All muscles of the upper limb, origin, insertion, function and innervations
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Ventral muscles of the shoulder girdle include:
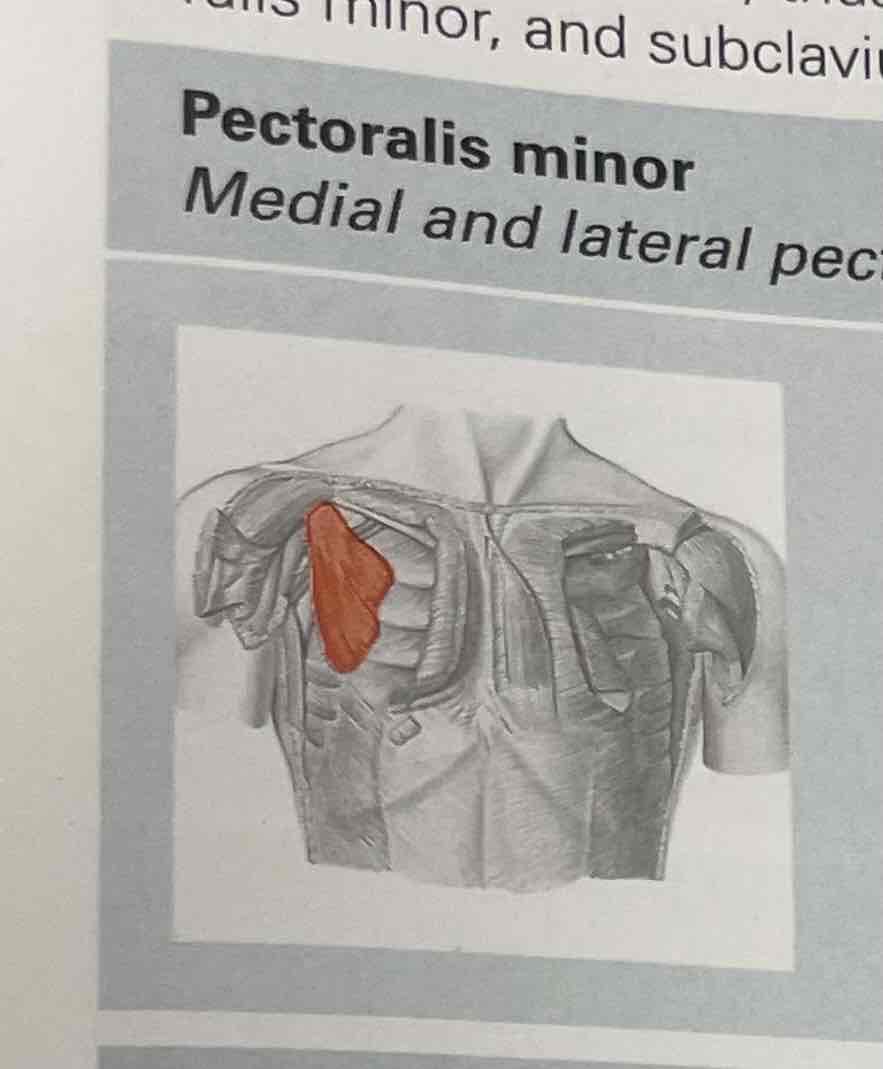
Pectoralis minor
Subclavius
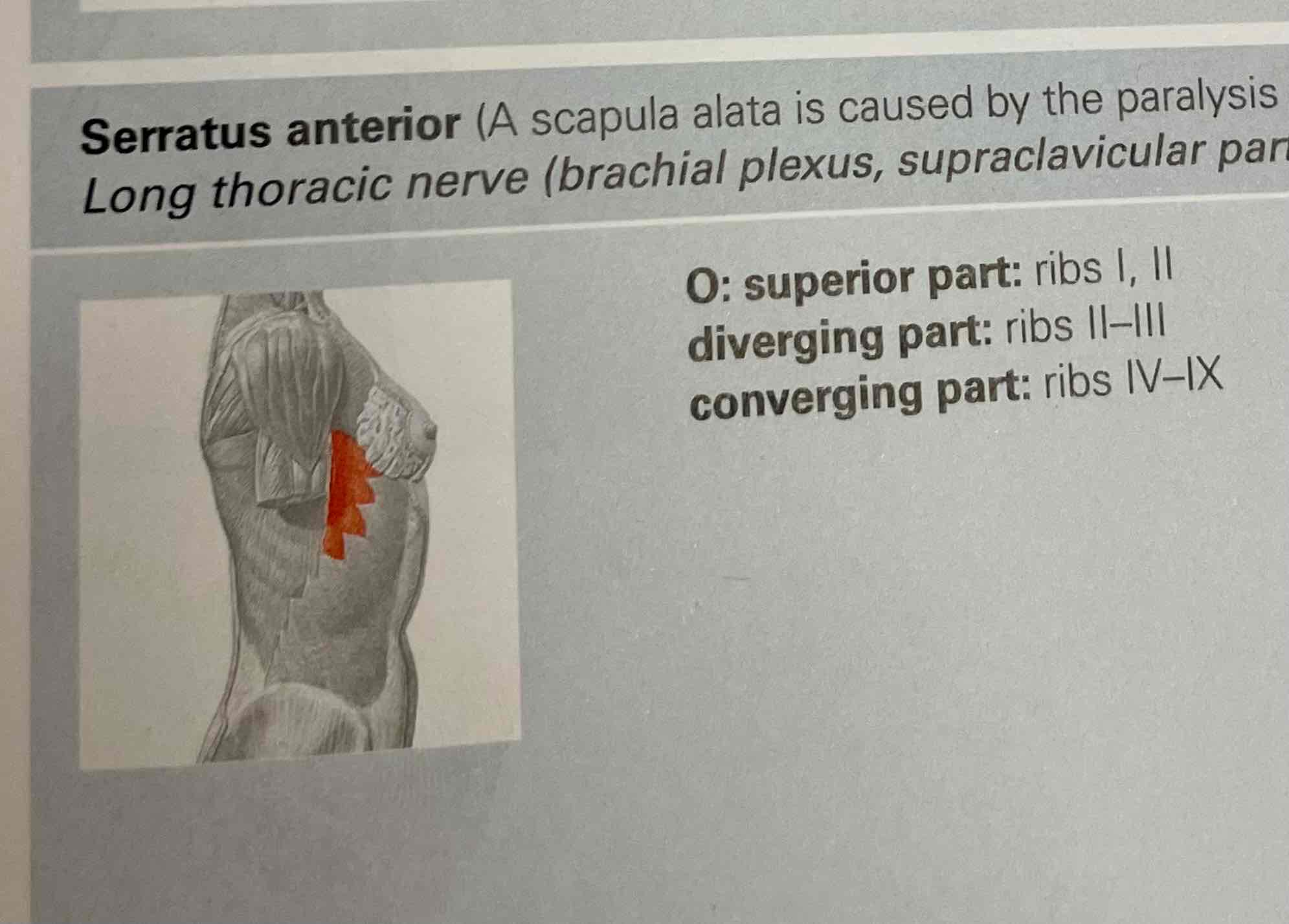
Serrated anterior
Pectoralis minor
Origin: ribs III -V close to the bone-cartilage margin.
Insertion: tip of the coracoid process of the scapula.
Function: shoulder girdle- depress. Thorax: elevating the upper ribs during inspiration (breathing in). It is an auxiliary breathing muscle.
