Lab Exam 1 a Questions Set to Study for the Lab Exam 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Why are agar plates incubated upside-down?
The prevent condensation from falling on the plates and disrupting the formation of the isolated colonies. Also prevents contaminants from setting on the agar.

Why are agar plates labeled on the bottom side (side containing the agar medium)?
In case of a mishap (like plate spillage) plate identity is still maintained.
Bacterial cultures in our lab are classified as this BSL.
BSL-1 or BSL-2
Bacteria are _______ or found everywhere.
ubiquitous

True or false There are many pure environmental and clinical samples.
False. Most cases, cultures are mixed or have multiple types of microbes.
Fungi growing on an agar plate can appear as __.
Large fuzzy (due to spores) colonies
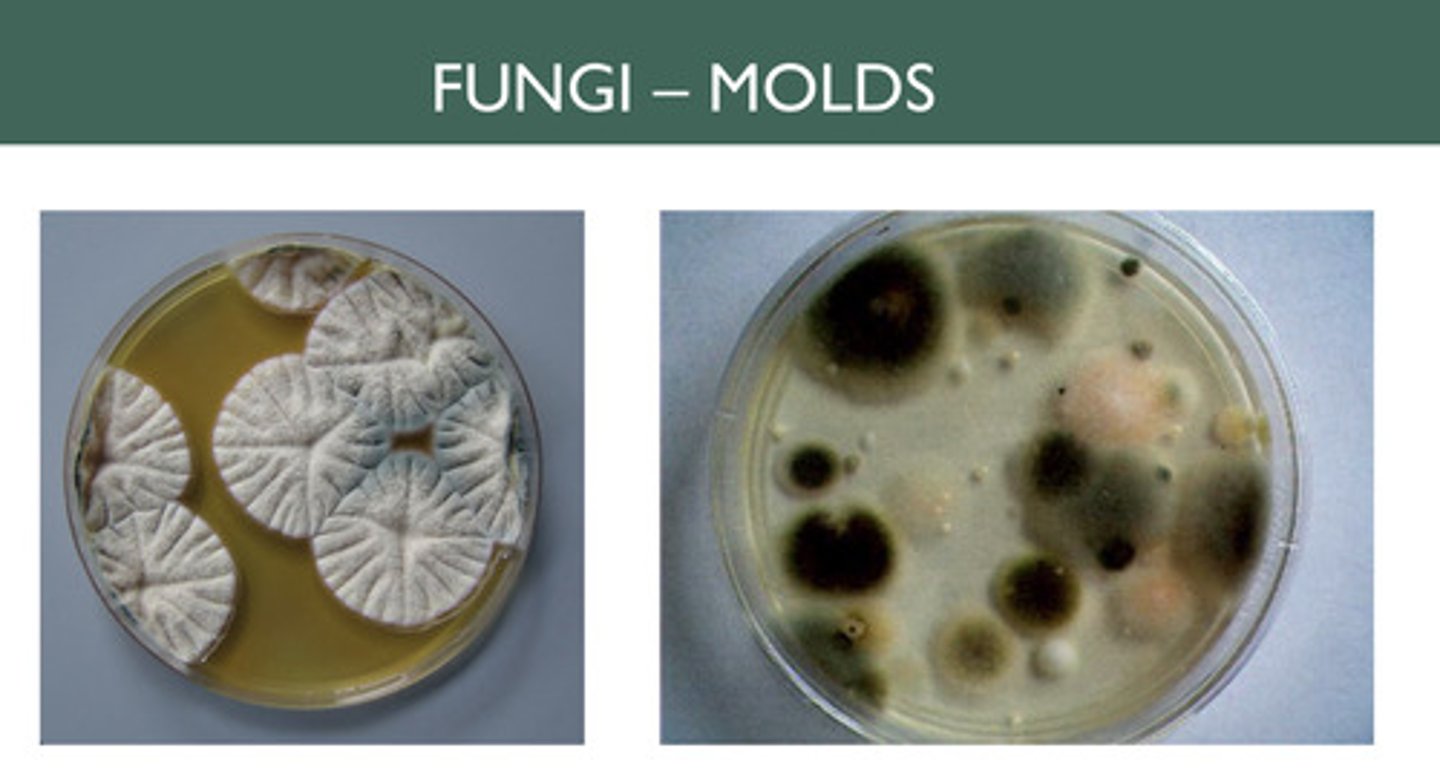
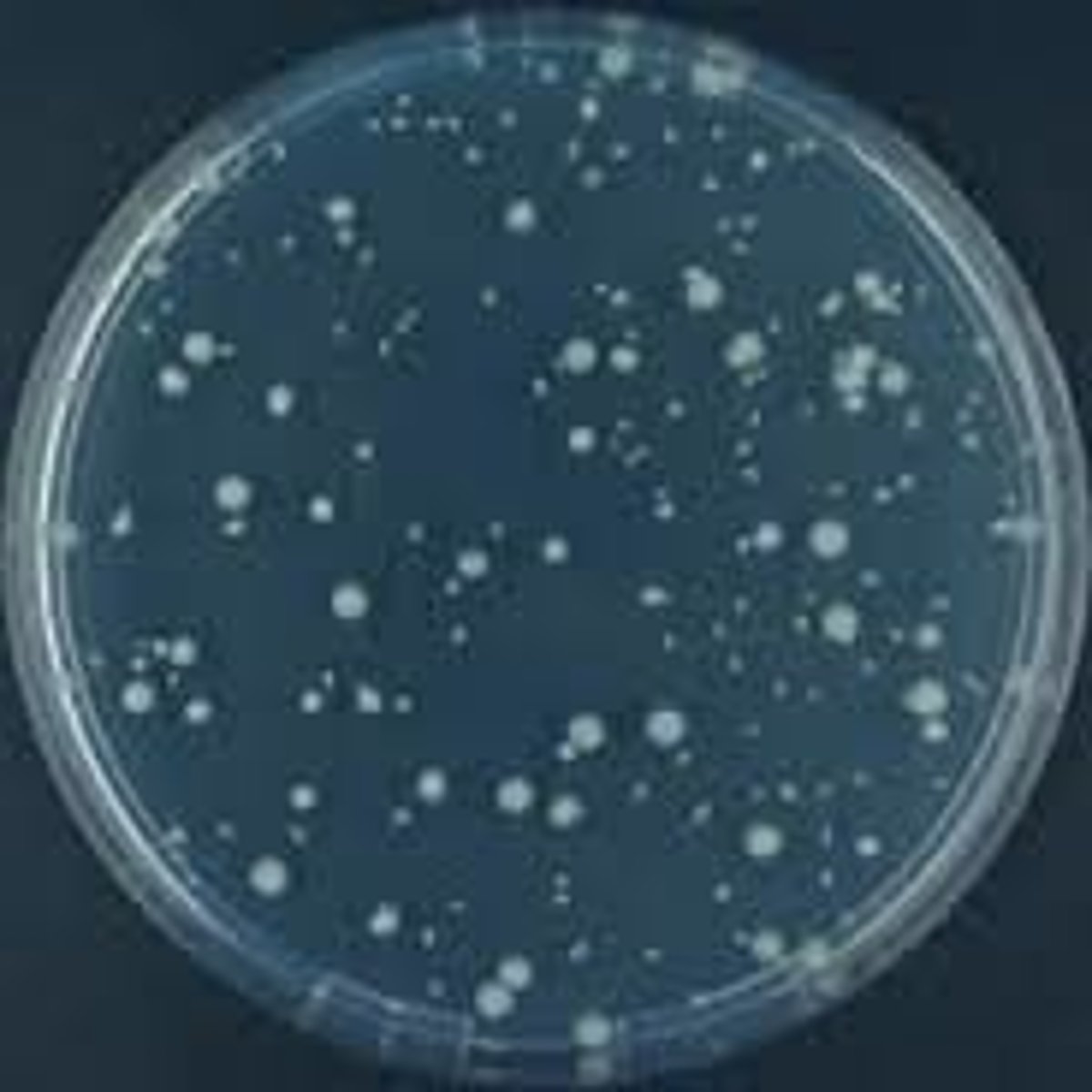
Bacteria growing on an agar plate can appear as __.
Small smooth round colonies with many possible colors
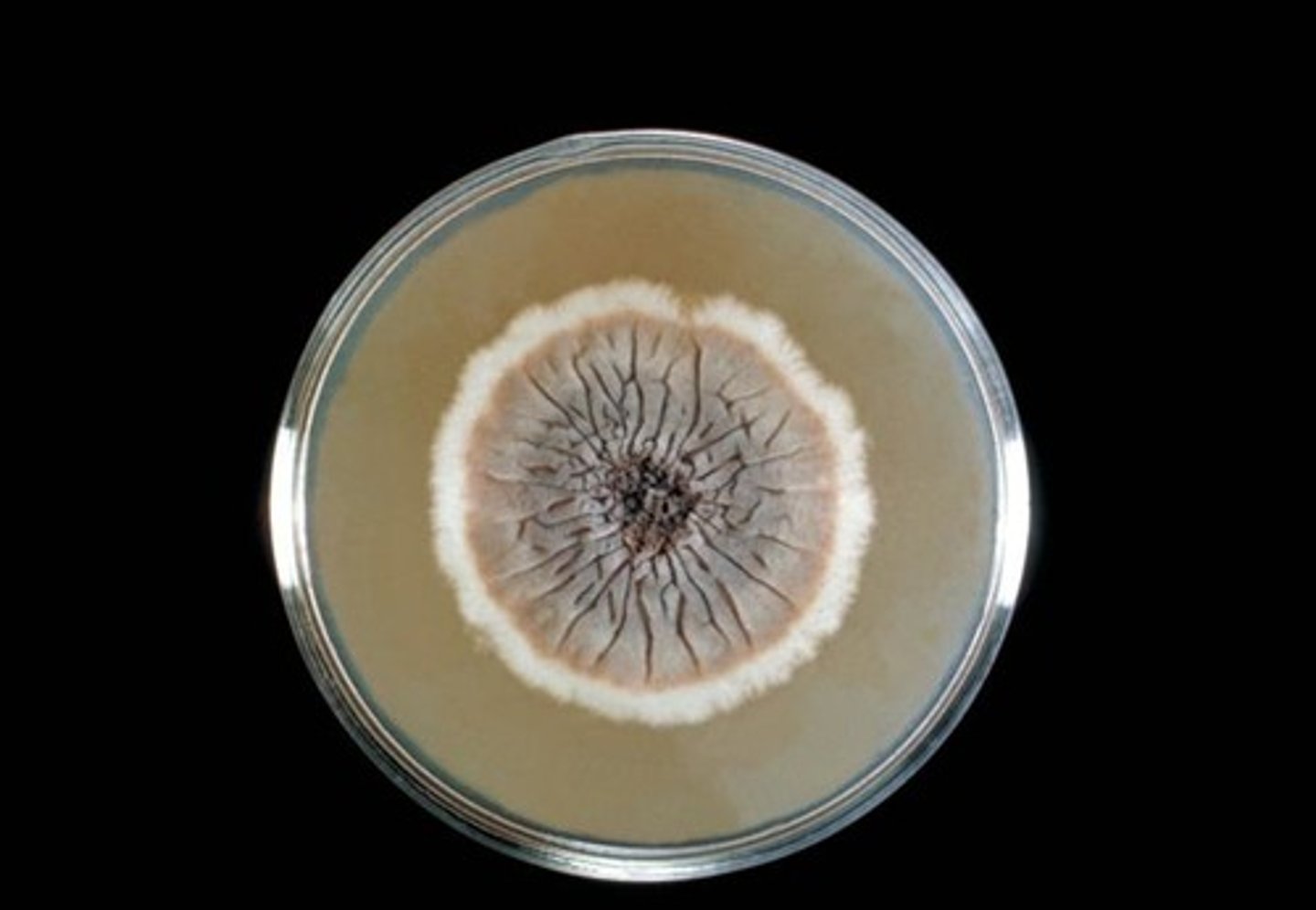
What type of agar medium can be use to select for fungal colonies?
Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA)
What type of agar medium can be used to select for bacterial colonies?
Trypticase Soy Agar (TSA)

What reagents and conditions in the Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) make the agar more suitable for fungi?
It has sugar and is more acidic in pH.

What reagents and conditions in the Trypticase Soy Agar (TSA) make the agar more suitable for bacteria?
It has protein and is more neutral in pH.

What applications use sterile loops?
Transferring of cultures in liquid media and streak plating
What applications use sterile needles?
Transferring of cultures in solid media and making stabs and smears
________ is the liquid form of culture media.
Broth

________ is the solid form of culture media found in a petri dish.
An agar plate
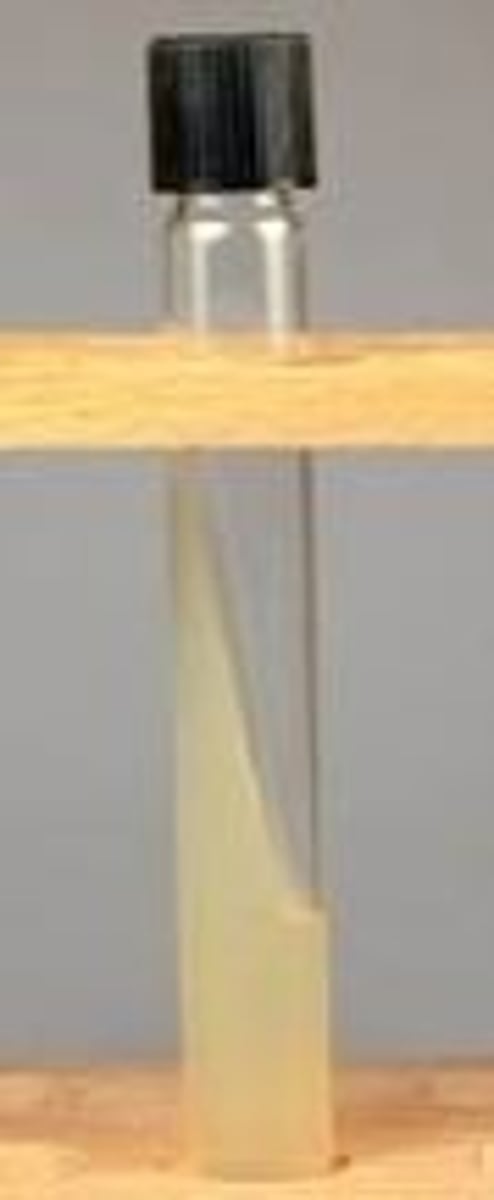
_____ is the solid form of culture media found in a test tube poured at an angle.
A slant

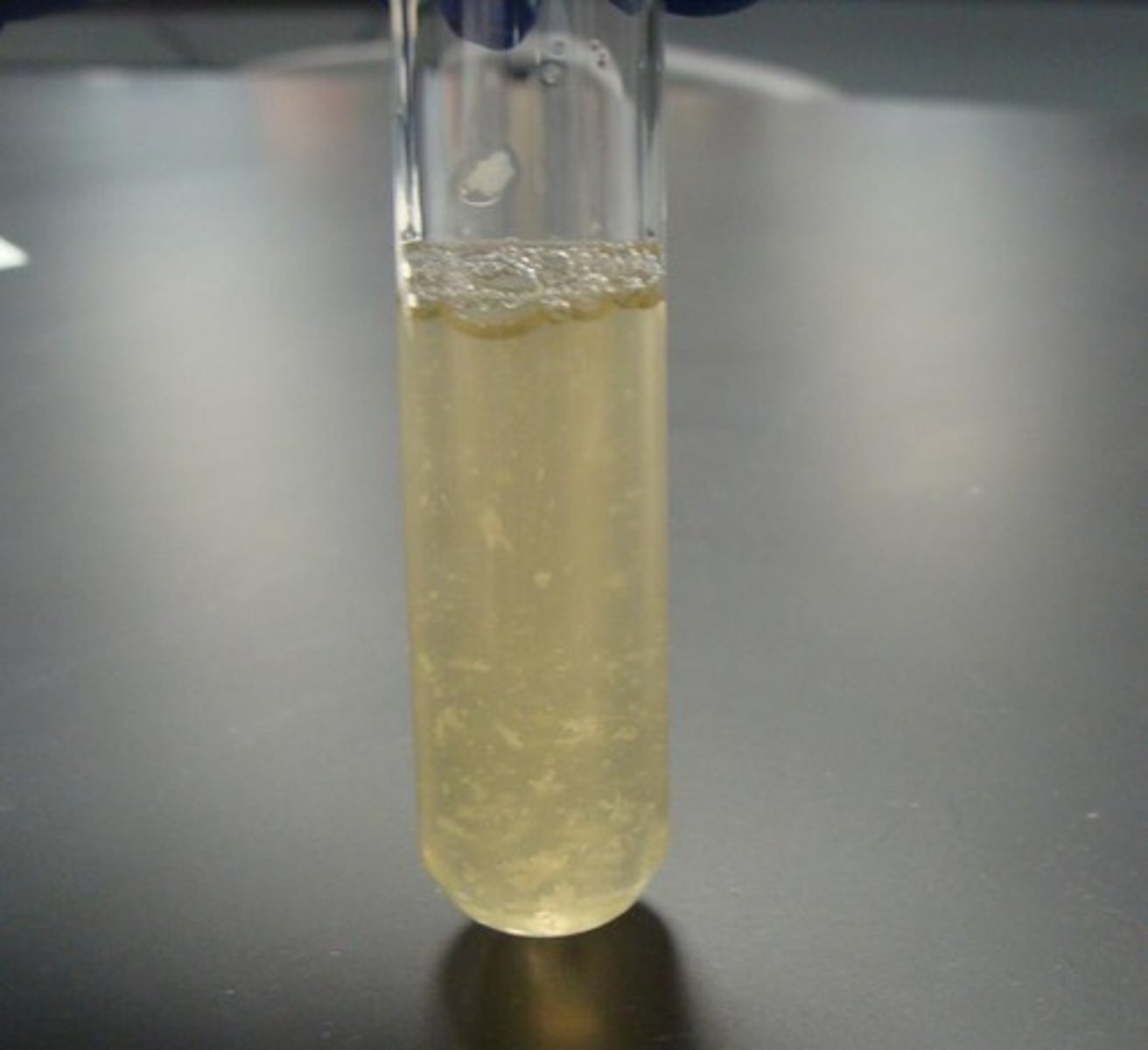
_____ is the semi-solid form of culture media found in a test tube.
Motility agar

Why is agar used for in culture media?
Agar is the solidifying agent (make the broth solid) and is NOT used for nutrition

Why are long term cultures inoculated on agar media versus broths?
The nutrients are harder to extract from agar media so the culture lives longer.
Which type of culture media is used for isolating colonies?
Agar plates
Why is an inoculated culture media placed in an incubator?
To allow the culture to grow/replicate

Why is an incubated culture media placed in the frig?
To slow culture growth
Where (on the hands) is it harder to remove microbes?
Around the thumb, Between the fingers closest to the palm and under the nails
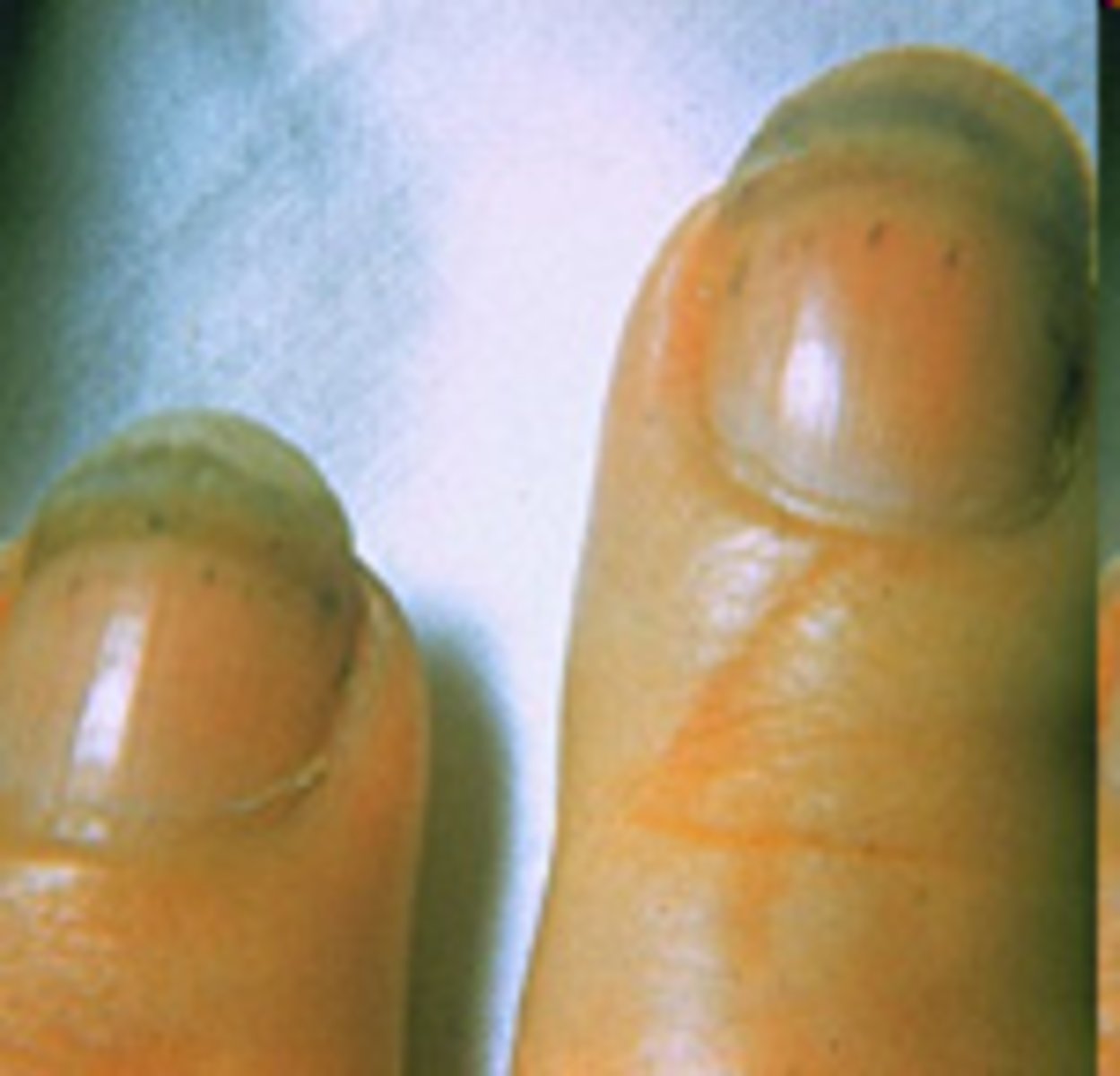
True or false Washing hands removes all microbes on hands
False Washing hands is a form of microbial control known as degermation (partial removal of microbes from living surfaces).

