Week 1 - Introduction to Brain Structure and Function
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Dorsal
Superior
Caudal
Posterior
Rostral
Anterior
Ventral
Inferior
How can infection spread from scalp to cranial cavity?
Emissary veins
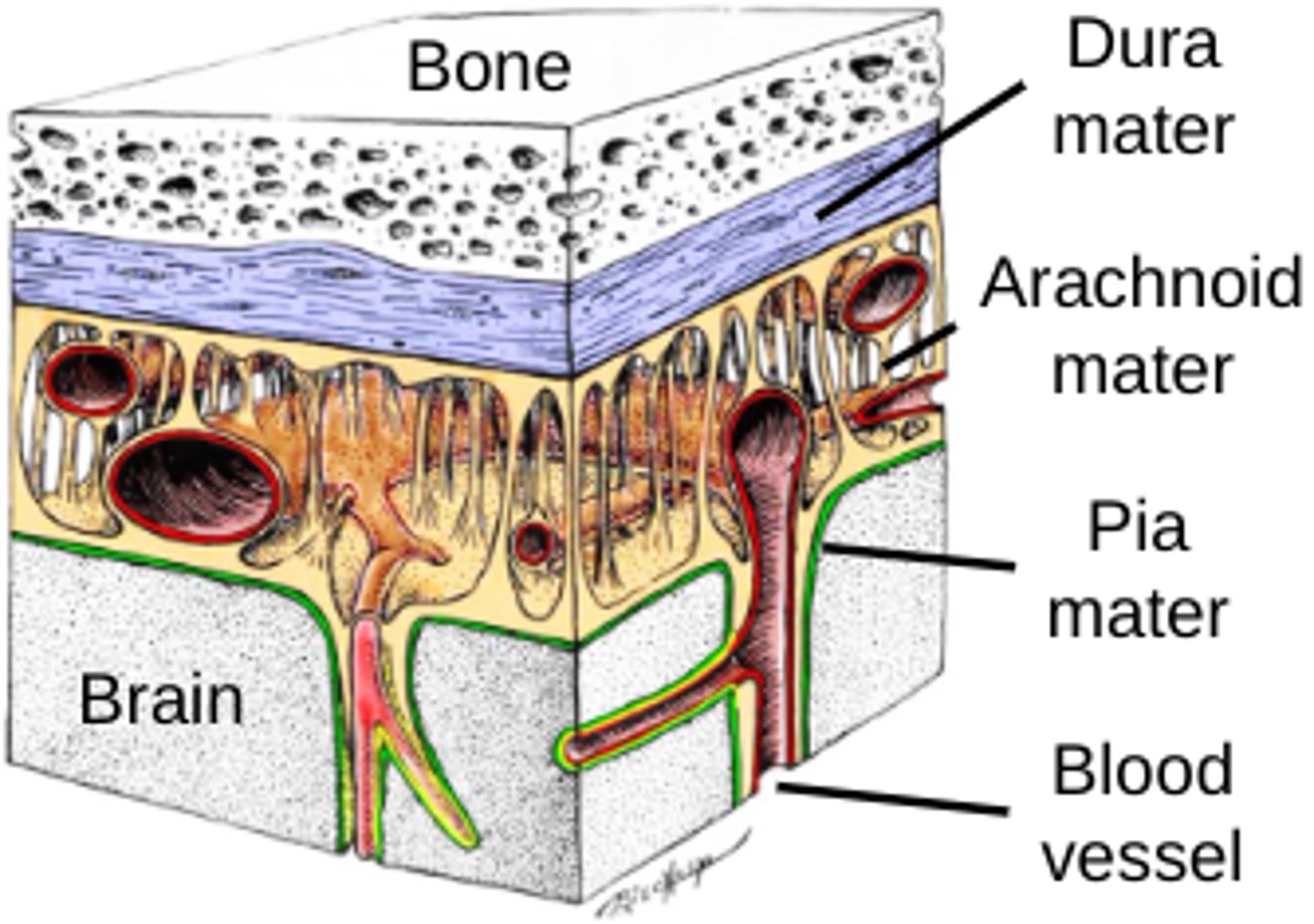
What is the brain contained by?
Three meninges
What are the 3 meninges of the nervous system?
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
What are the reflections/folds of the dura mater?
Falx cerebri
Tentorium cerebelli
Falx cerebelli
What are tentorial tumours?
Rare tumours formed in the tentorium cerebelli
They can be infratentorial and supratentorial
What is meningeal haematoma?
Blood clot that forms between layers of meninges
There are 3 types: subarachnoid, subdural and epidural
What is the role of falx cerebri?
Separates hemispheres
What is the role of tentorium cerebelli?
Separates occipital lobe from cerebellum
What is the role of falx cerebelli?
Separates cerebellar hemispheres
What does the arachnoid mater contain?
Blood vessels
Cerebral spinal fluid
Granulations to drain CSF back into the venous system
What does the pia mater follow?
The contour of the brain
What is cortical sulci?
Surface landmarks on the brain
Grooves or indentations between cortical gyri
What is the precentral sulcus?
Creates anterior border of the motor cortex
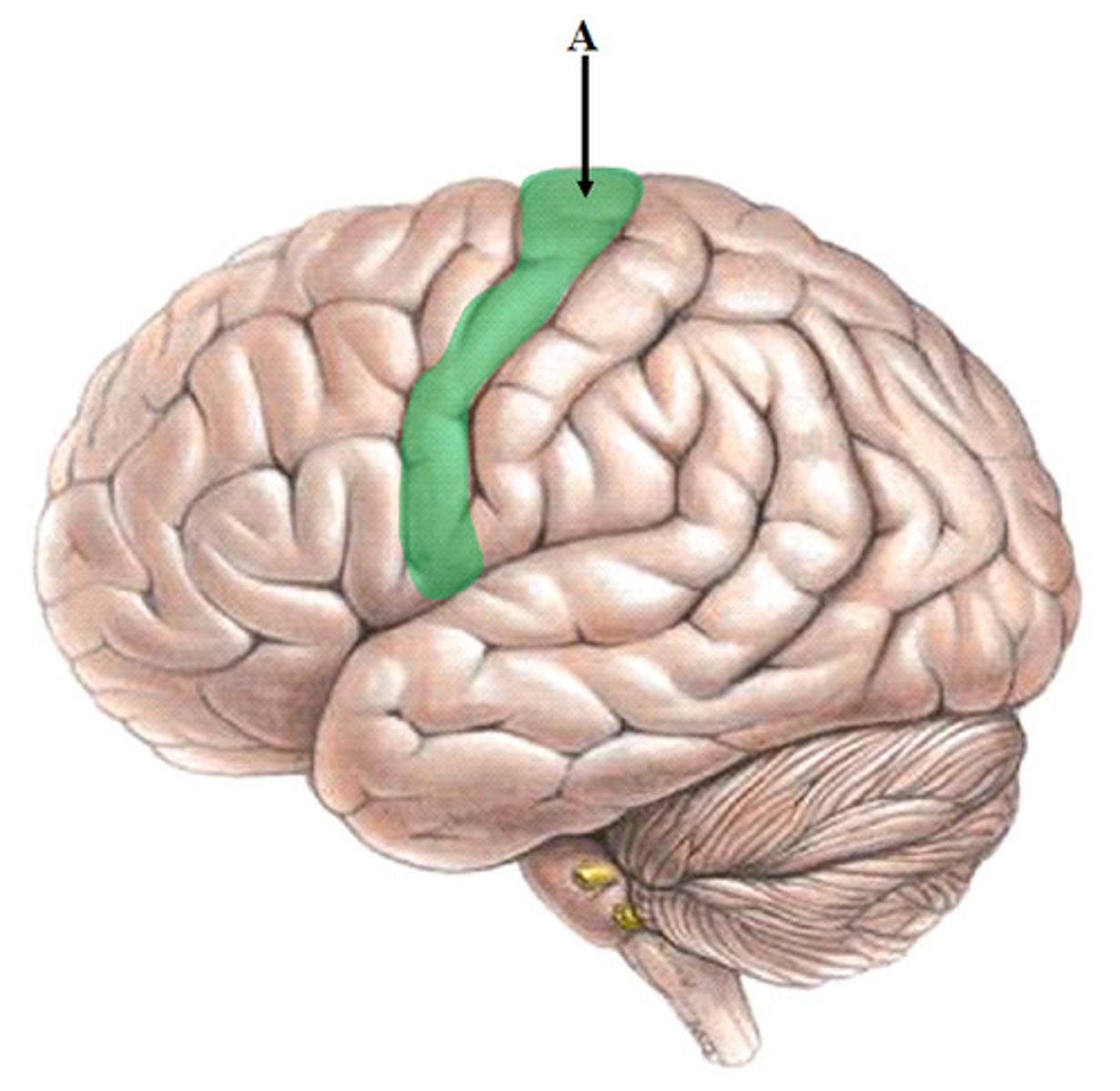
What is the central sulcus?
Separates frontal and parietal lobes
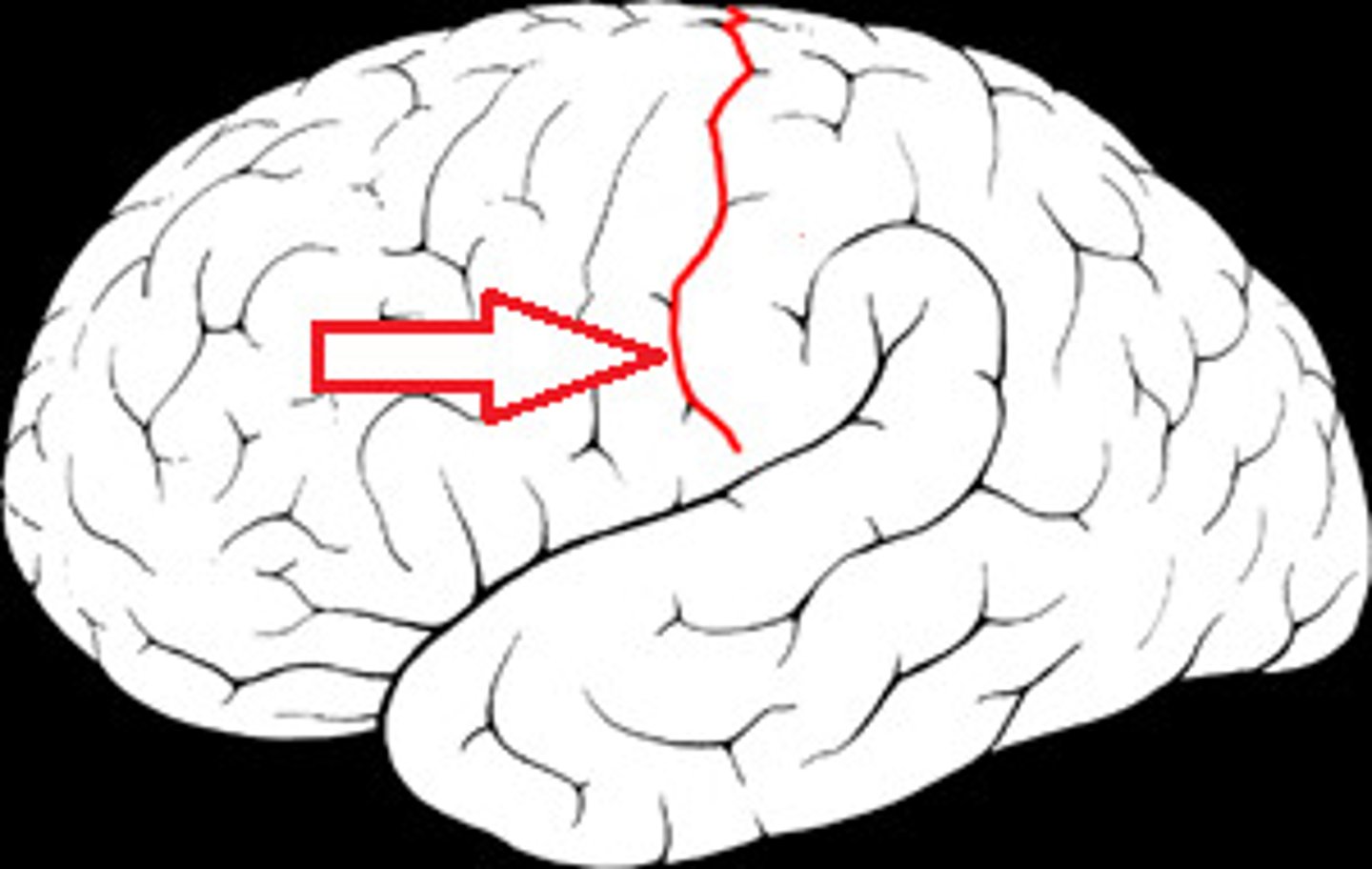
What is the lateral sulcus?
Separates the parietal and temporal lobes
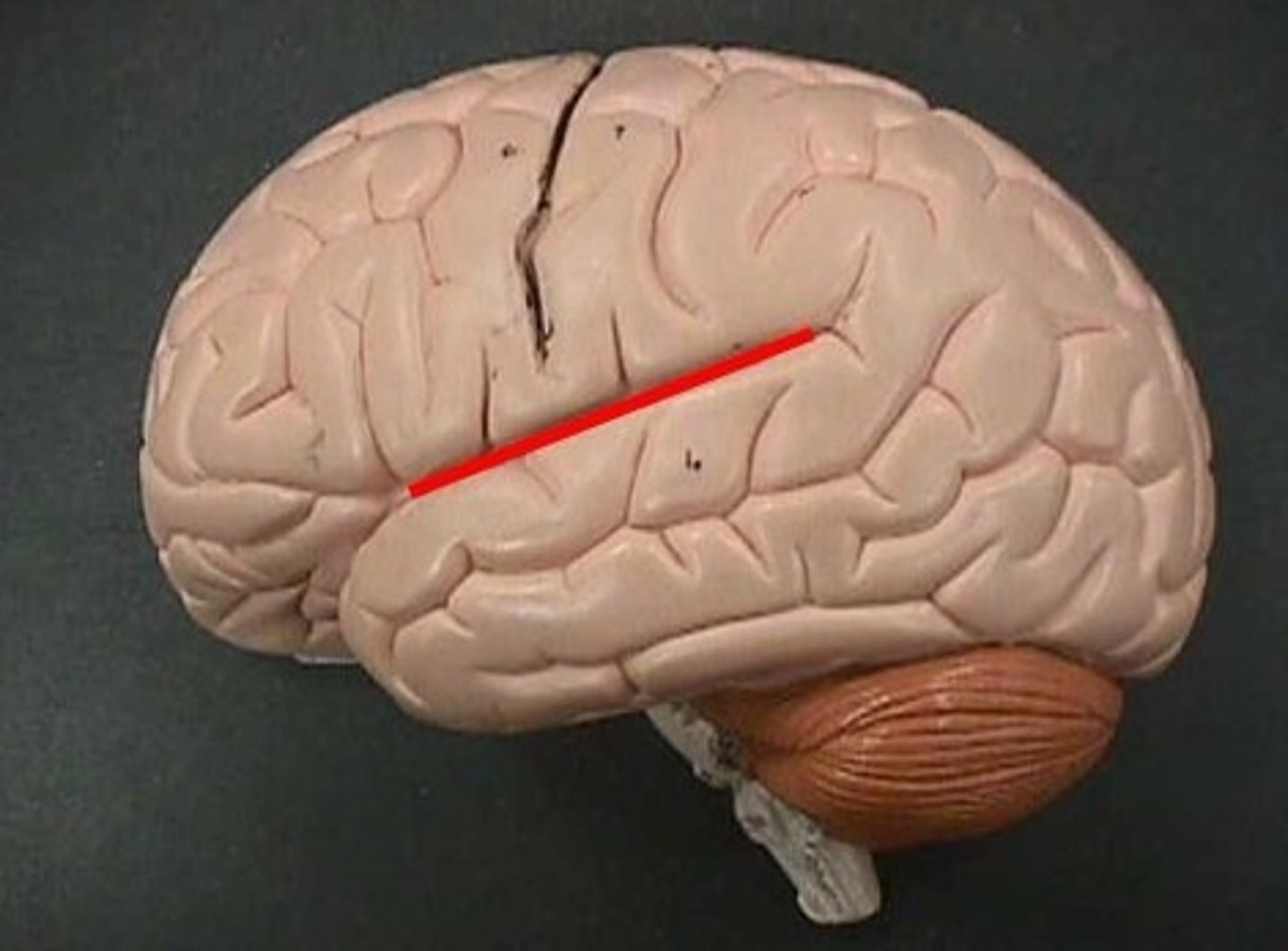
What is the parieto-occipital sulcus?