Innervations:
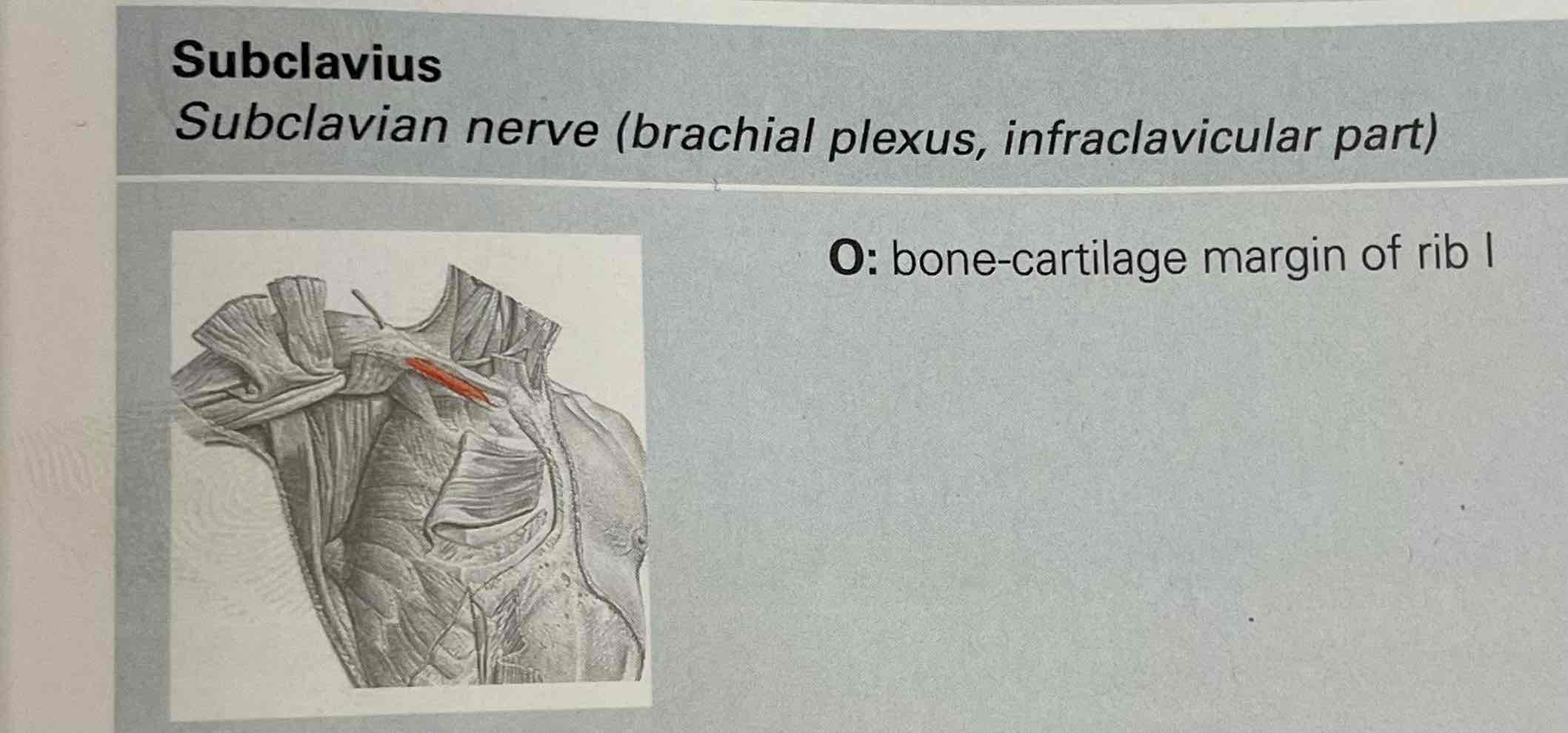
Subclavius muscle
Origin: bone-cartilage margin of the rib I
Insertion: lateral third of the clavicle
Function: shoulder girdle; stabilised the steenoclavicukat joint, protects the subclavian vessels.