What is the role of the ocular lens?
Lens closest to the eyes, Lens that forms the virtual image
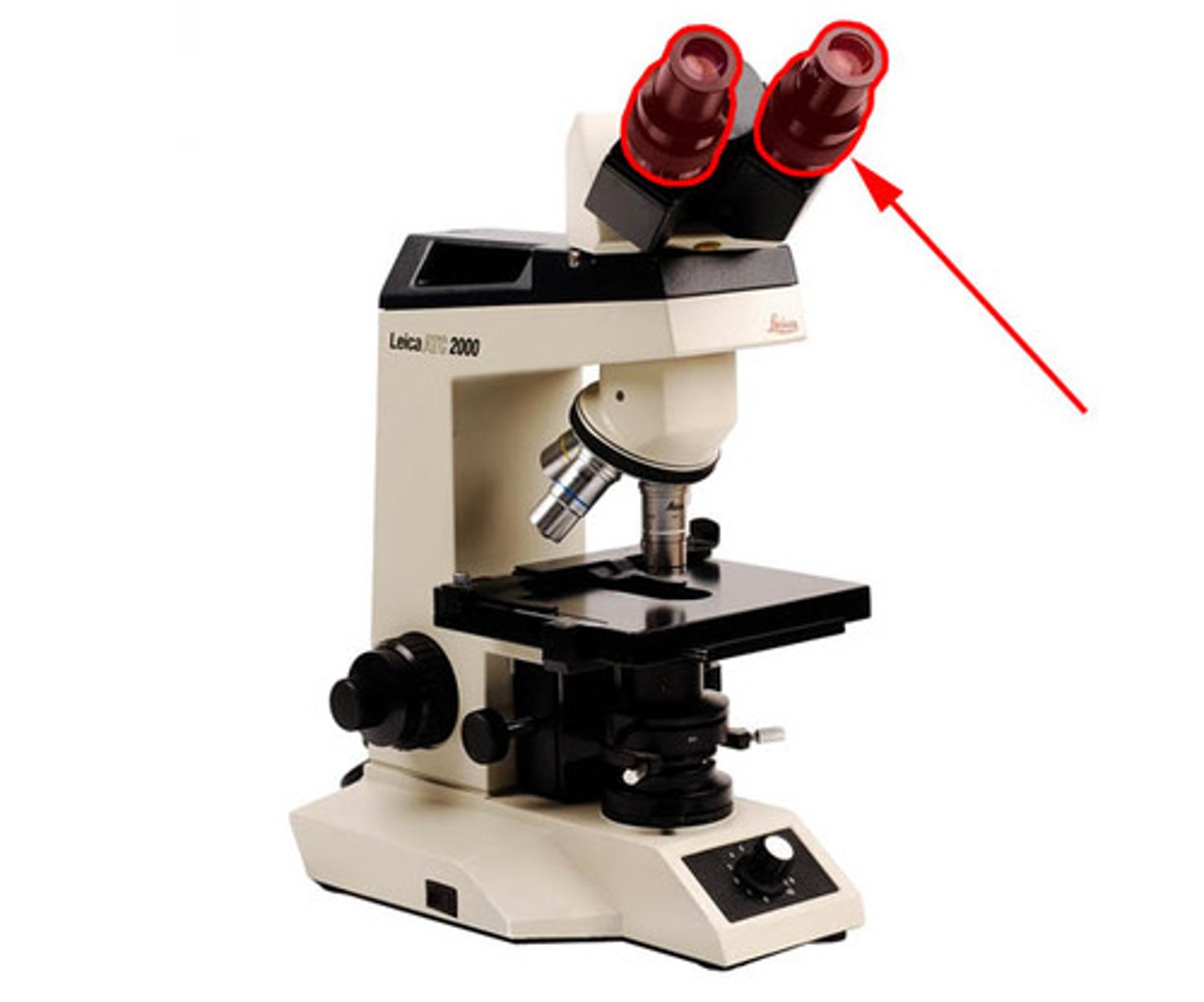
What is the role of the objective lens?
Lens above the specimen on the glass slide, Lens that forms the real image
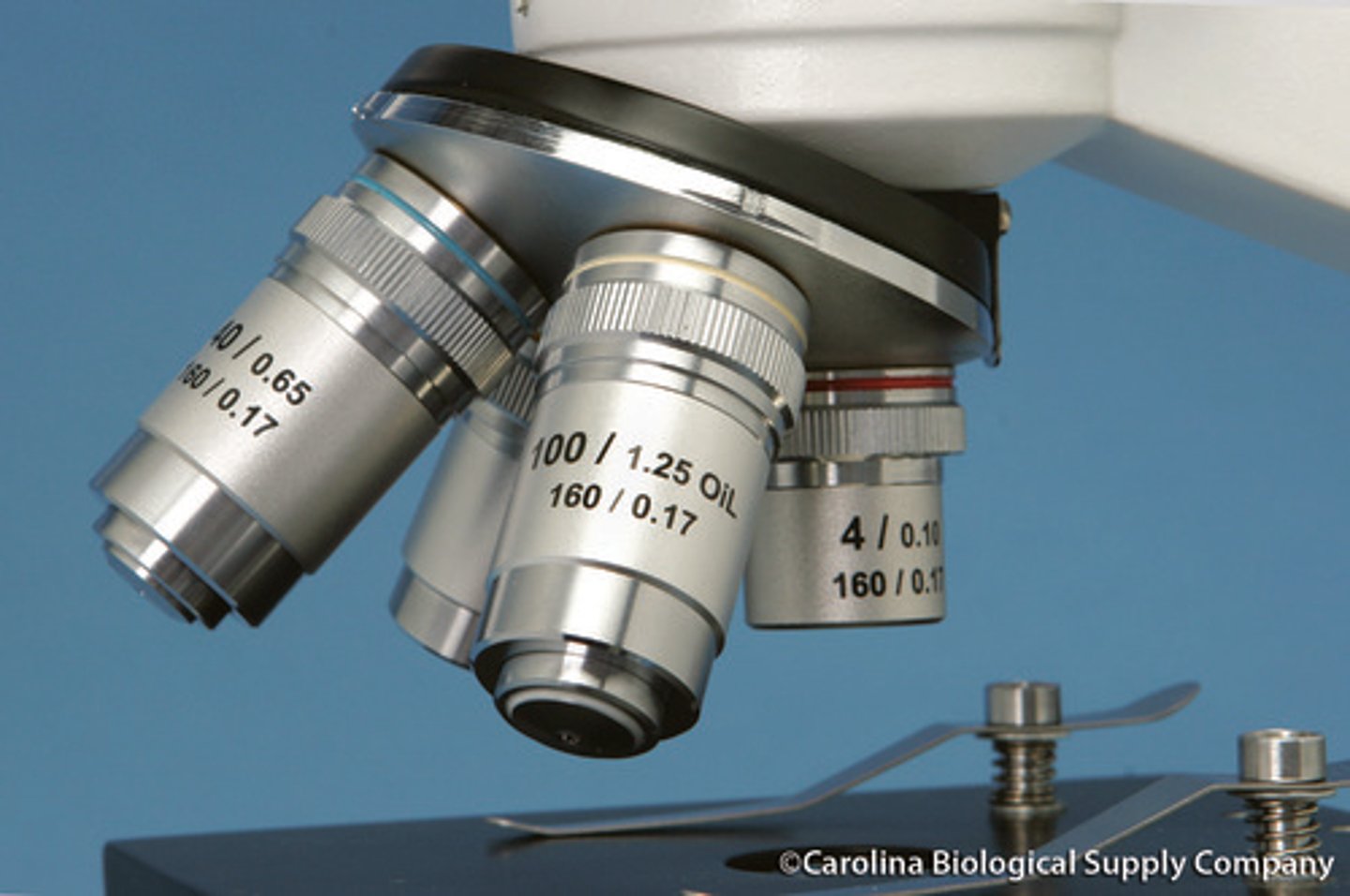

At what objective lenses can the course focus be used on?
Only the 10X magnification as there is increase chance of breaking slides when using the 40X or 100X lenses. It can be used on the 4X lens but this lens is not used in our lab.
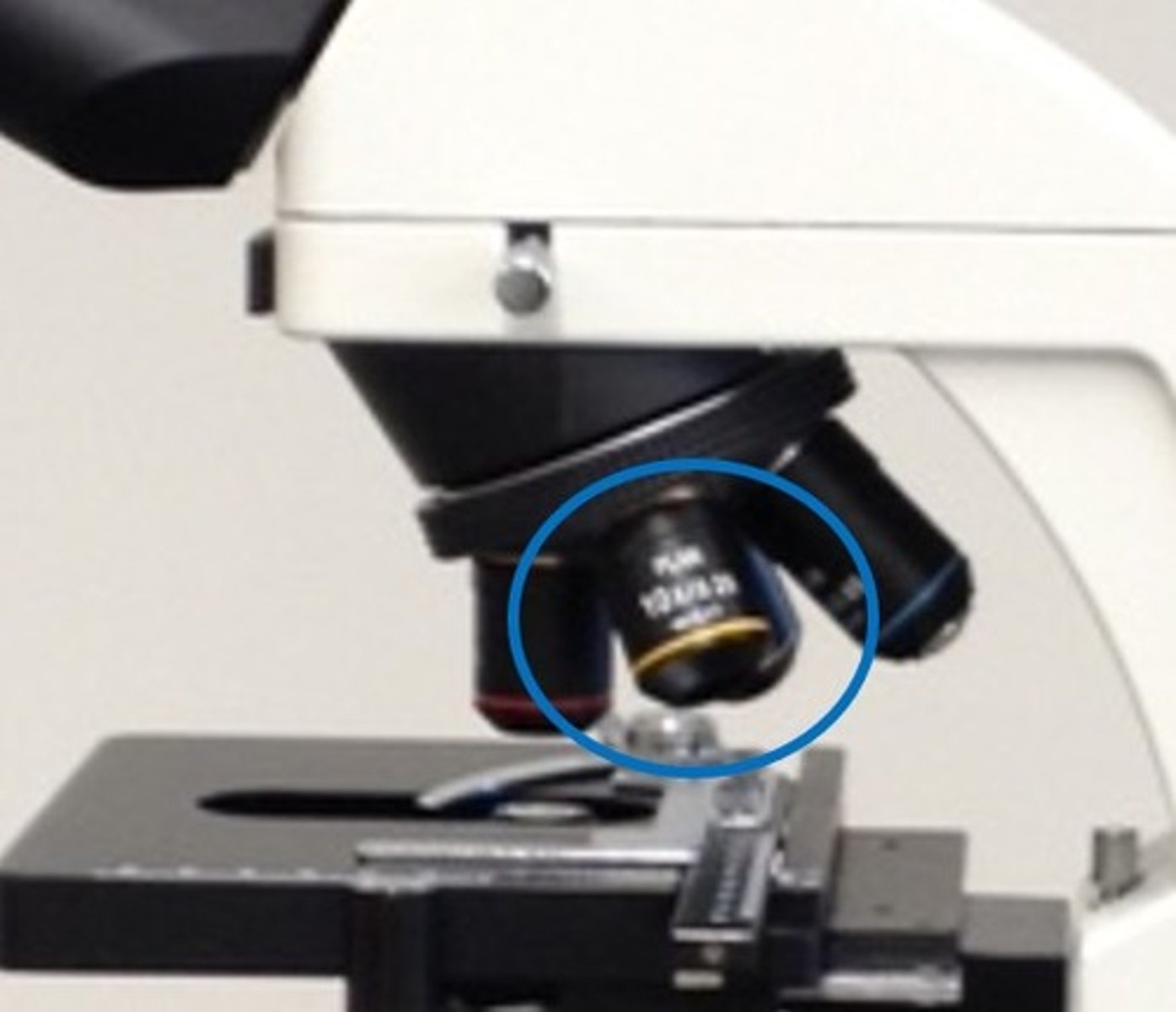
At what objective lenses can the fine focus be used on?
All magnifications (10X, 40X, 100X [the ones we used in the lab]). Also the 4X
![<p>All magnifications (10X, 40X, 100X [the ones we used in the lab]). Also the 4X</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3ffaa35a-b968-46bd-93fe-0a86f75b97c2.jpg)
The ocular lens on our microscopes is at this magnification.
10X

What objective lens are found on our microscopes?
4X (not used in our lab), 10X, 40X, 100X
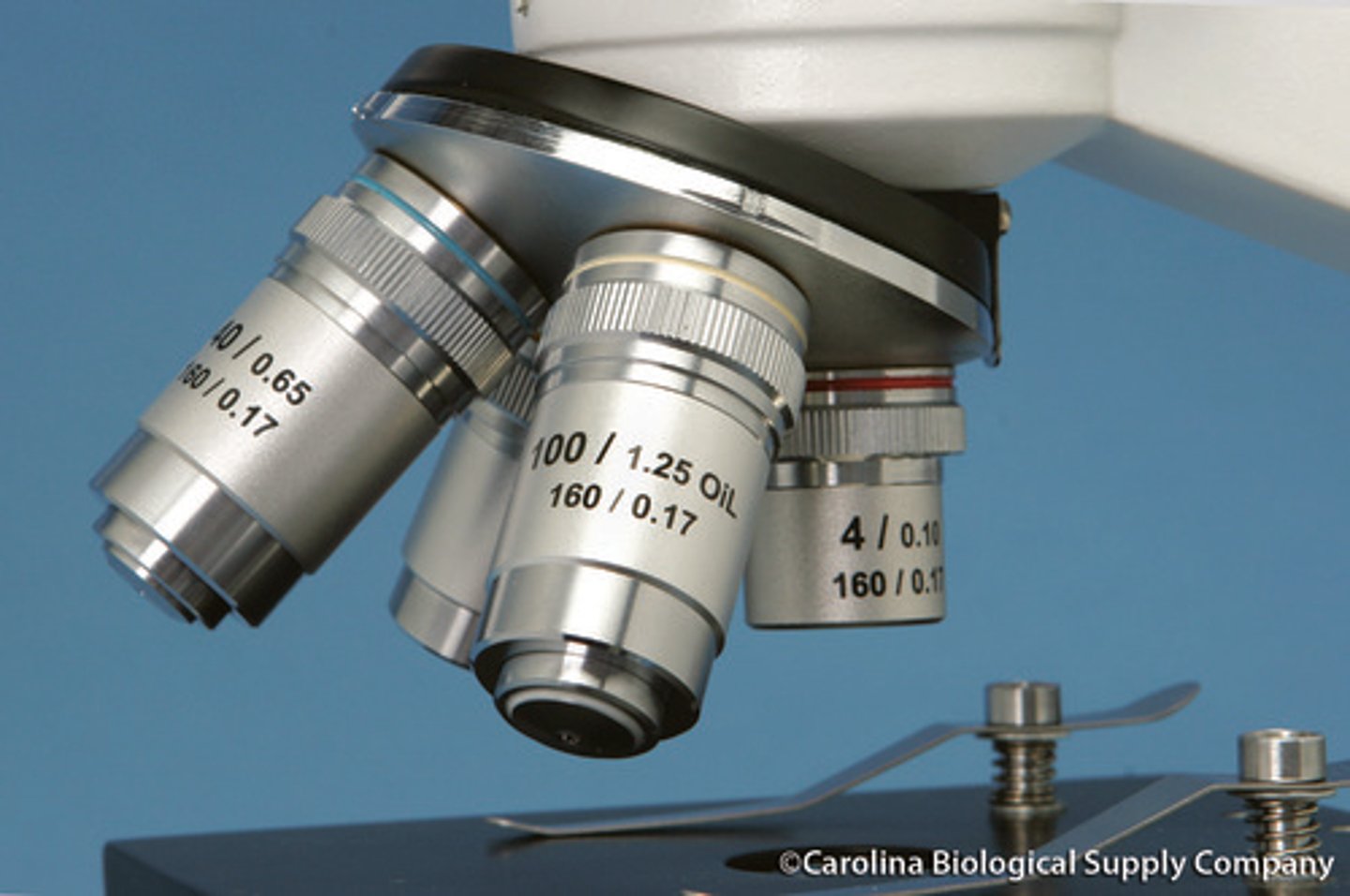

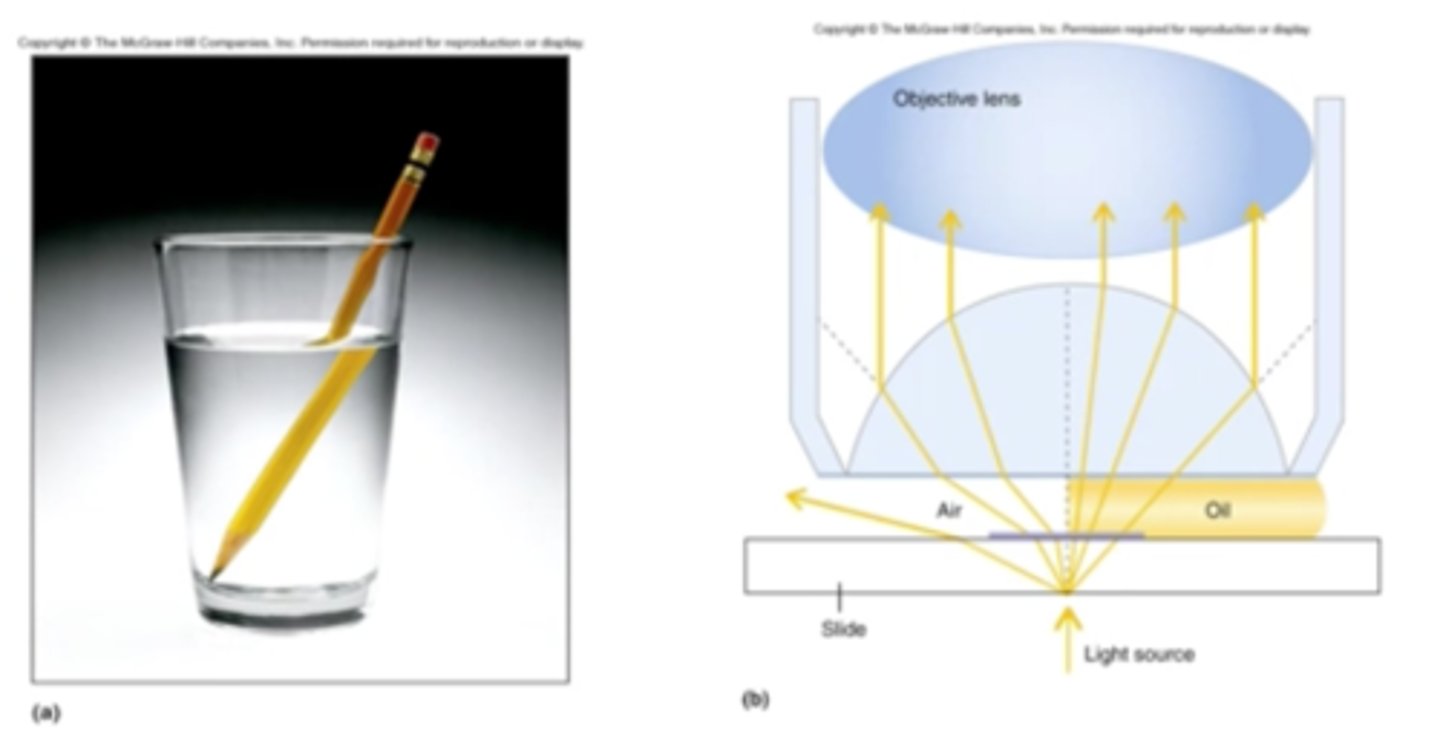
Why is immersion oil needed when using the 100X lens?
This lens has a high NA that needs oil to minimize the light refracted away from the lens. This is important since the image we view is made of this light so any light not reaching the lens will decrease the clarity of the image (resolution). Oil has a refractive index that is similar to glass (slide and lens)
What is the role of the revolving nosepiece?
This part of microscope holds the objectives.
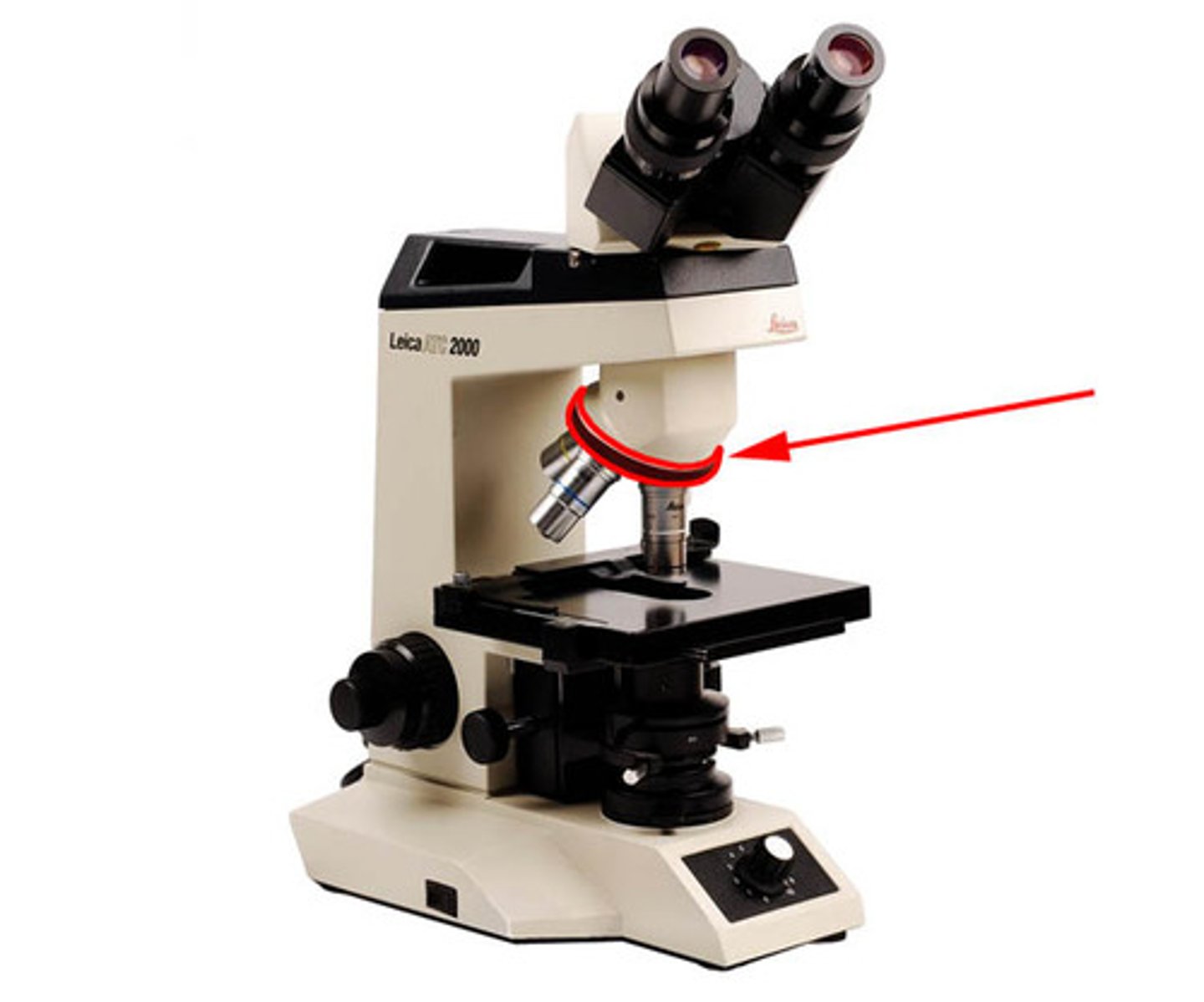
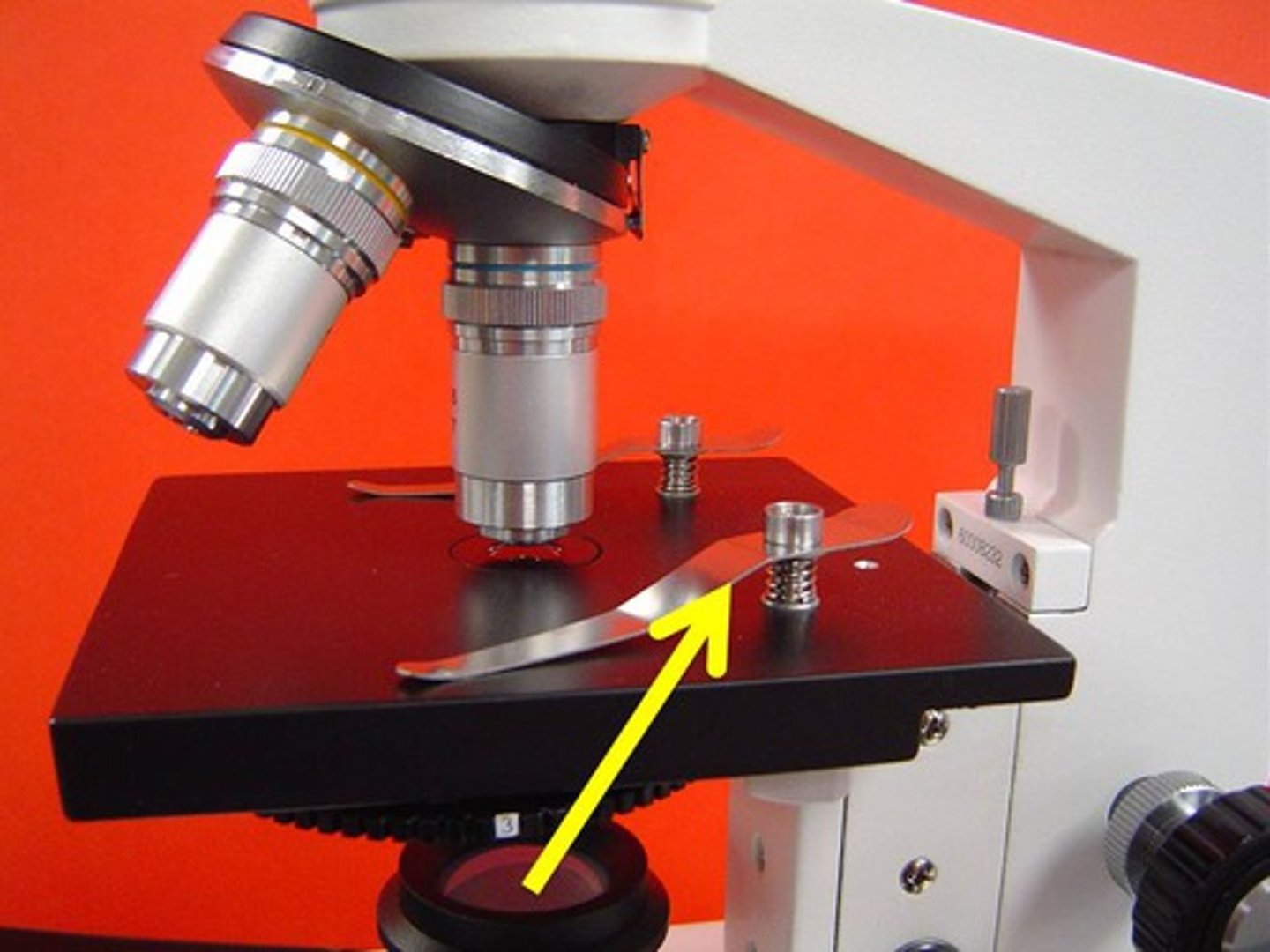
What is the role of the stage?
To hold the slide

