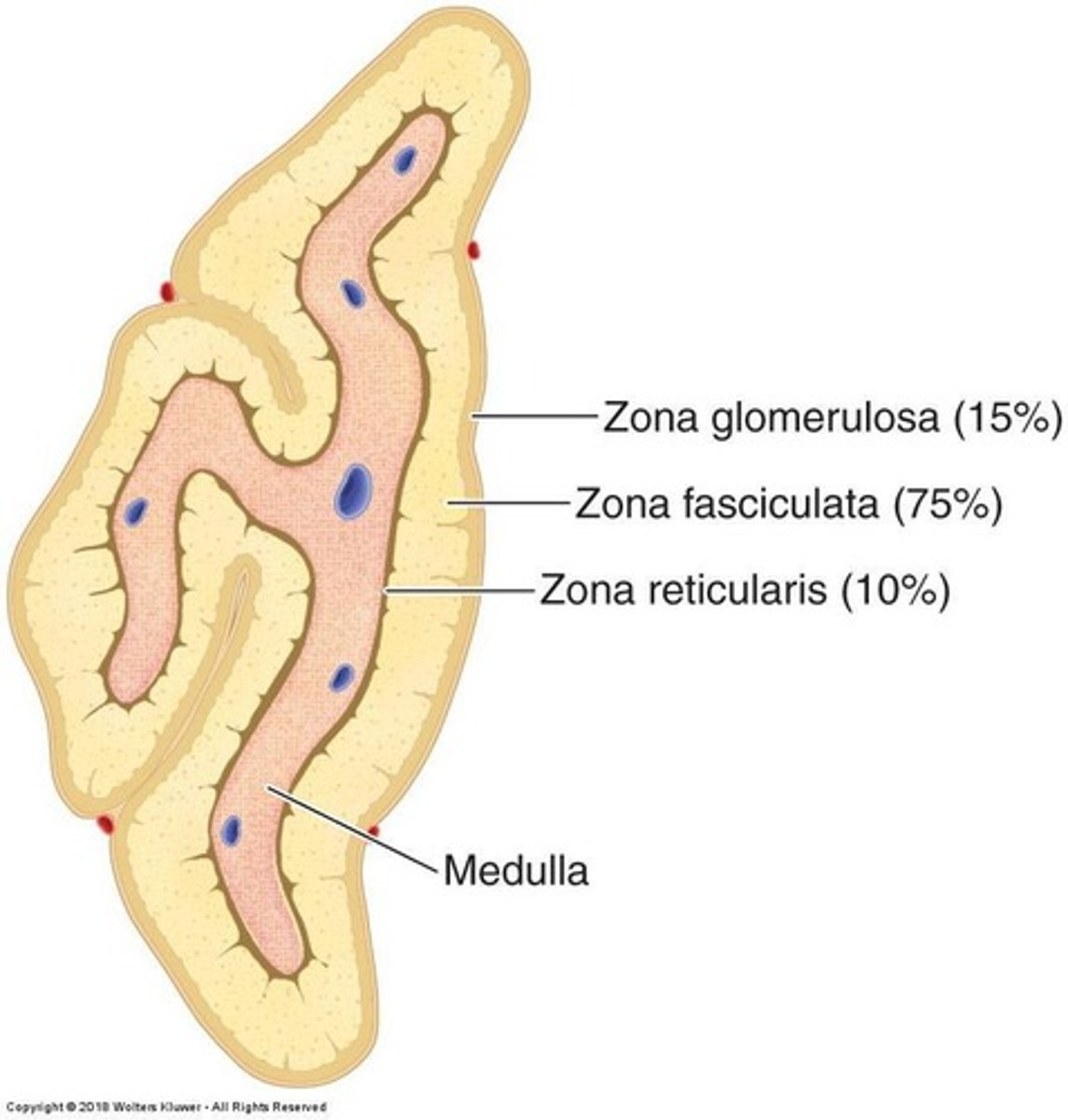
Adrenal Medulla
Inner layer of adrenal glands, secretes catecholamines.
