Theories of Emotion, Morality, and Cross-Cultural Psychology
1/330
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
331 Terms
What is the James-Lange theory of emotion?
It posits that physiological changes occur first, and we interpret these changes as emotions.
What does the facial feedback hypothesis suggest?
It suggests that facial expressions can influence emotional experiences.
What is a major issue with the James-Lange theory?
It assumes that all emotions have unique physiological responses, which is not always true.
What is the Two-Factor Theory of emotion?
It states that emotions are a combination of physiological arousal and cognitive interpretation.
How can misattribution of arousal occur?
Physiological arousal from one source (like a movie) can be misattributed to another source (like a date).
What does the James-Lange theory predict about emotions?
It predicts that emotions should be universal due to similar physiological responses across humans.
What does the Two-Factor Theory suggest about cultural variability in emotions?
It suggests that cultural experiences can lead to different interpretations of physiological responses.
What are emotional antecedents?
Events that lead up to or elicit certain emotions.
What are the physiological responses associated with emotions?
Responses can be categorized as ergotropic (energy-expending) or trophotropic (calming).
What is the ergotropic response?
Physiological responses that reflect the sympathetic nervous system, such as increased heart rate.
What is the trophotropic response?
Physiological responses that reflect the parasympathetic nervous system, such as calming effects.
What is 'felt temperature' in the context of emotions?
The internal temperature sensation experienced during emotions, like feeling hot with anger.
What are the six basic emotions identified in psychology?
Anger, happiness, sadness, surprise, disgust, and fear.
What is the significance of stimulus evaluation checks (SEC)?
They involve appraising antecedents along dimensions like expectedness, pleasantness, and fairness.
How does expectedness affect emotional appraisal?
Events that are unexpected can lead to lower pleasantness and fairness, influencing emotional responses.
What is emotional expression variability?
Differences in emotional expression can arise from cultural display rules that dictate appropriate expressions.
What are display rules in emotional expression?
Cultural rules that dictate the appropriateness and intensity of emotional expressions.
What is the relationship between economic inequality and social outcomes?
Economic inequality can lead to different outcomes in authoritarianism and political engagement.
How does socioeconomic status (SES) impact psychology?
SES influences psychological outcomes, including mental health and cognitive capacity.
What is the impact of a scarcity mindset on cognitive capacity?
A scarcity mindset can reduce bandwidth, affecting cognitive capacity and executive control.
What is the knowledge gap in psychology?
The difference between what is known and what is needed to make informed decisions.
What is the desirability gap?
The difference between what people want and what they can realistically achieve.
What is the action gap?
The gap between knowledge and the actions taken based on that knowledge.
What is emotional universality?
The concept that certain emotional responses are consistent across different cultures.
What evidence supports emotional universality?
Evidence includes similarities in emotional antecedents, physiological responses, appraisal, and expression.
What is amplification in emotional expression?
Emotional expression is stronger than the emotional experience, resulting in exaggerated outward expressions.
What does deamplification refer to?
Emotional expression is less intense than the emotional experience, often to maintain group harmony.
Define neutralisation in emotional expression.
Expressing no emotion at all, even when feeling a real emotion.
What is simulation in terms of emotional expression?
Expressing an emotion that is not actually felt internally.
What does masking mean in emotional expression?
When emotional experience and emotional expression do not match.
What is qualification in emotional expression?
Emotional expression reflects the underlying emotional experience but includes additional mixed emotions.
What is the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis?
The theory that language influences thought and perception of experiences.
What is the hard version of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis?
Language determines how we think and perceive experiences.
What is the soft version of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis?
Language affects how we think but is not deterministic.
What did the study by Gendron et al. (2014) investigate?
It compared emotional expression recognition between the Himba ethnic group in Namibia and individuals from the USA.
What were the two tasks used in the Gendron et al. study?
Anchored sort task and free sort task.