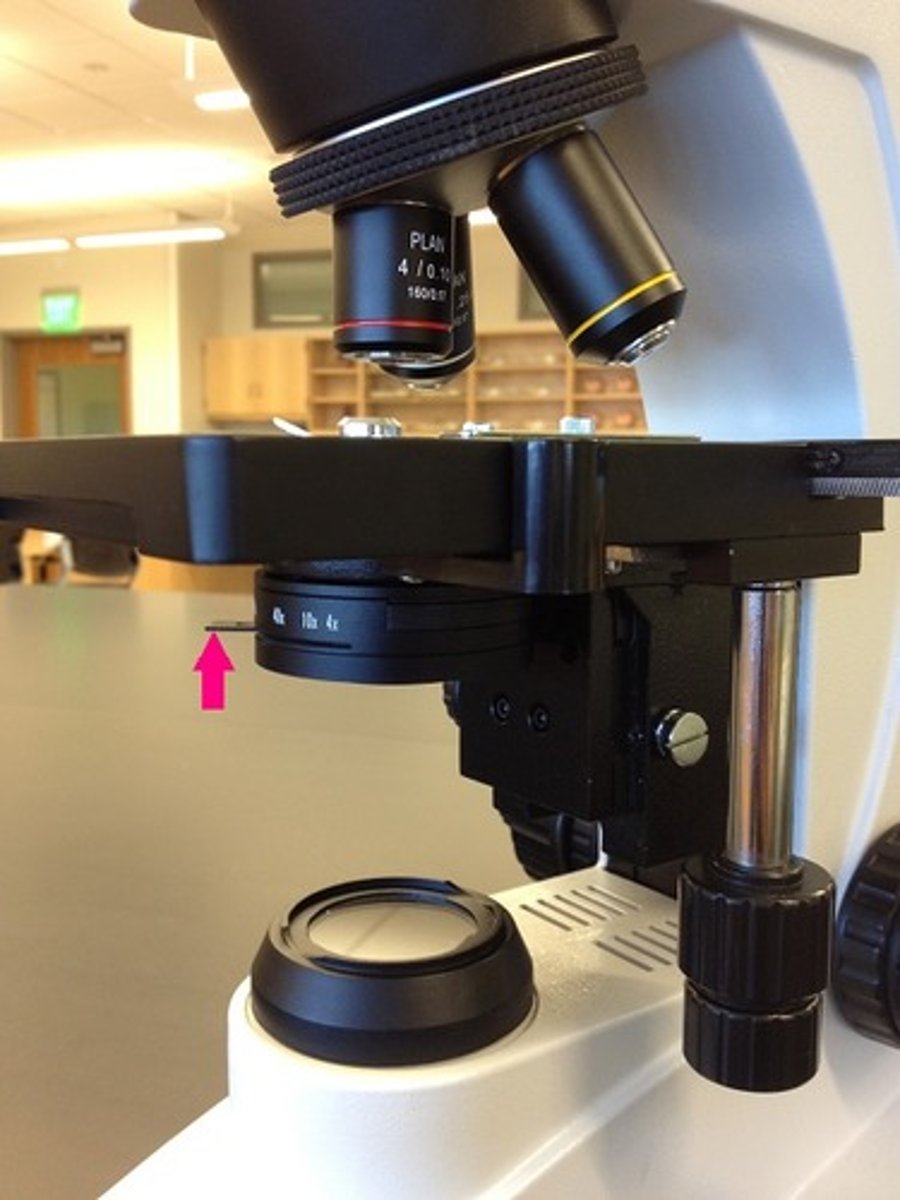
What is the role of the condenser lens?
This lens focuses light emitted by the lamp onto the specimen on the slide
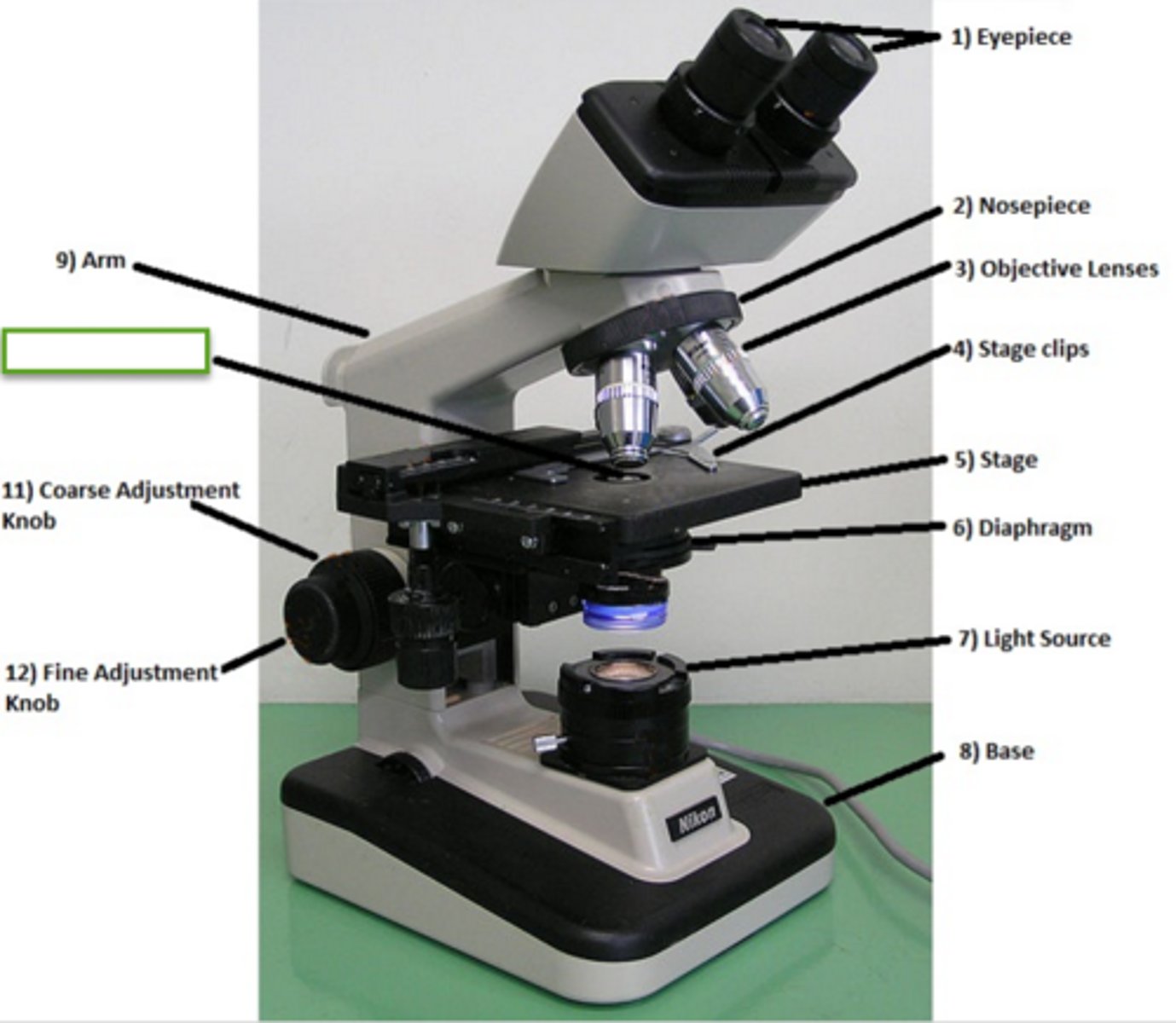
What is the role of the iris diaphragm?
This slide is used to control how much light leaves the condenser (controls the intensity) and reaches the specimen

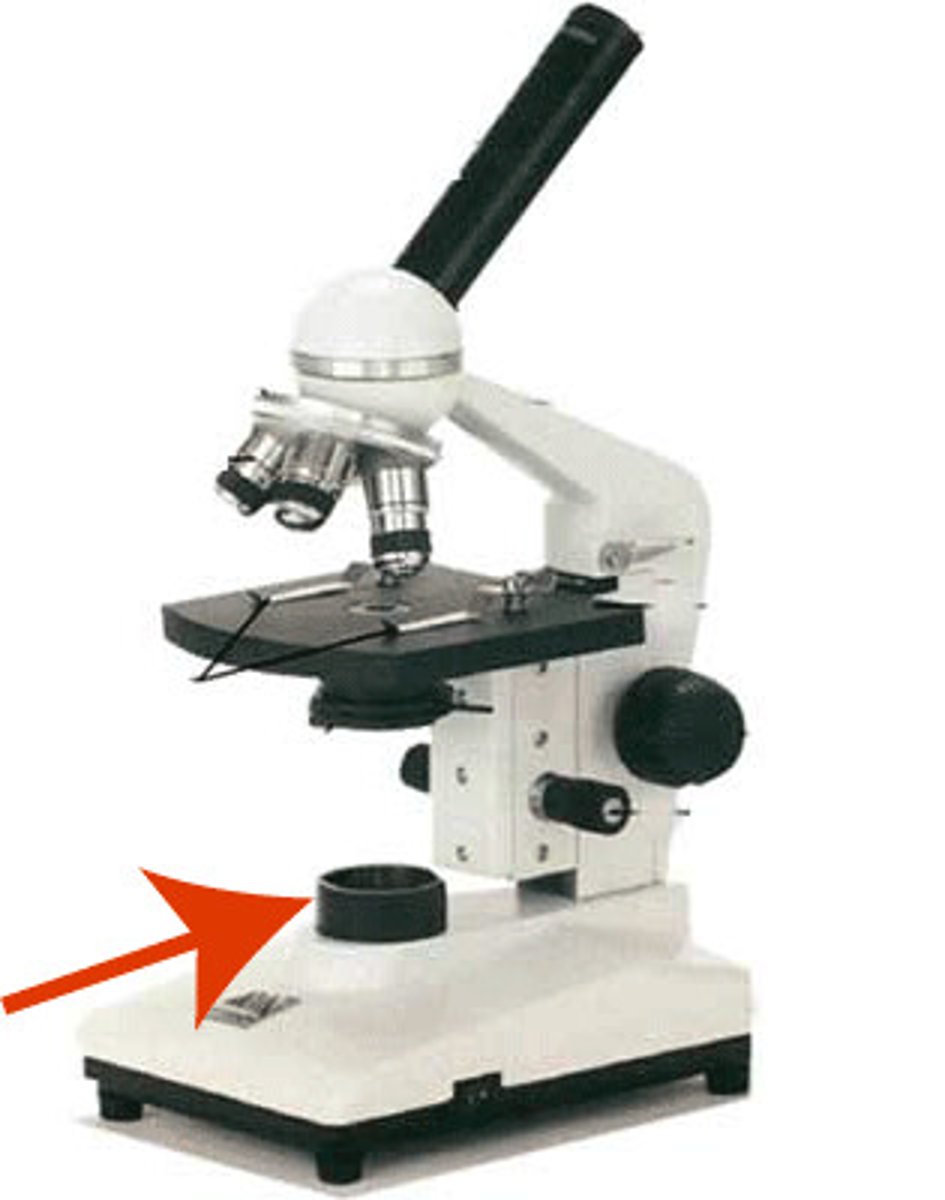
What is the role of the lamp?
To provide light needed to form the image we view

What is the rheostat?
This knob controls the intensity of light from the lamp
What is parfocal?
Once an image is focused at one objective lens, it will remain mostly focused when switching to the other objective lens.

What is magnification?
The ability of the microscope to increase the size of specimen image

What is resolution?
The ability of a microscope to see two objects as separate

If you are viewing a specimen using our microscopes at the 10X objective lens, what is the total magnification of the image?
100 (10X for the ocular, 10X for the objective)
10 X 10 = 100