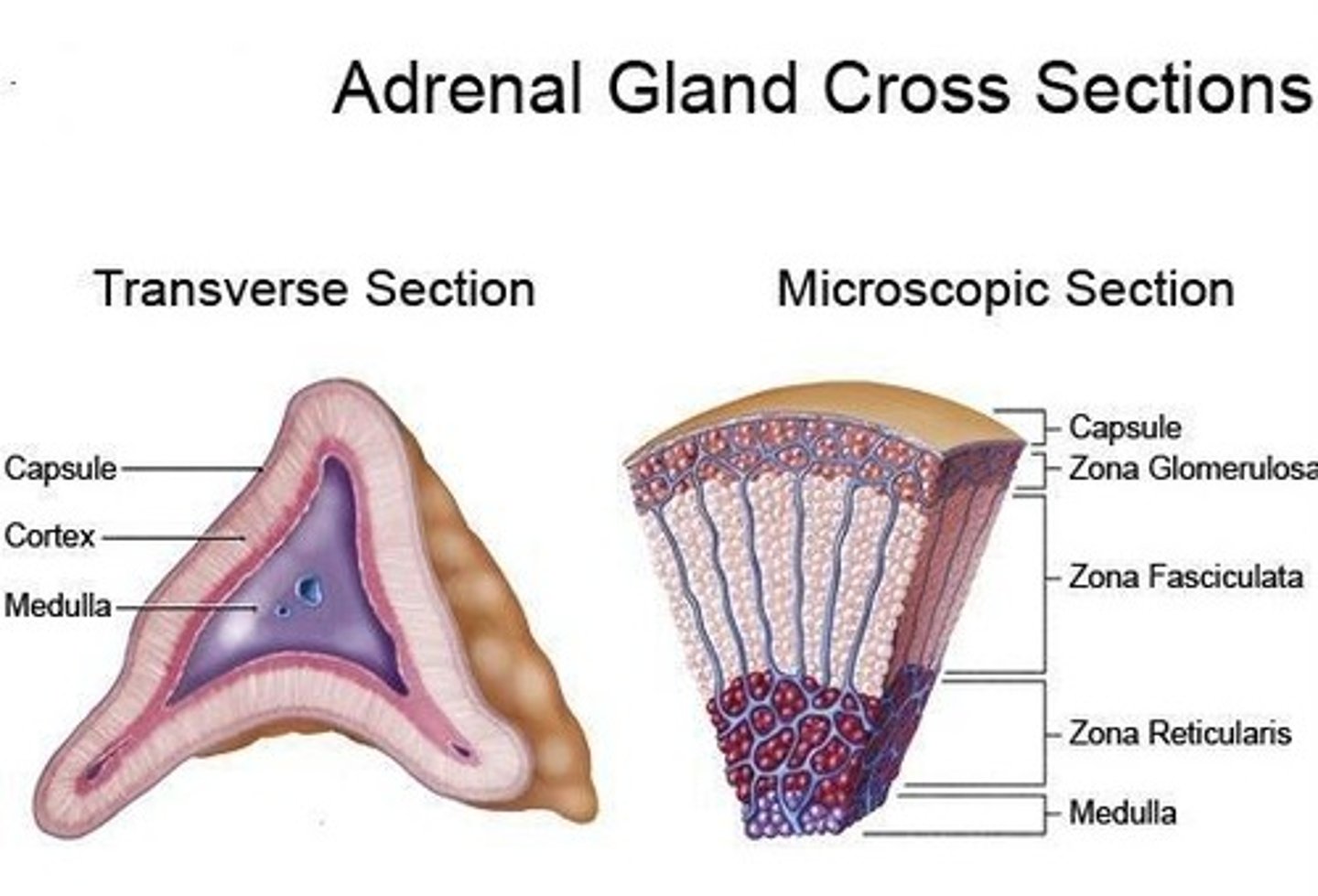
Zona Glomerulosa
Layer producing mineralocorticoids like aldosterone.