Separates parietal and occipital lobes
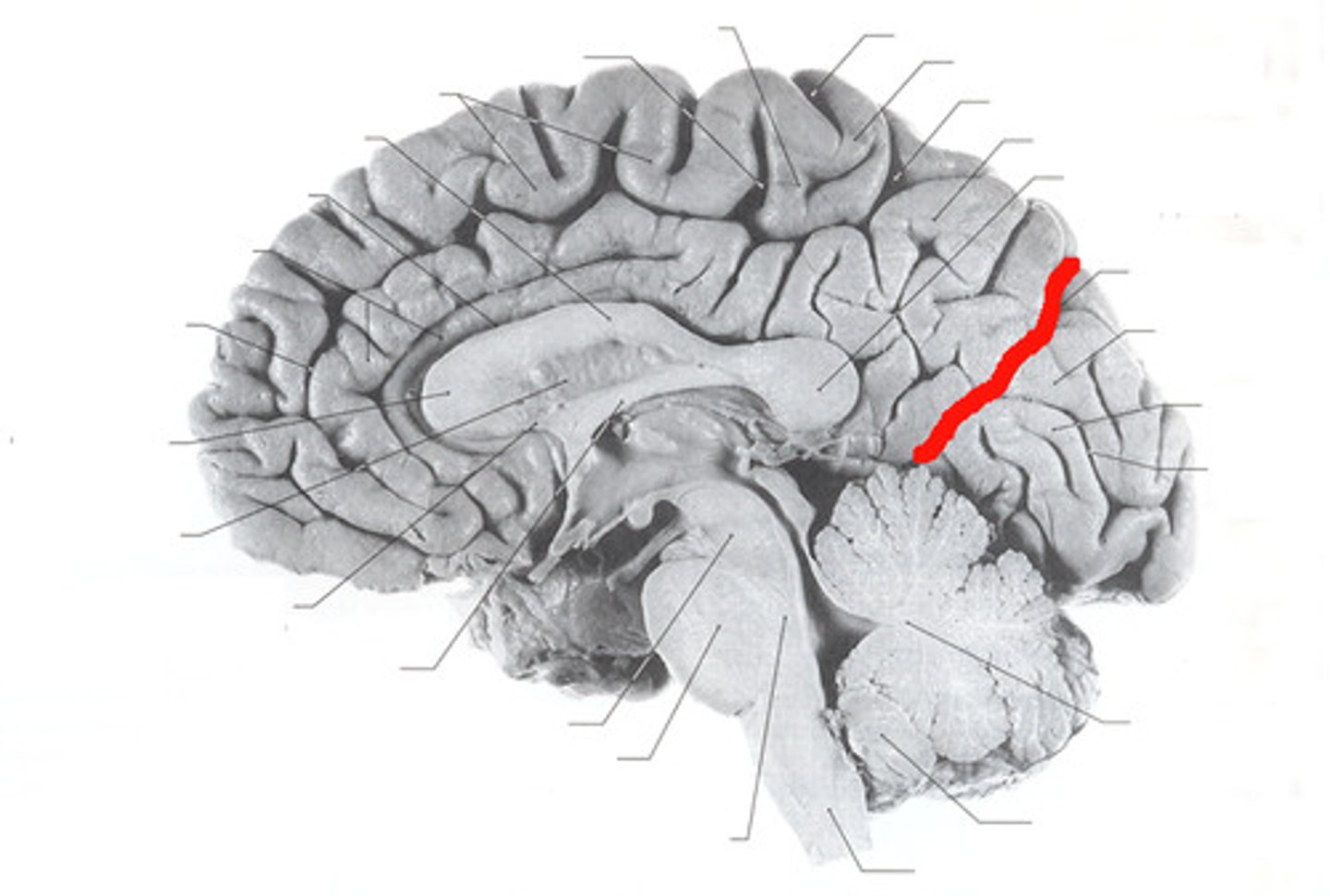
What is the marginal sulcus?
Separates the precuneus from the paracentral lobule
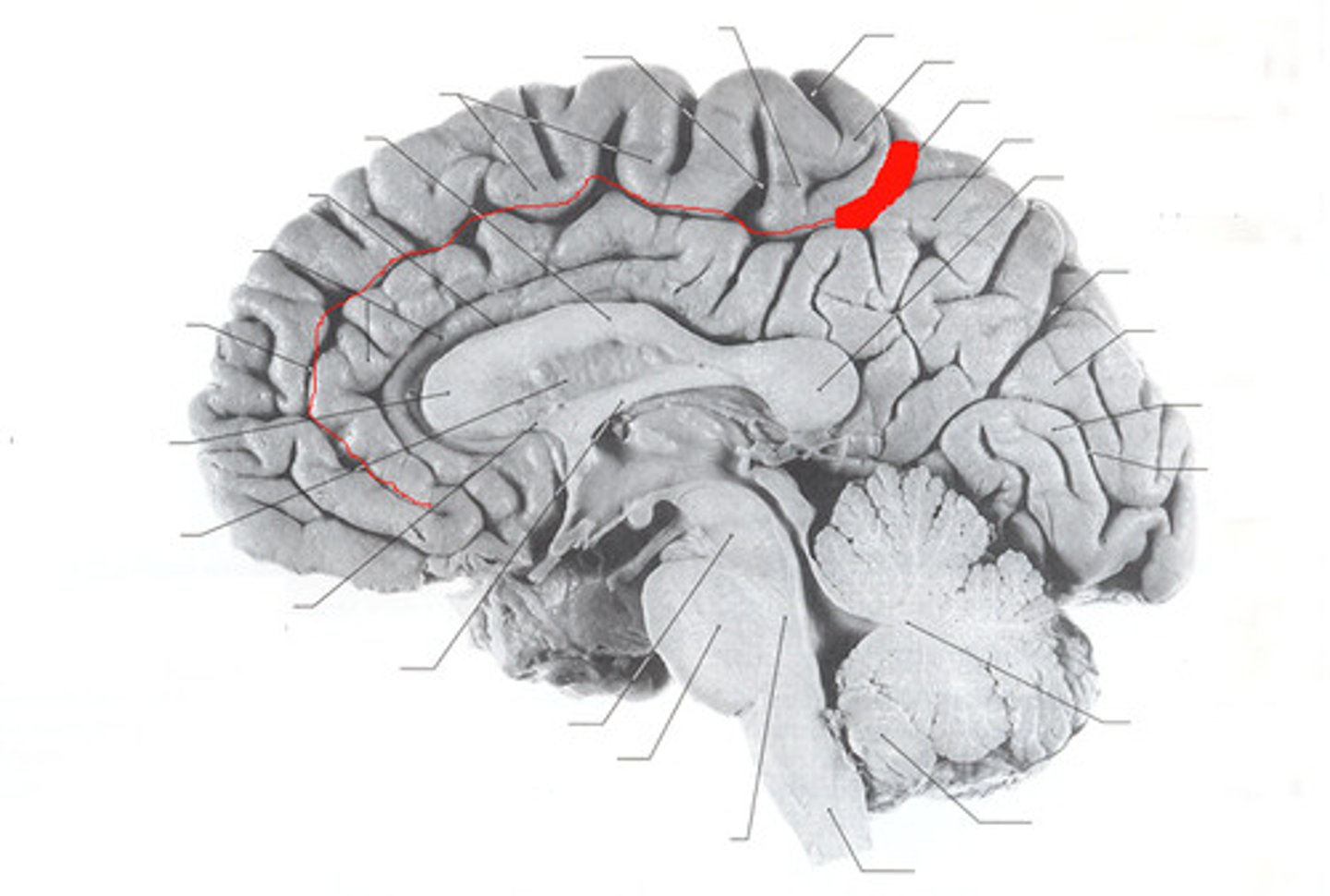
What is the cingulate sulcus?
Separates limbic and frontal lobes
A cortical sulci
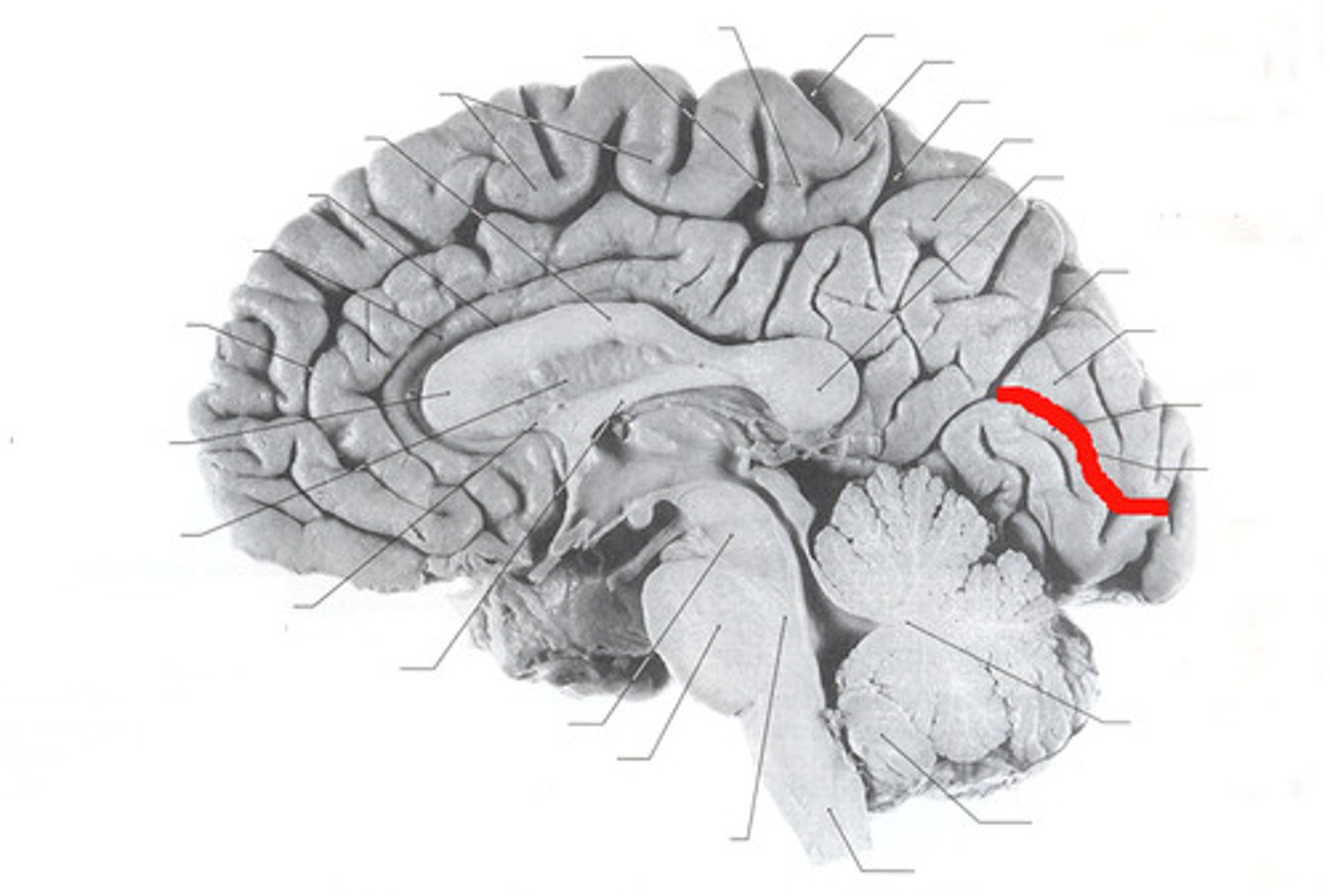
What is the calcarine sulcus?
Separates the occipital lobe into superior and inferior halves
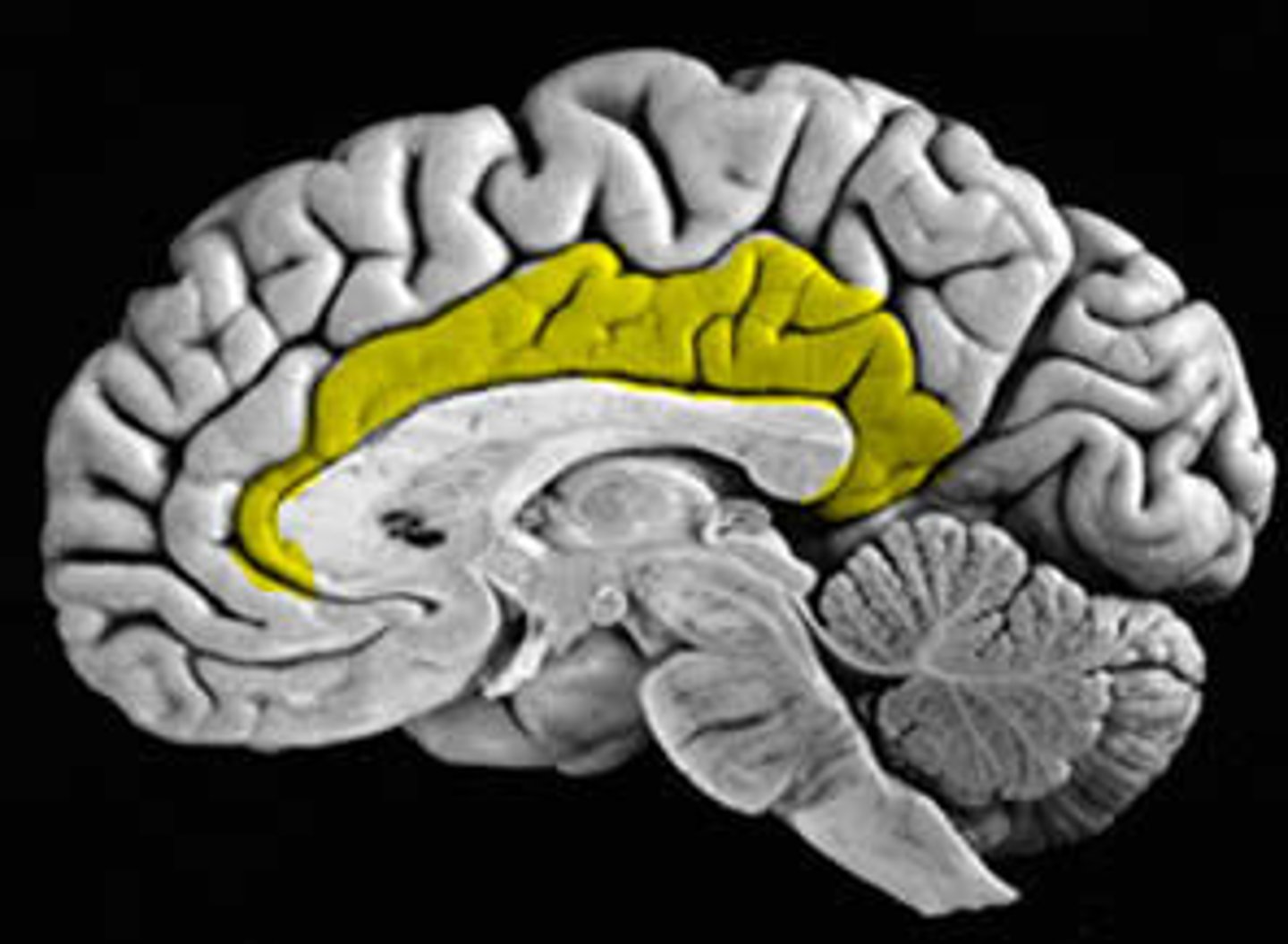
What is cortical gyri?