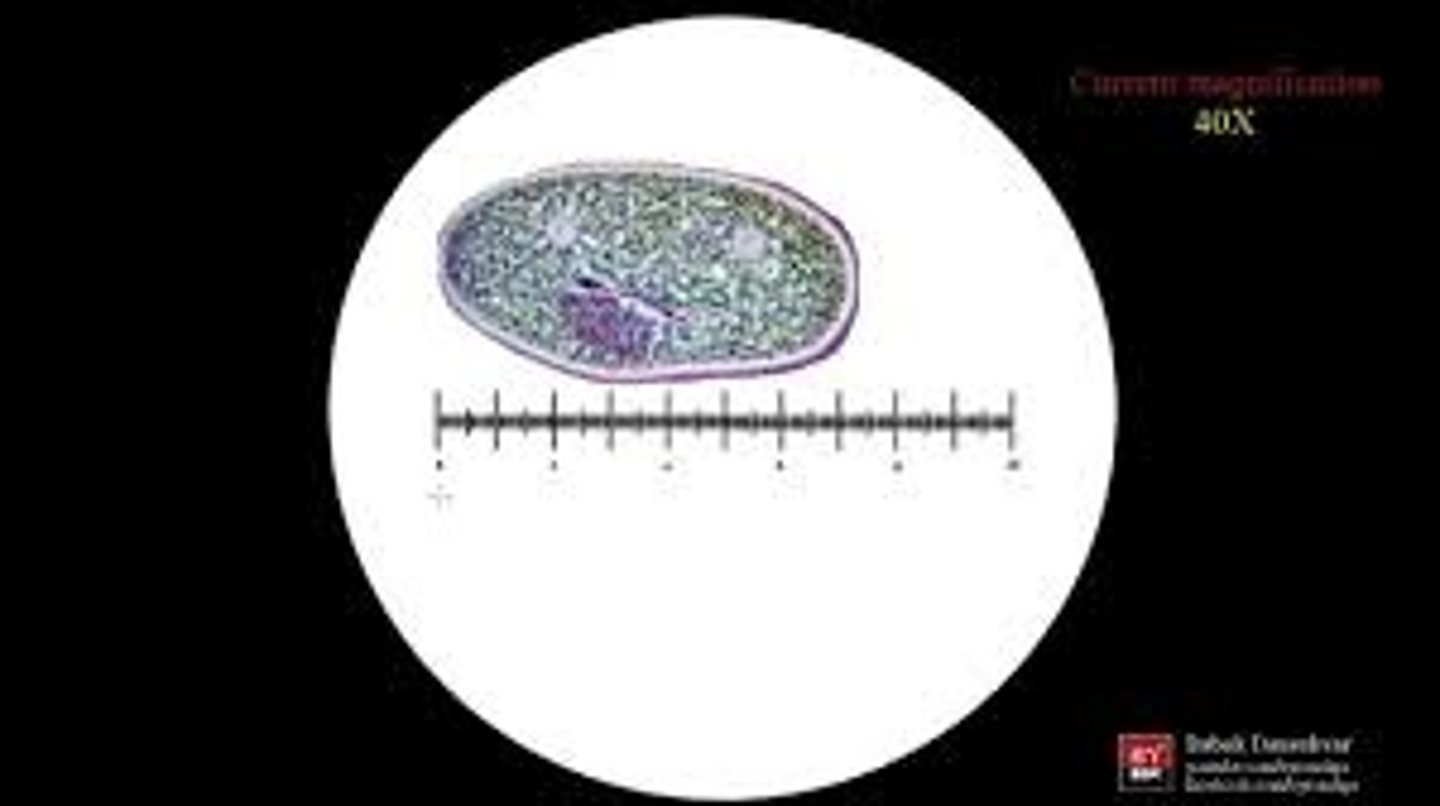
You are viewing a microbe that is 3 bars long and 2 bars wide using the 10X objective. What is the size in um of the microbe?
Each bar is equal to 10 um since you are using the 10X objective
3 (10 um) X 2 (10 um) = 30 um X 20 um
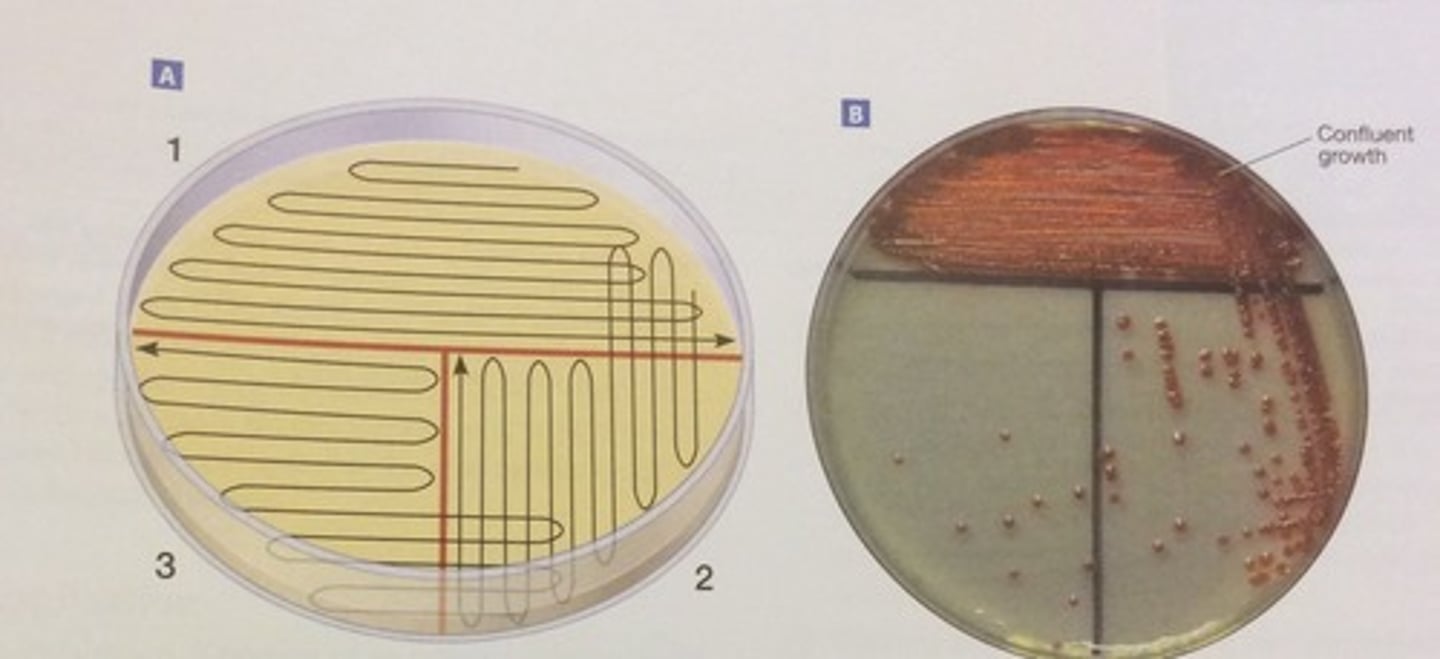
What method is used to obtain a pure culture?
Streak plating
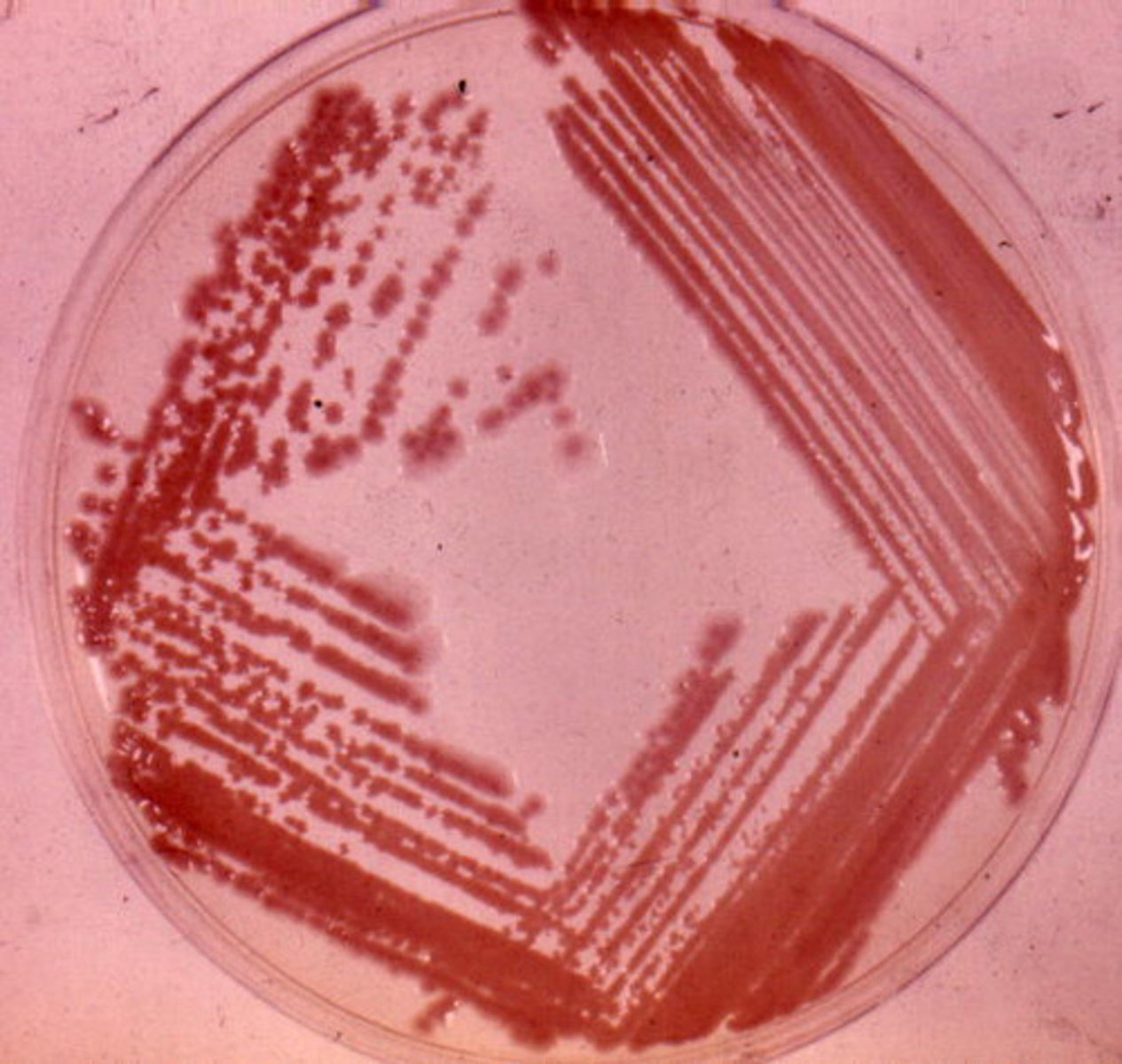
How can you tell if a culture is pure?
There should uniform looking colonies on the plate (multiple colonies that should look the same)
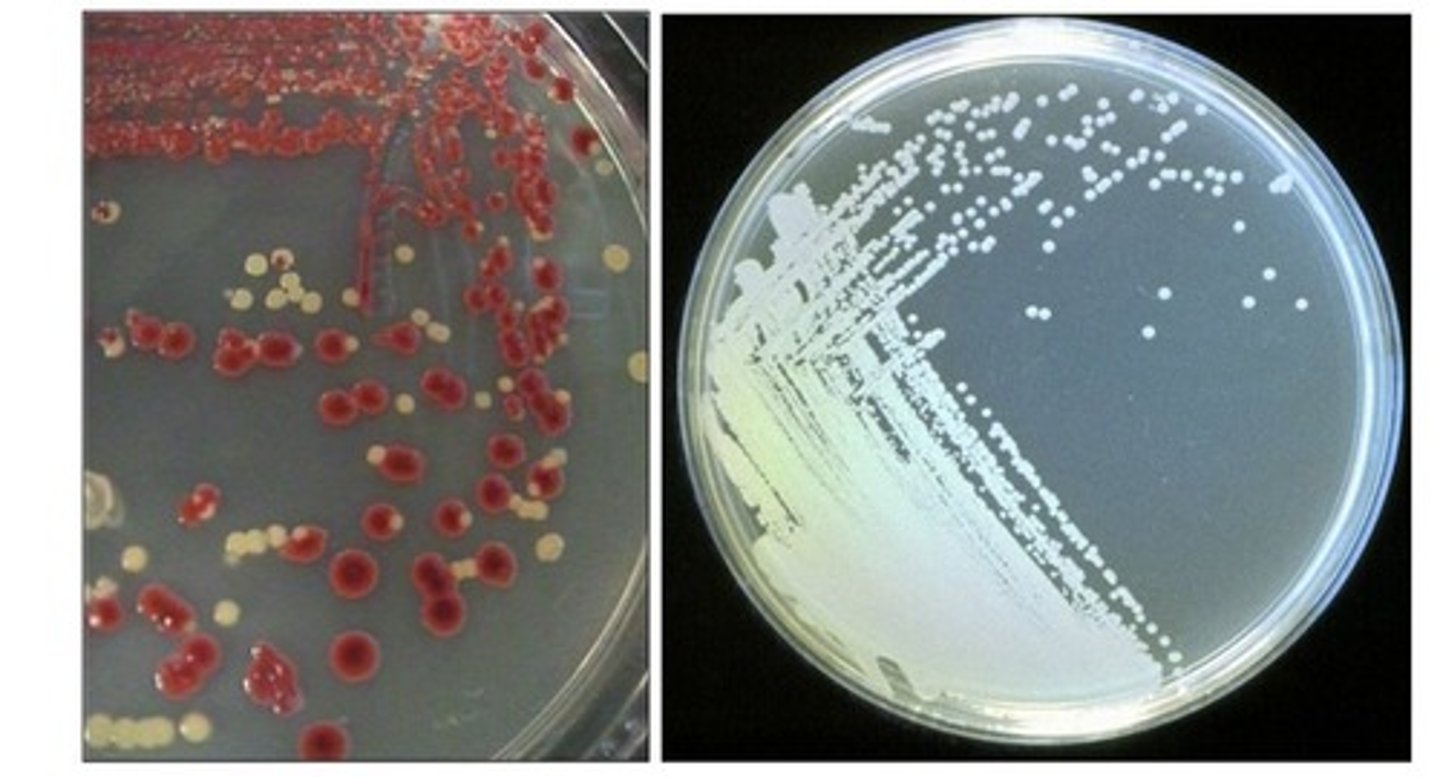
What is the purpose of heat fixing during the preparation of a smear?
To kill the cells
To adhere cells to the slide
To denature/coagulate proteins so the stain is retained better
_____ are basic or catonic dyes that stain the cell since the stain is attracted by the negative parts of the cell.
Positive stains
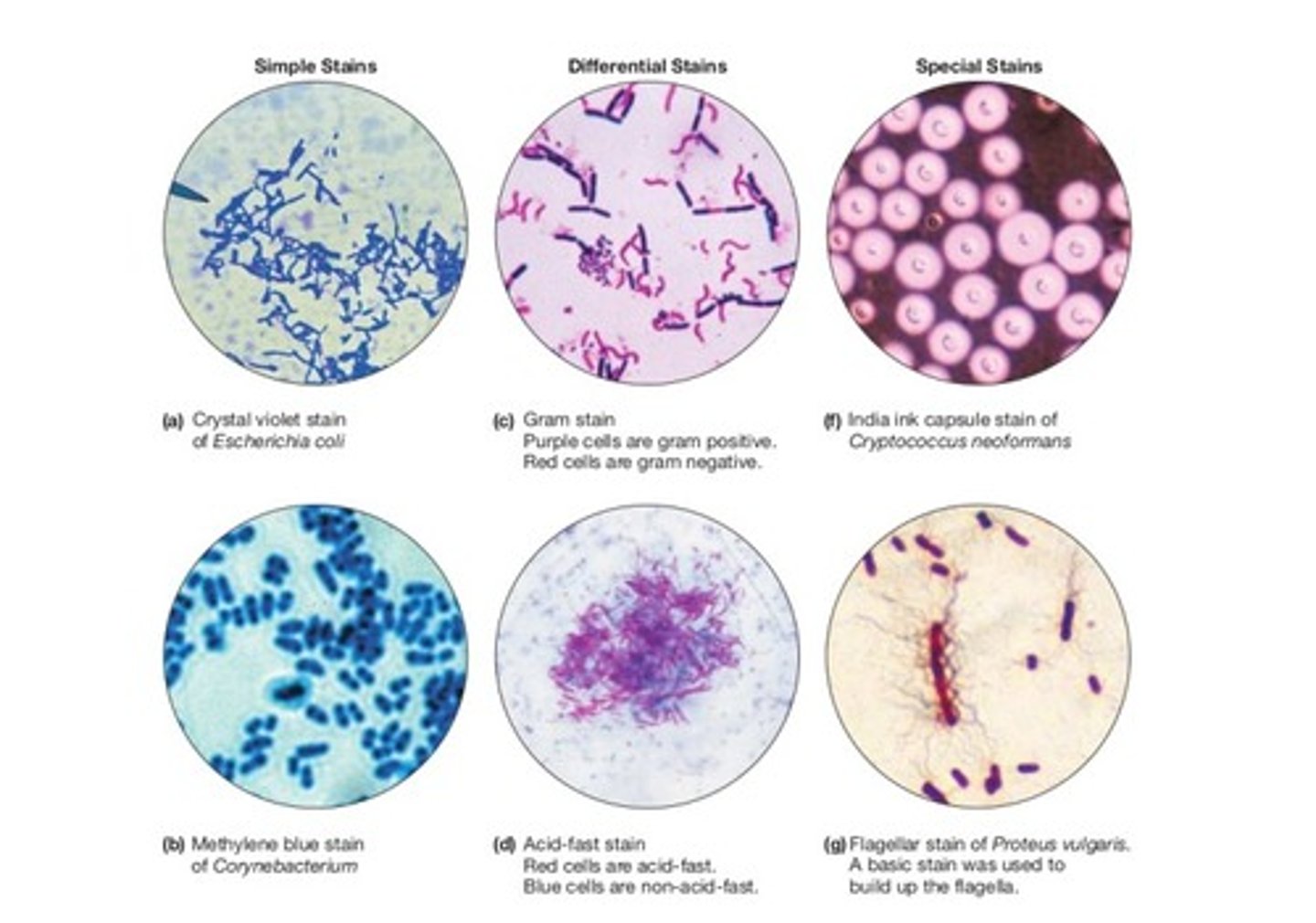
_____ are acidic or anionic dyes that stain the background since the stain is repelled by the cell.
Negative stains
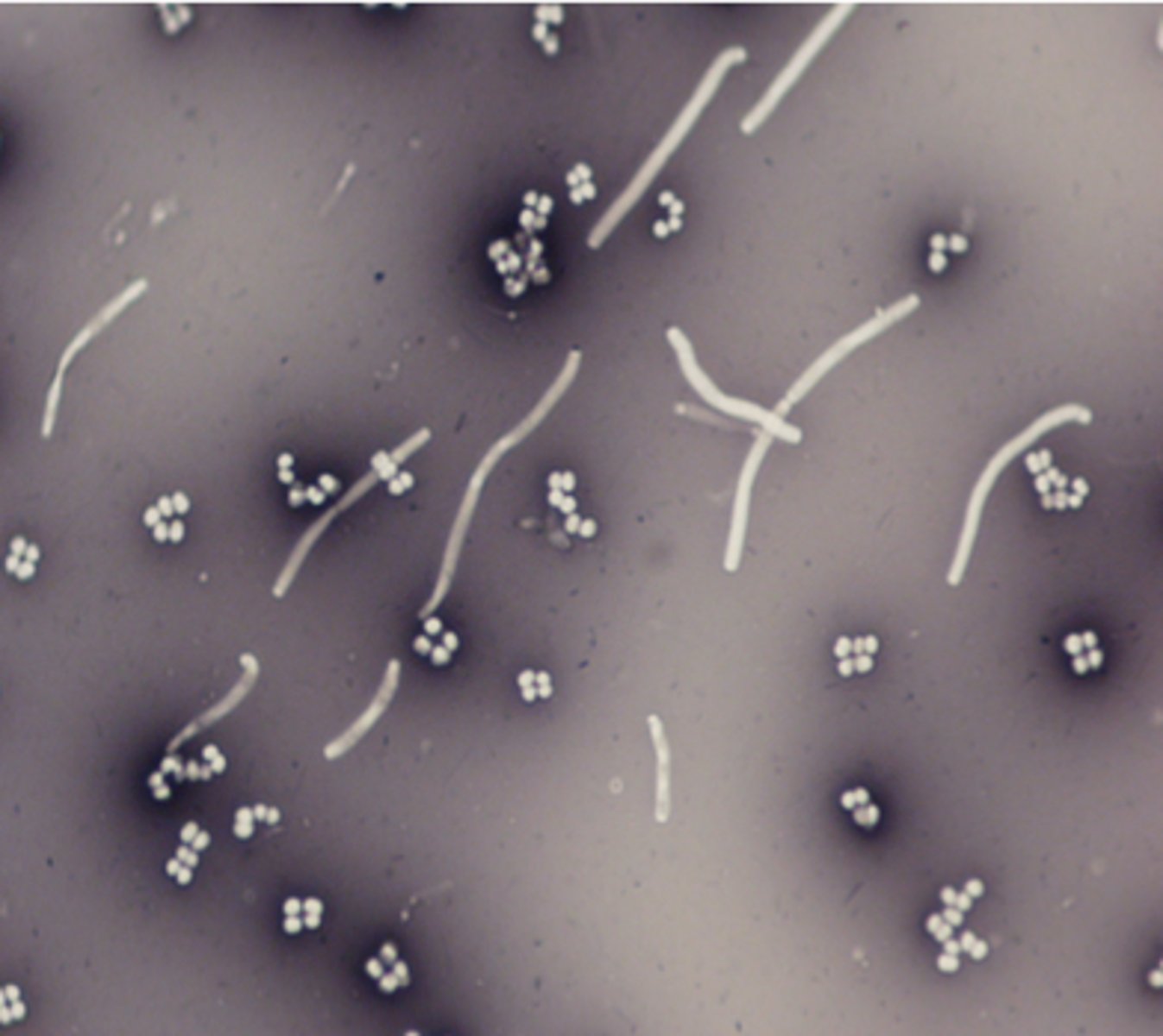
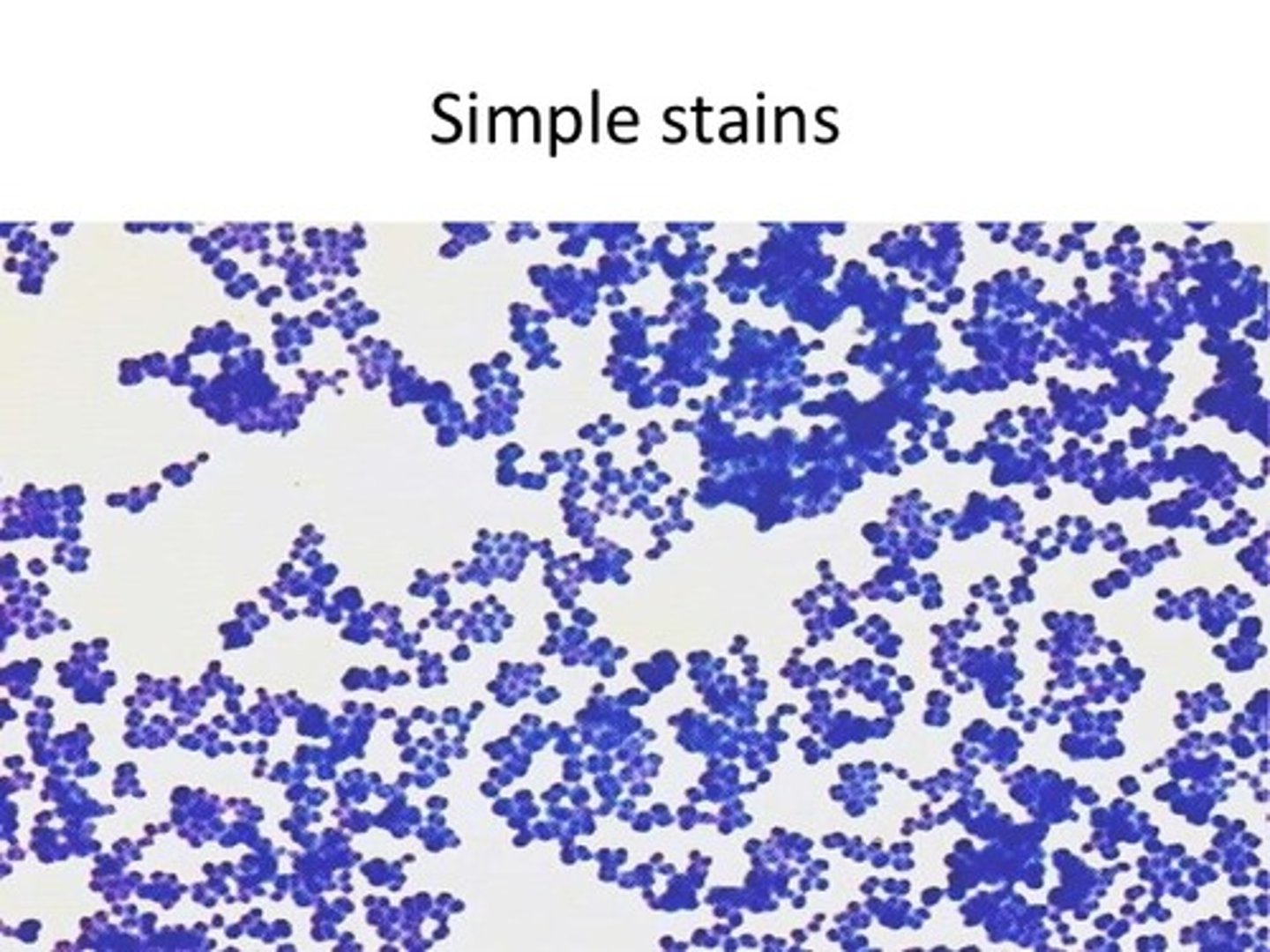
_______ use one dye and allow for the shape and arrangement to be determined.
Simple staining
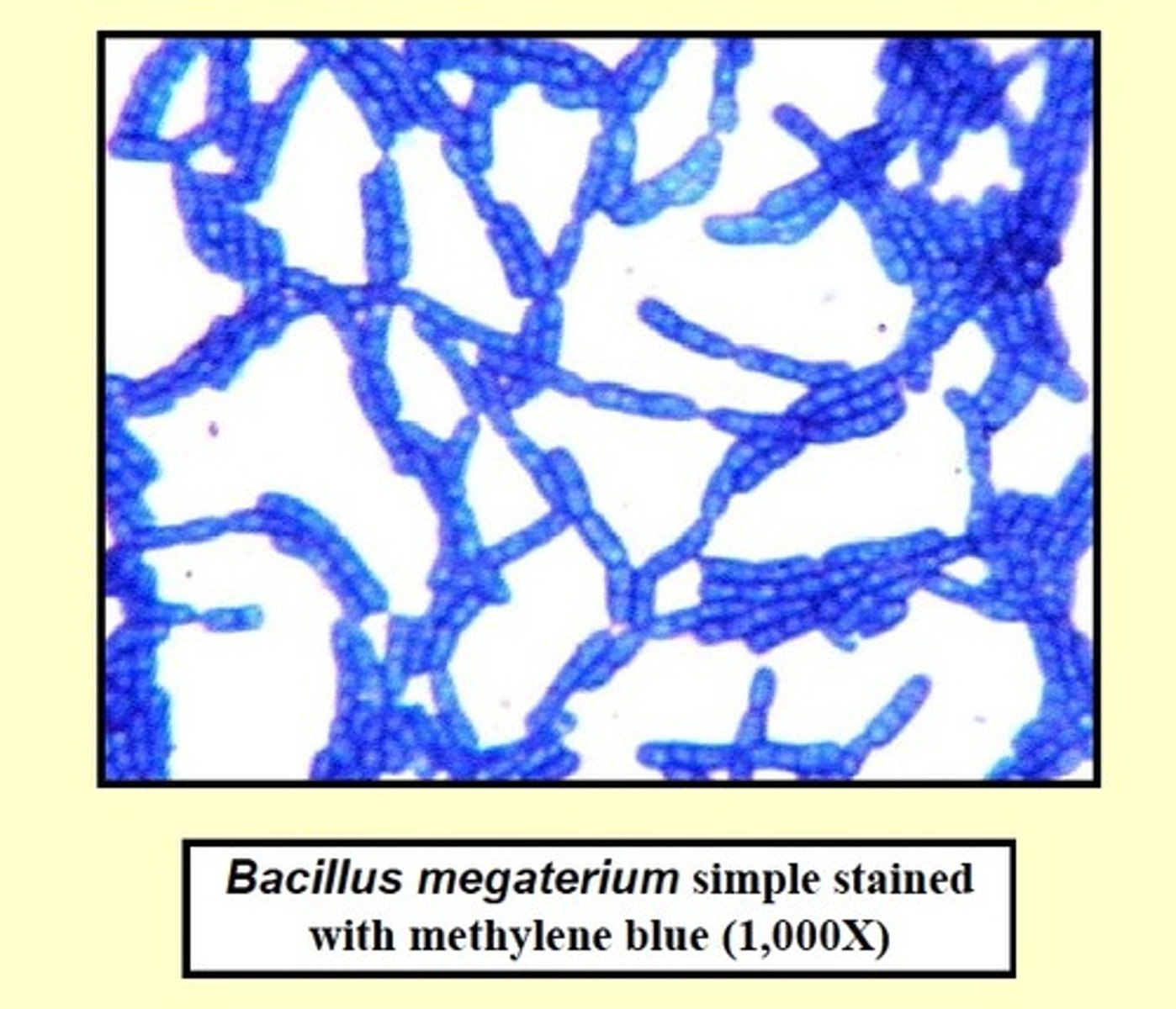
What information can you get about a microbe from a simple stain?
True size, shape/morphology and arrangement

