4.3 - NS: afferent - special senses
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
special senses
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what part of the electromagnetic spectrum can our eyes detect?
visible light
Our eye receptors can detect wavelengths between ___ and _____ nm
between 400 and 750 nm
what determines colour?
diff wavelengths
general job of they eye structures:
refract lightwaves and focus them on the retina where the sensory receptors are.
phototransduction:
what does it do, where does it occur?
turn light (photons) into a neural signal
occurs at the retina
2 types of photoreceptors
rods and cones
rods
sensitivity level
what do they help see? (what kind of light)
very sensitive
respond to low light - see in the dark
cones
sensitivity level
what do they help see? (what kind of light)
less sensitive
bright light - help see colour
photoreceptors have two parts:
name and their purpose/components
outer segment - composed of discs
discs respond to light
inner segment - contain mitochondria and org.
photoreceptors contain ______ that ____ ____
they contain photopigments that absorb light
rhodopsin - what is it
photopigment found in rods. they absorb light
photopigments contain what molecules?
contain proteins called opsins which are bound to a chromophore molecule
chromophore is …
light sensitive.
overall: explain photoreceptors.
photoreceptors have inner and outer segments. the outer segments are composed of discs that have mechanisms that respond to light.
they have photopigments that absorb light.
in rods, that pp is rhodopsin.
PPs contain proteins called opsins which are bound to chromophore molecule.
chromophore is light sensitive
compare Photoreceptors when depolarized to regular cells.
most cells get depolarized when stimulated. But photoreceptor cells get hyperpolarized when stimulated.
at rest and when there is a stimulus:
photoreceptors are … (and number)
at rest = depolarized (-35mV)
when stimulus = hyperpolarized (-70mV)
what happens when photoreceptor is at rest? and when there is a stimulus?
(what happens to the ion channels and whatever)
when at rest, there is open cation channel (constant + ion flow), and it closes in response to light stimulus.
clarification: what happens when photoreceptors are stimulated by light?
the cation channel closes.
when at rest, cation channels open.
photoreceptors can generate what? and what can they not generate?
photoreceptors can generate graded potentials, not APs.
photoreceptor cells → ______ cells → _______ cells
photoreceptors —> bipolar cells —> ganglion cells
which cell in the eye generates APs?
(which ones do not generate APs?)
(which generate graded potentials?)
ganglion cells generate APs.
photoreceptors and bipolar cells do not.
photoreceptors generate graded potentials.
map the path of the action potential production starting with light going into the retina…
light goes in to the retina, photoreceptors …
light goes in eye, to retina, photoreceptors generate graded potentials, that connect with bipolar cells , which connect with ganglion cells, which generate APs.
what do the axons of the ganglion cells form?
their axons form the optic nerve to carry info to CNS
defects in colour vision result from