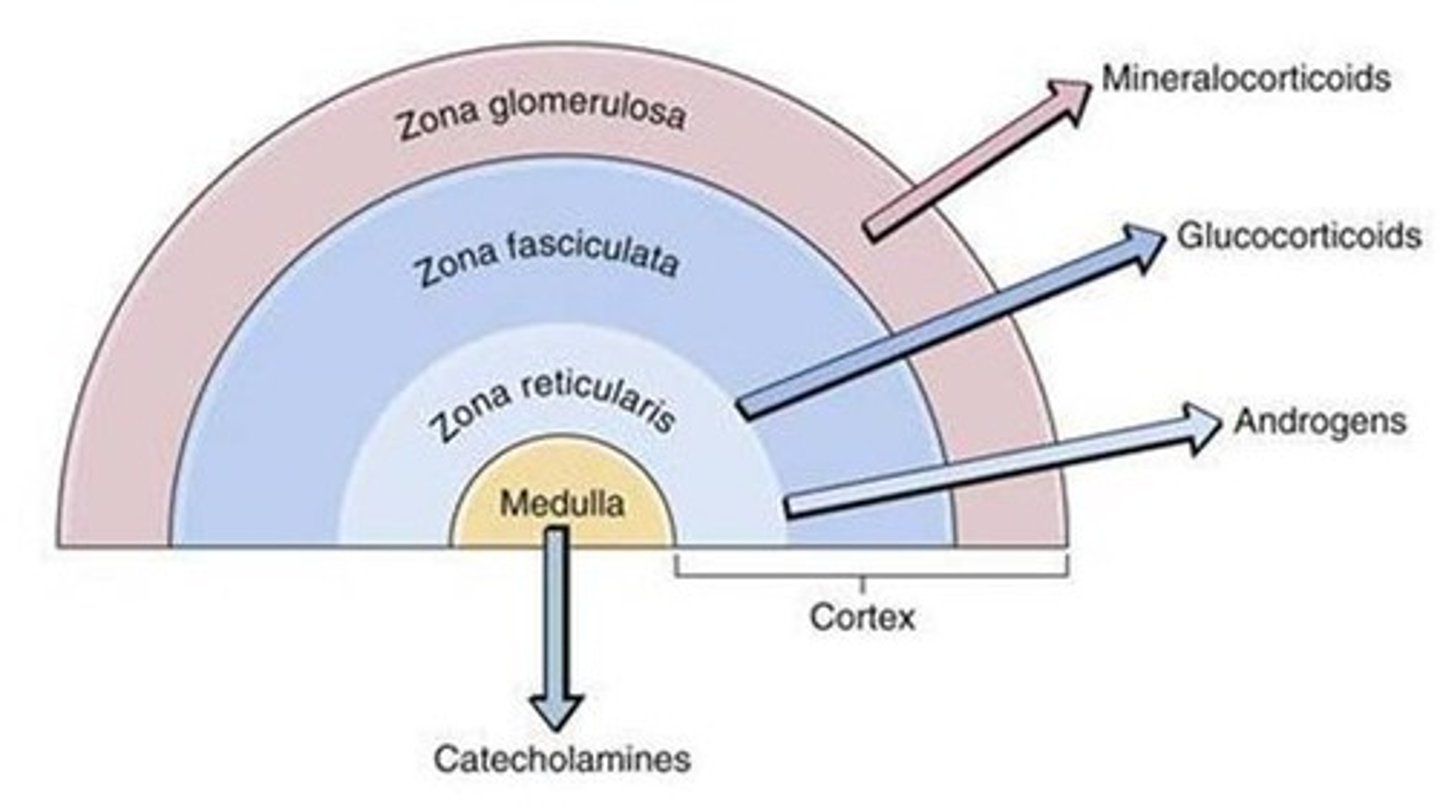
Zona Fasciculata
Layer producing glucocorticoids like cortisol.