Gram stain and acid fast stains are examples of _______, staining techniques that use two stains and allow you to distinguish between two cell types.
Differential staining
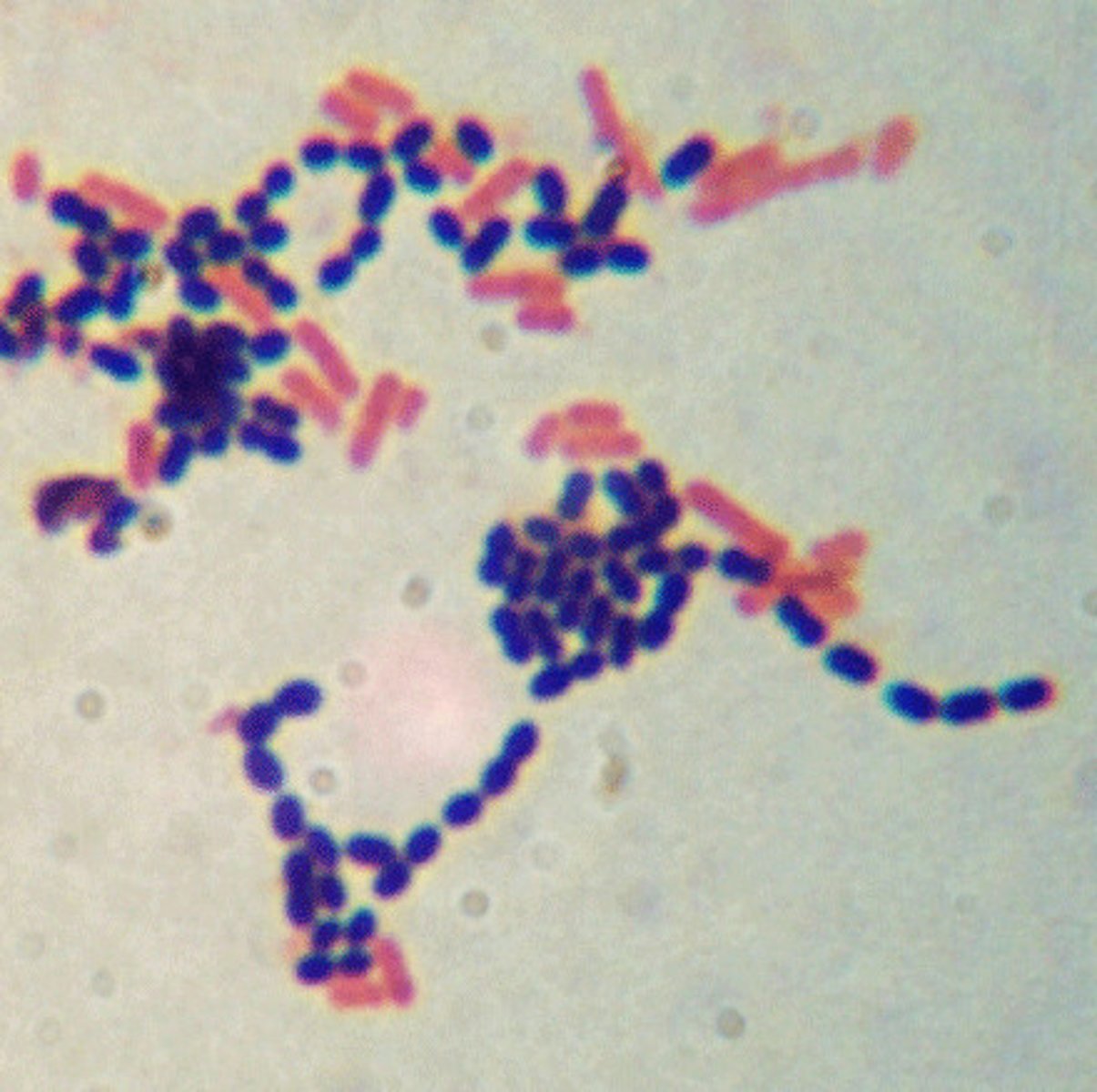
What is the role of a primary stain in differential staining?
Stains all cells in the stain and is the stain that is lost by some cells
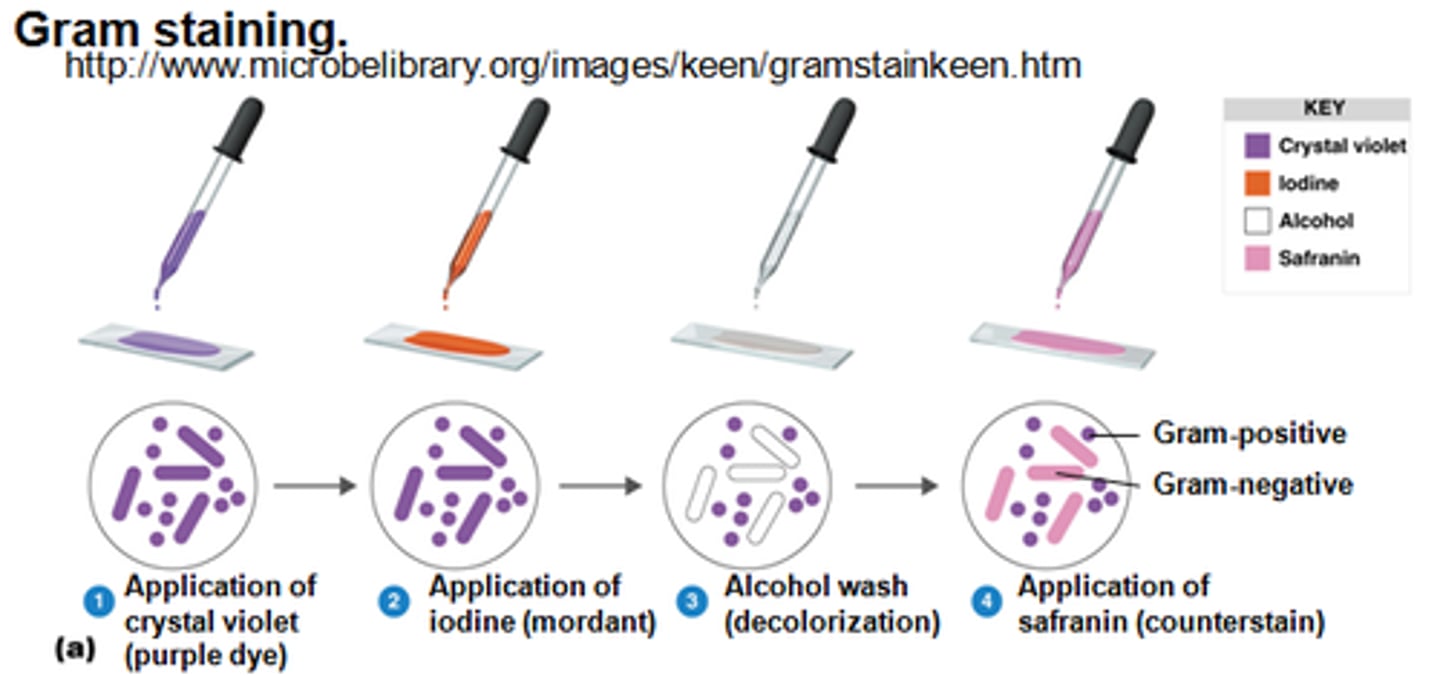
What is the role of a mordant in differential staining?
Forms complexes with the primary stain to keep the stain inside the cell. Note: that not all differential stains have this reagent. The Gram stain does include a mordant.
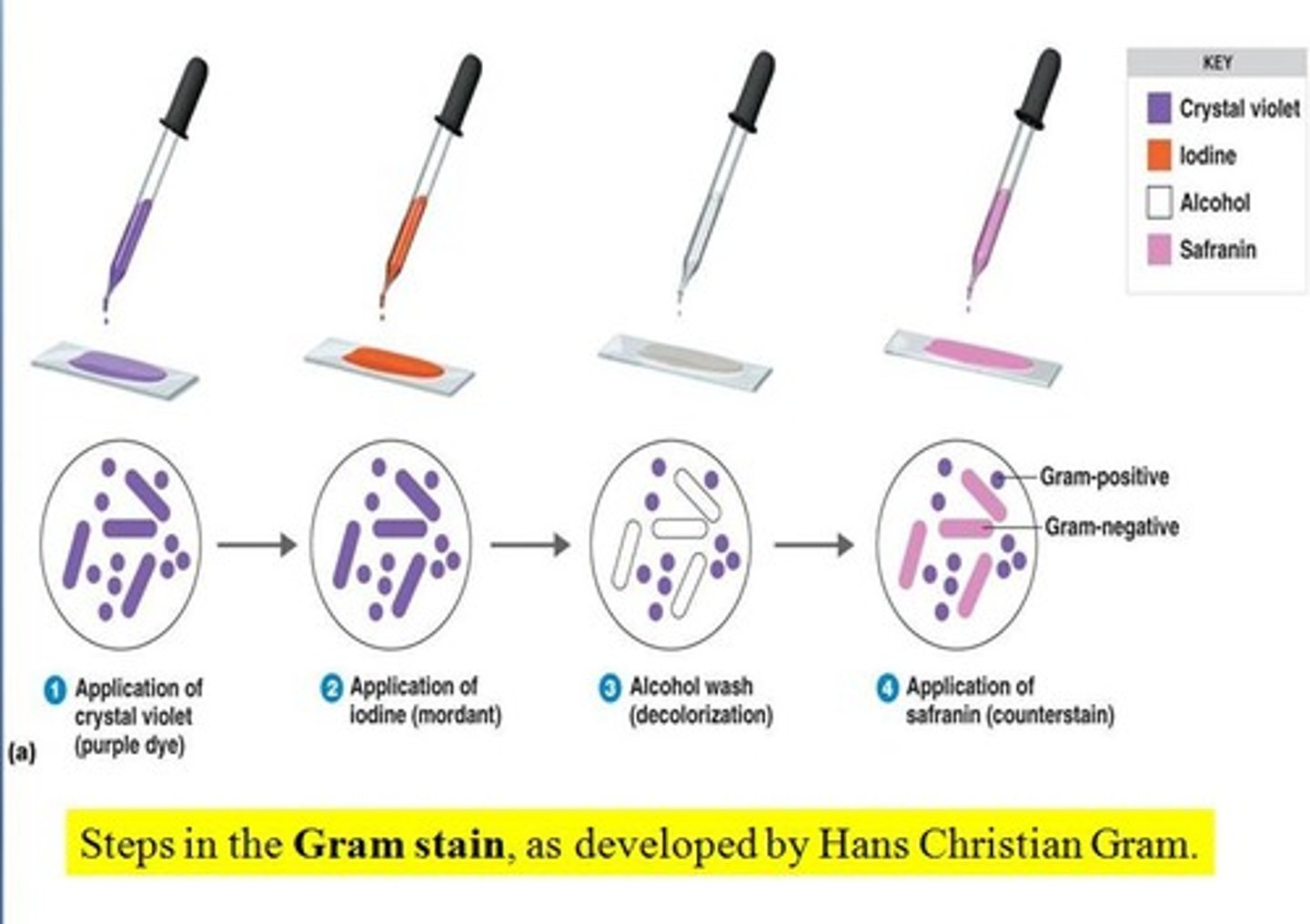
What is the role of a decolorizer in differential staining?
Removes the primary stain from some cells, critical step in a differential stain to be able to tell the difference between two cell types
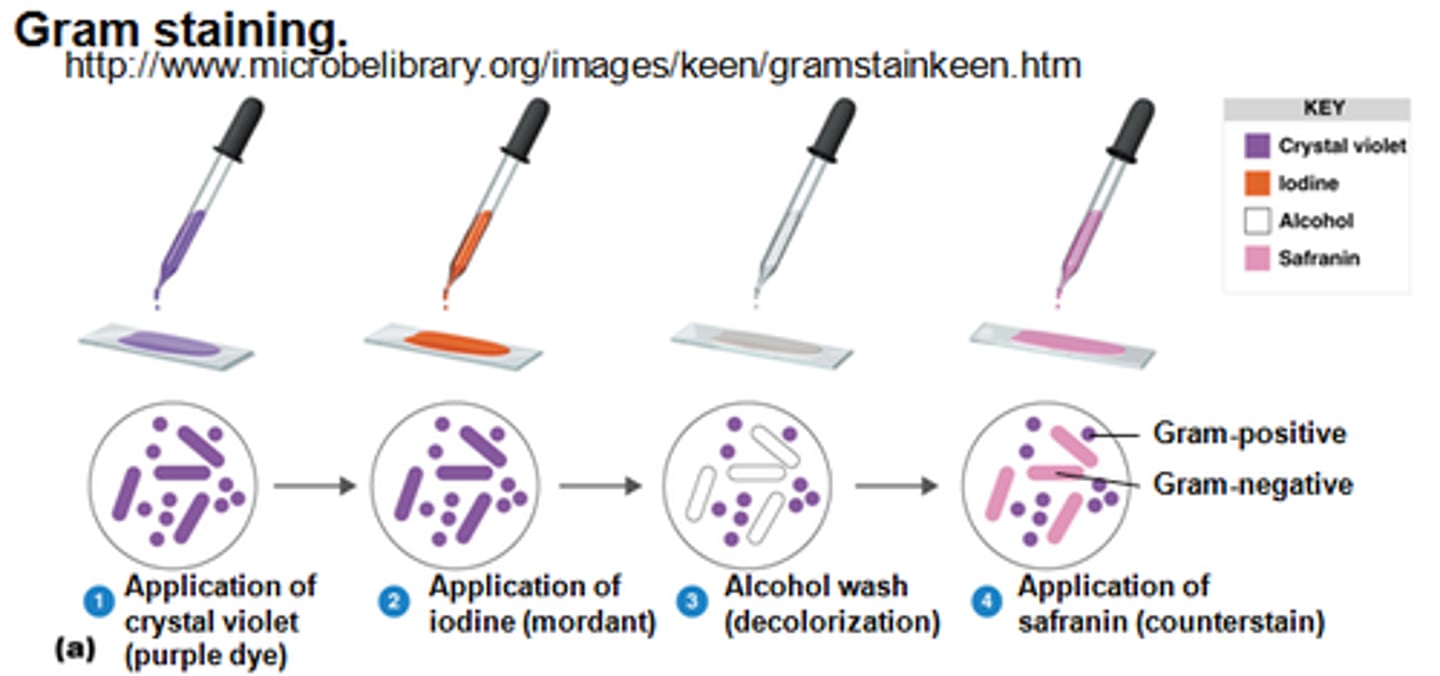
What is the role of a counterstain in differential staining?
Stains all cells after the decolorizer step, This stain is needed to see the cells that lost the primary stain.
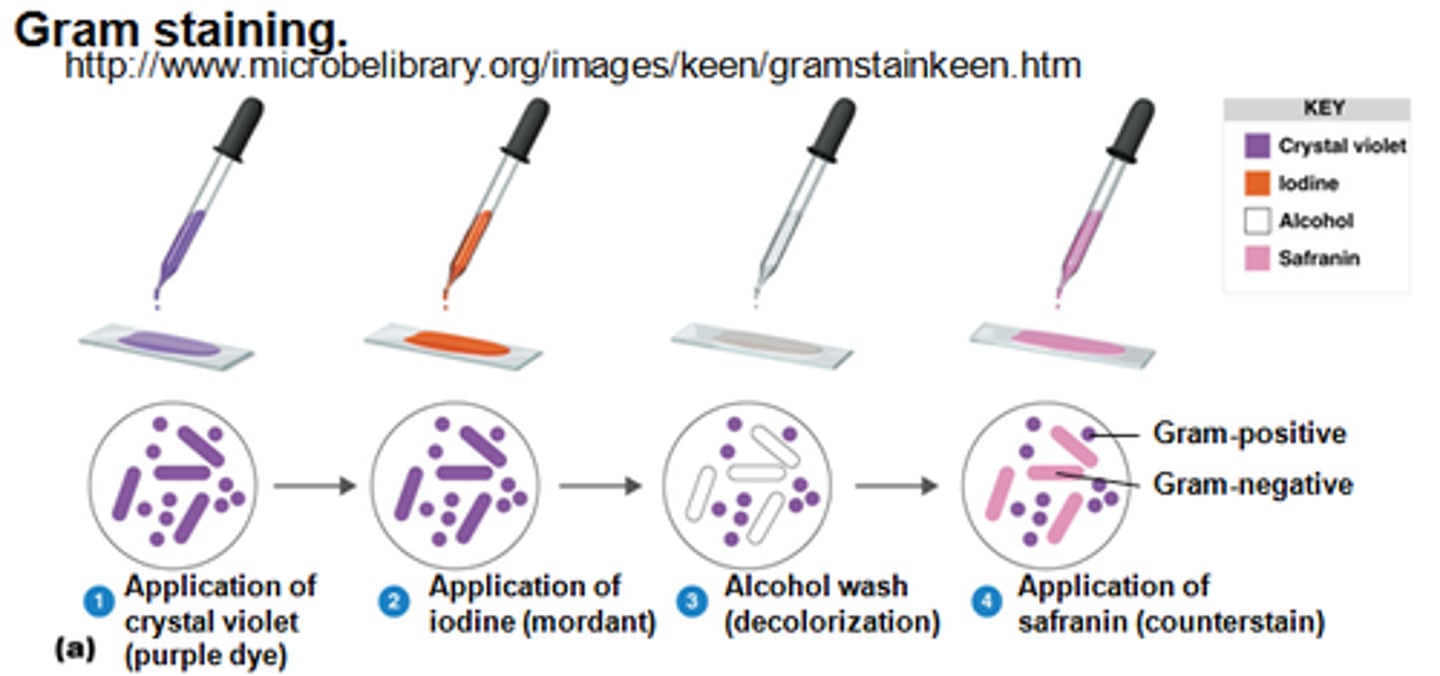
Any cells that retain the gram stain are referred to as _____.
gram positive
Any cells the lose the gram stain and are stained by the counterstain are referred to as ____.
gram negative
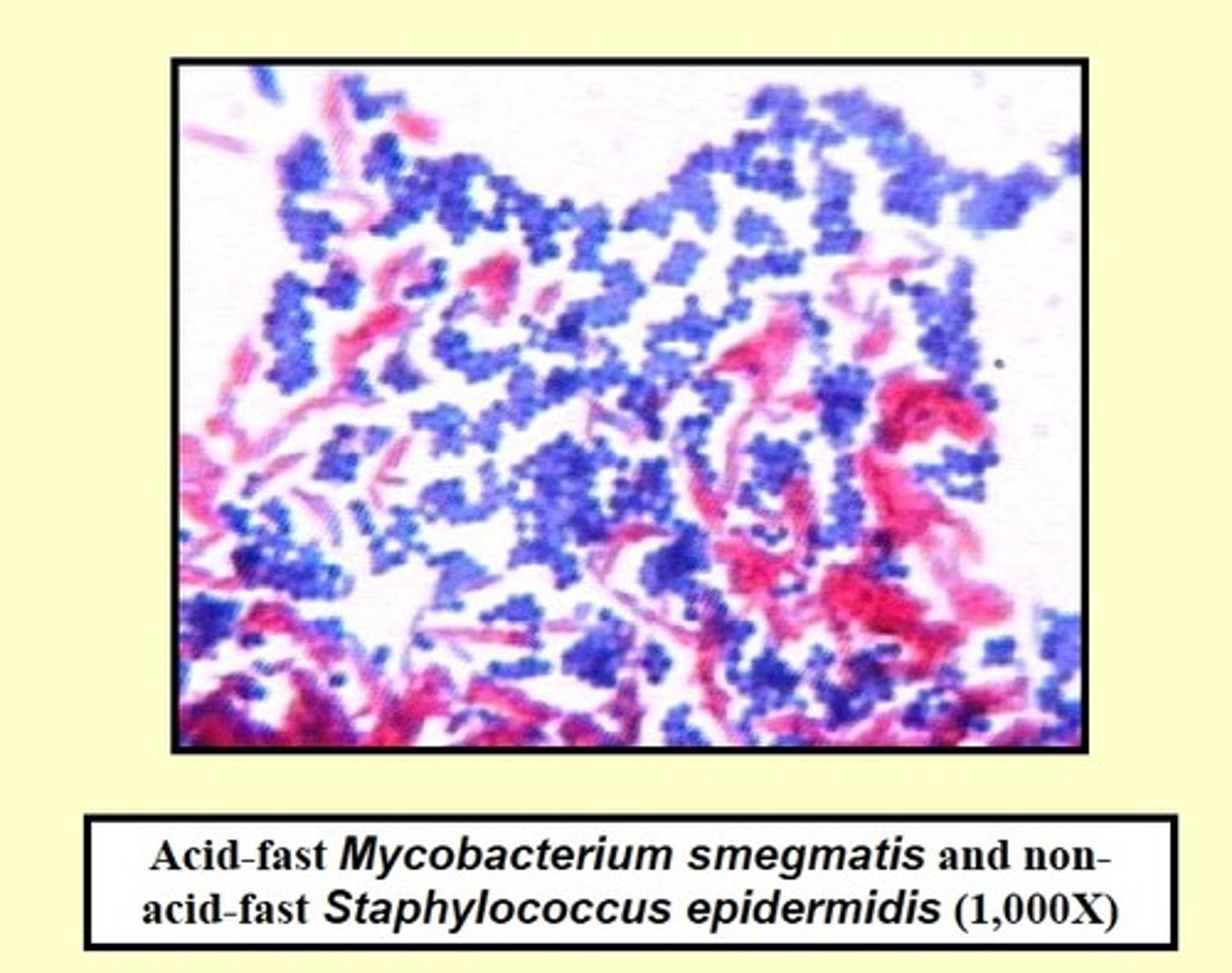
Any cells that retain carbolfuschin are referred to as ________.
Acid fast (acid fast positive)
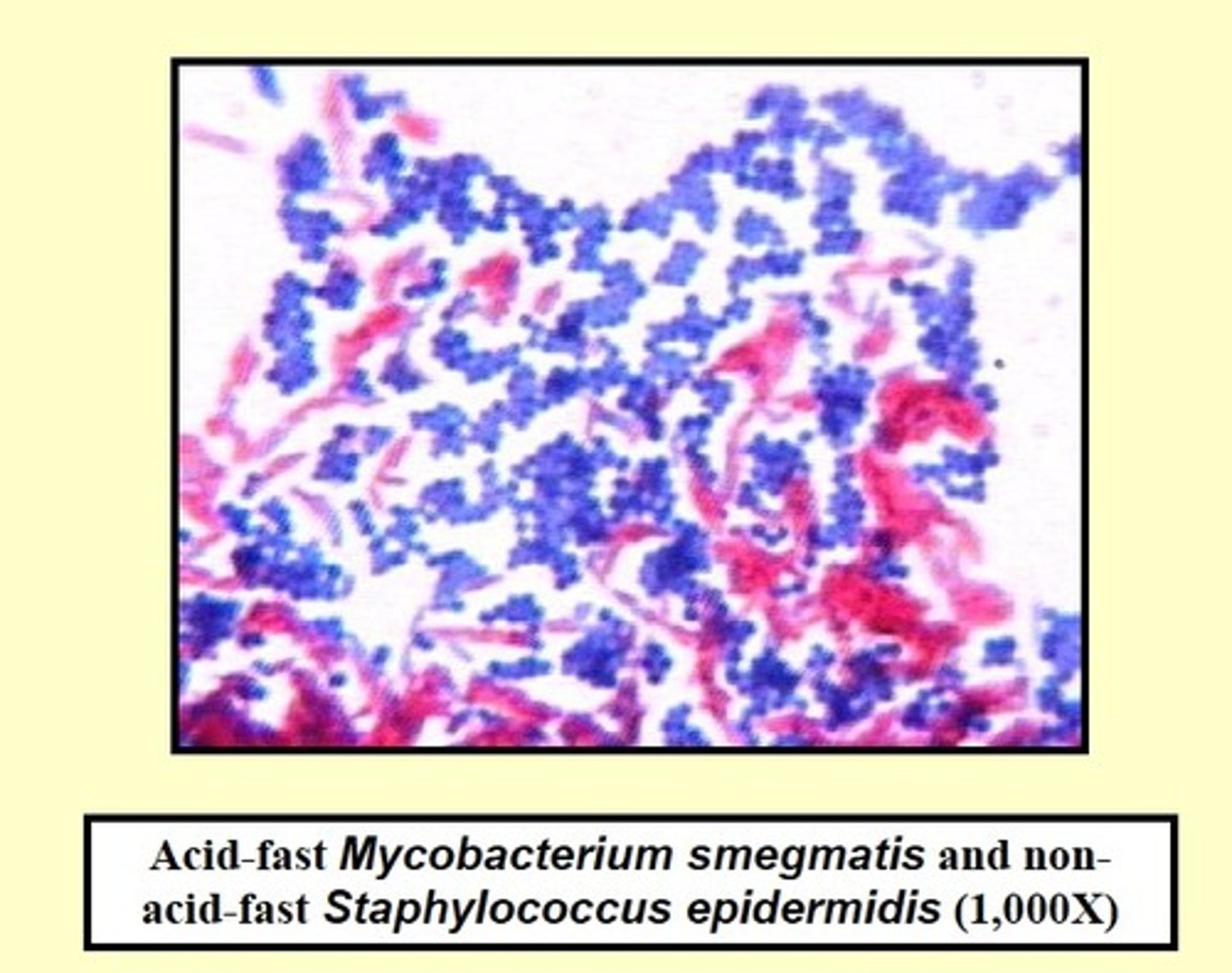
Any cells that lose carbolfuschin and are stained by the counterstain are referred to as _______.
Non-acid fast (acid fast negative)
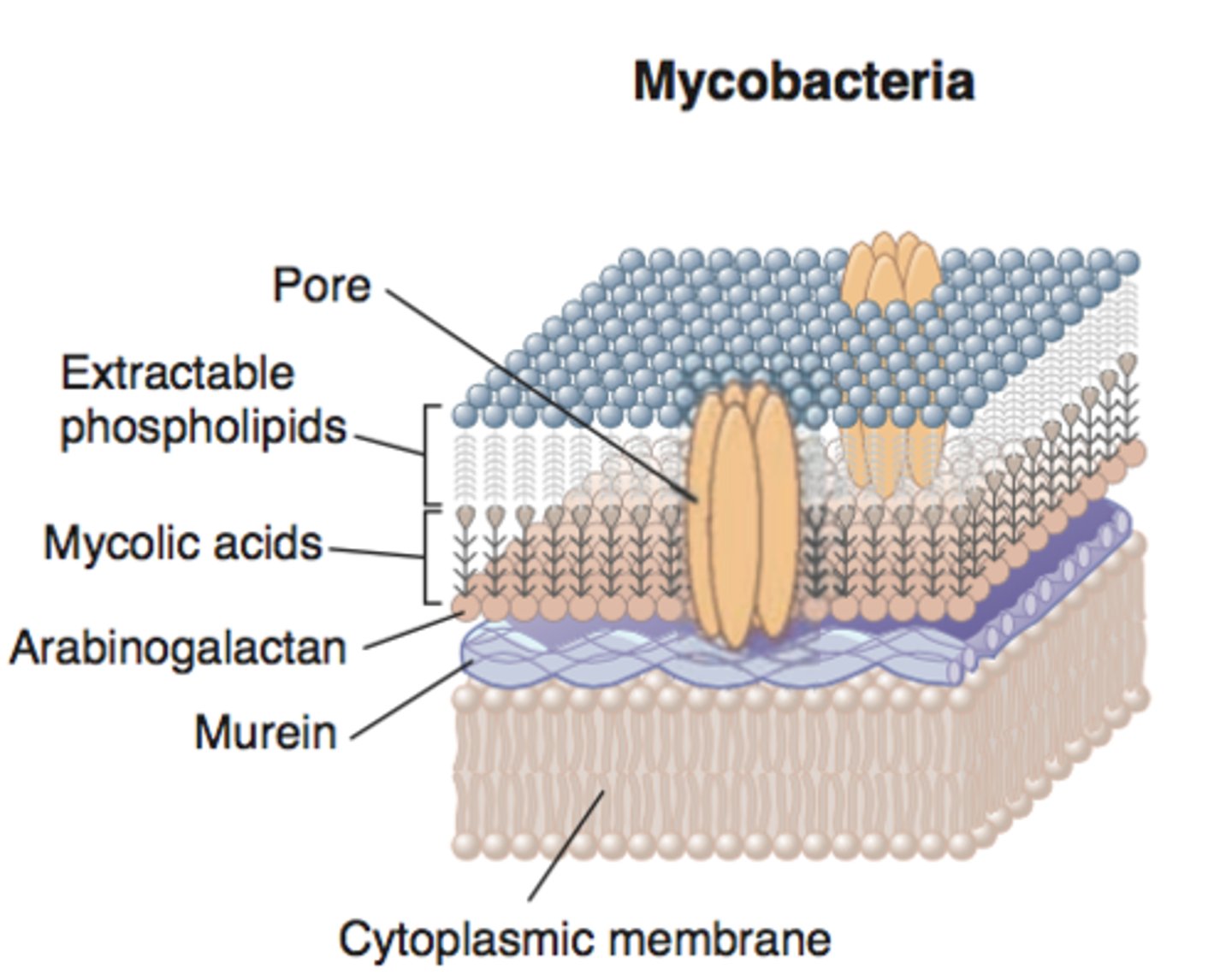
Acid fast cell walls contain this waxy substance that repels stains like the Gram stain.
Mycolic acid
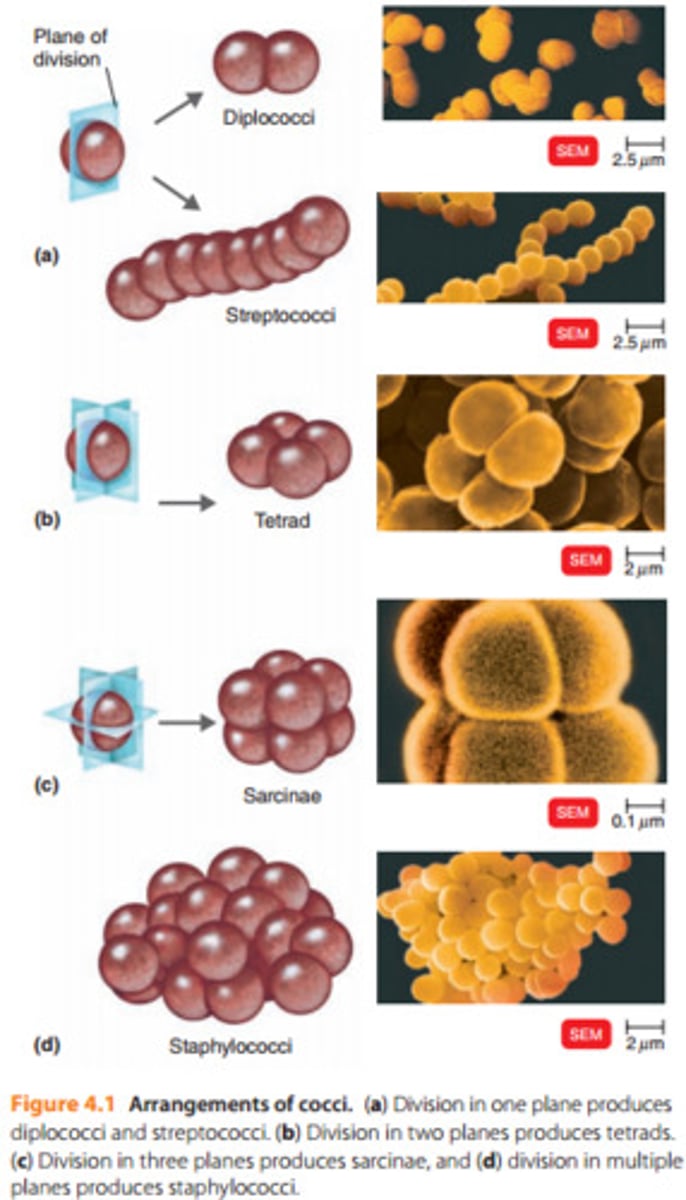
What possible microscopic arrangements can cocci have?
Single, diplococcus, staphylococcus, tetrad, streptococcus, sarcina
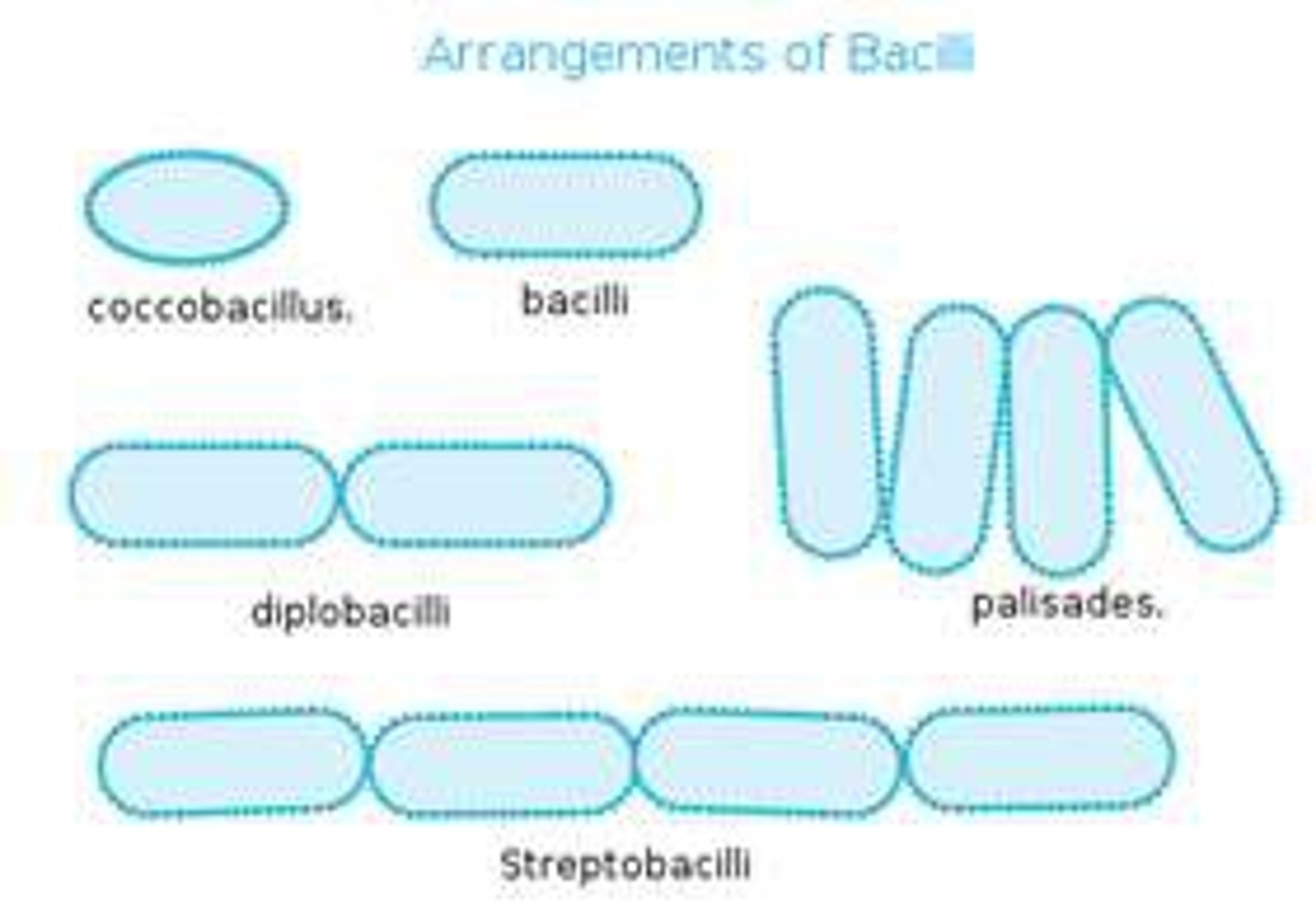
What possible microscopic arrangements can bacilli have?
Single, diplobacilli, streptobacilli
____ is not used for the negative stain since it will disrupt the cells and allow viewing of the true size.
Heat