innervations:
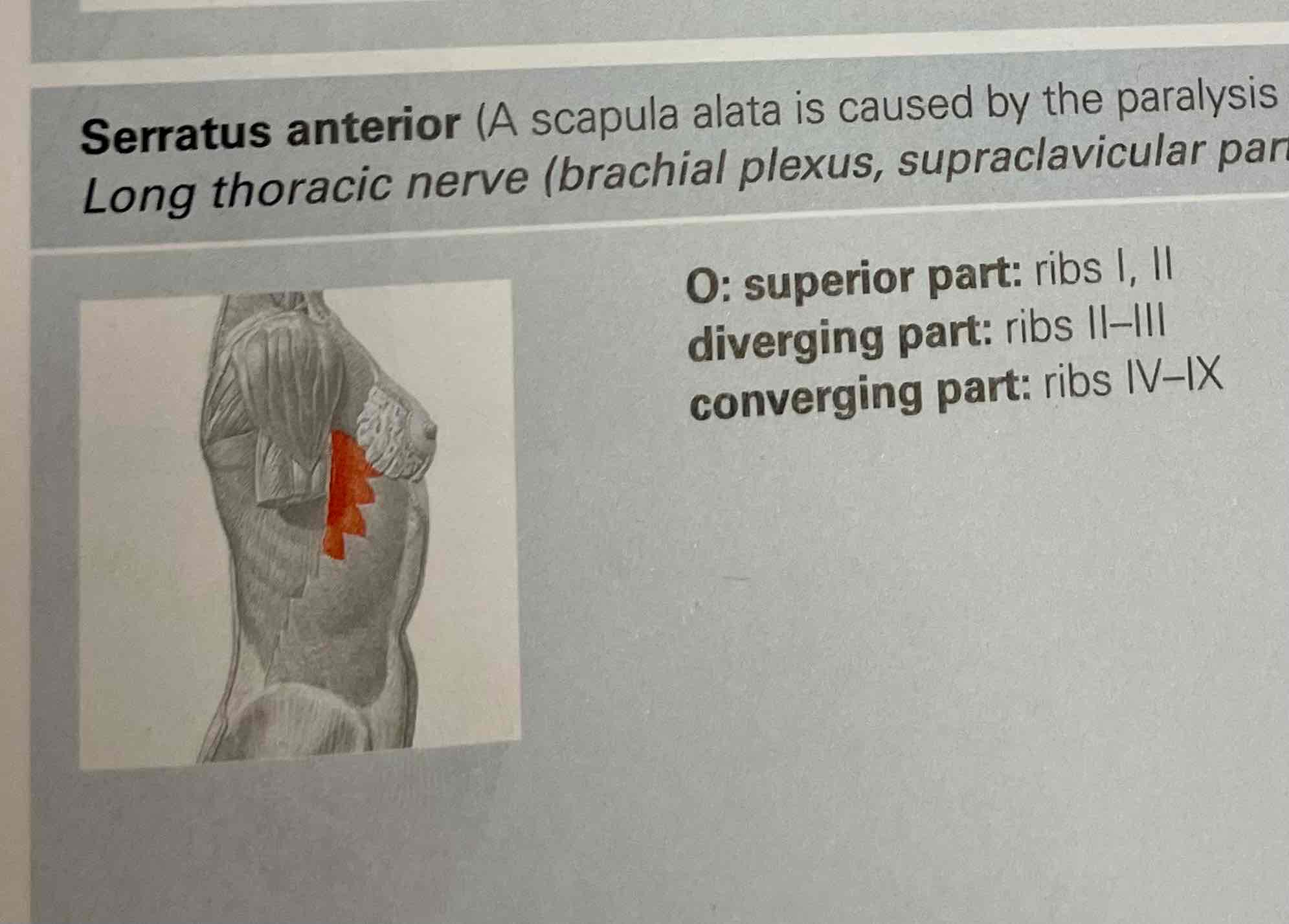
Serratus anterior muscle
Origin:
superior part: rib I, II;
diverging part: rib II-III.
Converging part: rib IV-IX.
Insertion:
Superior part: superior angle of the scapula
Diverging part: medial angle of the scapula.
Converging part: inferior angle of the scapula.
Function: shoulder girdle: holds the scapula against the trunk, together with the rhomboids presses the scapula against the thorax
superior part: elevates the scapula.
diverging part: depresses the scapula converging part: depresses the scapula and, together with the trapezius, rotates its lower angle outwards for the elevation of the arm over the horizontal axis
thorax: elevates the ribs when the scapula is in a fixed position (inspiration)
Ventral muscles of the shoulder
Pectoralis major
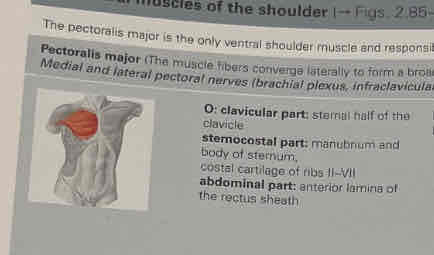
Pectoralis major
Origin:
clavicular part: sternal half of the clavicle
sternocostal part: manubrium and body of sternum,
costal cartilage of ribs II-VII
abdominal part: anterior lamina of the rectus sheath.