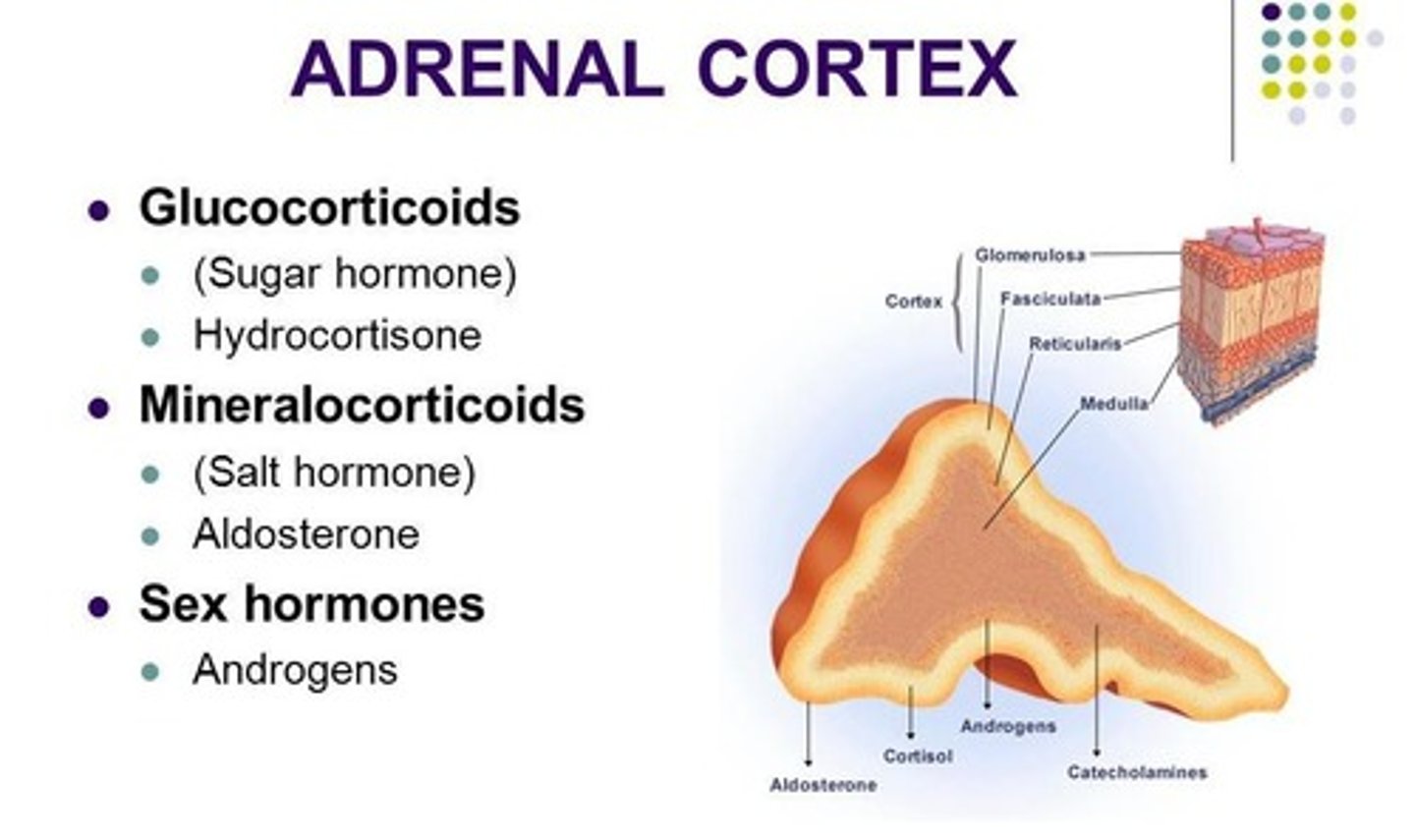
Zona Reticularis
Layer producing sex hormones and androgens.
Epinephrine
Increases heart rate and blood pressure during stress.
Norepinephrine
Accelerates heart rate and contracts blood vessels.
Fetal Adrenal Size
10-20 times larger than adult adrenal glands.
Infant Adrenal Size
1/3 of renal length compared to adults.
Adult Adrenal Size
1/13 of renal length, smaller than infants.