The ___ is stained in the negative stain.
Background
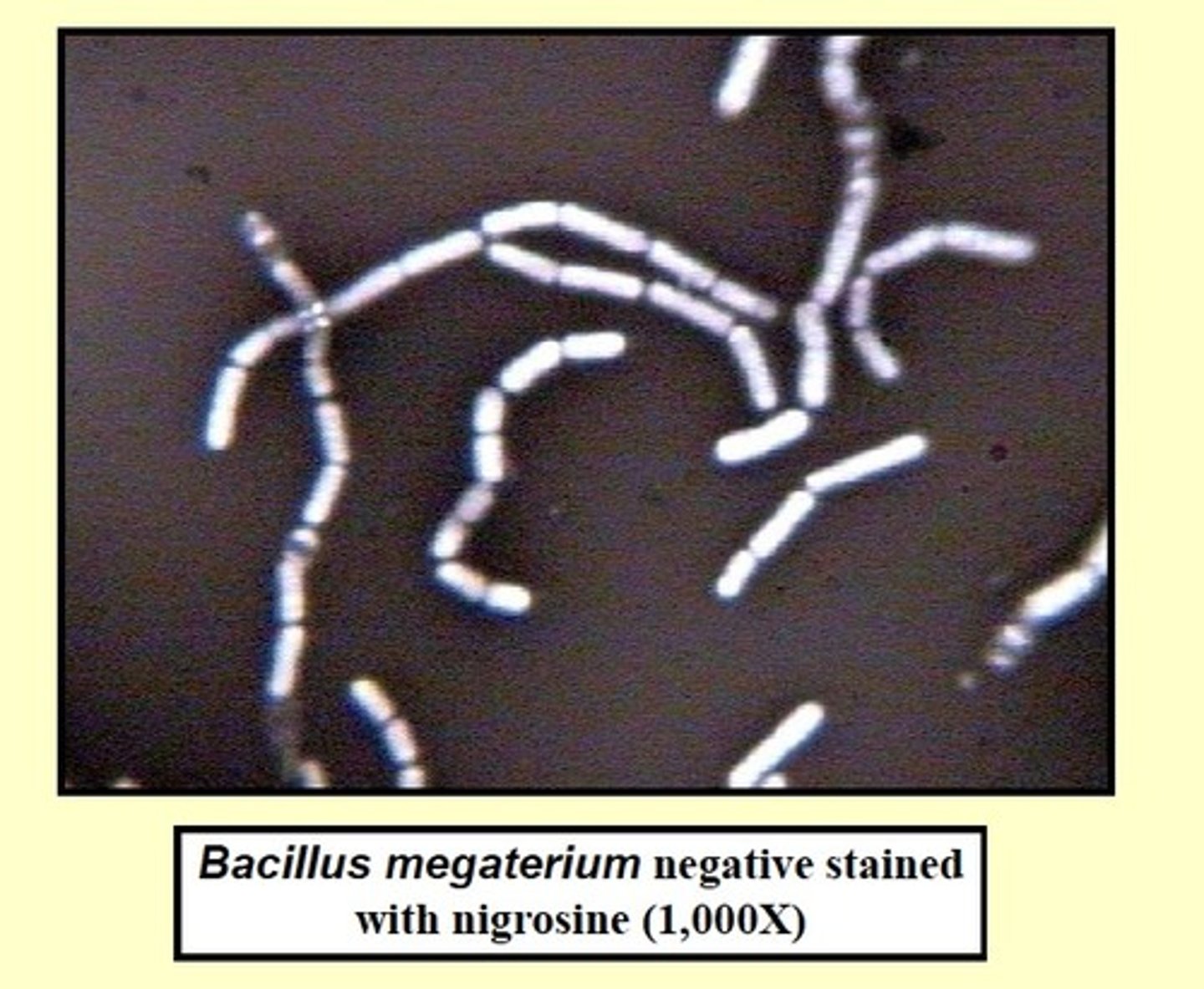