Insertions: crest of the greater tubercle of the humerus
Function: shoulder joint: adduction (most important muscle), inwards rotation clavicular part: anteversion (most important muscle); retroversion from an anteverted position
shoulder girdle: depression, antever-sion
thorax: elevates the sternum and the upper ribs when the shoulder girdle is
in a fixed position (inspiration: auxiliary breathing muscle)
lateral muscles of the shoulder
Deltoid muscle
Supraspinatus muscle
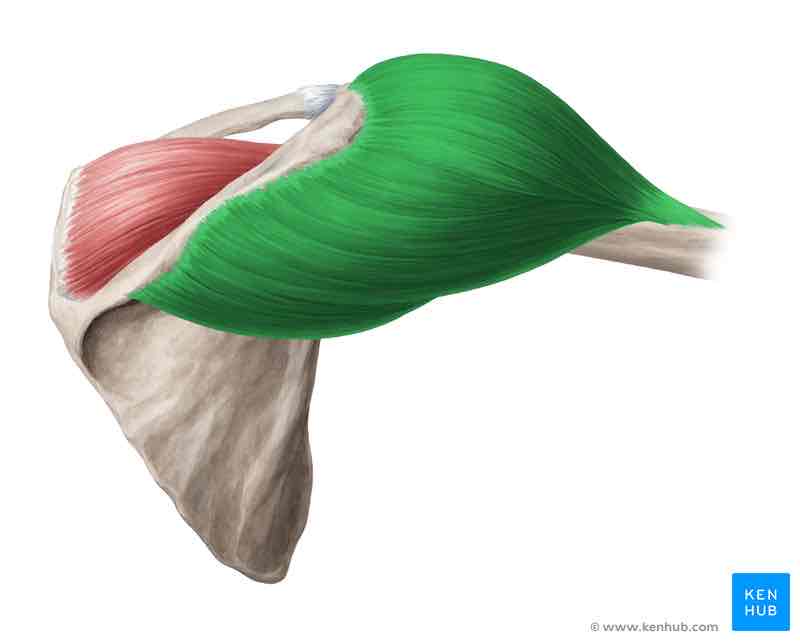
Deltoid muscle
Origin: clavicular part: acromial third of the clavicle acromial part: acromion spinal part: spine of scapula.
insertion: deltoid tuberosity
Function: shoulder joint: clavicular part: adduction (from approx. 60° onwards increasingly abduction), medial rotation, anteversion.
acromial part: abduction to the horizontal plane
