General Relativity Year 3
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are the classical tests of general relativity?
The gravitational red shift
The perihelion shift of mercury
The bending of light rays
The Shapiro Delay
What is µ in the equation 2µ/c2R?
µ = GM, where G is the gravitational constant and M is the mass of the object.
Define a Geodesic in terms of general relativity
A geodesic is the path a particle (or photon) would take through space time when no external forces EXCEPT GRAVITY are acting on it
This is, in general, not the same as a World Line. A World Line is the actual path a particle or photon takes through space-time. In a Schwartzschild Universe though, both massive particles and photons will always follow geodesics: except for gravity there is nothing to affect their trajectory
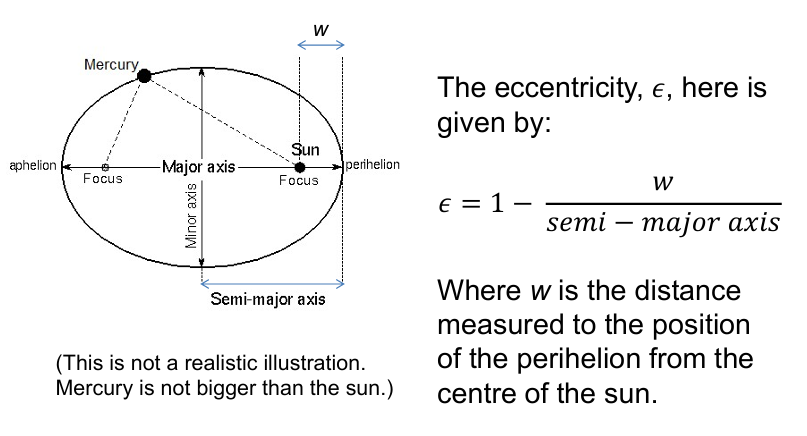
What causes the perihelion shift of Mercury?
This aperiodic orbital behaviour is due, in part, to the small aperiodic term that arises from relativistic gravity
It is also partly due to the gravitational tugs of other planets
And the Oblateness of the Sun
The magnitude of the observed shift cannot be explained by classical physics
What are the effects that occur in a binary pulsar?
The spacing of the pulses varies according to whether the pulsar is moving toward or away from us in accordance with the Relativistic Doppler Effect
The spacing of the pulses gets longer as the two bodies get closer together, due to gravitational time dilation (a GR effect)
The orbital period gradually decreases due to the loss of energy to gravitational waves (a GR effect)
The pericentre of the binary shifts (a GR effect
What is a dark star?
It is a star so massive and so dense that the escape velocity predicted by Newtonian mechanics exceeds the speed of light.
State the principle of equivalence.
The effect on any system of a uniform gravitational field of strength g is the same as an acceleration -g of an identical system relative to an inertial frame in a zero-g field
What does a Metric equation describe?
The metric equation describes the geometry of space time of a particular universe
Write down the Schwarzschild Metric, explaining the terms in the expression.
Image

Briefly describe the Schwarzschild Universe.
It’s a spherically symmetric universe that is empty apart from a point mass in its centre
It is a curved space-time
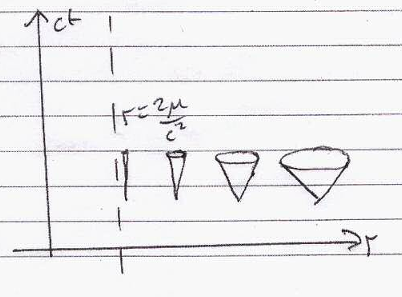
Sketch and briefly explain what happens to the light cone as it approaches the event horizon of a black hole from infinity.
The light cone closes up as it approaches the surface r = 2µ/c2
At the surface the light cone collapse and therefore can only move in time