2.1 Coastal Landforms - Erosional Landforms
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Define Cliffs
Cliffs are steep or sloping rock faces, by which the shape depends on geology and wave energy
→ high-energy waves erode the cliff base more than low-energy waves
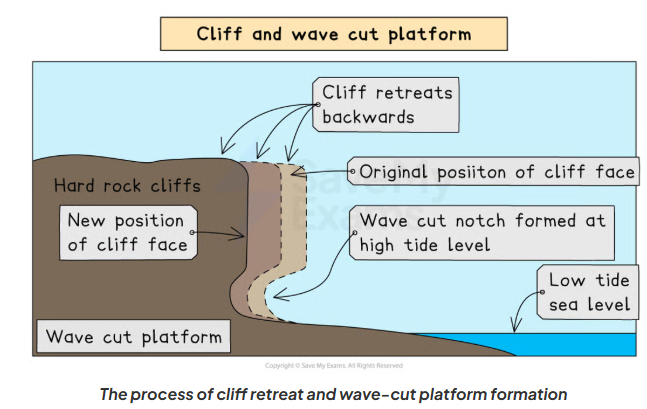
How do cliffs and wave-cut platforms form?
Waves attack the base at high-water mark, forming a wave-cut notch (knick-point)
Hydraulic action, abrasion and corrosion widen and deepen the notch
Continued undercutting makes the cliff unstable
The overhanging rock collapses due to the lack of support
Backwash removes the debris (remainders), leaving a wave-cut platform
Repeated collapse causes a cliff retreat (coastal retreat)
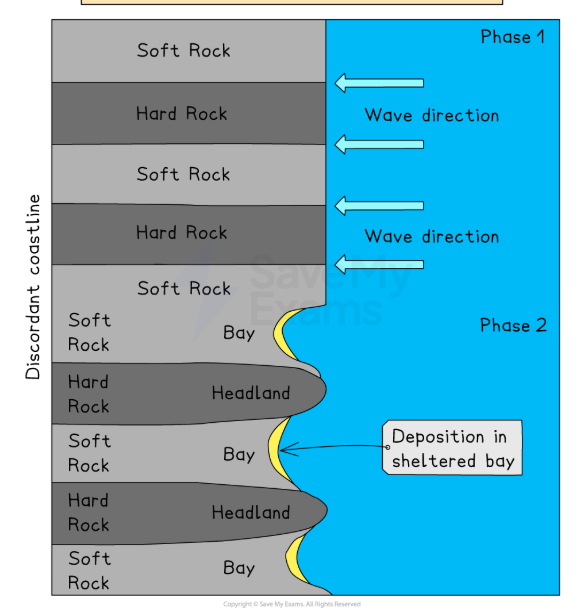
Define Discordant coastlines
A discordant coastline is where different types of rock lie at right angles to the sea
Define a bay
A bay is an inlet of the sea where the land curves inward, usually with a beach.
Where do headlands and bays take place?
Occur on a discordant coastline (an alternating hard rock and soft rock at right angles to waves)
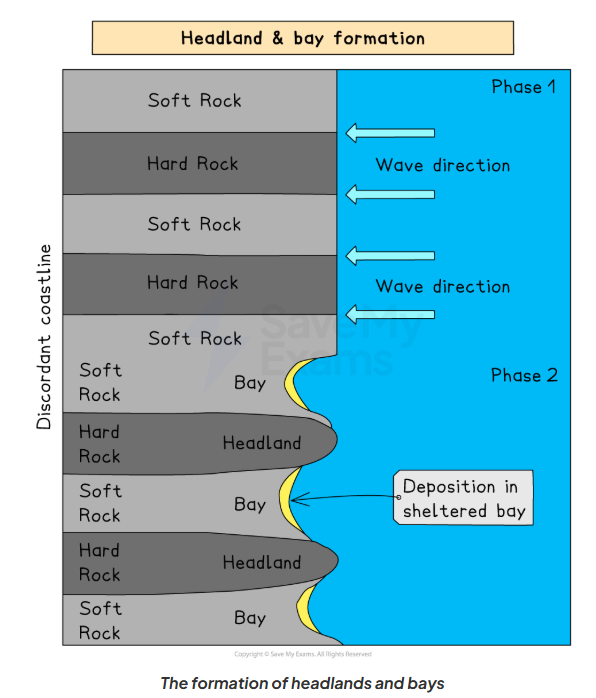
How do Headlands and bays form?
Soft rock (clay) is eroded more quickly by wave action
Softer rock is therefore worn back to form a bay (backwards dent)
Hard rock (limestone) erodes more slowly
Therefore, resistant rock is left jutting out into the sea as a headland (remains outwards)
Describe a headlands appearance
projects out to sea
has cliffs along its sides
is usually longer than it is wide
has a geology of resistant rock
Describe a bays appearance
a wide, open entrance from the sea
a roughly semi-circular shape extending into the coastline (backwards)
land that is lower than the headlands surrounding it
a bay may or may not have a beach
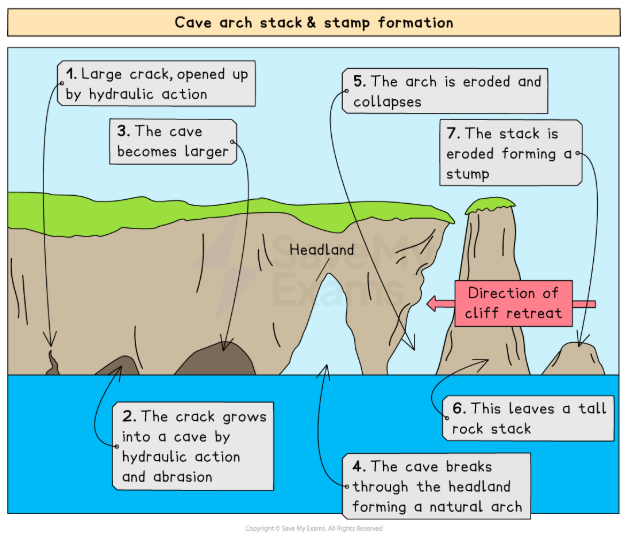
How do caves, arches, stacks and stumps form?
As waves approach the coast, wave speed decreases
waves bend so crests become more parallel to the coast → causing wave refraction
Refraction concentrates wave energy on headlands
Hydraulic action, abrasion and corrosion exploit weaknesses (cracks)
Cracks widen to form a cave
Continued erosion enlarges cave until it breaks through, forming an arch
weathering from above and erosion at the base weaken the arch
the arch collapses, leaving a stack
the stack is undercut and weathered until it collapses into a stump
State the order of arches, caves, stumps and stacks
cave
arch
stack
stump