spinal part: adduction (from approx.60° onwards increasingly abduction), lateral rotation, retroversion.
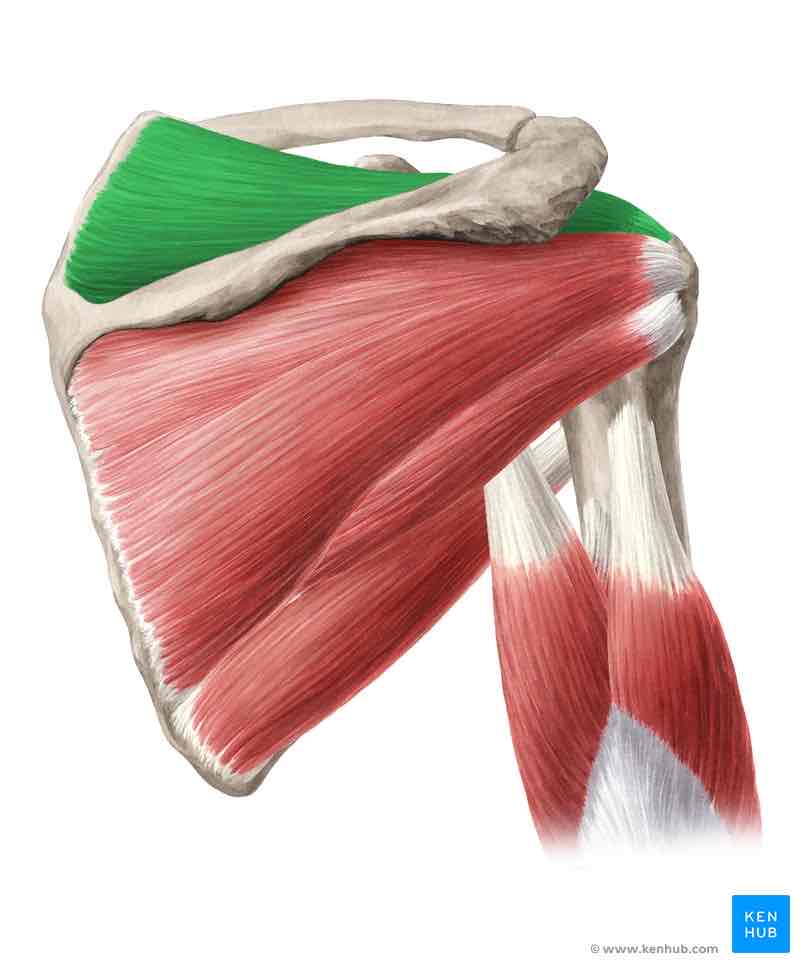
Supraspinatus muscle
Origin: supraspinous fossa. Supraspinous fascia
Insertion: upper facet of the greater tubercle, joint capsule
Function: shoulder joint:
abduction at the scapular level up to the horizontal plane, small lateral rotation.
Dorsal muscles of the shoulder girdle
Trapezius
Elevator scapulae
Rhomboid minor
Rhomboid mahor
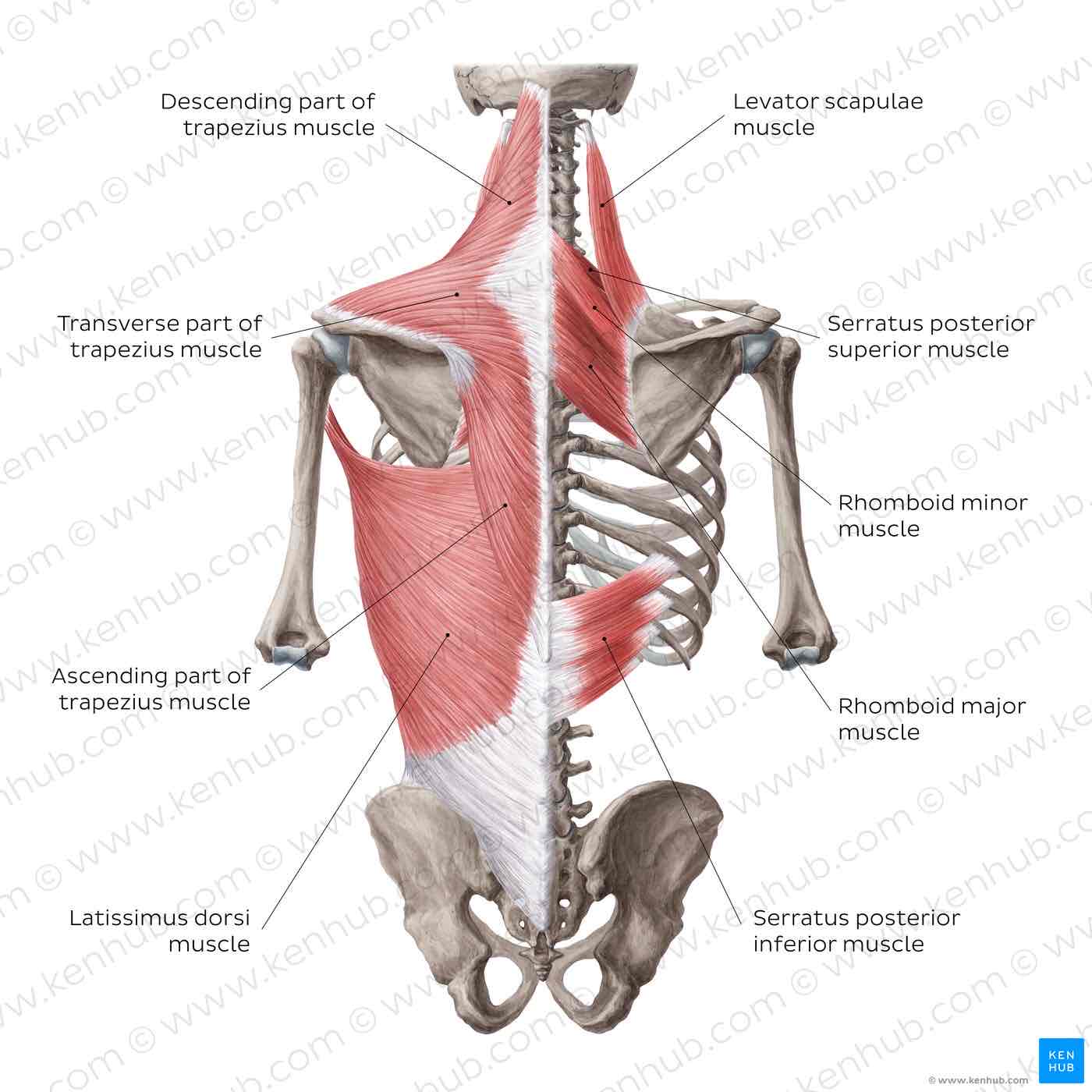
Trapezius muscle
Origin: descending part: at the occipital bone between highest nuchal line and superior nuchal line, spinous processes of the upper cervical vertebrae
transverse part: spinous processes of the lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae
ascending part: spinous processes of the middle and lower thoracic vertebrae
Insertion:
descending part: acromial third of the clavicle transverse part: acromion ascending part: spine of scapula
Function:
descending part: prevents lowering of the shoulder girdle and arm (e.g. carrying a suitcase), elevates the scapula and rotates its lower tip laterally to allow the elevation of the arm above the horizontal plane together with the serratus anterior, rotates the head to the contralateral side when the shoulder is in a fixed position, erects the cervical part of the vertebral column when innervated bilaterally
transverse part: pulls the scapula downwards
ascending part: depresses the scapula and rotates it downwards
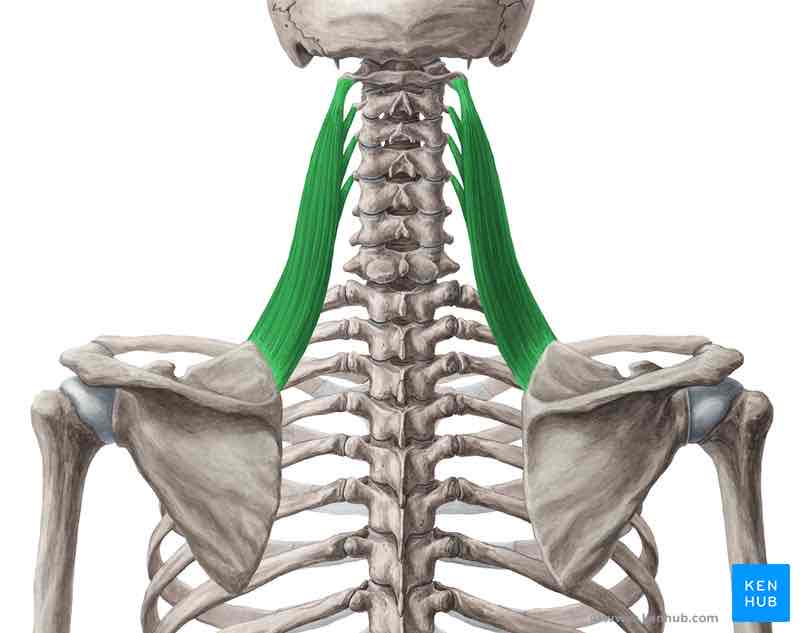
Levator scapulae
Origin: posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the 1st -4th cervical vertebrae.
Insertion: superior angle of the scapula
Function : shoulder girdle: elevate the scapula.