Raised, ridged parts of the cortex
What is the precentral gyrus?
Primary motor cortex
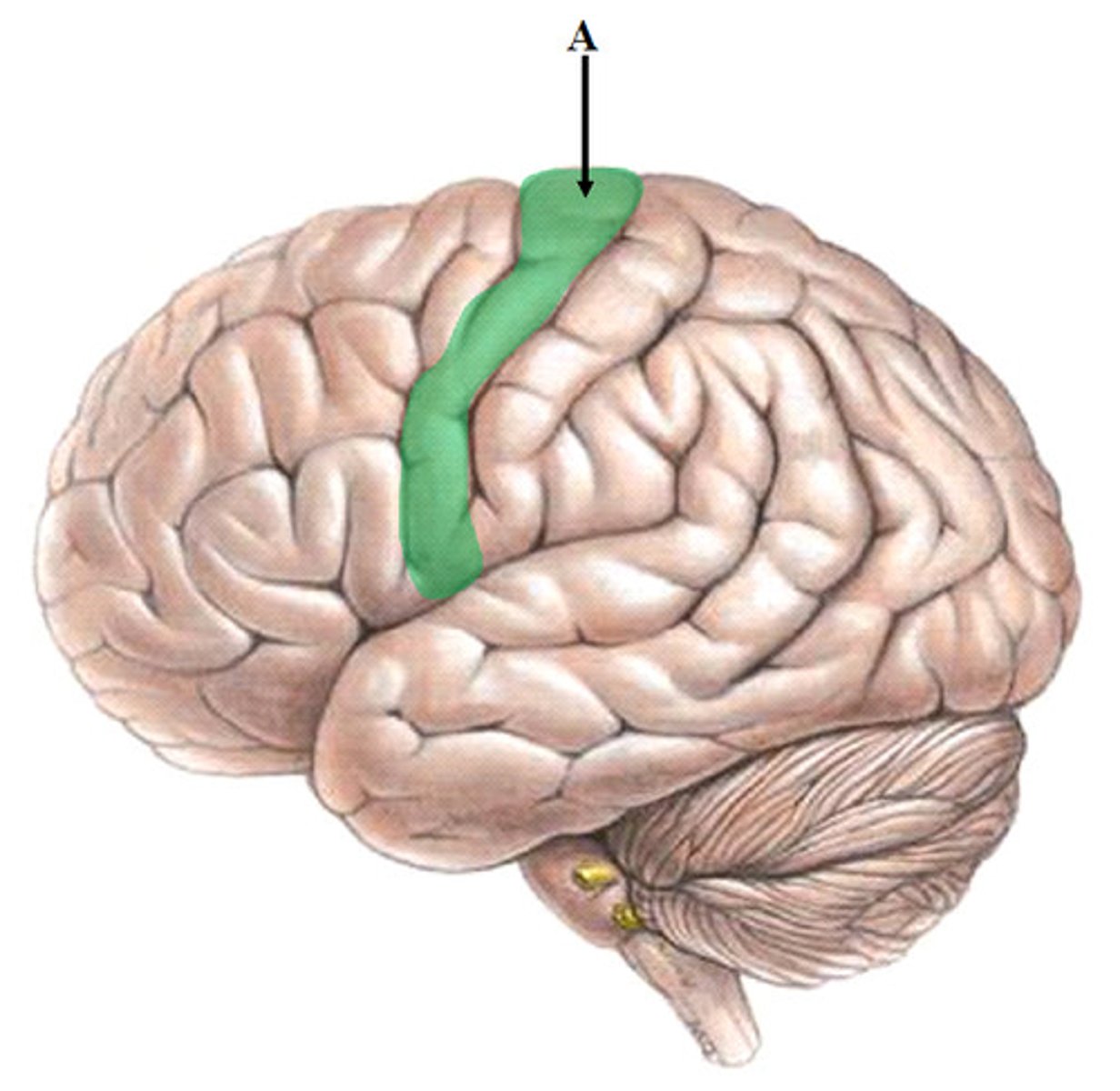
What is postcentral gyrus?
Primary somatosensory cortex
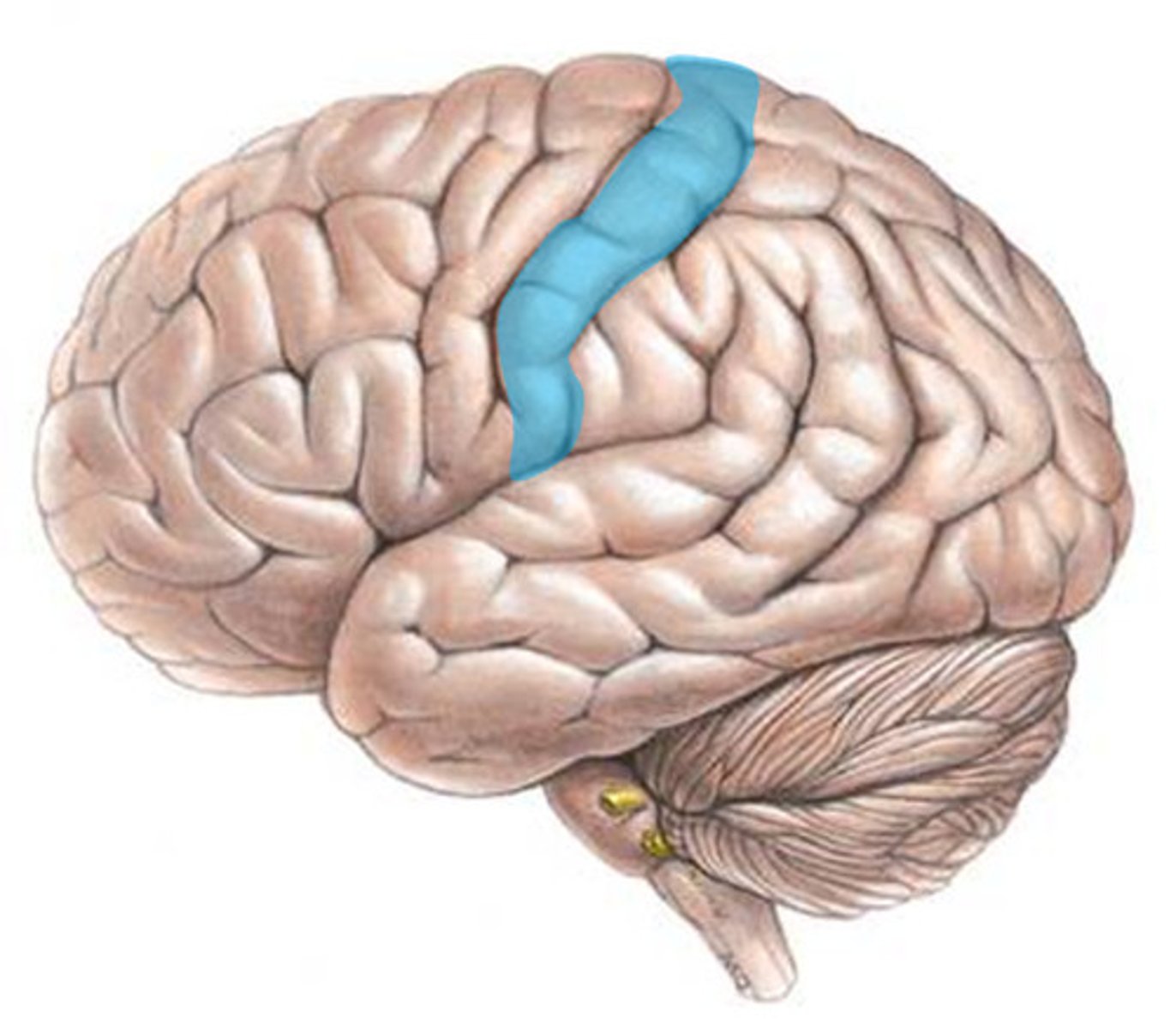
Where is the central sulcus located?
Between the precentral gyrus and the postcentral gyrus
What are the cortical lobes?
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobe
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobe
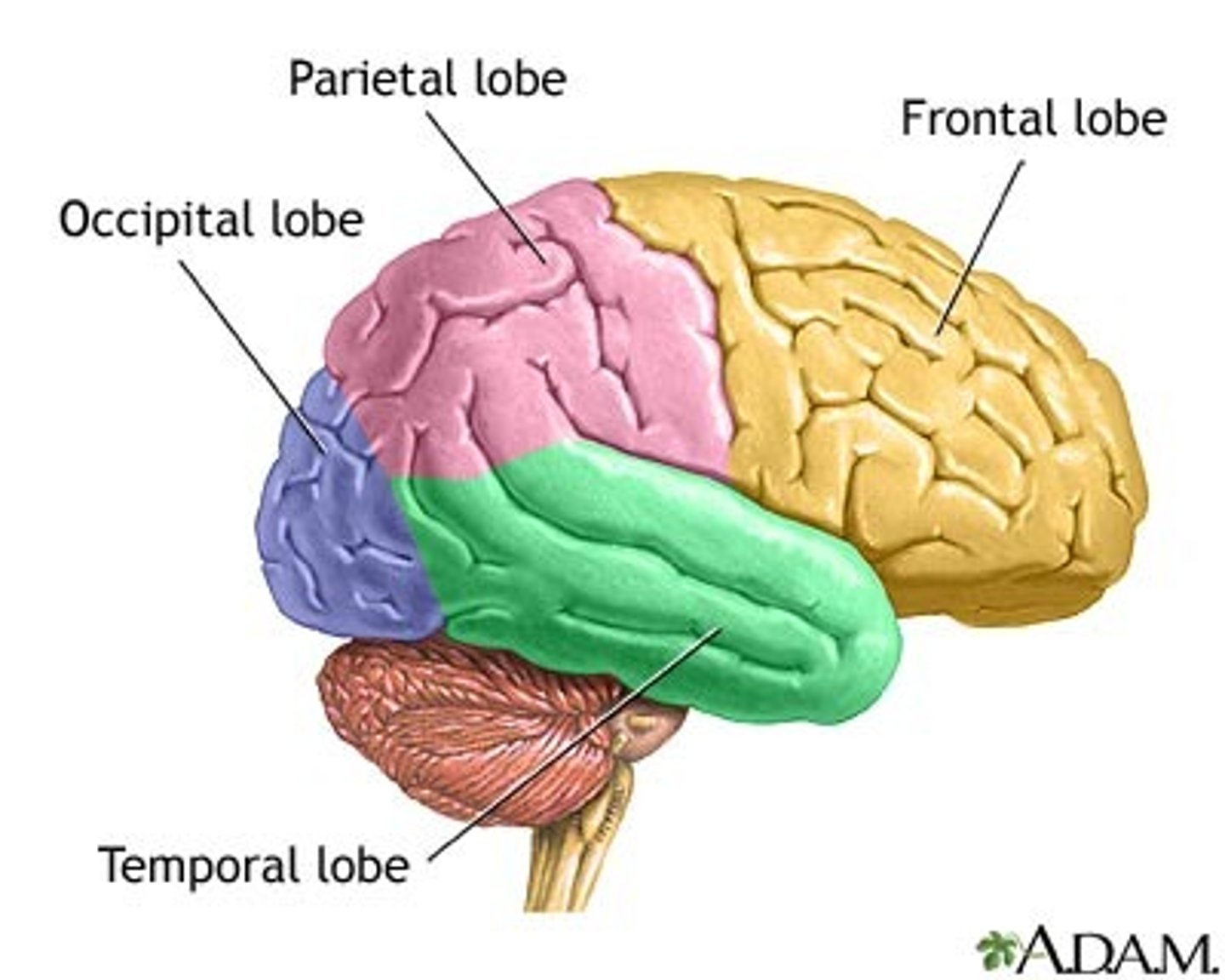
What separates the frontal lobe from the central lobe?
Central sulcus
What is the role of the frontal lobe?
Personality
Attention
Motivation
Planning movement
What is the role of the parietal lobe?
Integrating sensory information
Language processing
What is the role of the temporal lobe?
Memory
Sensory processing
Language comprehension
What is the role of the occipital lobe?
Vision
What is the rhombencephalon?
Hindbrain
What is hindbrain made up of?
Metencephalon and myelencephalon
What does the metencephalon become?
Pons and cerebellum
What does the myelencephalon become?
Medulla oblongata
What is the mesencephalon?
Midbrain
What does the mesencephalon become?
Tectum (colliculi)
Tegmentum
Cerebral peduncles
What is the prosencephalon?
Forebrain
What is the forebrain separated into?
Diencephalon
Telencephalon
What does the diencephalon become?
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
What does the telencephalon become?
Basal ganglia and cortex
Building the brain diagram
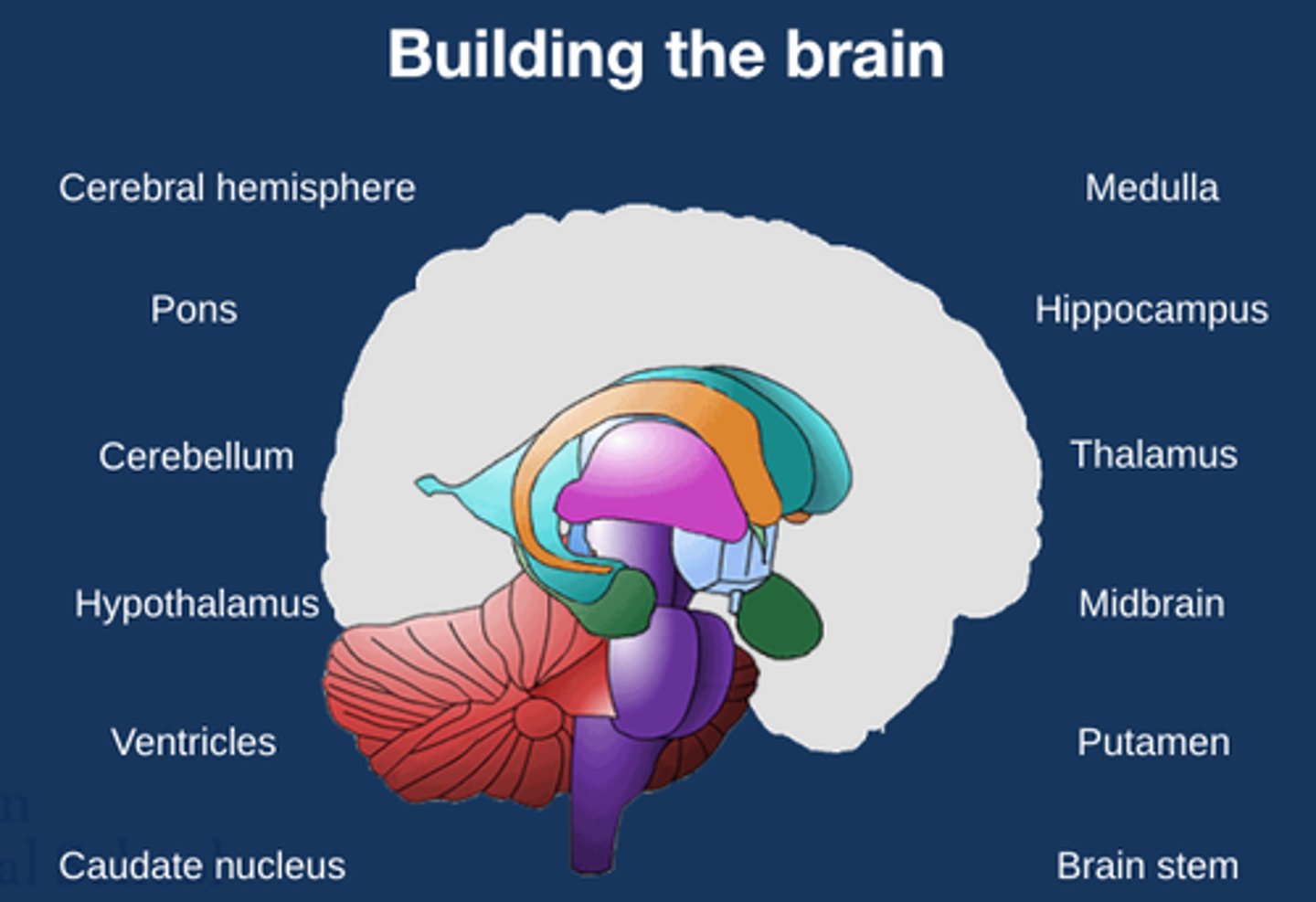
What is the role of the cerebellum?