What is the primary stain of the gram stain?
Crystal violet- the first applied stain
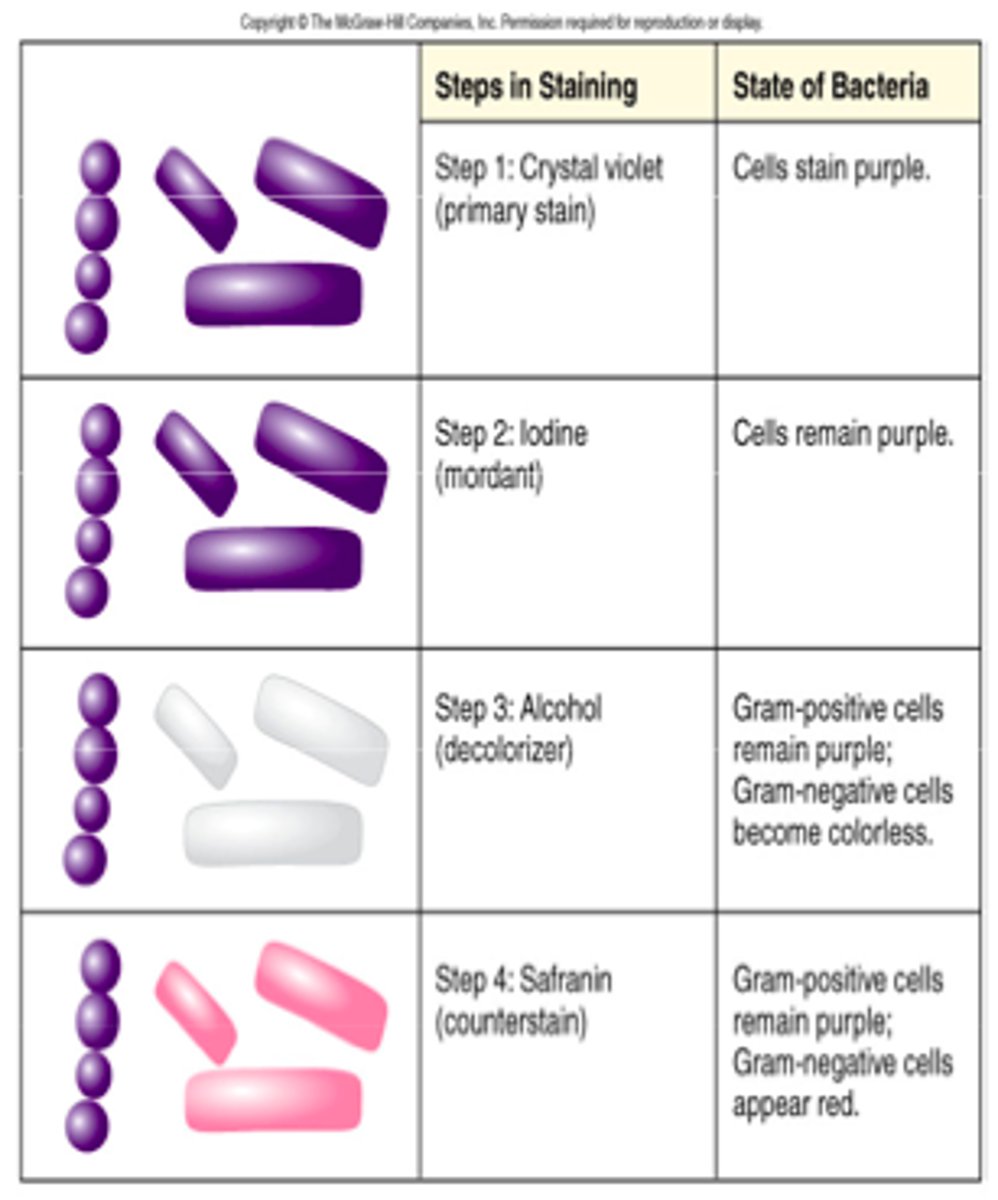
What is the mordant of the gram stain?
Iodine, which combine with crystal violet to form insoluable crystalline compounds that only stay trapped in thick peptidoglycan. Do not stay trapped in thin layers of peptidoglycan
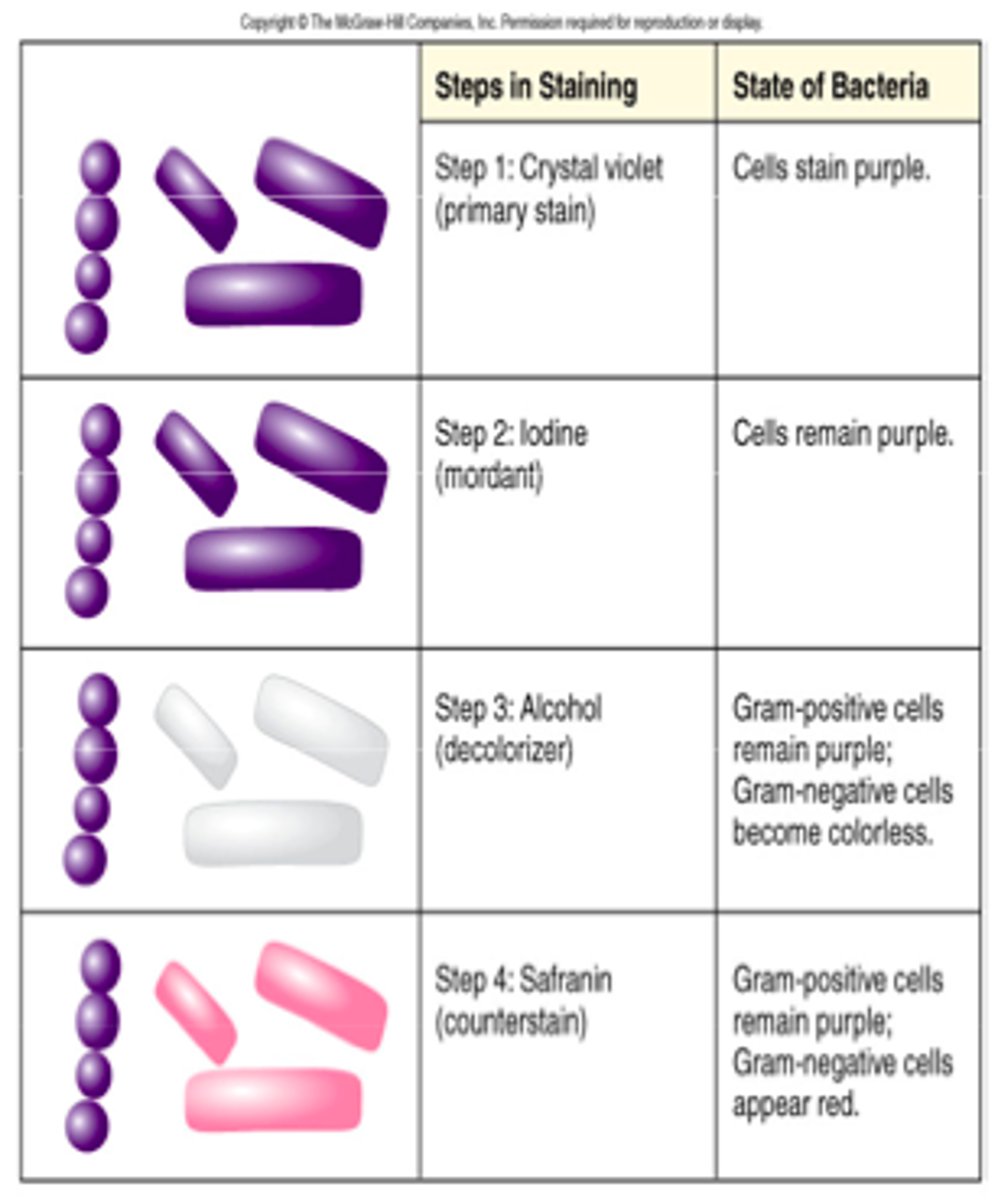
What is the decolorizer of the gram stain?
*95% ETHANOL*
-will remove the Crystal violet-iodine complex from Gram-Negative Cells
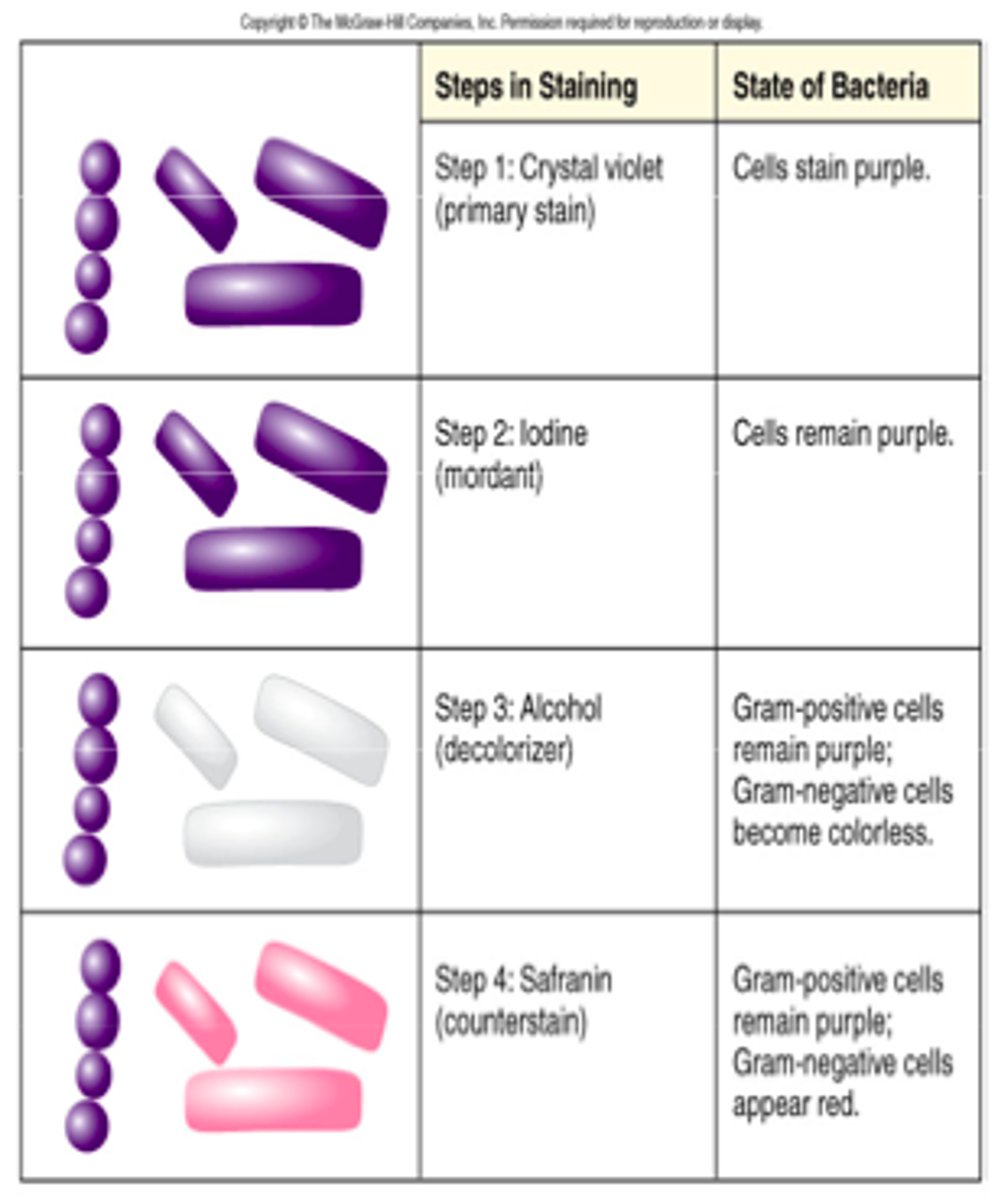
What is the counterstain of the gram stain?
Safranin
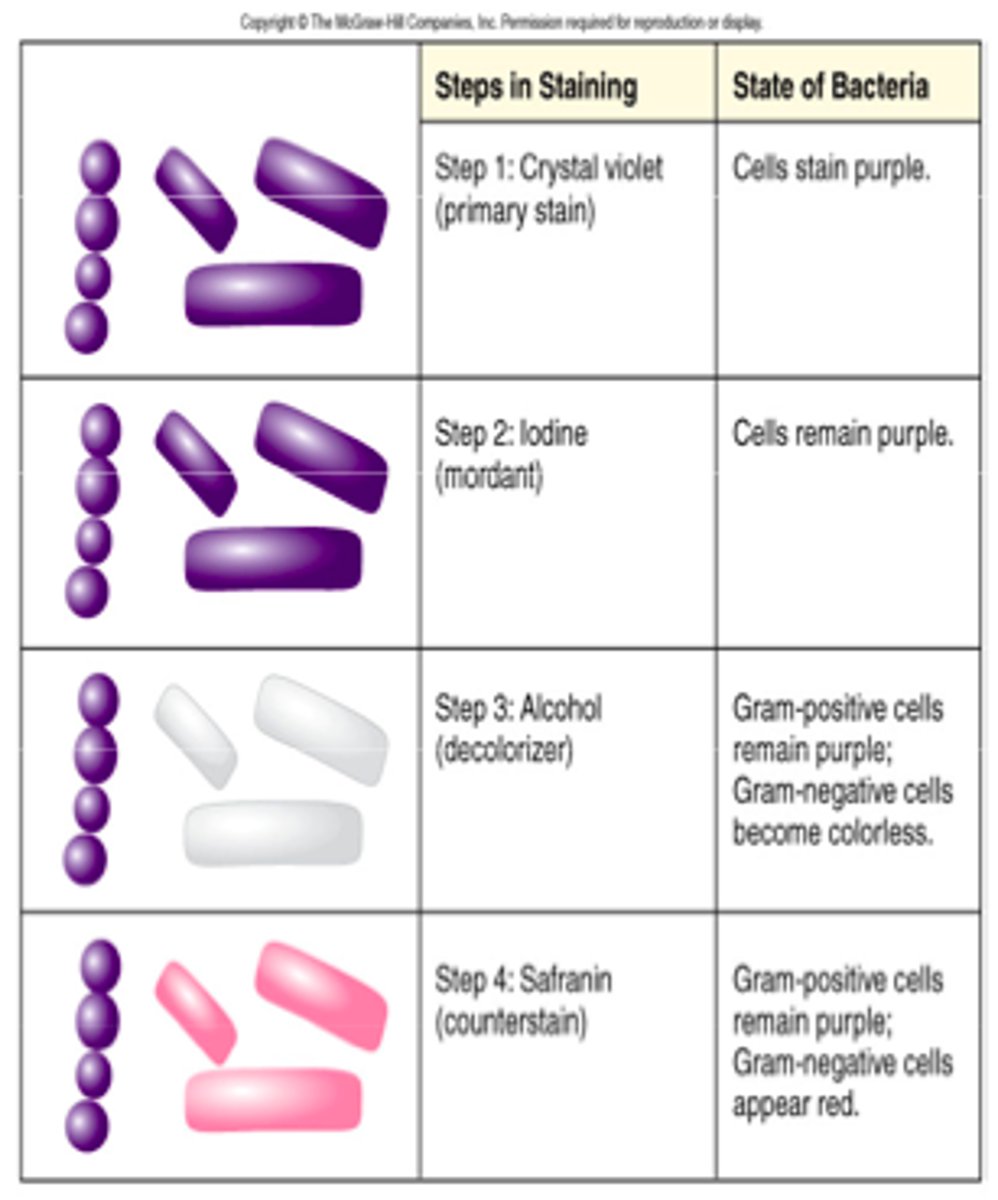
After staining with crystal violet during the gram stain, _____ appear purple.
Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
If the iodine is left out of the gram stain, how will gram negative cells appear?
Pink (iodine helps to retain the gram stain so crystal violet is not retained, cell is then stained with safranin/pink). Be familiar with other examples.
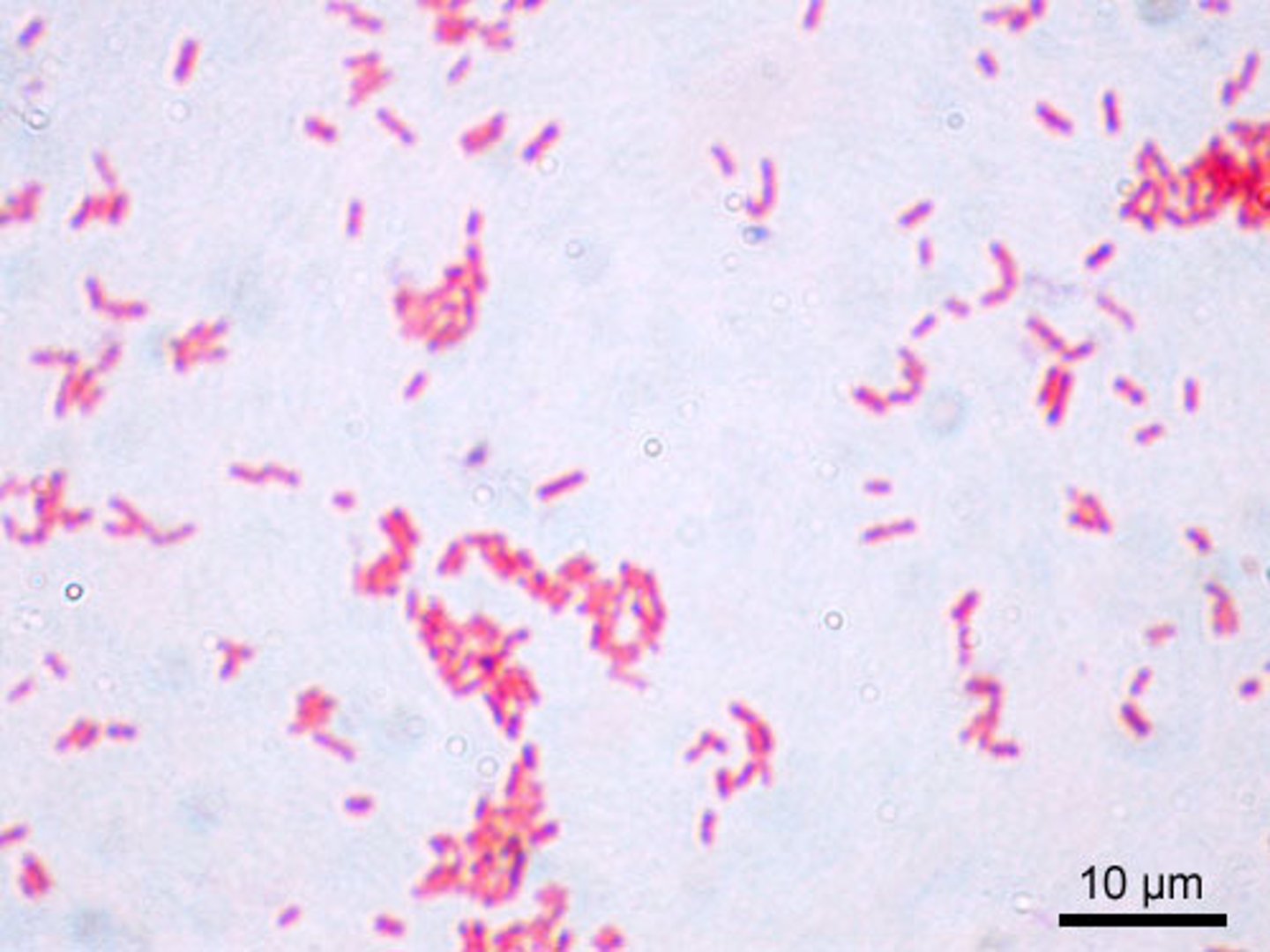
What color are gram positive cells?
Purple
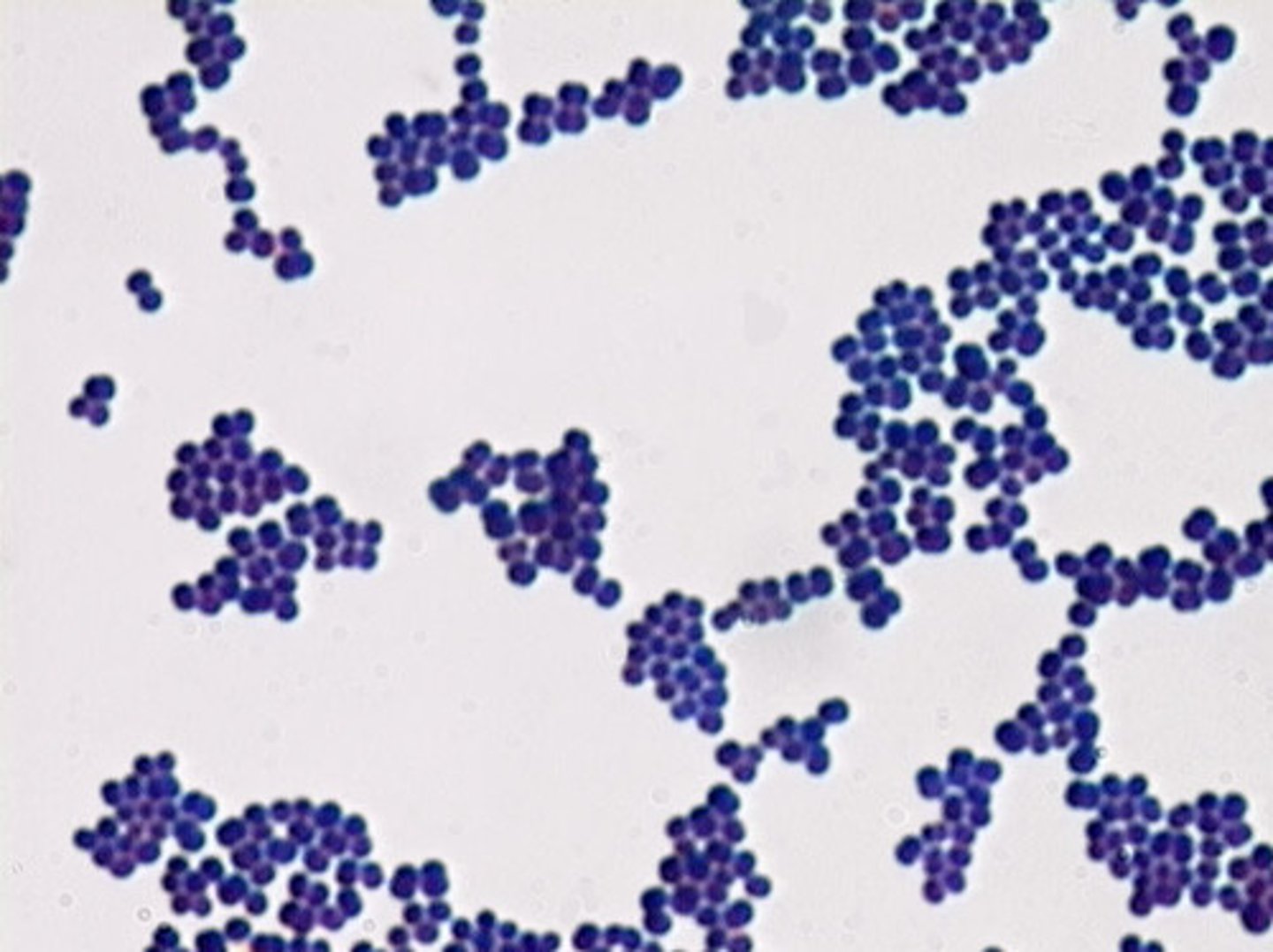
What color are gram negative cells?
Pink
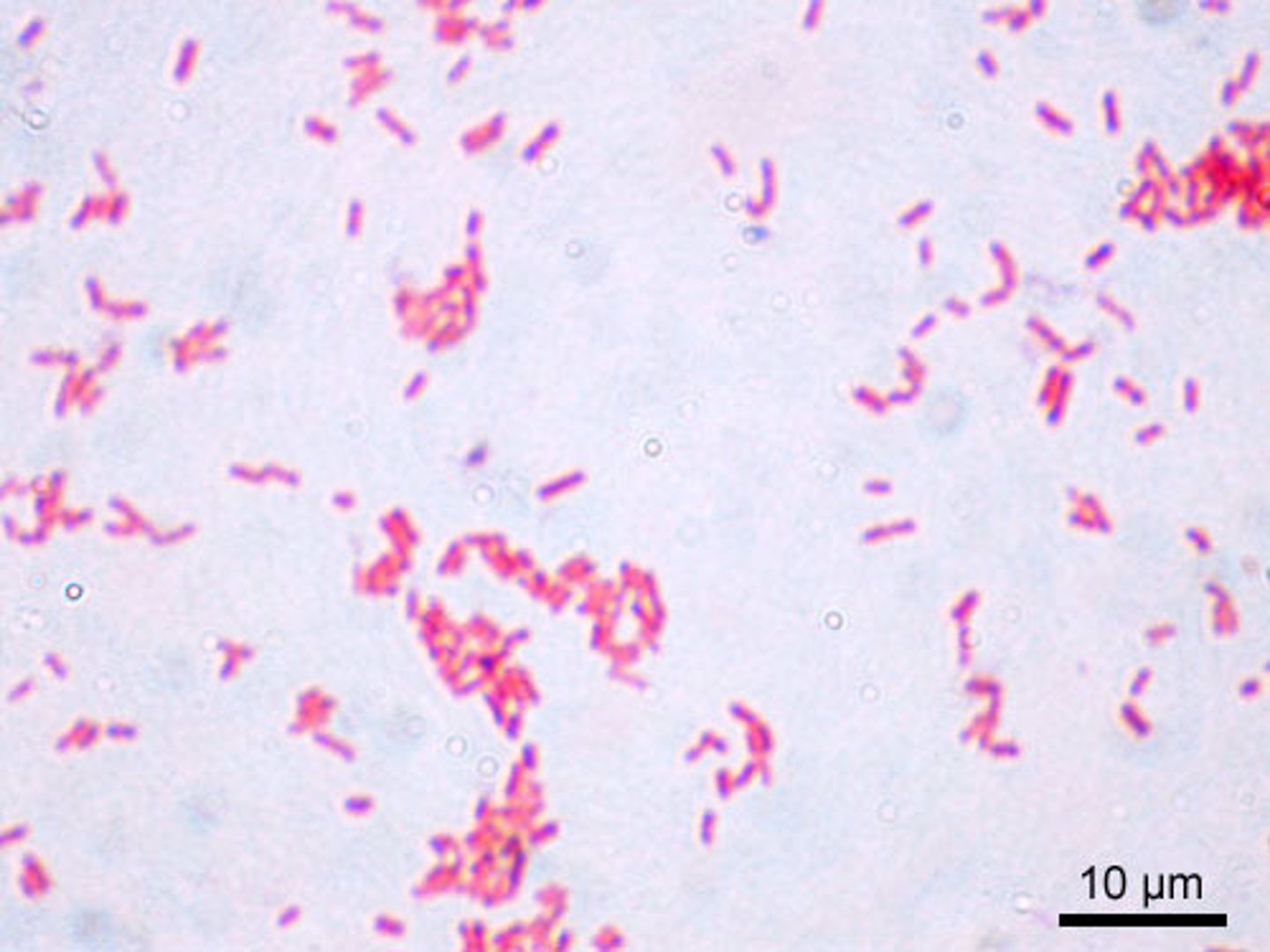
What endospore forming organisms (genera/genus of bacteria) cause disease?
Bacillus, Clostridium
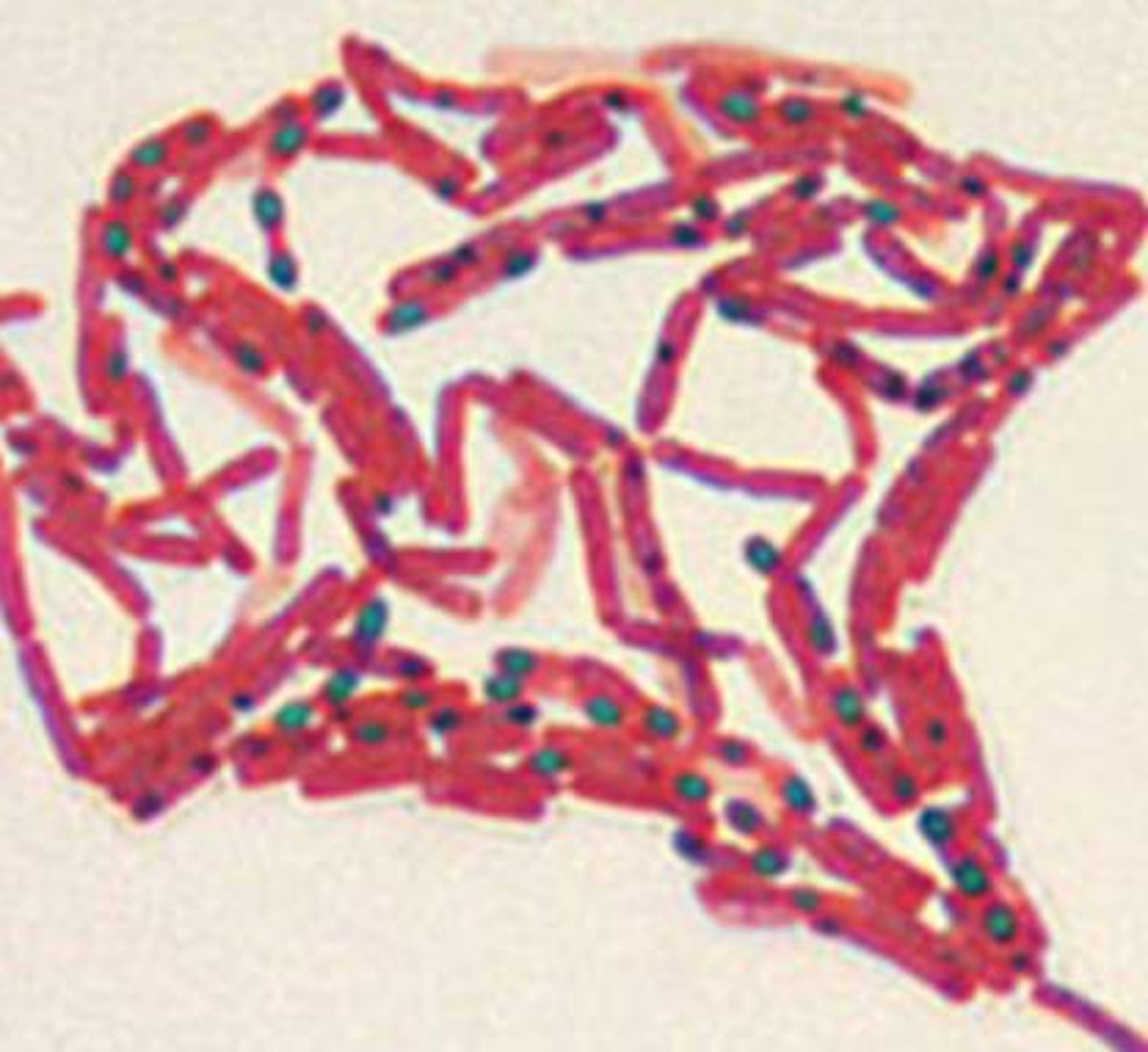
What diseases are caused by endospore formers?
Anthrax, tetanus, gangrene, botulism, pseudomembraneous colitis
What is the primary stain of the endospore stain?
Malachite green
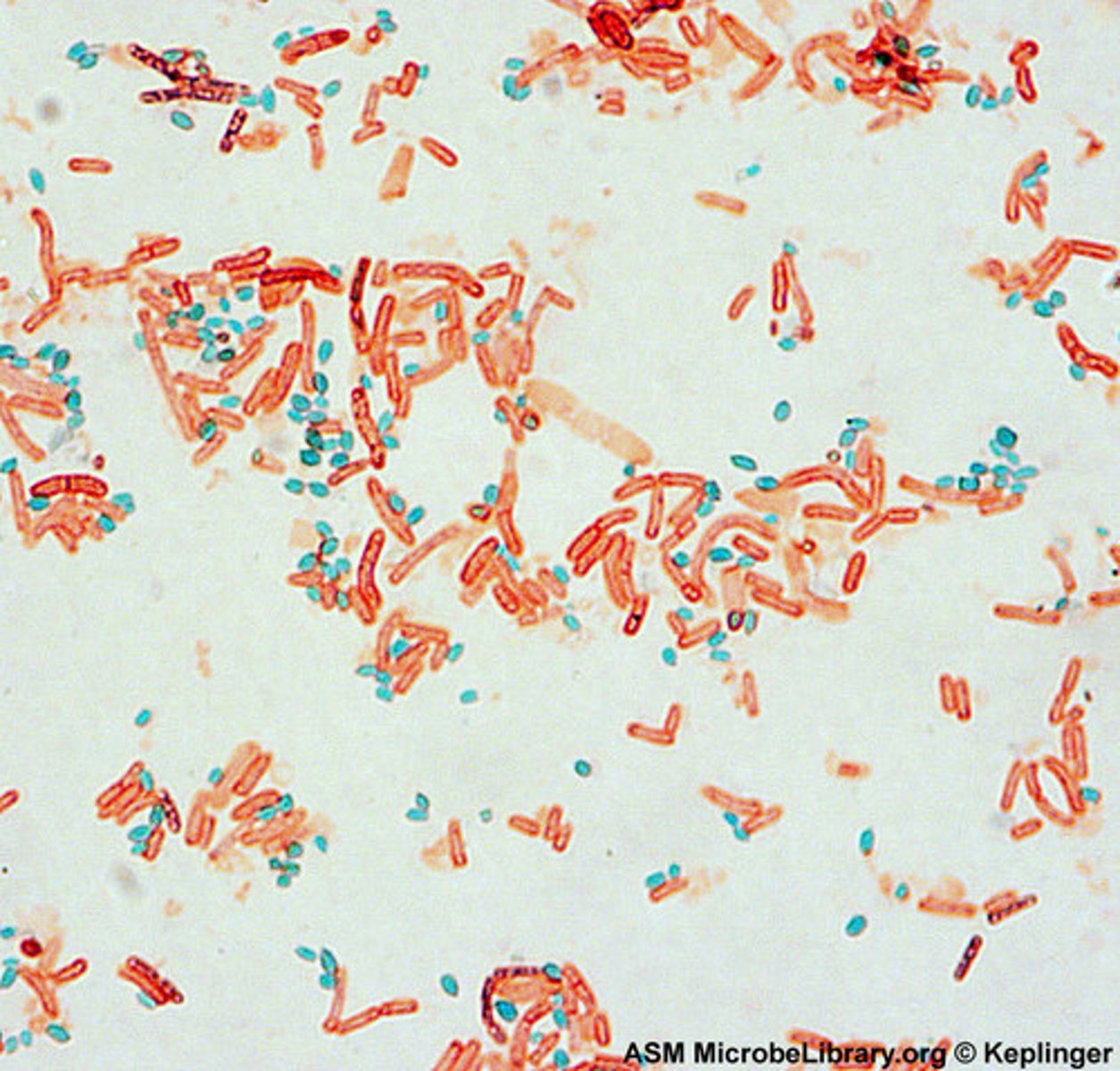
What is the decolorizer of the endospore stain?
Water