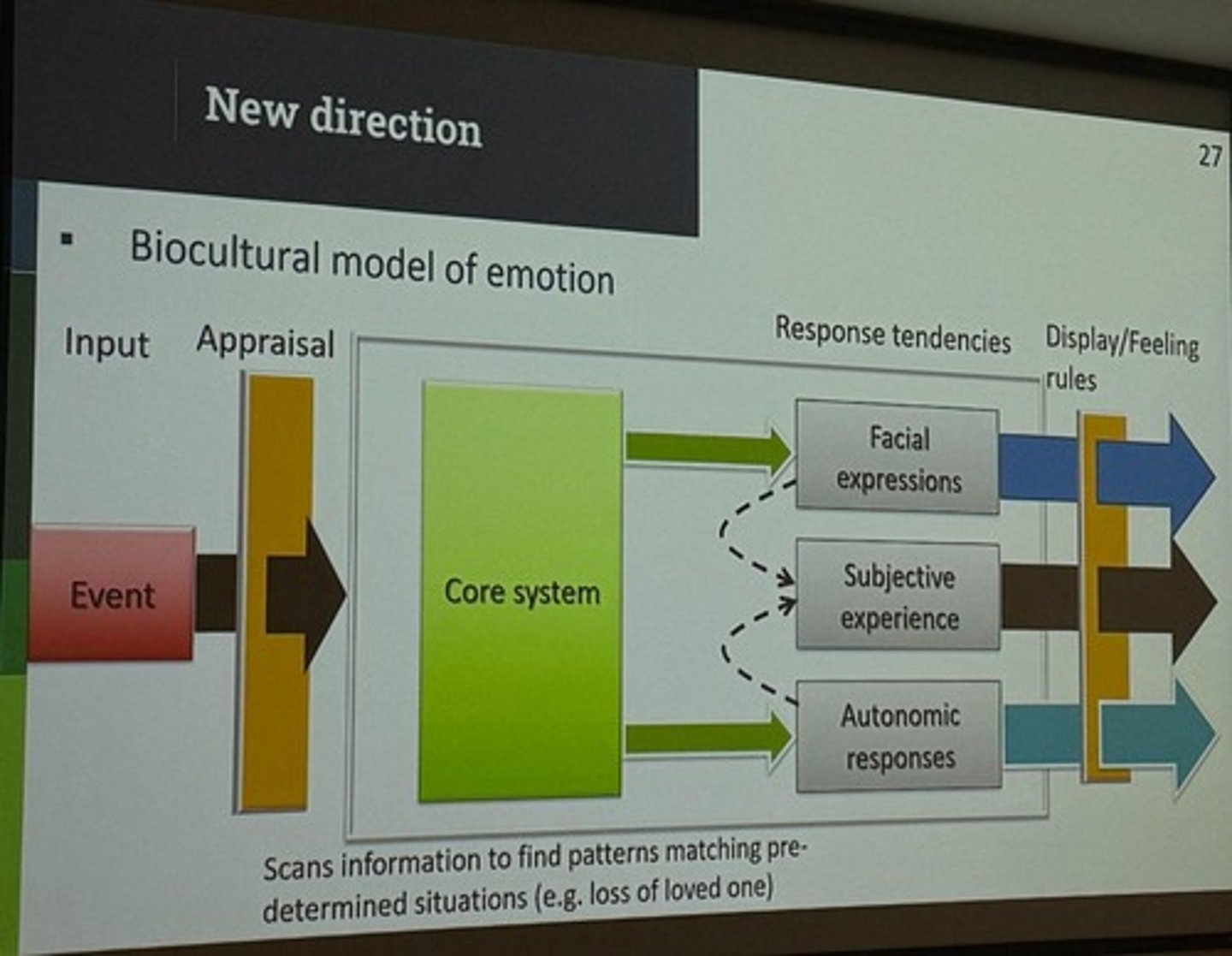
What is the biocultural theory of emotion?