mutations in cone pigments, making it hard to differentiate shades.
what is sound?
airwaves coming into the ear
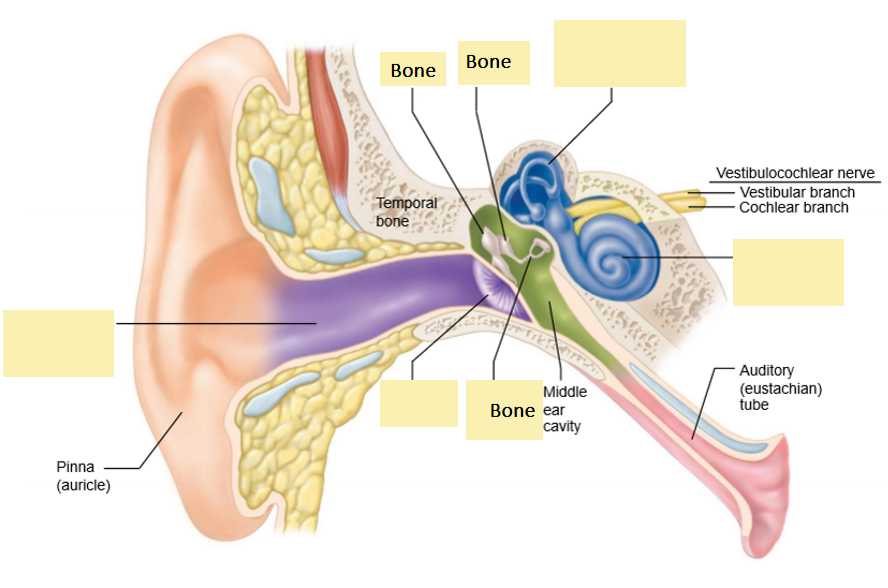
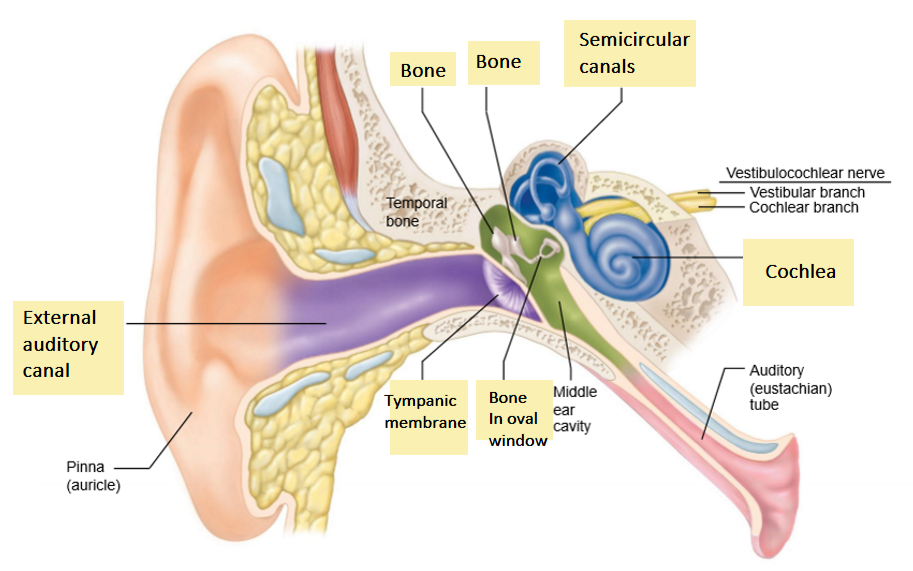
Map the path of sound:
start with sound funnels into EAC
sound funneled into external auditory canal
tympanic membrane
sound hits here and it vibrates
middle ear bones
amplify vibrations.
connect eardrum to oval window
cochlea
vibrations enter cochlea fluid:
Organ of Corti:
Hair cells on the organ of Corti detect fluid movement
converted to electrical signal for nerve to send to CNS
organ of Corti:
where is it?
receptors name and type? and detail
function
organ of Corti is in the cochlea.
mechanoreceptors in here are the hair cells.
they have stereocilia on top
as pressure waves move thru, these cells are stimulated. turn waves to signal to CNS
what happens when the hair cells get pushed in the long direction and the other direction?
when pushed, ion channels, opens, calcium enters, depolarized, and NT released to neuron to carry signal to brain.
other direction = repolarize. ion channels close.
vestibular system
where is it located?
what does it do?
in inner ear, next to cochlea
it determines the position of the head, which determines balance
Parts of the VS:
1. Semicircular canals
2. Utricle
3. Saccule
semicircular canals detect…
angular acceleration during rotation of head along 3 axes
Utricle and Saccule provide info about…
linear acceleration of head.
changes in position relative to gravity (straight line)
describe how semicircular canals detect rotation
Stereocilia surrounded by a jelly mass (aka cupula), which is in ampulla.
as you turn ur head, fluid lags, and when it catches up, you get used to the movement. then same when it stops.
fluid moves relative to bone. (moves differently)
How does the utricle and saccule detect linear movement.
Steroecilia on hair cells are covered with gel layer with crystals on top. (otoliths)
Otoliths are calcium carbonate crystals.
Otoliths make the gel heavier, so it pushes on hair cells when you change direction
gravity
vestibular info is used to: (3)
Control eye movements
Maintain upright posture and balance (bc it determines head position)
Provide awareness of body position, acceleration, spatial info.
what’s the pathway of info from vestibular nerve fibers?
start with thru brainstem …
info goes thru brainstem, then thru thalamus, then to vestibular centers in parietal lobe of the c.cortex.
chemical senses include: (2)
taste and smell
what detects chemicals to detect taste and smell
chemoeceptors
what are the sensory organs for taste? and where
sensory organs are the taste buds in mouth and throat
what are the 5 taste receptors (the tastes)
sweet - fr sugar
sour - from acid
salty - from sodium
bitter - some base
umami - glutamate protein
sour and salty : signaling pathway
direct changes to ion channel flow
sweet, bitter, umami : signaling pathway
uses G protein-coupled receptors
(indirect)
pathway for olfactory: how do odorants lead to smell signal
Odorant go up the nasal cavity to the olfactory epithelium
They bind to oderant receptors and activate G-proteins
Cation channels open and cell depolarizes → AP → signal to brain