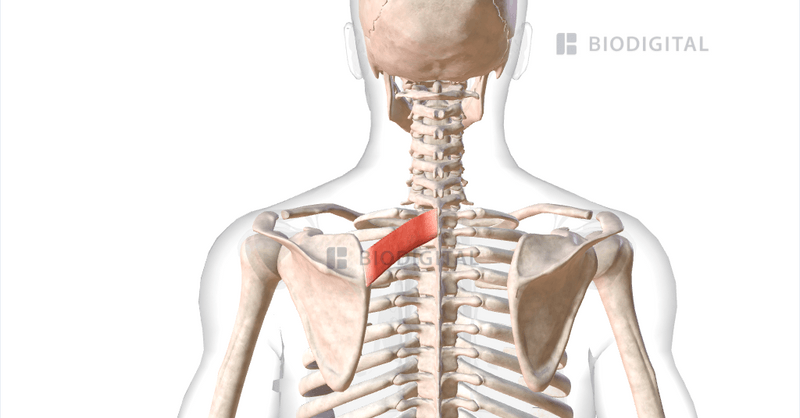
Rhomboid minor
Origin: spinous process of the 6th and 7th cervical vertebrae.
Insertion: medial border of the scapula cranial to the spine of the scapula.
Function: pulls the scapula medically and cranially, fixes the scapula to the torso together with the serrated anterior.
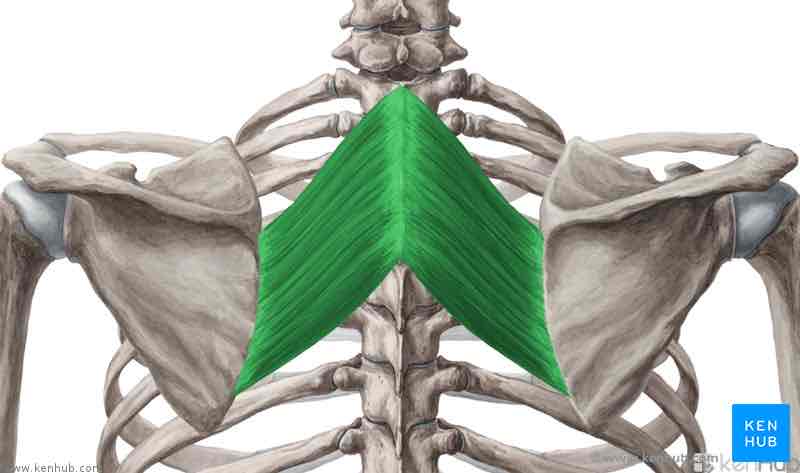
Rhomboid major
Origin: spinous process if the upper four thoracic vertebrae.
Insertion: medial border of the scapula caudal to the spine if the scapula.
Function.: pull the scapula medically and cranial, fixes the scapula to the torso together with the serrated anterior.
Dorsal muscle of the shoulder
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Teres major
Subscapularis
Latissimus dorsi
Infraspinatus muscle
Origin: infraspinous fossa, infraspinous fascia
Insertion: middle facet of the greater tubercle, joint capsule
Function: shoulder joint: cranial part: lateral rotation (most important muscle)
Teres minor
Origin: middle third of the lateral border
Insertion: lower facet of the greater tubercle, joint capsule.
Function: shoulder joint: lateral rotation, adduction in the scapular plane
Teres major
Origin: inferior angle of the scapula
Insertion: crest of lesser tubercle medial to the latissimus dorsi
Function: shoulder joint: medial rotation, adduction, retroversion.
Subscapularis
Origin: subscapular fossa
Insertion: lesser tubercle, joint capsule.
Function: shoulder joint: medial rotation (most important muscle)
Ventral muscles of the upper
Biceps brachii
Coracobrachialis
Brachialis
Biceps brachii
Origin:
long head: Supraglenoid tubercle short head: tip of the coracoid process.
Insertion: radial tuberosity via the bicipital aponeurosis at the antebrachial fascia
Function:
shoulder joint: long head: abduction, anteversion, medial rotation
short head: adduction, anteversion, medial rotation elbow joint:
flexion (most important muscle), supination (most important muscle with flexed elbow)
Innervations: