DNA and genetic diversity
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what is a diploid cell
a cell that has a full set of chromosomes
what is a haploid cell
a cell that has half the number of chromosomes
what are the features of homologous chromosomes
pair of maternal (mum) and paternal (dad) chromosomes
two chromosomes that carry the same genes but not necessarily the same alleles of the genes
chromosomes are same shape and size
genes are at the same loci
describe the features of DNA in eukaryotes
enclosed in the nucleus
long
linear
wrapped around histone proteins
in chromosomes (form)
contain more genes than prokaryotic DNA
describe DNA found in prokaryotes
not enclosed in a nucleus
short
circular (plasmids and free DNA)
not wrapped around proteins
contain fewer genes than eukaryotes
describe DNA found in the mitochondria and the chloroplast
the mitochondria and chloroplast are prokaryotic cells that were absorbed by eukaryotic cell via endosymbiosis. So their features of DNA are the same as prokaryotic cells
short
circular
not enclosed in a nucleus
fewer genes than eukaryotic cells
not wrapped around proteins
what is a gene
A section of DNA that codes for the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain and functional RNA
what is the locus of a gene
the position/location of a gene on a chromosome
what is an allele
one of a number of alternate forms of a gene
what is a codon
a sequence of three bases in mRNA
what is a triplet
a sequence of three bases in DNA
what is the role of a triplet in DNA
codes for a codon in mRNA which during translation codes for a specific amino acid that makes up a polypeptide chain
what does it mean by the genetic code being universal
each triplet codes for the same amino acid in all organisms
what does it mean by the genetic code being non-overlapping
each base sequence is only read once
what does it mean by the genetic code being degenerate
most amino acids can be coded for by more than one codon or triplet
what is a benefit of the genetic code being degenerate
some mutations may have no effect on the polypeptide formed
why are amino acids coded for by triplets and codons (3 bases)
triplets and codons consist of a sequence of three bases
there are a total of 20 different amino acids that we need to code for
there are a total of 4 base pairs
if each base coded for an amino acid we could only code for 4 different amino acids (4^1 = 4)
if we used base pairs to code for an amino acid we could only code for a total of 16 different amino acids 4² = 16
we use triplets because 4³ = 64
do only prokaryotes or eukaryotes have introns and exons
only eukaryotes have introns and exons
what are introns and exons
exons- coding sections of a gene that code for amino acids
introns- non coding sections of a gene. They are removed (spliced) before protein synthesis occurs
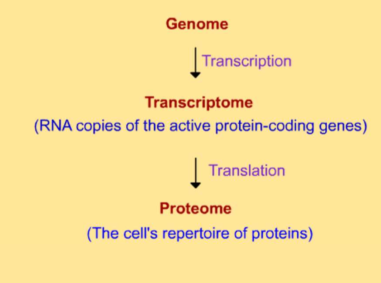
what is the genome
complete sets of genes in a cell, including mitochondria and chloroplasts
what is the proteome
the full set of proteins that a cell is able to produce at a given time
what is the transcriptome
all the mRNA within a cell
how does a cells genome, proteome, and transcriptome relate to each other
what is the structure of RNA
polynucleotide
single stranded
contains ribose sugars
4 bases- A U C G
phosphate group
phosphodiester bonds
describe the structure of mRNA
single polynucleotide chain
linear
pentose sugar is ribose
phosphate group
phosphodiester bonds
shorter chain than DNA but longer than tRNA
less stable than DNA and tRNA
describe the structure of tRNA
single polynucleotide chain
clover shaped
pentose sugar is ribose
phosphate group
phosphodiester bonds
shorter chain than DNA and mRNA
less stable than DNA but more stable than mRNA
what is the order of the processes involved in protein synthesis
transcription- reading the DNA and copying it into RNA
splicing
translation- where the cell uses information from the mRNA to produce proteins
describe the process of transcription
free nucleotides in the nucleus become phosphorylated via the hydrolysis of ATP to become activatedFree
RNA polymerase binds to the promotor region
the two strands of DNA start to unzip and hydrogen bonds between complementary bases on either strand are broken. This is catalysed by DNA helicase
the phosphorylated nucleotides line up opposite the exposed bases on the template strand according to complementary base pairing
temporary hydrogen bonds form between the complementary base pairs so that the order of the bases is maintained
RNA polymerase forms phosphodiester bonds between the adjacent nucleotides
RNA synthesis stops when RNA polymerase reaches the terminator region
what happens in the process of splicing
occurs in the nucleus immediately after transcription
introns are removed/spliced from the gene by a spliceosome enzyme
only occurs in eukaryotic cells because prokaryotes don’t have introns
after this, the mRNA strand moves out of the nucleus via the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm where it binds to a ribosome
describe the process of translation
following transcription mRNA leaves the nucleus via the nuclear pores and enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome
tRNA molecules carry a specific single amino acid and have an anticodon that codes for the tRNA molecules’ amino acid
the tRNA molecule with a complimentary anticodon to the start codon on the mRNA strand brings over the first amino acid to the mRNA chain due to complementary base pairing
when the tRNA molecule brings the amino acid over to the mRNA strand hydrogen bonds form between the tRNA and mRNA molecules
a second tRNA molecule binds to the adjacent codon on the mRNA molecule and peptide bonds are formed between the two amino acid molecules via a condensation reaction
then the first tRNA molecule leaves the ribosome
the ribosome then moves along the mRNA molecule and the process repeats and the length of polypeptide chain increases
the length of the polypeptide chain increases until the ribosome reaches the stop codon on the mRNA strand
why do we need cells to divide by meiosis
sexual reproduction requires the fusion of male and female gametes (n) too produce an offspring (2n)
what are the stages of meiosis
interphase
cell replicates its DNA (2n→4n)
prophase 1
nuclear envelope breaks down, spindle fibres form and crossing over occurs
metaphase 1
independent assortment occurs here when homologous pairs are lined up along the equator of the cell
anaphase 1
spindle fibres pull homologous chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell
telophase and cytokinesis 1
chromosomes gather at poles of the cell and the cytoplasm splits
prophase 2
new spindle fibres form
metaphase 2
independent assortment occurs again as homologous pairs are lined up along the equator of the cell
anaphase 2 centromeres’s divide and chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
telophase and cytokinesis 2
nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes and the cytoplasm divides resulting in 4 haploid cells
what are the 3 ways in which meiosis causes genetic variation in offspring
independent assortment
crossing over
random fertilisation
how does independent assortment cause genetic variation
it is random which way round homologous chromosomes line up during metaphase 1 and 2, so maternal and paternal chromosomes can get mixed up (varied) into daughter cells
how does crossing over increase genetic variation in offspring
occurs during prophase 1 between homologous pairs of chromosomes. Chromatids on each homologous pair become twisted and cross over, this region is called the chiasma. During this process tensions are created and portions of the chromatid break off and rejoin the other homologous chromosome, leading to a new combination of alleles
how does random fertilisation cause genetic variability
random in which male gamete fuses with which female gamete
what is non disjunction
when chromosomes aren’t split into daughter cells correctly during meiosis divisions, leading to incorrect numbers of chromosomes in daughter cells
the incorrect numbers of chromatids may mean that they won’t be able to form chromosome pairs as there are uneven numbers
what is polyploidy
more common in plants
results in changes to chromosome numbers in plant cells