It posits that emotions are hardwired responses with cultural variability in appraisals and interpretations.
How do appraisal theories differ from evolutionary theories in emotions?
Appraisal theories recognize cultural variability in emotional experiences, while evolutionary theories focus on universality.
What is the core system in the biocultural model of emotion?
A black box-like mechanism in the brain that scans for patterns and activates response tendencies.
What components are involved in the biocultural model of emotion?
Core biological system, subjective experience, and autonomic responses.
What is historical heterogeneity in the context of emotion?
The concept that historical differences influence emotional experiences across cultures.
What is the significance of cultural factors in emotional experiences?
Culture influences appraisals and interpretations, affecting emotional experiences.
What is the relationship between facial expressions and cultural variation?
Facial expressions may vary culturally, while autonomic responses are less likely to be impacted by cultural factors.
What does emotional lexicon variability refer to?
Some languages have unique words for specific emotions, which may affect emotional experiences.
What is the implication of lacking words for emotions in a language?
It may hinder the ability to articulate and discuss those emotions or experiences.
What does the term 'bilateral asymmetry' refer to in emotional expression?
Differences in expression on either side of the face, often seen in mixed emotional expressions.
What is the role of schemas in emotional responses?
Schemas lead to different response tendencies based on pre-existing reactions to events.
How do cultural factors affect subjective emotional experiences?
Subjective experiences are influenced by cultural context, affecting how emotions are felt and expressed.
What is the significance of the study's findings on emotional recognition?
It highlights the potential for cultural variability in emotional recognition beyond pre-existing terms.
What are the implications of the biocultural model for understanding emotions?
It integrates different theories of emotion and acknowledges the complexity of emotional experiences influenced by culture.
How does culture impact emotions?
The impact varies depending on aspects of emotional complexity, type of emotion, emotional context, and the individual.
What are the aspects of emotion that culture influences?
Intensity of the emotion, type of emotion, emotional context, and the individual.
What happens to highly intense emotions in relation to culture?
They 'flood' the internal system, making facial expressions, physiological responses, and subjective experiences less impacted by culture.
What distinguishes culturally based emotions from basic emotions?
Culturally based emotions are less rooted in survival functions and more influenced by socialization and culture.
What role does emotional context play in emotional expressivity?
Cues for emotional expressions are influenced by culture, indicating appropriate emotional expressions.
How does cultural identification affect emotional expressivity?
Identifying strongly with a cultural environment influences emotional expressivity.
What is the biocultural model?
A broad perspective that considers how cultural and biological factors interact in emotional expressivity.
What is historical heterogeneity?
The extent to which a country's modern population has come from migration in the last 500 years.
What characterizes low historical heterogeneity in a country?
A population sourced mostly from its own country, leading to more certainty in customs, values, and beliefs.
What is the communication style in high context cultures?
Less reliance on explicit verbal communication, focusing more on assumed intentions.
What characterizes high historical heterogeneity in a country?
A diverse population from many countries, leading to uncertainty in communication and a need for explicit communication.
How do people from highly heterogeneous countries express emotions?
They tend to have more expressive facial expressions and body language, recognized by both in-group and out-group members.
What is the Twenty Statements Test?
A self-description exercise where individuals fill in 'I am ________' to reveal cultural influences on self-concept.
What were the results of the Twenty Statements Test comparing Americans and Kenyans?
Americans focused on personal traits (48%), while Kenyans emphasized social identity (over 60% for Masai and Samburu).
How did Kenyan university students' self-descriptions compare to Americans?
They were closer to the American pattern, while traditional groups reflected more social identity.
What is the significance of individual accomplishments and social interactions?
Survival and fitness depend on both individual achievements and successful interactions with others.
What is the impact of cultural exposure on self-concept in Kenyans?
Greater exposure to Western culture leads to more personal characteristic statements in self-descriptions.