Balance
Coordination
Synchorization of muscles
What is the brain stem made up of?
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
What is the role of the midbrain?
Motor control via cerebral peduncles (motor tracts)
Vision and hearing tectum
Consciousness via reticular formation
Also contains the substantia nigra and red nucleus
What is the role of the cerebral peduncles?
Controls motor processes
Motor tracts
What is the role of the substantia nigra?
Produces dopamine
What is the role of red nucleus?
Coordinates movement
What is the role of the tectum?
Vision and hearing
What is the role of the reticular formation?
Consciousness
What is the role of the pons?
Relays information to the cerebellum
Some direct connections with cortex
What is the role of the medulla oblongata?
Respiration
Heart rate
Vomiting
Sneezing
What is the role of the thalamus?
Major relay station for sensory information from body
What is the role of the hippocampus?
Memory and spatial navigation
What is the role of hypothalamus?
Hormone synthesis
Temperature
Hunger
Thirst
Sleep
What is the role of ventricles?
Series of inter-connected, fluid filled cavities that cushion the brain and bathe it in cerebral spinal fluid
-Lateral ventricles
-Third ventricle
-Cerebral aqueduct
-Fourth ventricle
What is the role of the caudate nucleus and putamen (basal ganglia)?
Planning movement
Cognition
Emotion
Diagram to show the ventricular system
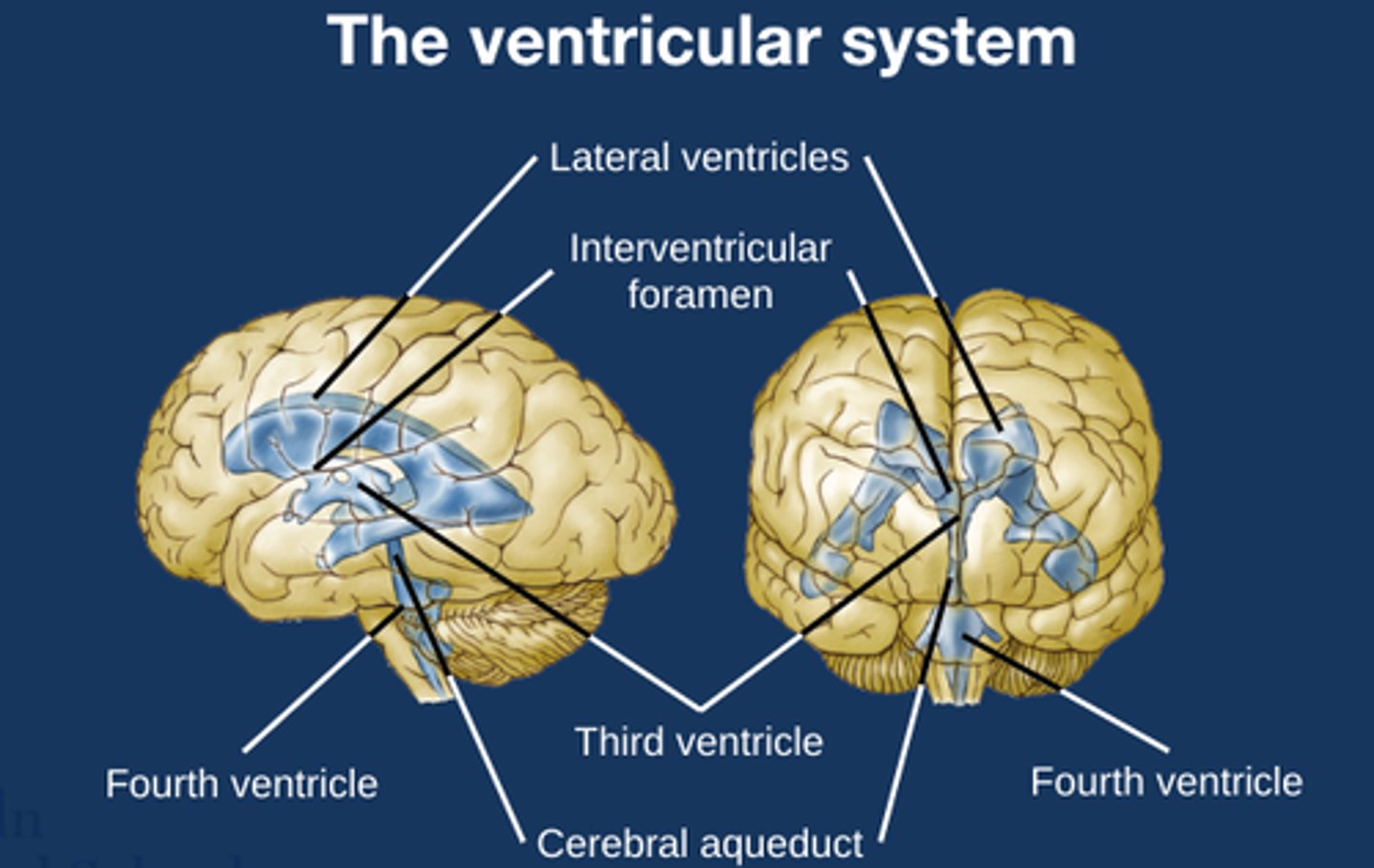
What are ventricles filled with?
Cerebral spinal fluid
How is CSF produced?
Produced in choroid plexus
Approx 150mL of CSF is exchanged 3 times each day
We produce approx 500mL of CSF every day
What is the role of CSF?
Colour-less liquid that baths the brain
Assists in circulating substances
Provides cushioning
Absorbs shock
What is the choroid plexus?
A group of cells that line ventricles
Produces CSF and then induces CSF circulation
Medium of exchange between the extra cellular fluid and the bloodstream
What is the role of the inter-ventricular foramen?
Connection between lateral ventricle and the third ventricle
Allows CSF circulation
How does CSF circulate?
Lateral ventricles →
Interventricular foramen →
Third ventricle →
Cerebral aqueduct →
Fourth ventricle →
Subarachnoid space (around the brain and spinal cord) and central canal (in the spinal cord).
CSF then gets reabsorbed into the bloodstream via the arachnoid villi in the dural sinuses, completing the cycle.
What is hydrocephalus?
Accumulation of CSF
Causes enlarged ventricles
Which vertebral levels is safe for CSF sampling in adults?
L3-L4
L4-L5
Which vertebral levels is safe for CSF sampling in infants?
At or below L4-L5
How does CSF enter the cisterns and subarachnoid space?
Via a series of apertures
Occurs before being circulated upwards
How is CSF reabsorbed?
Arachnoid granulations
What is the arterial supply of the brain?
The internal carotid arteries (anterior circulation)
The vertebral arteries (posterior circulation)
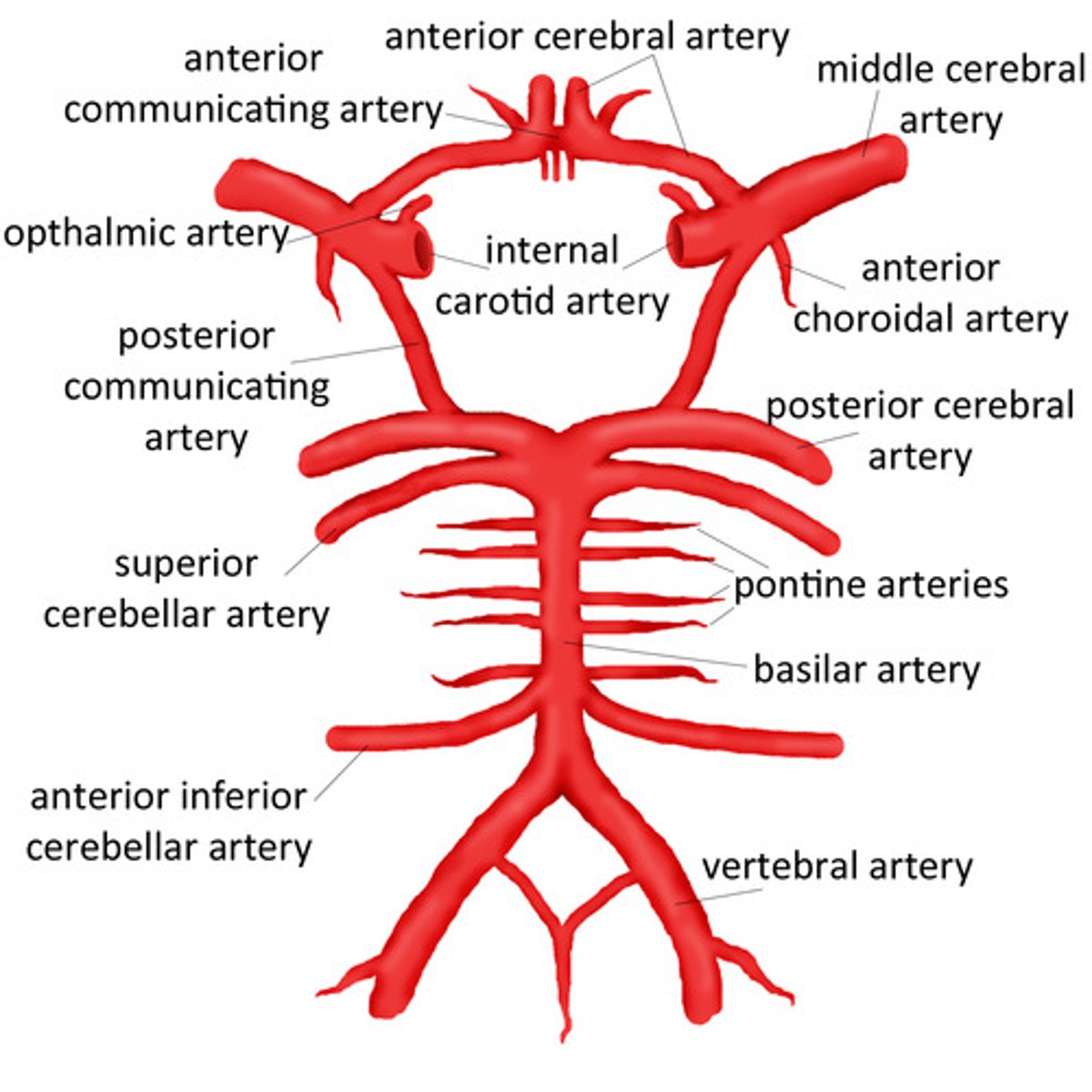
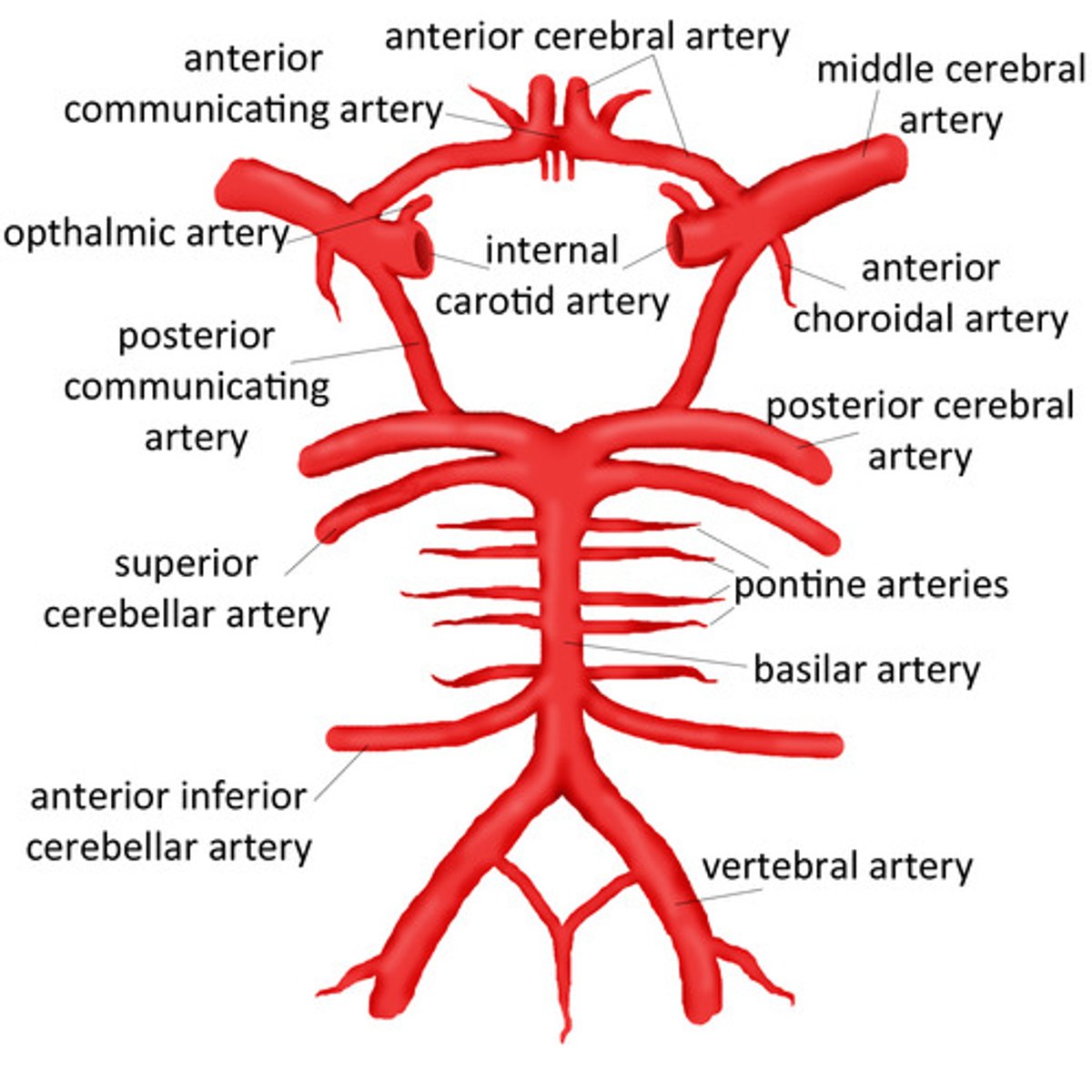
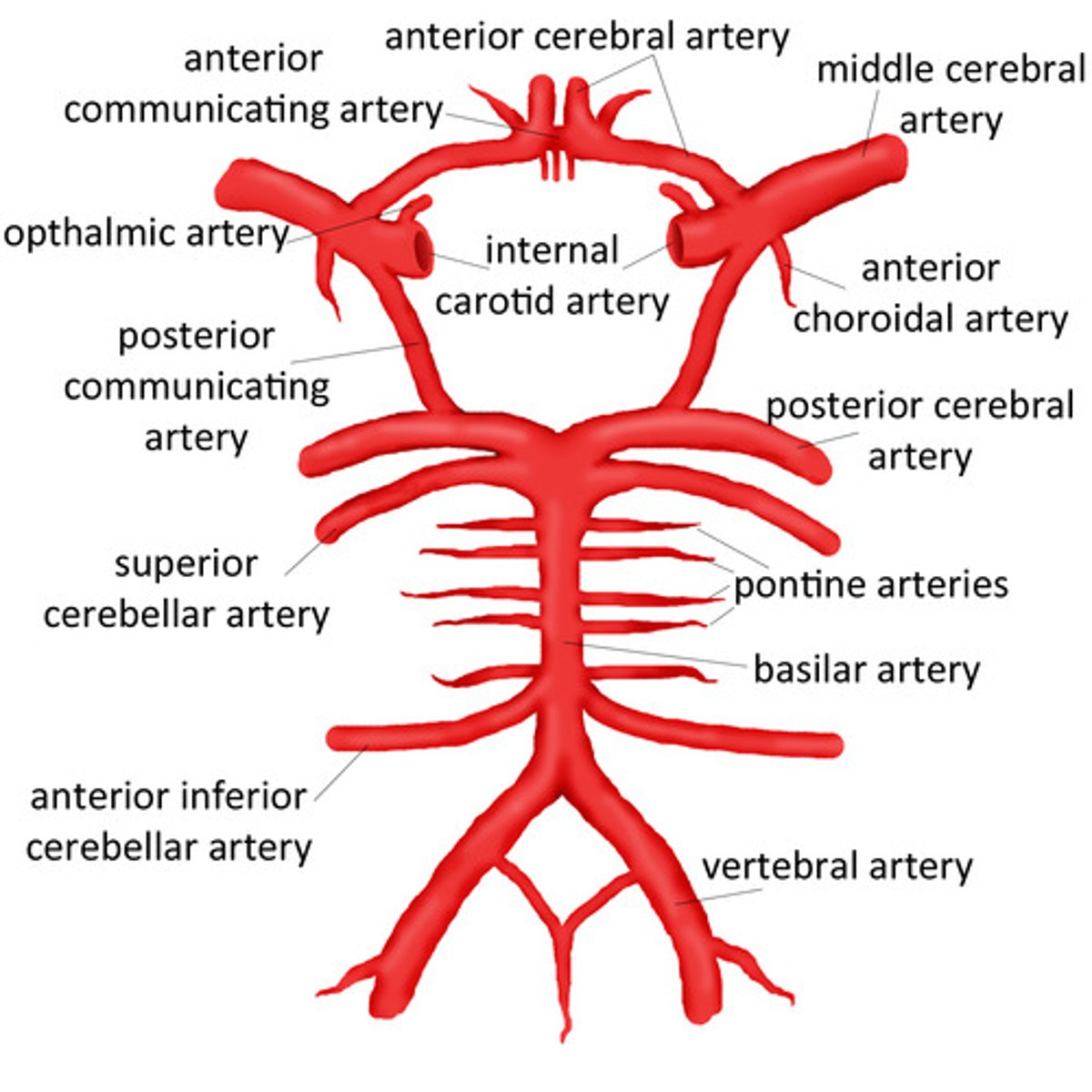
What are the terminal branches of the internal carotid artery?
