nitrogen cycle
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
give 5 examples of nitrogen containing molecules:
amino acids
DNA
RNA
ATP
ADP
what is the significance of the N2 cycle?
shows how different microorganisms are needed to convert N2 gas into nitrogen-containing compounds that can be absorbed by plants and animals
give 3 conditions required for decomposition:
warm temperature
moisture
oxygen
what is a detritivore? give 4 examples:
organism that ingests/digests dead/decaying organic matter internally
e.g. worms, millipedes, woodlice, slugs
what is a saprobiont? give an example:
microorganism which secretes enzymes to decompose N containing compounds externally and absorbs simpler molecules
e.g. microbes, primarily bacteria and fungi
give the stages of the nitrogen cycle:
nitrogen fixation
ammonification
nitrification
denitrification
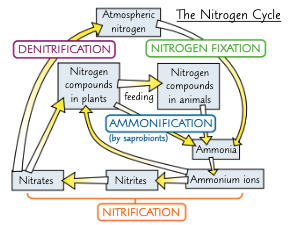
describe the process of nitrogen fixation:
free living nitrogen-fixing bacteria fix N2 → NH3/NH4+
mutualistic nitrogen fixing bacteria (e.g. Rhizobium) in root nodules of leguminous plants fix N2 into NH3 which is converted into amino acids
in turn, the plant provides the bacteria w/ carbohydrates
abiotic processes - lighting, artificial fertilisers, Haber process - can also fix N2
what is nitrogen-fixation?
the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen gas into nitrogen containing compounds like ammonia
describe the process of ammonification:
death/excretion of living organisms releases nitrogen-rich containing substances e.g. urea, proteins, nucleic acids, vitamins
saprobionts decompose these into ammonium ions (NH4+)
NH4+ can now be absorbed (AT through root hair cells) and assimilated by plants
what is ammonification?
conversion of organic N2 containing compounds in dead organisms or waste into NH3 or NH4+ ions by saprobionts
describe the process of nitrification:
nitrifying bacteria oxidise NH4+ ions to nitrite ions - NO2-
these are then oxidised again into nitrate ions - NO3-
(most nitrogen taken up by plants is in the form of nitrate ions)
what is nitrification?
NH3 and NH4+ are oxidised to NO2- then NO3- which plants can absorb via AT and assimilate
what is denitrification?
the conversion of NO3- ions back into N2 gas by anaerobic denitrifying bacteria
what conditions might allow denitrification to take place?
anaerobic conditions
how might excessive denitrification -vely impact plant growth? what farming techniques can prevent this?
excessive denitrification may lead to stunted growth as prevents the plant from making proteins
to prevent this: frequently aerate the soil, keeping conditions aerobic