What cultural factors influence emotional expressivity?
Historical context, cultural identification, and the degree of cultural heterogeneity.
What is the relationship between emotional expressivity and cultural context?
Cultural context shapes how emotions are expressed and understood within different groups.
How does cultural background influence self-concept?
The words and categories used to describe oneself reflect cultural influences on identity.
What is the role of cues in emotional expressions?
Cues indicate appropriate emotional expressions and are influenced by cultural norms.
What is the difference between high and low context cultures?
High context cultures rely on implicit communication, while low context cultures depend on explicit communication.
How does emotional context affect communication in heterogeneous societies?
In heterogeneous societies, there is a greater need for explicit communication due to diverse backgrounds.
What is the independent view of self based on?
Inner attributes that reflect a person's essence and form the basis of identity.
How is the independent self perceived in terms of stability?
It is stable across situations and throughout the lifespan.
What is a key characteristic of individuals with an independent self-view?
They perceive themselves as unique, with no one having the same configuration of attributes.
From where do attributes in an independent self arise?
They arise from the individual and not from interactions with others.
How do independent individuals regulate their behavior?
They feel an obligation to present themselves consistently with their inner attributes.
How do independent individuals view their relationships?
They experience their identity as largely distinct from their relationships.
What is the interdependent view of self?
The self is defined by social relationships and roles, fundamentally connected to others.
How does behavior depend on perception in an interdependent self-view?
Behavior depends on the perception of others' thoughts, feelings, and actions.
What is a significant aspect of identity in an interdependent view?
Identity is reflexive and contingent on one's position relative to others.
How do ingroup relationships function in an interdependent view?
They serve to direct appropriate behaviors and create obligations towards those relationships.
What cultural differences are observed in self-concept regarding brain activation?
Westerners show distinct brain activation for self and mother, while Chinese show similar patterns.
What are the seven importance aspects of self-concept?
1. Organizes info about ourselves, 2. Directs attention to relevant info, 3. Shapes concerns, 4. Guides relationship choices, 5. Influences relationship maintenance, 6. Affects interpretation of situations, 7. Influences emotional experiences.
How do individualistic cultures relate to self-concept?
They are more likely to promote an independent self-concept.
How do collectivist cultures relate to self-concept?
They are more likely to promote an interdependent self-concept.
What is the relationship between socioeconomic status (SES) and self-concept?
Higher SES is associated with more individualistic views, while lower SES is associated with more collectivist views.
What gender differences exist in self-concept?
Interdependent self-concept is more characteristic of women, while independent self-concept is more characteristic of men.
What did the study on self-consistency reveal about American and Japanese students?
Americans had more positive self-assessments regardless of context, while Japanese responses varied based on social context.
What is cognitive dissonance?
The distressing feeling experienced when one behaves inconsistently with their sense of self-consistency.
What is subjective self-awareness?
Considering oneself from the inside out, focusing on external concerns and largely unaware of oneself.
What is objective self-awareness?
Considering oneself from the outside in, perceiving oneself as an object like the rest of the world.
What is the impact of gender norms on self-concept?
Gender norms influence perceptions of independence and interdependence, with cultural variations.
What is the significance of ingroup and outgroup relations in interdependent views?
Individuals tend to view ingroup and outgroup members distinctly and behave differently towards them.
What does the term 'fluid ingroup/outgroup boundary' refer to?
In independent views, new relationships can form and old ones dissolve without significantly impacting identity.
What is the role of relationships in the interdependent self-concept?
Relationships are central to identity and are contrasted against other networks of individuals.
How do cultural practices influence gender roles?
Cultures with plow cultivation tend to have more traditional gender roles compared to those with shifting cultivation.
What is the relationship between urbanization and gender views?
More urban, Protestant, individualistic cultures tend to have more egalitarian gender views.
What is the significance of the 20 statement test in self-concept research?
It reveals how self-assessment varies based on social context and cultural background.