Anterior cerebral arteries
Middle cerebral arteries
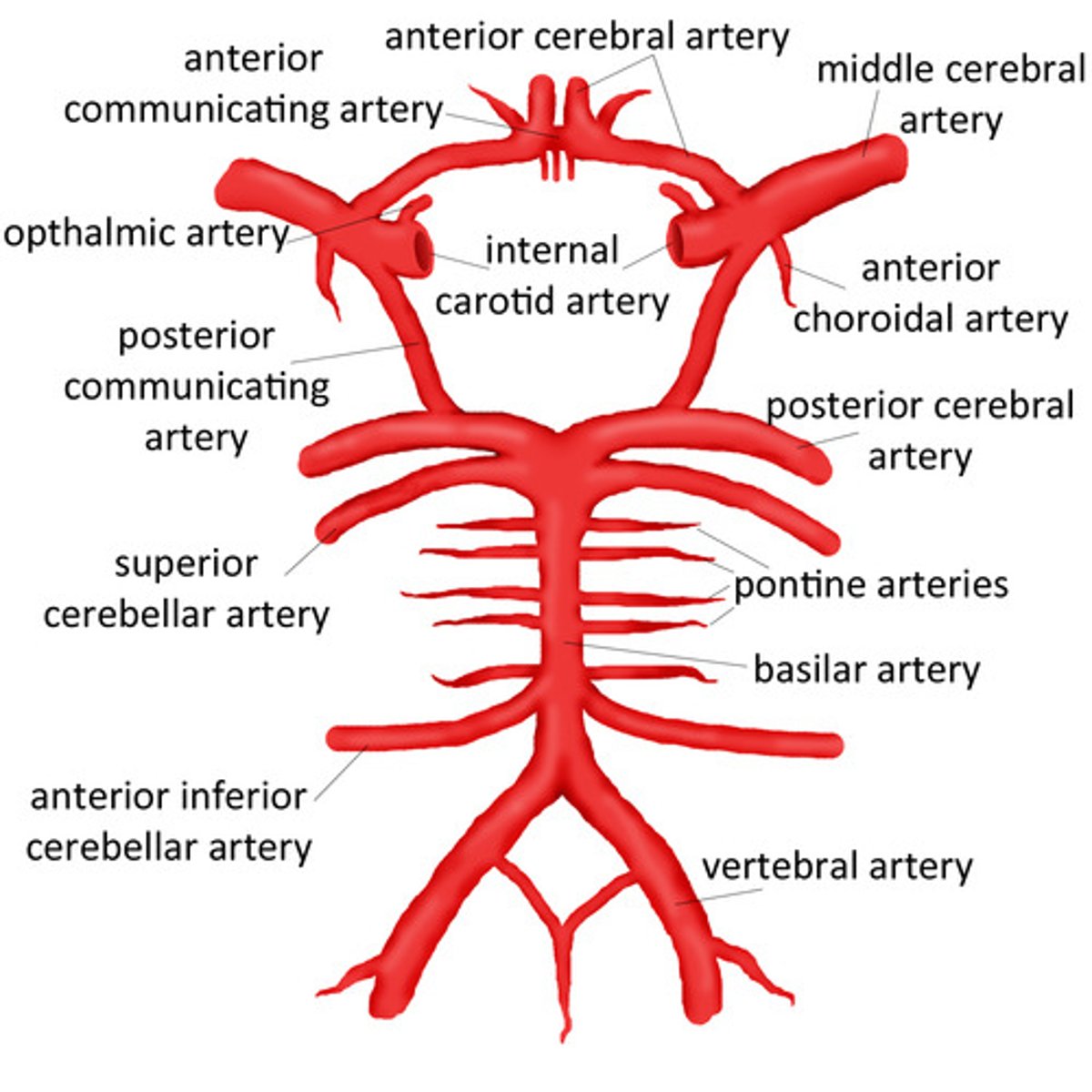
What do the vertebral arteries form?
Merges to form the basilar artery
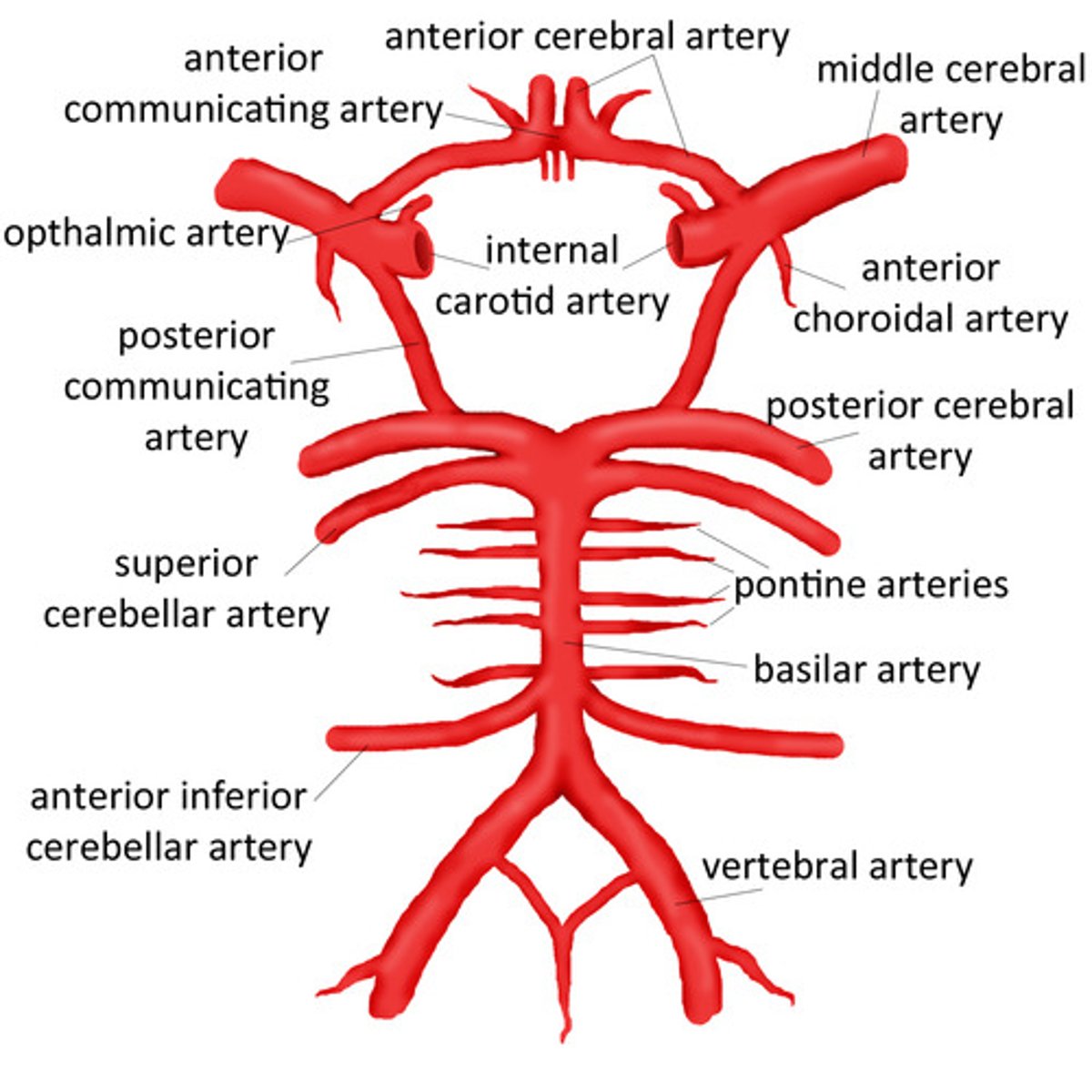
What does the basilar artery give rise to?
Branches:
Anterior inferior cerebral arteries
Pontine arteries
Superior cerebral arteries
Terminates with posterior cerebral arteries
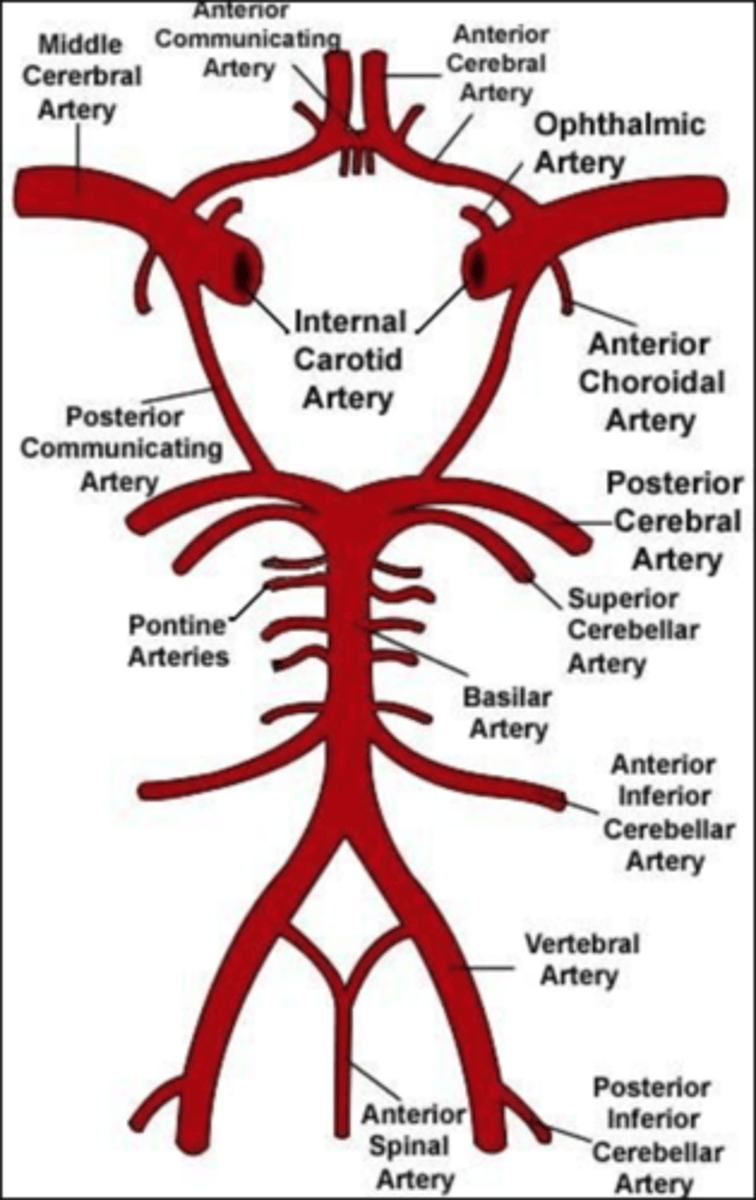
How does the brain have dual blood supply?
Two pairs of vessels: internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries
What is the circle of Willis?