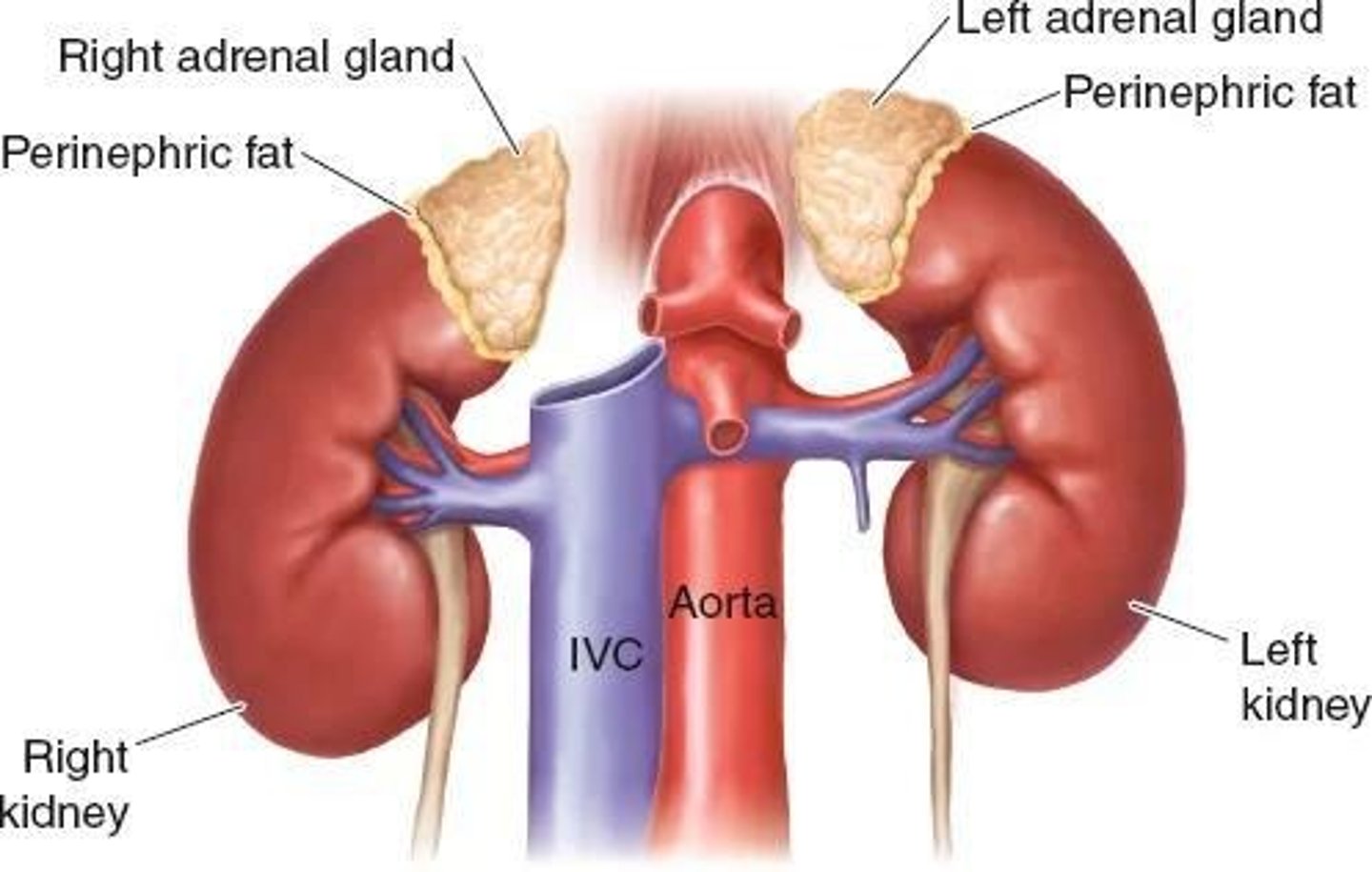
Right Adrenal Gland
Triangular or pyramid-shaped, located near IVC.
Left Adrenal Gland
Semilunar or crescent-shaped, medial to left kidney.
Vascular Supply
Three arteries supply blood to each adrenal gland.
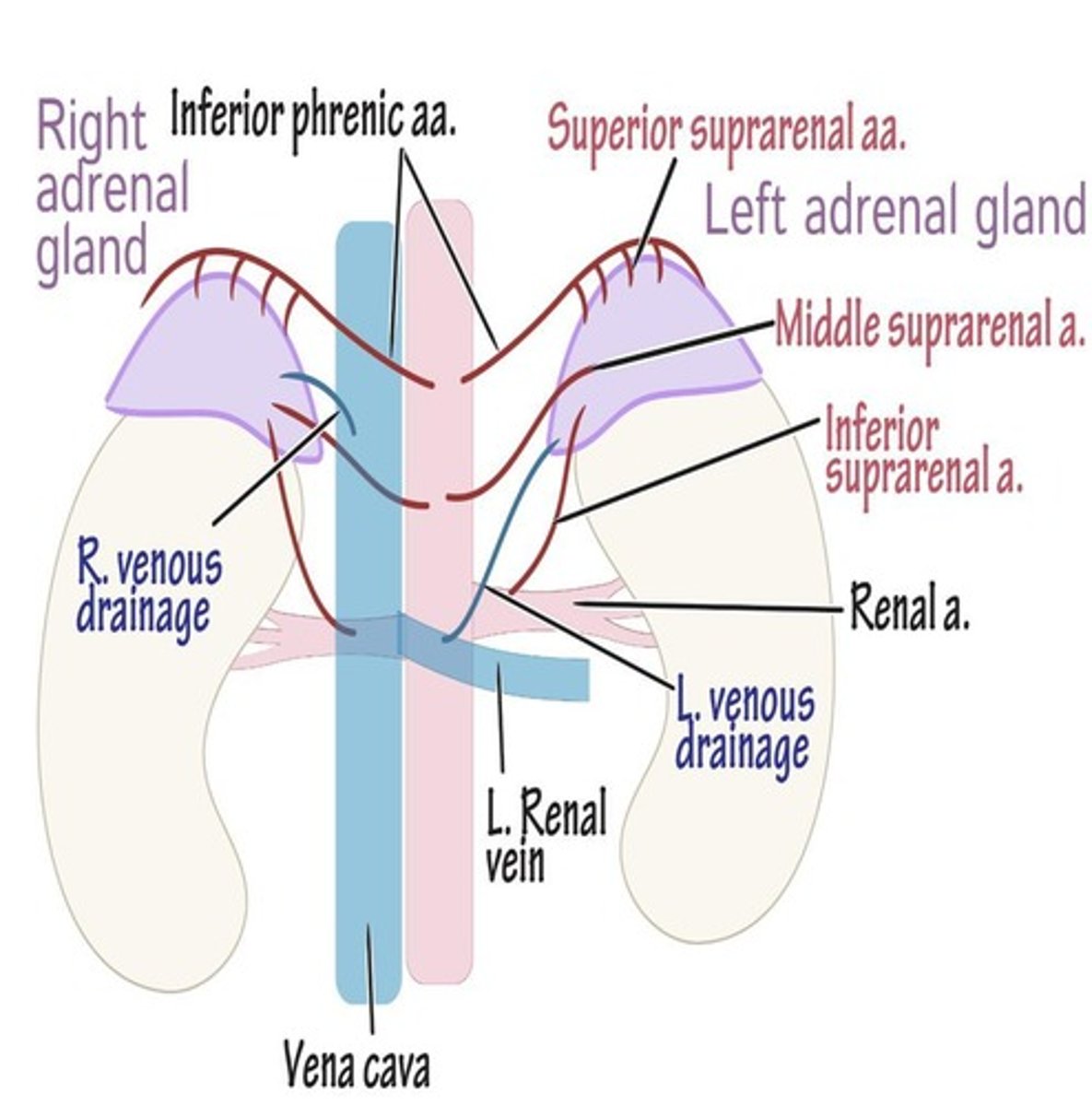
Sup. Suprarenal Artery
Branches off inferior phrenic artery to adrenal glands.
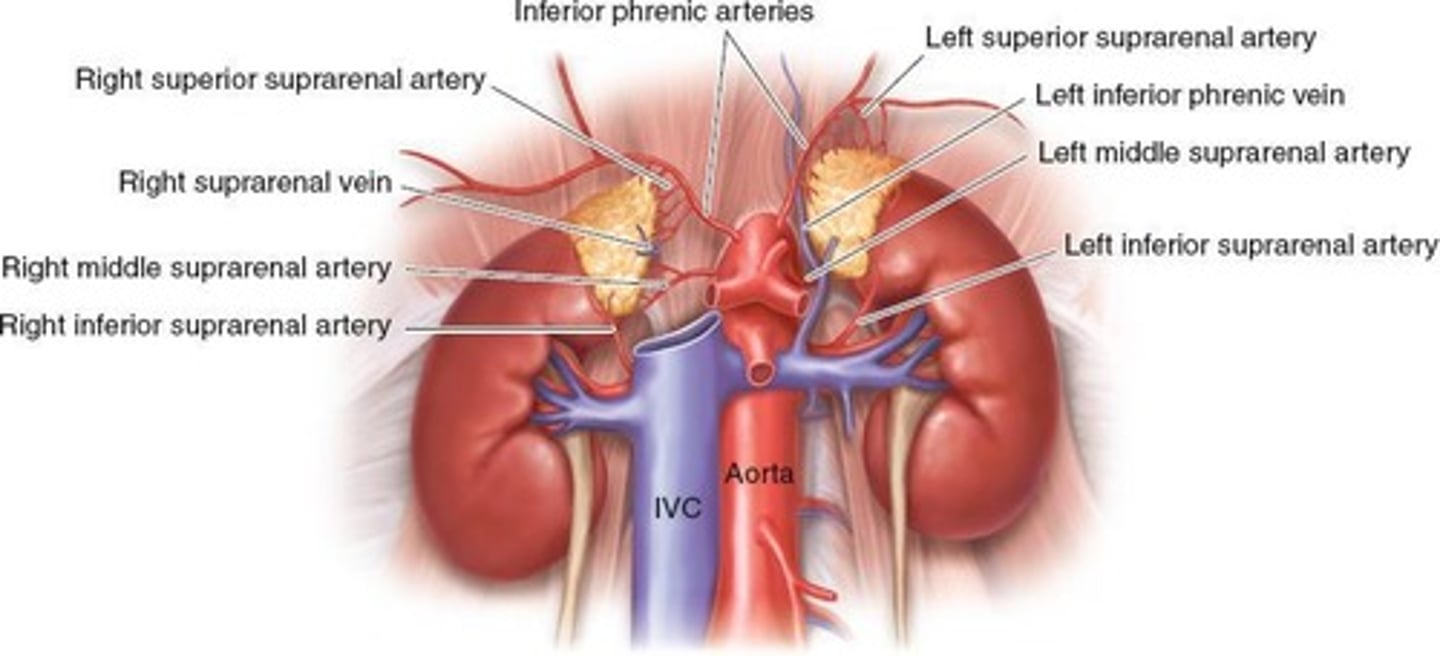
Middle Suprarenal Artery