Major anastomosis for the brain
Connects posterior and anterior circulation using anterior communicating artery and posterior communicating artery
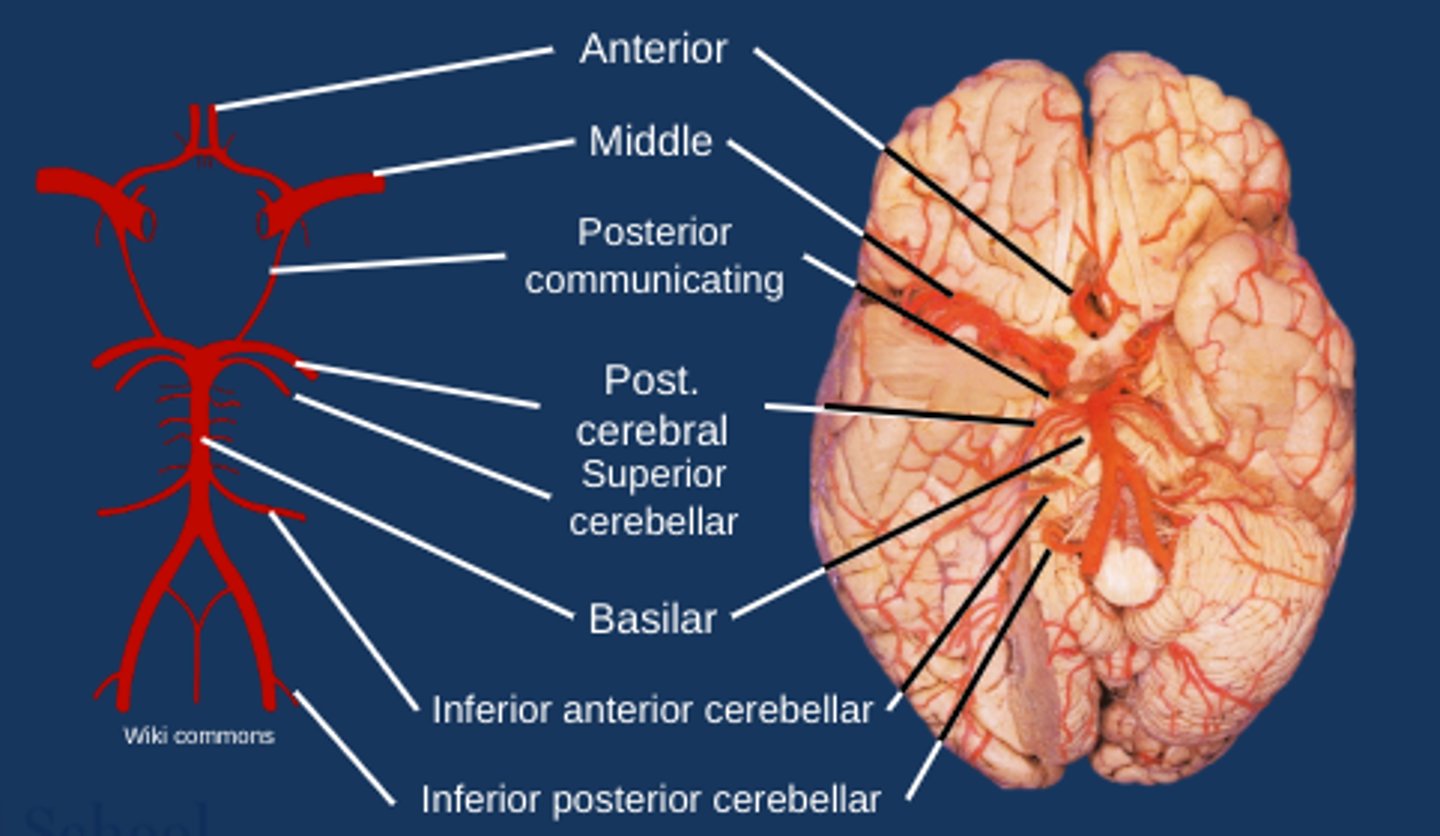
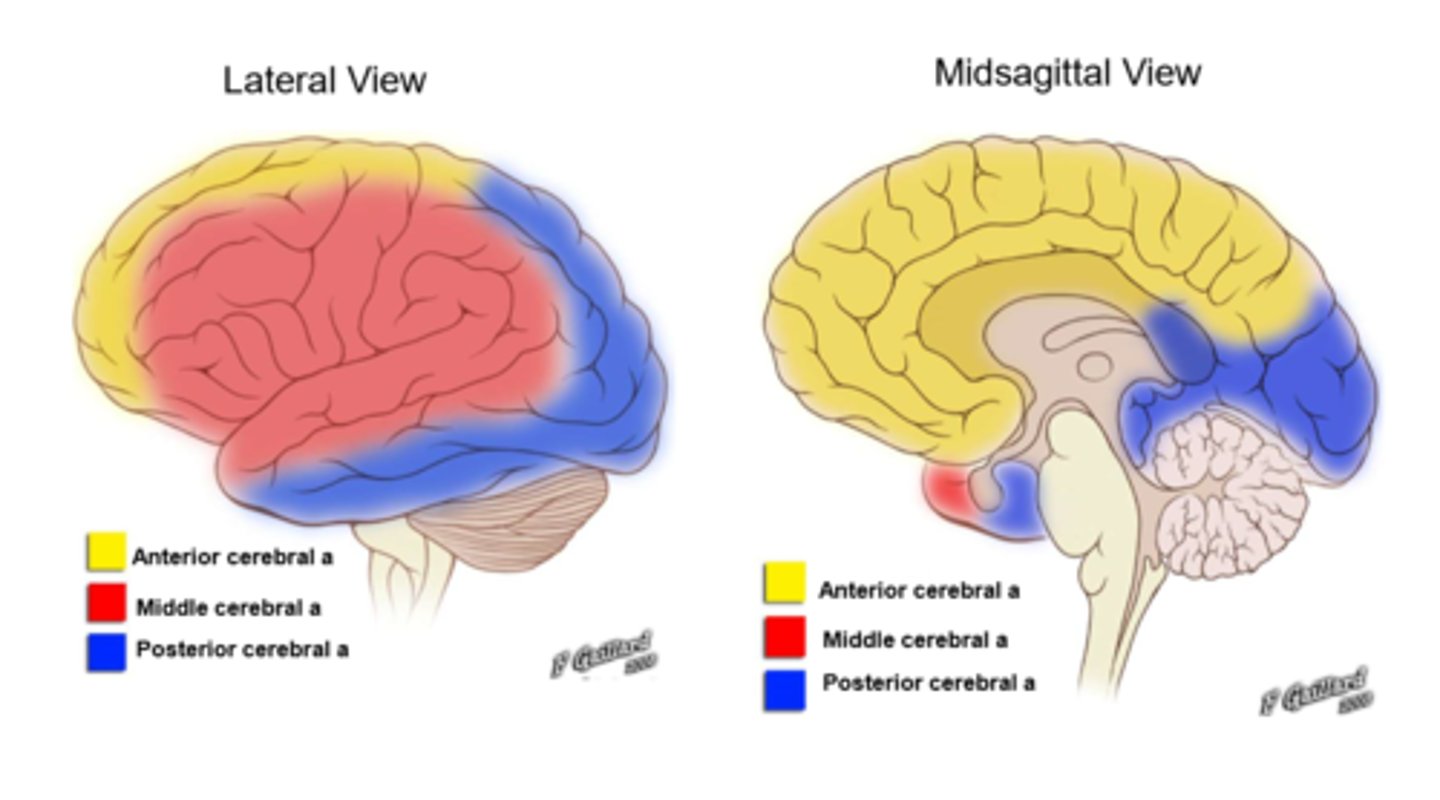
Diagram to show arterial territories
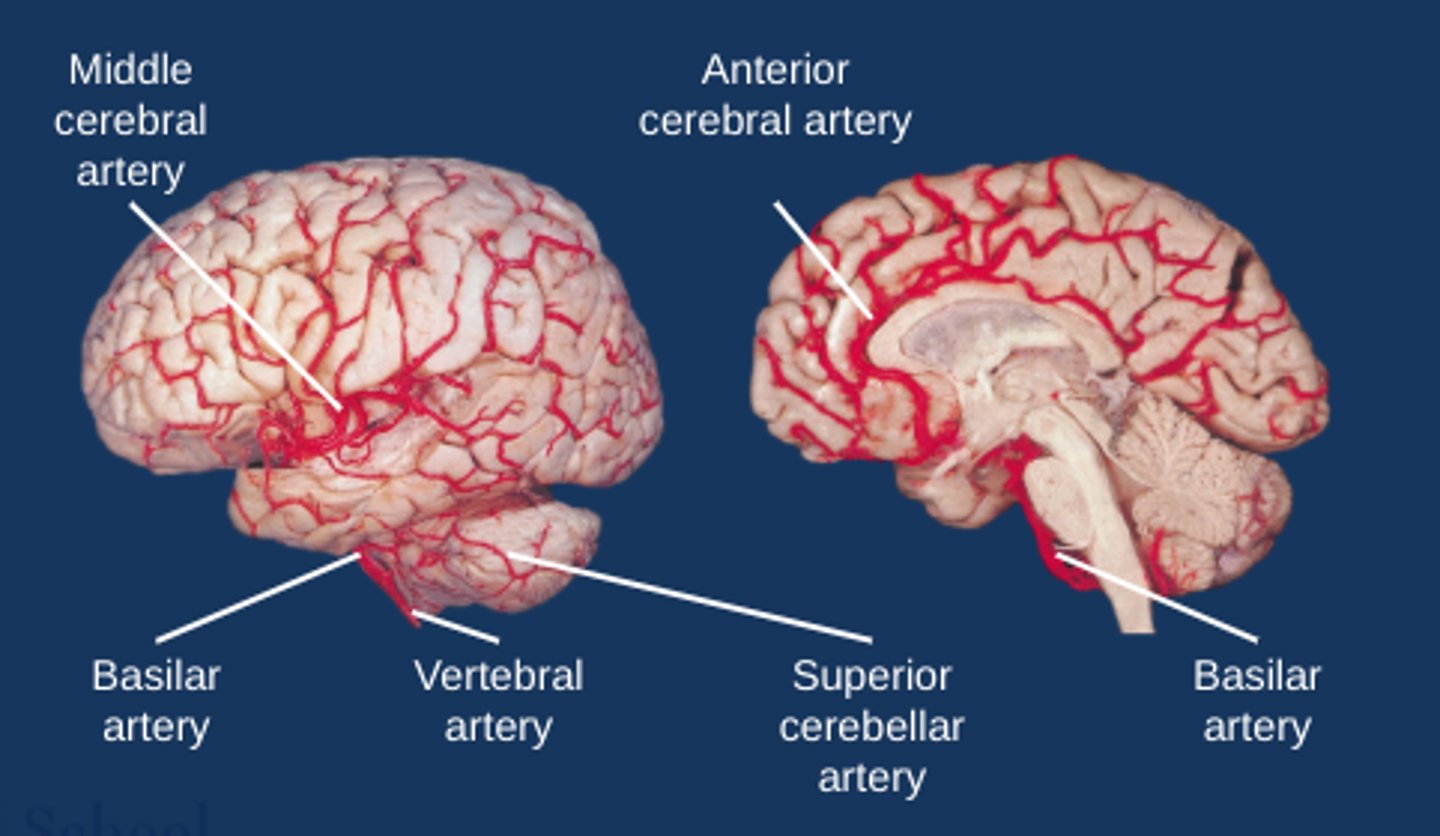
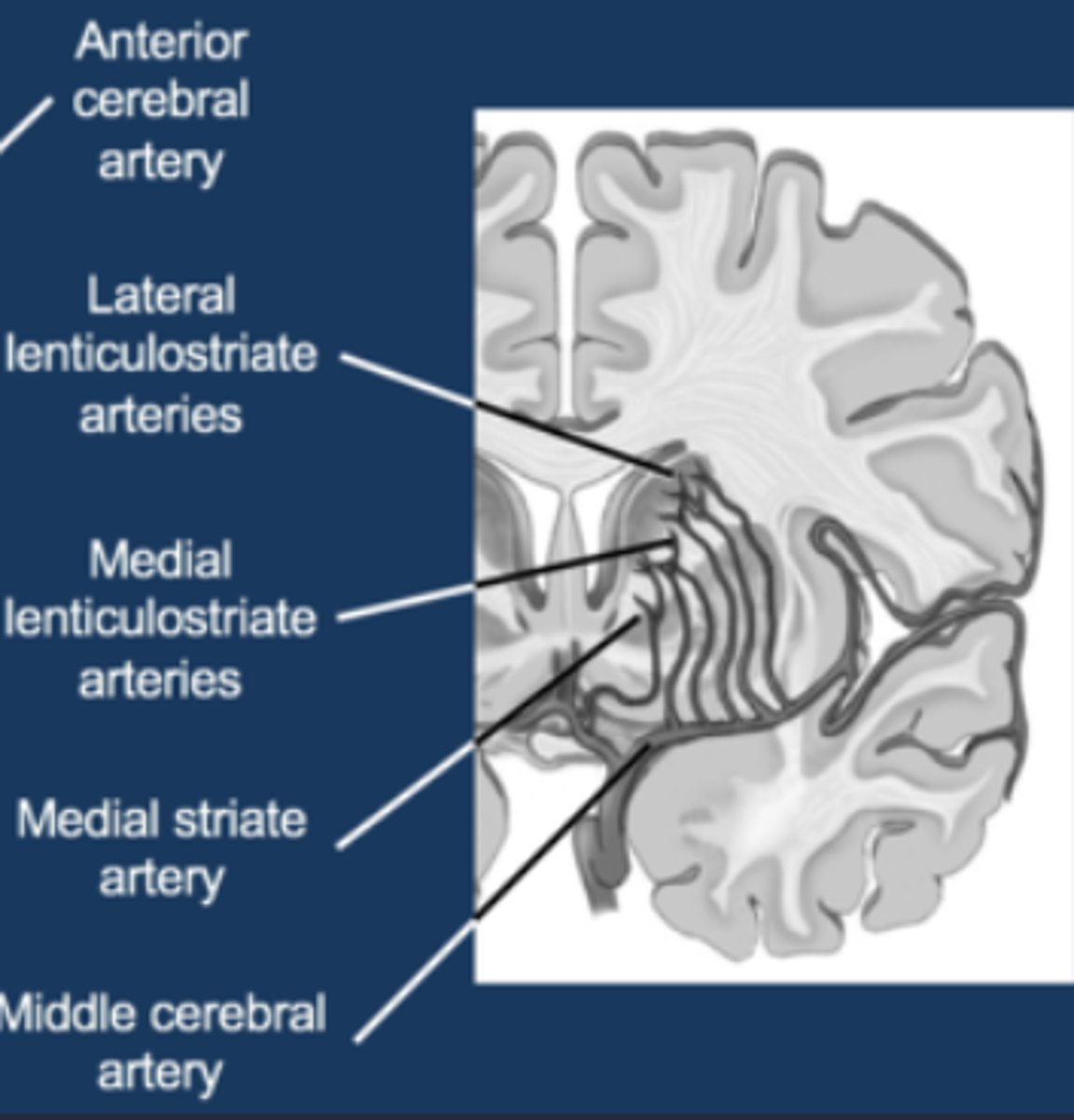
Diagram to show subcortical blood supply
What do the vertebral arteries specifically supply?
Posterior aspect of the brain
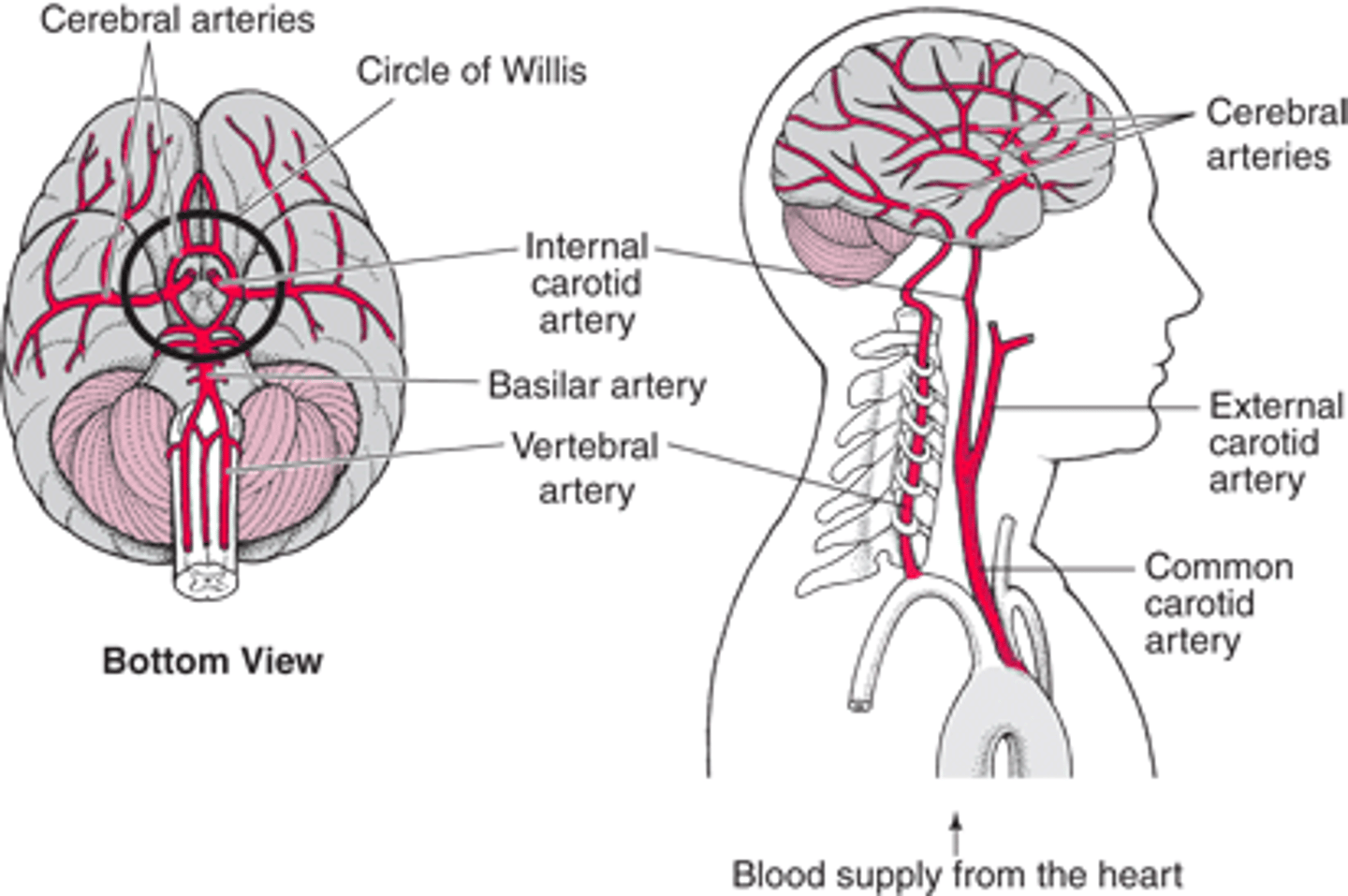
What do the posterior inferior cerebellar arteries supply?