Branches off the aorta to supply adrenal glands.
Inf. Suprarenal Artery
Branches off renal artery supplying adrenal glands.
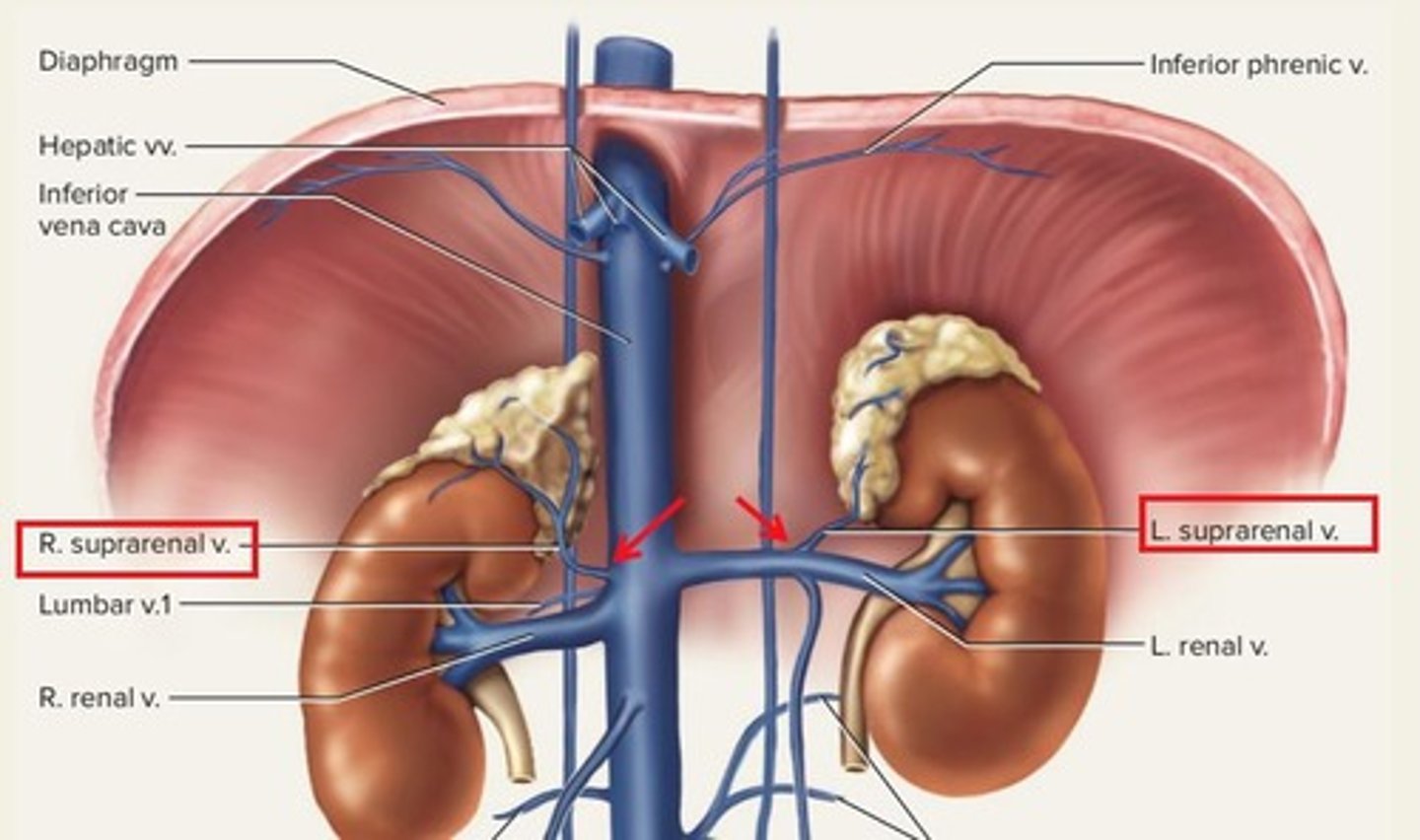
Suprarenal Vein
Single vein draining each adrenal gland into IVC.
Catecholamines
Hormones secreted by adrenal medulla for stress response. Includes epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Left suprarenal vein
Drains into the left renal vein.
Aldosterone
Regulates blood pressure and electrolyte levels and blood pressure via sodium and water control.
Cortisol
Aids in glucose metabolism and inflammatory response.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Controls adrenal cortex hormone production.
Total metanephrines
Used to assess catecholamine production.
Vanillymandelic acid
Metabolite of catecholamines in urine.
Conn syndrome
Overproduction of aldosterone causing hypertension.
Cushing syndrome
Overproduction of cortisol leading to various symptoms.
Addison's disease
Adrenal insufficiency resulting in low hormone production.
Adrenal adenoma
Benign tumor of the adrenal gland.
Adrenal adenocarcinoma
Malignant tumor of the adrenal cortex.
Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia
Enlargement of both adrenal glands.
Hyperpituitarism
Excessive hormone production by the pituitary gland.
Adrenal hyperplasia
Increased number of adrenal cells.
Androgens
Hormones like testosterone and estrogen from adrenal glands.
DHEA-S
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, an androgen precursor.
Sonographic evaluation
Ultrasound assessment of adrenal glands.
Patient positioning
Oblique or decubitus position for adrenal imaging.
Adrenal hemorrhage
Most common adrenal mass in newborns.
Adrenal cyst
Rare benign lesion, often asymptomatic.
Neuroblastoma
Malignant tumor often originating in adrenal glands.
Adrenal myolipoma
Benign tumor composed of fat and muscle.
Unilocular cyst
Simple cyst in the adrenal gland, typically benign.
Complex cyst
Cyst with multiple components, may indicate pathology.
Calcified cyst
Cyst containing calcium deposits, often benign.
Adrenal Adenoma
Most common benign adrenal mass, <3 cm.
Hyperfunctioning adenoma
Secretes hormones, associated with Cushing's or Conn's.
Asymptomatic presentation
No symptoms, often found incidentally during imaging.
Cushing's syndrome
Hormonal disorder from excess cortisol production.
Conn's disease
Hyperaldosteronism causing hypertension and electrolyte imbalance.
Sonographic appearance
Visual characteristics of masses on ultrasound imaging.
Pheochromocytoma
Rare, vascular tumor secreting excess catecholamines, may be malignant.
Chromaffin tissue
Tissue in adrenal medulla producing epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Uncontrolled hypertension
High blood pressure not managed by treatment.
Adrenal Myolipoma
Benign mass with fat and bony elements, nonfunctioning.
Propagation speed artifact
Ultrasound artifact due to differing tissue speeds.
Adrenal Neuroblastoma
Most common malignant tumor in children, arises in medulla.
Pediatric sarcoma
Cancerous tumor occurring in children, often aggressive.
Elevated catecholamines
Increased hormone levels indicating adrenal gland dysfunction.
Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma
Rare malignant tumor, aggressive, poor prognosis.
Androgenital syndrome
Hormonal disorder causing abnormal sexual development. Excess androgens causing virilism in females.
Metastasis
Spread of cancer from primary site to adrenal glands.
Heterogeneous appearance
Varied texture and composition seen in tumors.
Internal vascularity
Blood supply within a tumor, indicating potential malignancy.