Posterior cerebellum
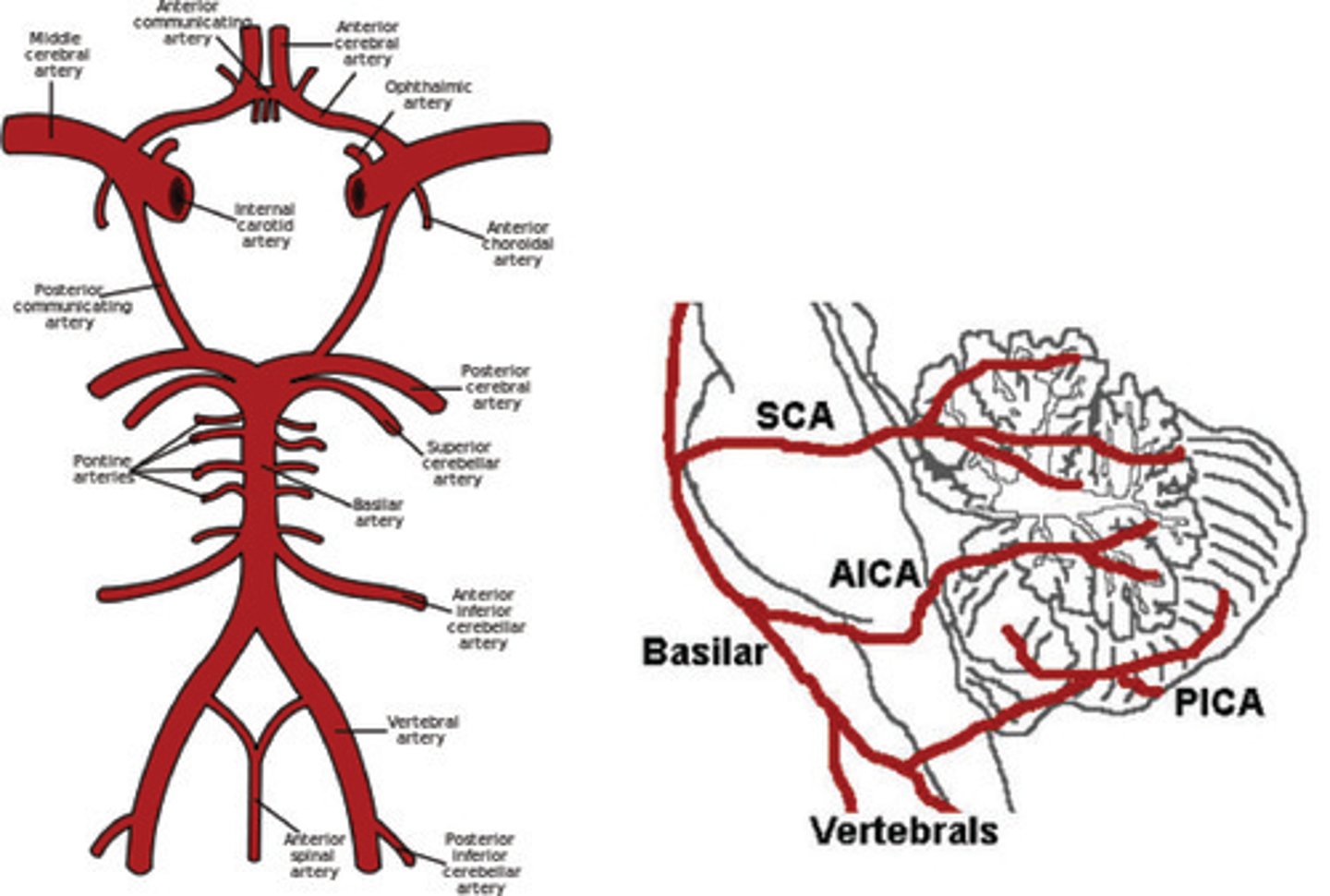
What does the basilar artery supply?
Brainstem
What do the inferior anterior cerebellar arteries supply?
Anterior cerebellum
What do the superior cerebellar arteries supply?
Cerebellum
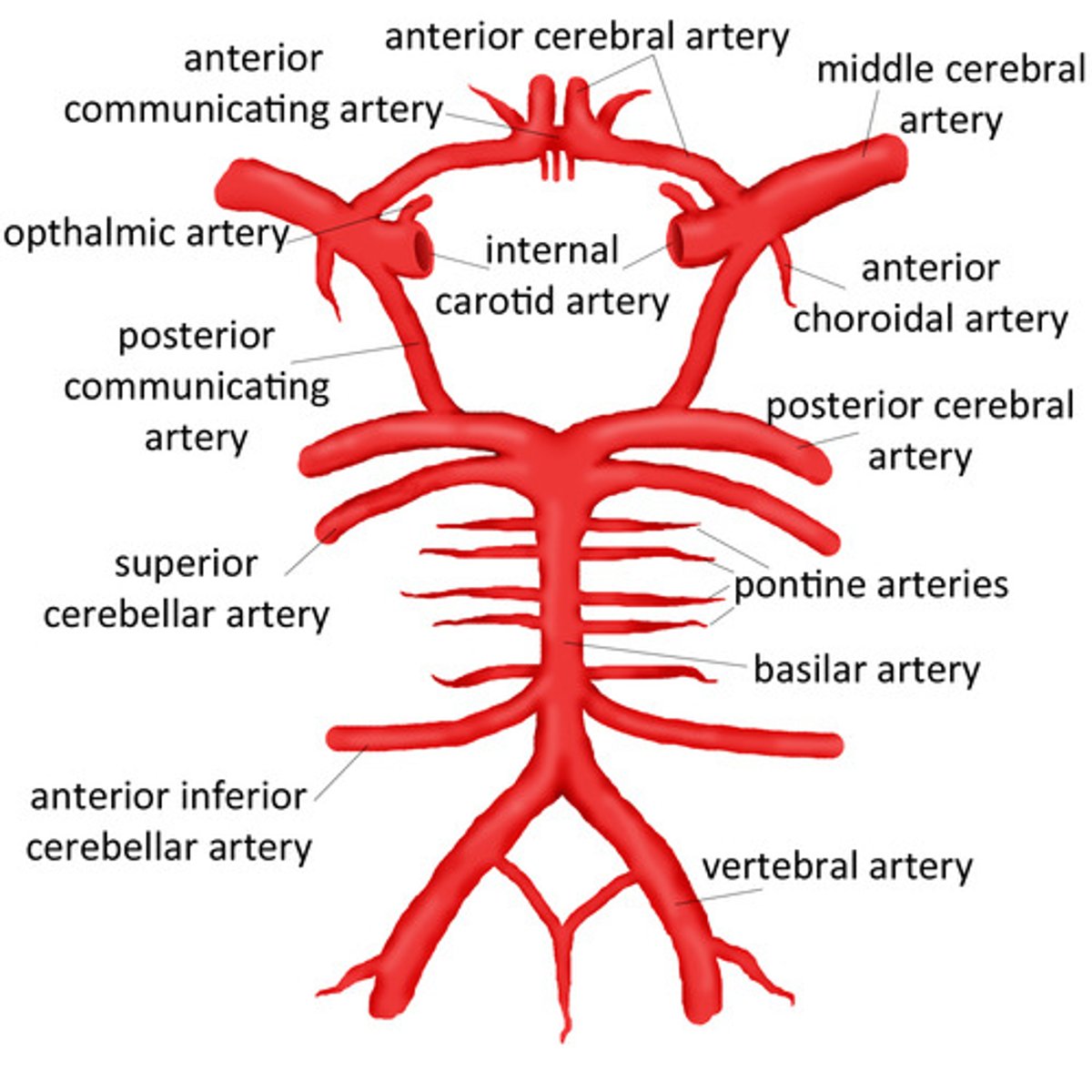
What do the posterior cerebral arteries supply?
Medial occipital
Inferior temporal lobe
Hippocampus
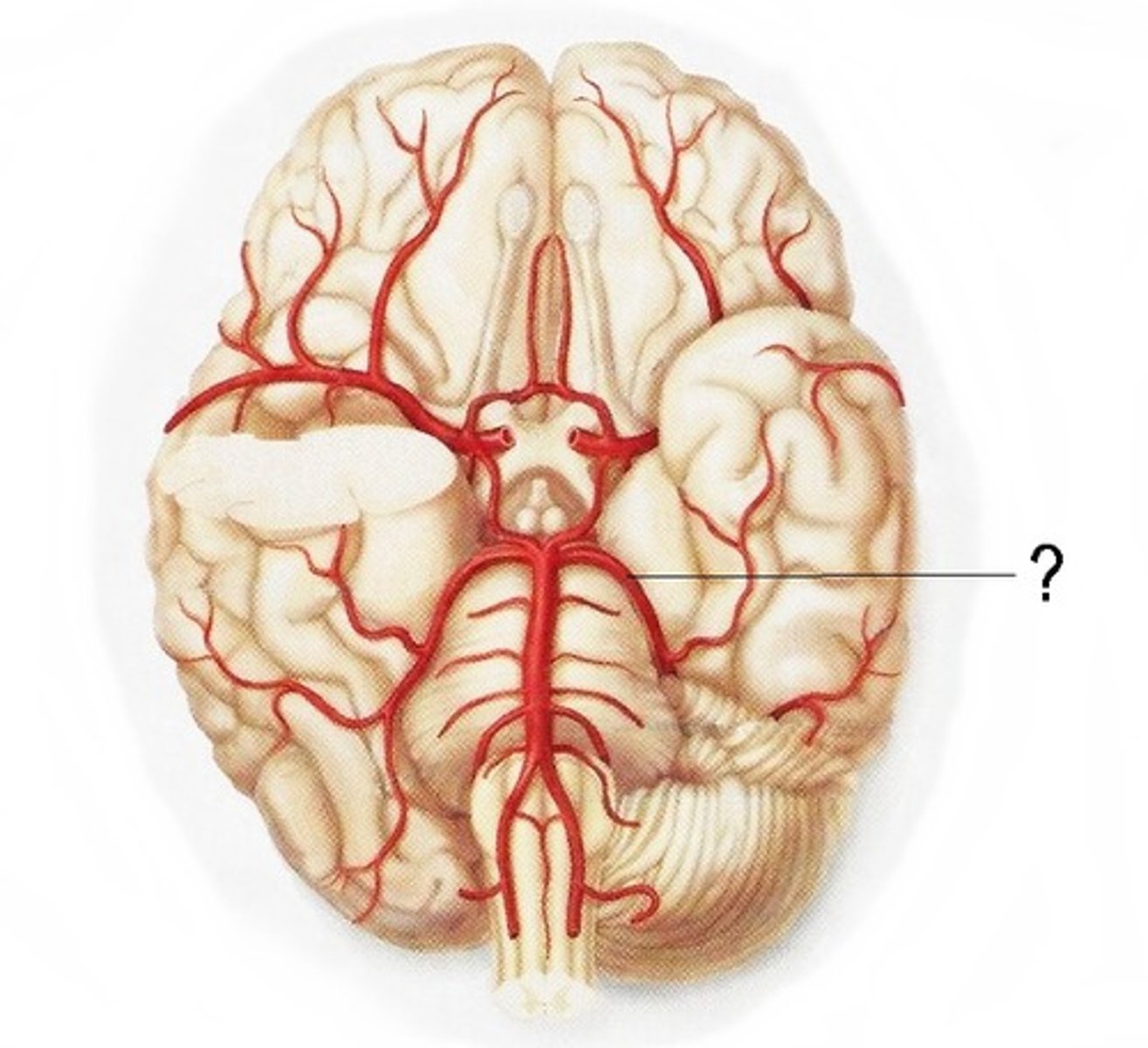
What do the carotid arteries supply?
Anterior aspect of the brain
What do the carotid arteries divide into?
Anterior cerebral arteries
Middle cerebral arteries
Lenticulostriate arteries
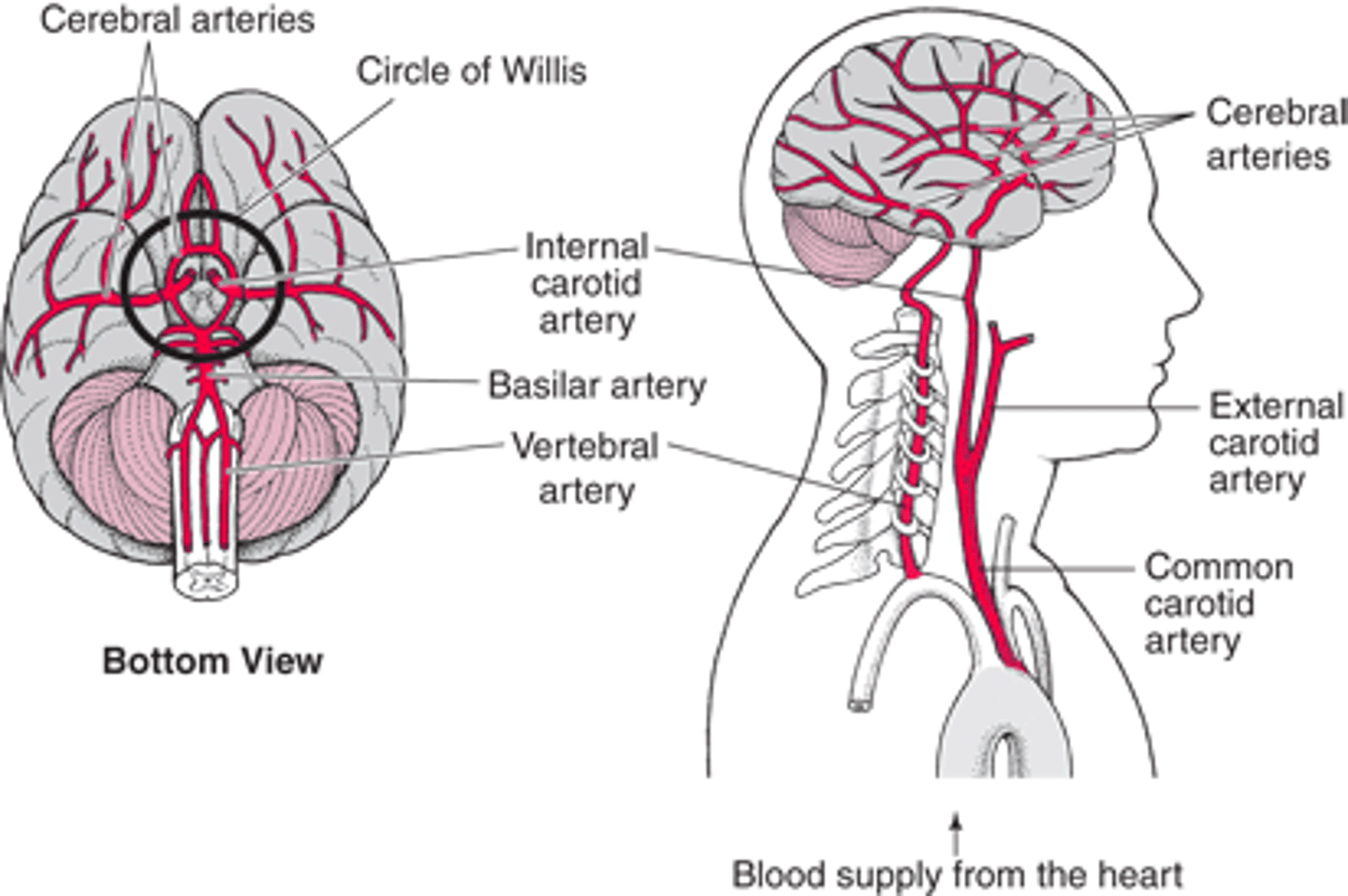
What do the anterior cerebral arteries supply?
Medial frontal and superior parietal lobe
Corpus callosum
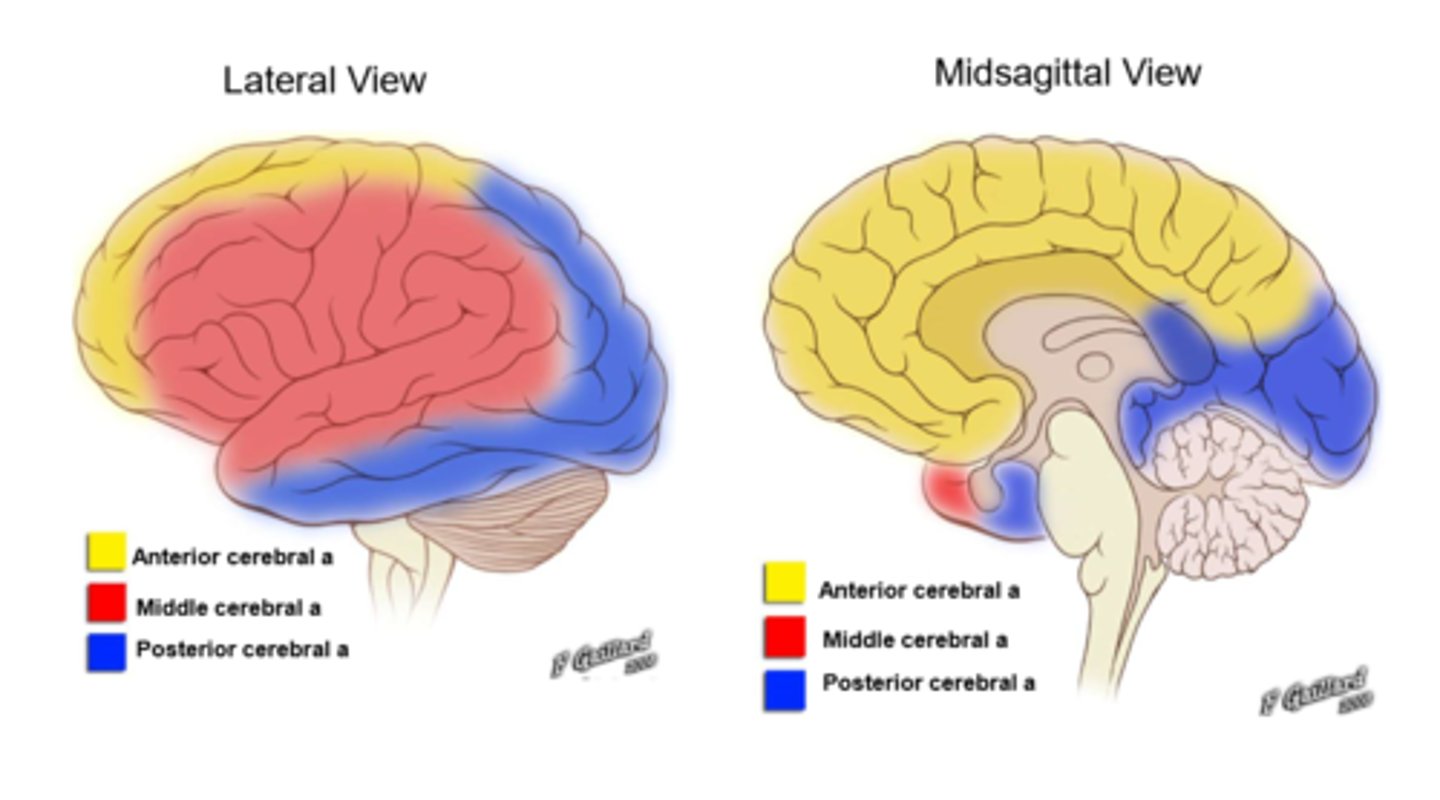
What do the middle cerebral arteries supply?
Lateral temporal and parietal lobes
Posterior frontal lobe
What are lenticulostriate arteries?
Subcortical structures
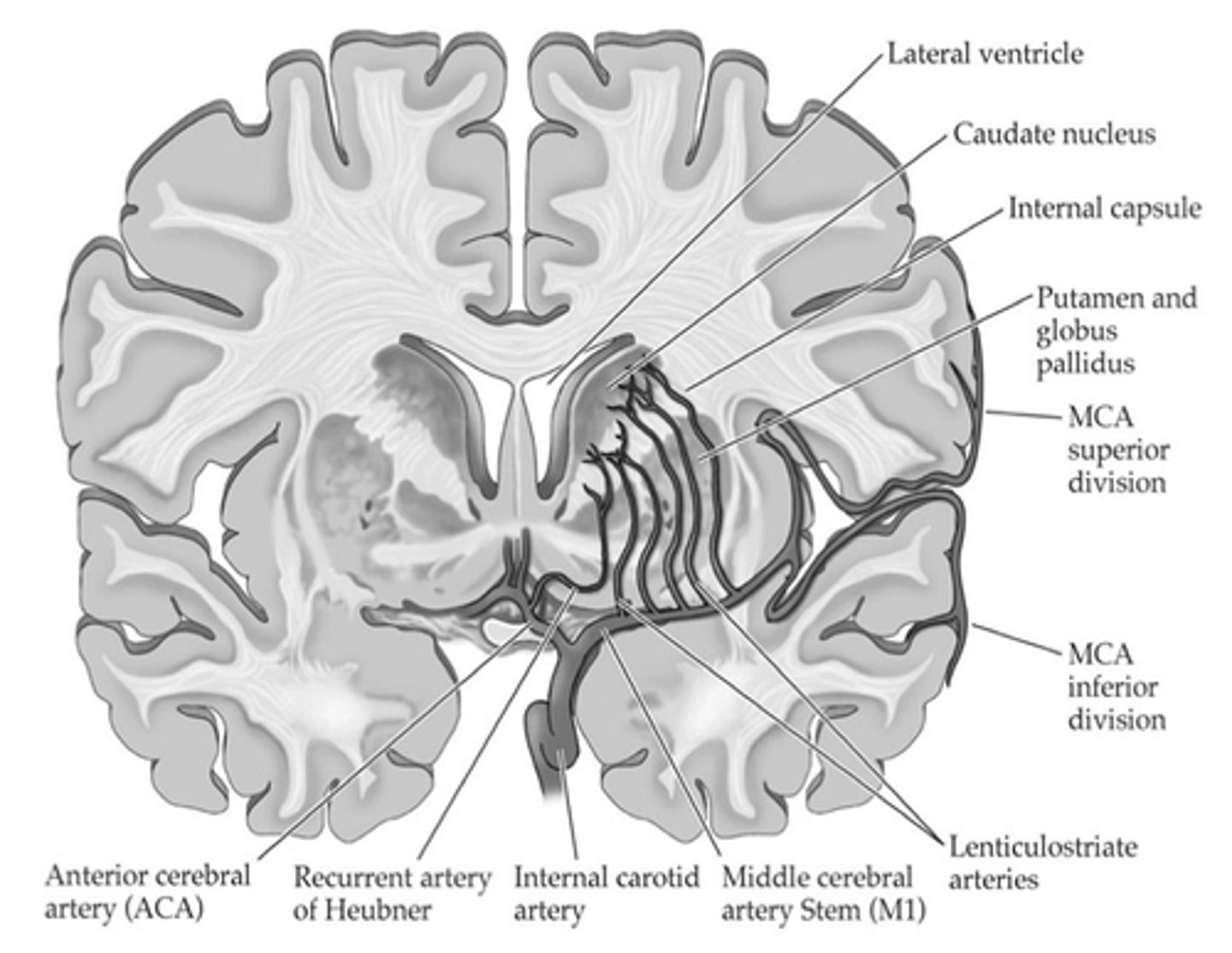
Diagram to show surface venous drainage of the brain
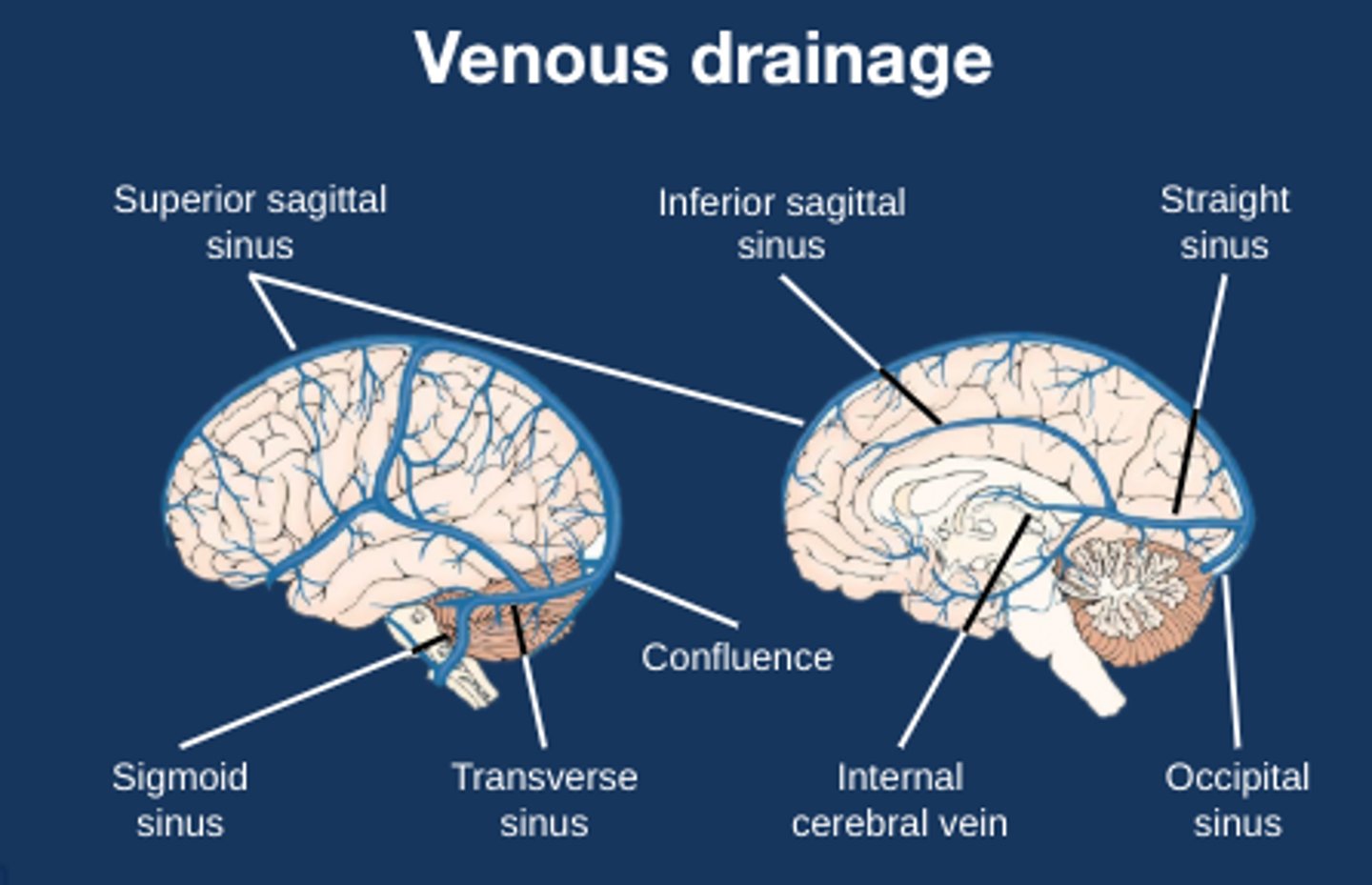
Diagram to show medial venous drainage of the brain
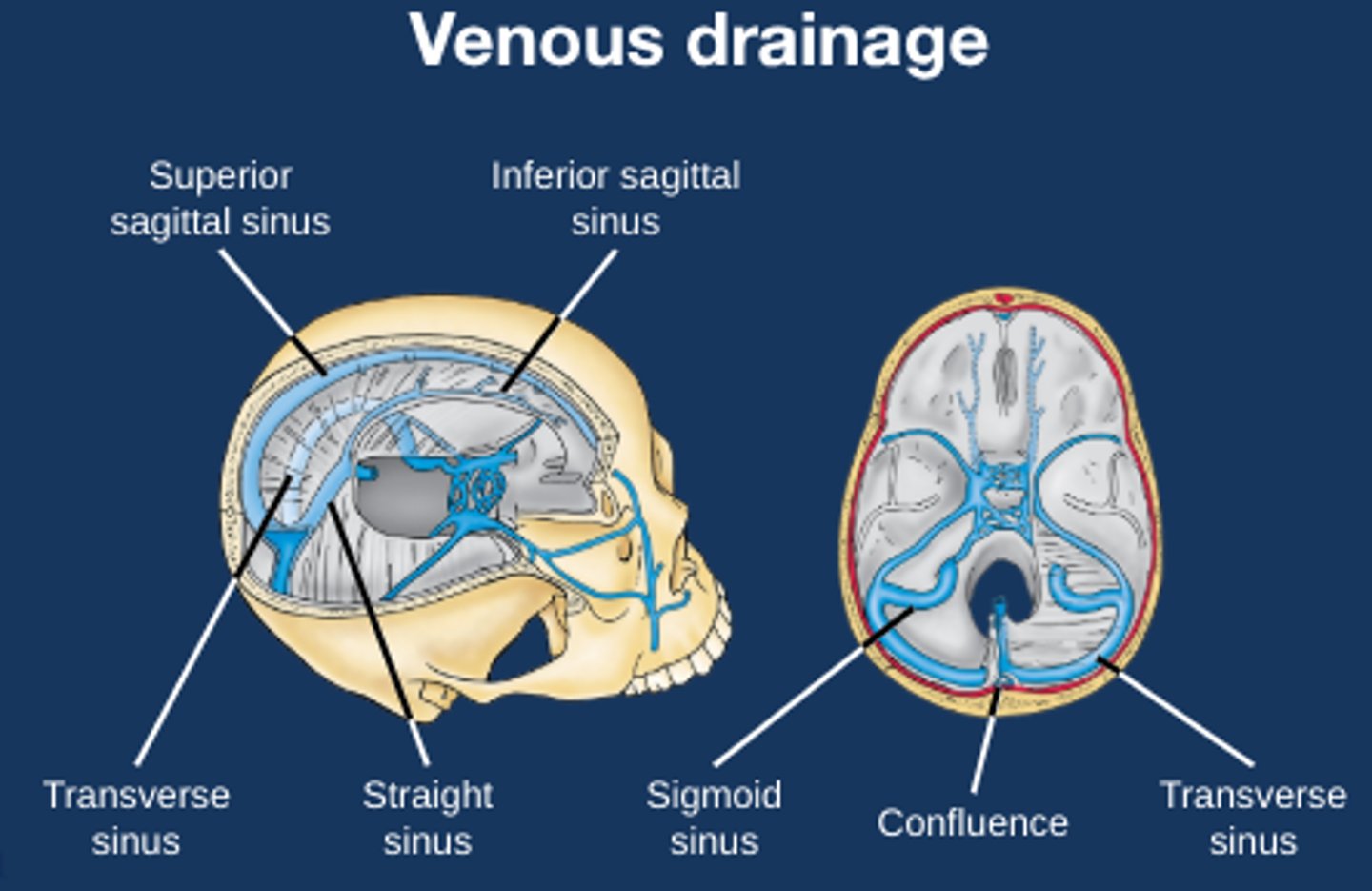
Which sinuses do surface venous drainage?
Superior sagittal sinus
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse sinuses
Sigmoid sinus
Which sinuses and veins do medial venous drainage?
Inferior sagittal sinus
Straight sinus
Internal cerebral veins
What is the role of the blood brain barrier?
An interface that ensures the circulatory system is kept separate from CSF
Which cell junction forms the blood brain barrier?
Tight junctions
How do tight junctions form in the blood brain barrier?
Blood vessels are composed of a layer of endothelial cells
When two cells touch their membranes together create a barrier
This barrier only allows passage of selected material between the blood and the brain
Which molecules are allowed through the blood brain barrier?
Small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose or select amino acids)
Which cells are responsible for maintaining the BBB?
Pericytes and astrocytes
What surrounds endothelial cells?
Basement membrane