What is the counterstain of the endospore stain?
Safranin
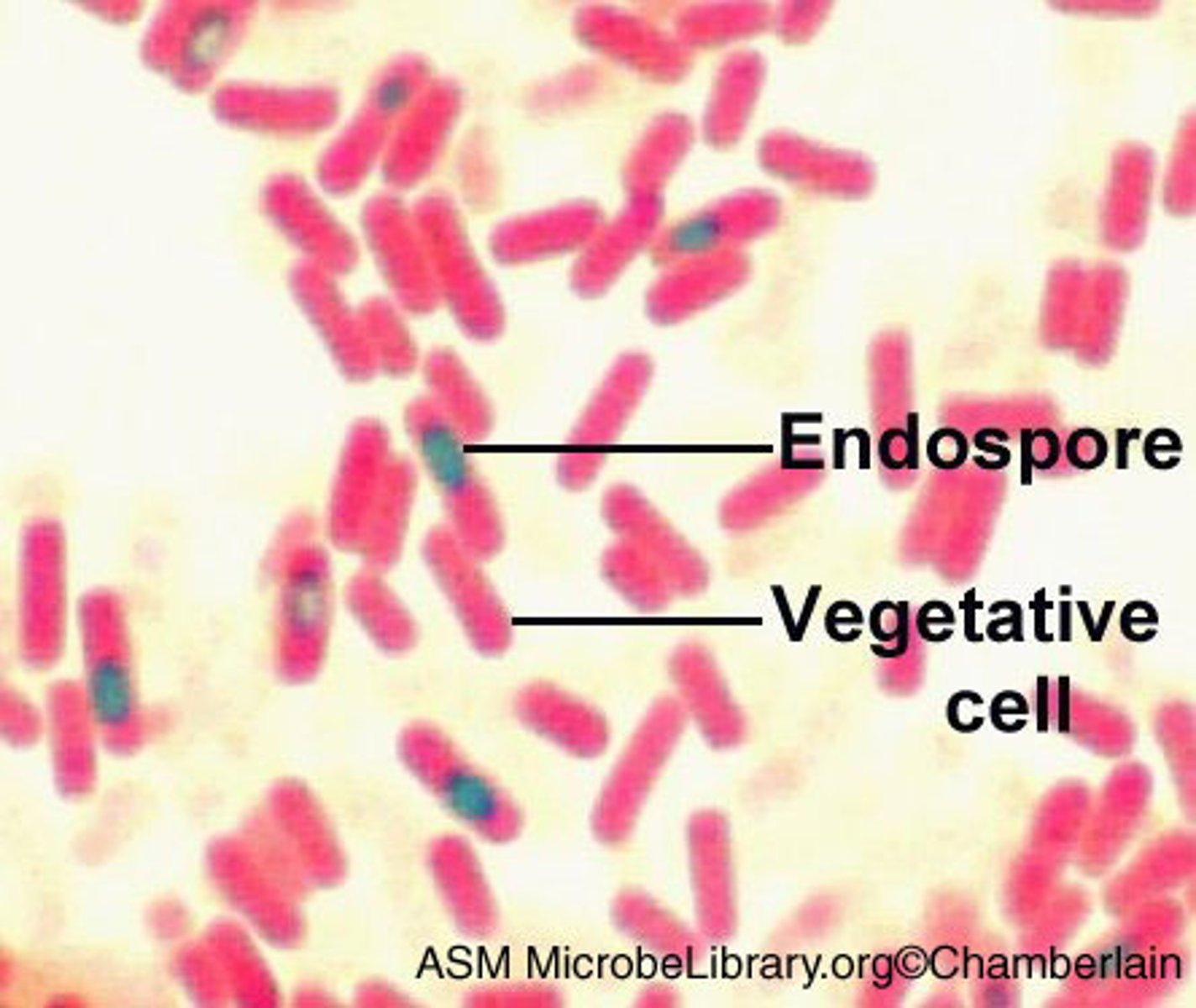
What color are endospores after the endospore stain?
Green
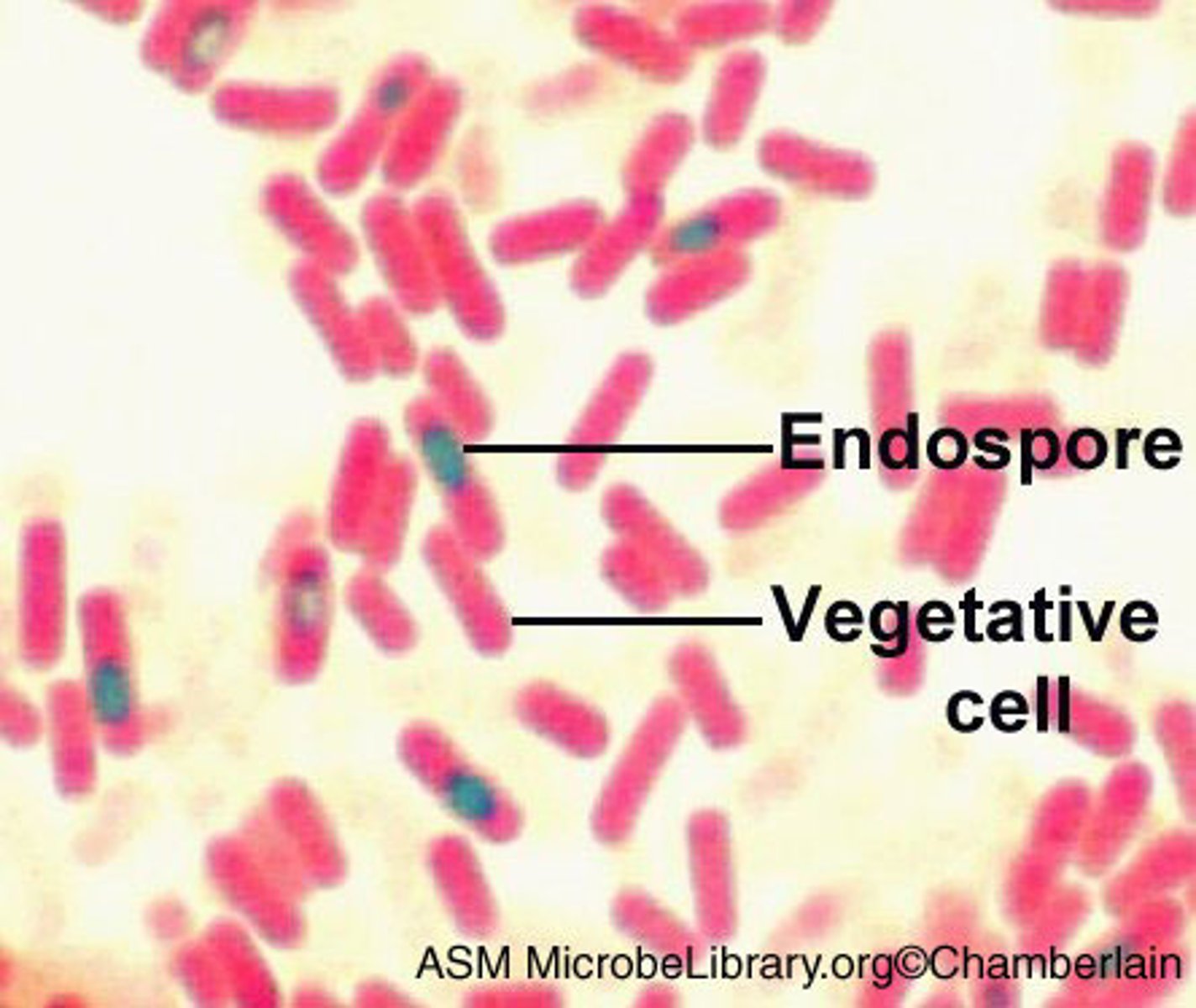
What color are nonsporeforming cells and sporangia after the endospore stain?
Pink
What color are endospores after the gram stain?
Endospores are clear after the gram stain since the stain cannot penetrate the endospore. This is why we use another stain to detect the endospores bacteria can make.
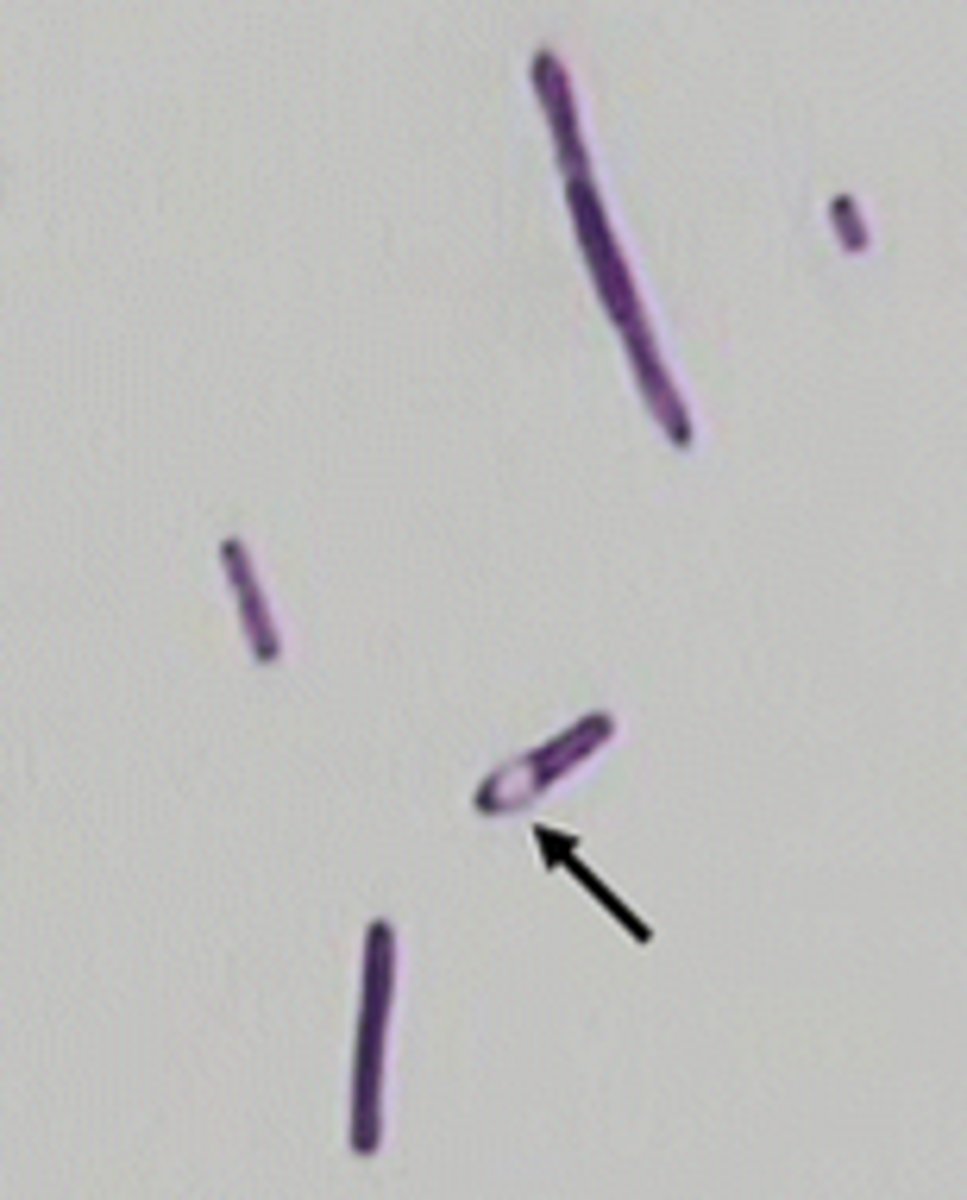
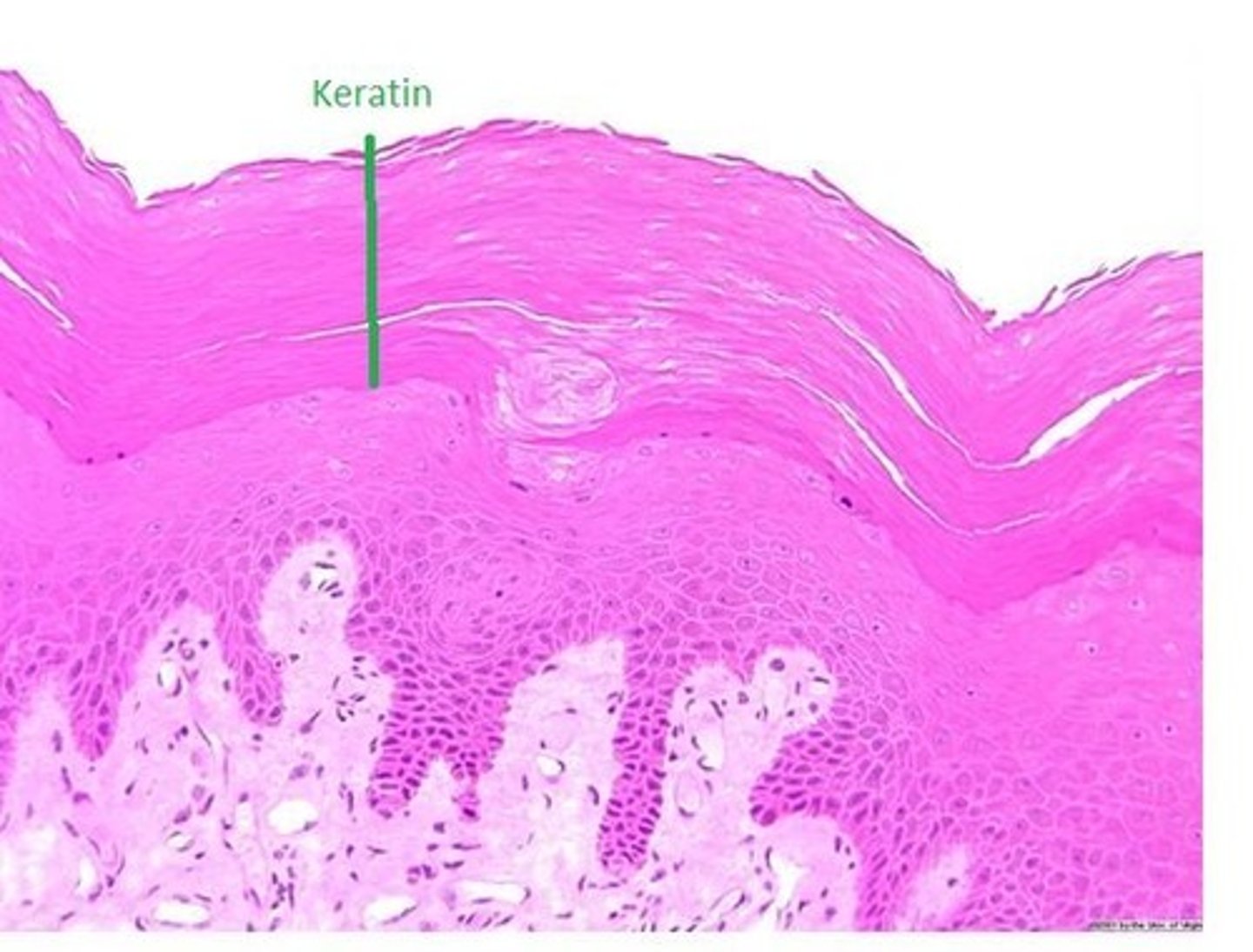
The waterproofing protein ______ prevents most stains from penetrating the endospore.
Keratin
Why are endospore made?
As a survival measure when severe conditions are present (low nutrients, dryness)

What chemical keeps endospores dormant?
Dipicolinic acid (along with calcium)
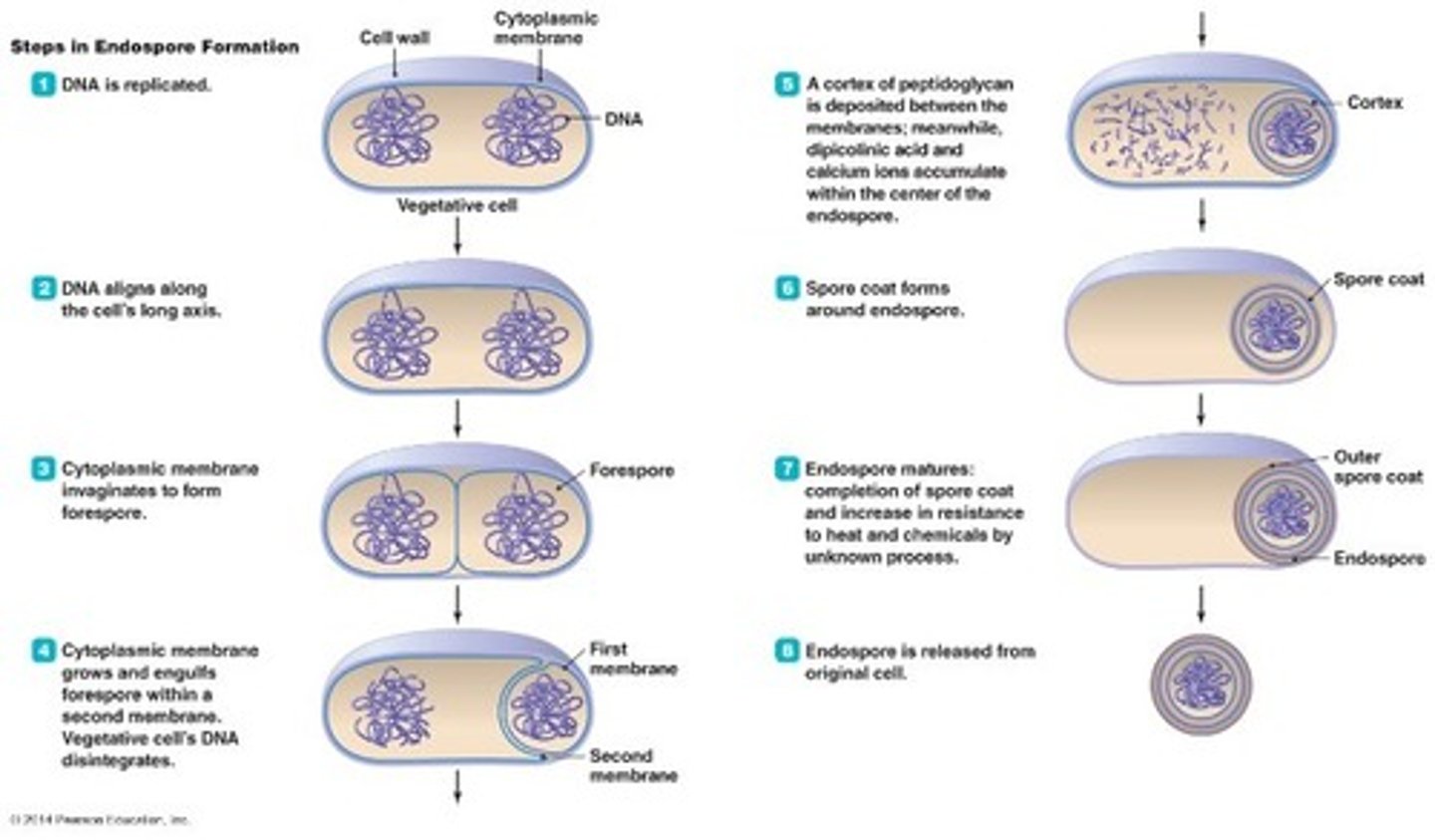
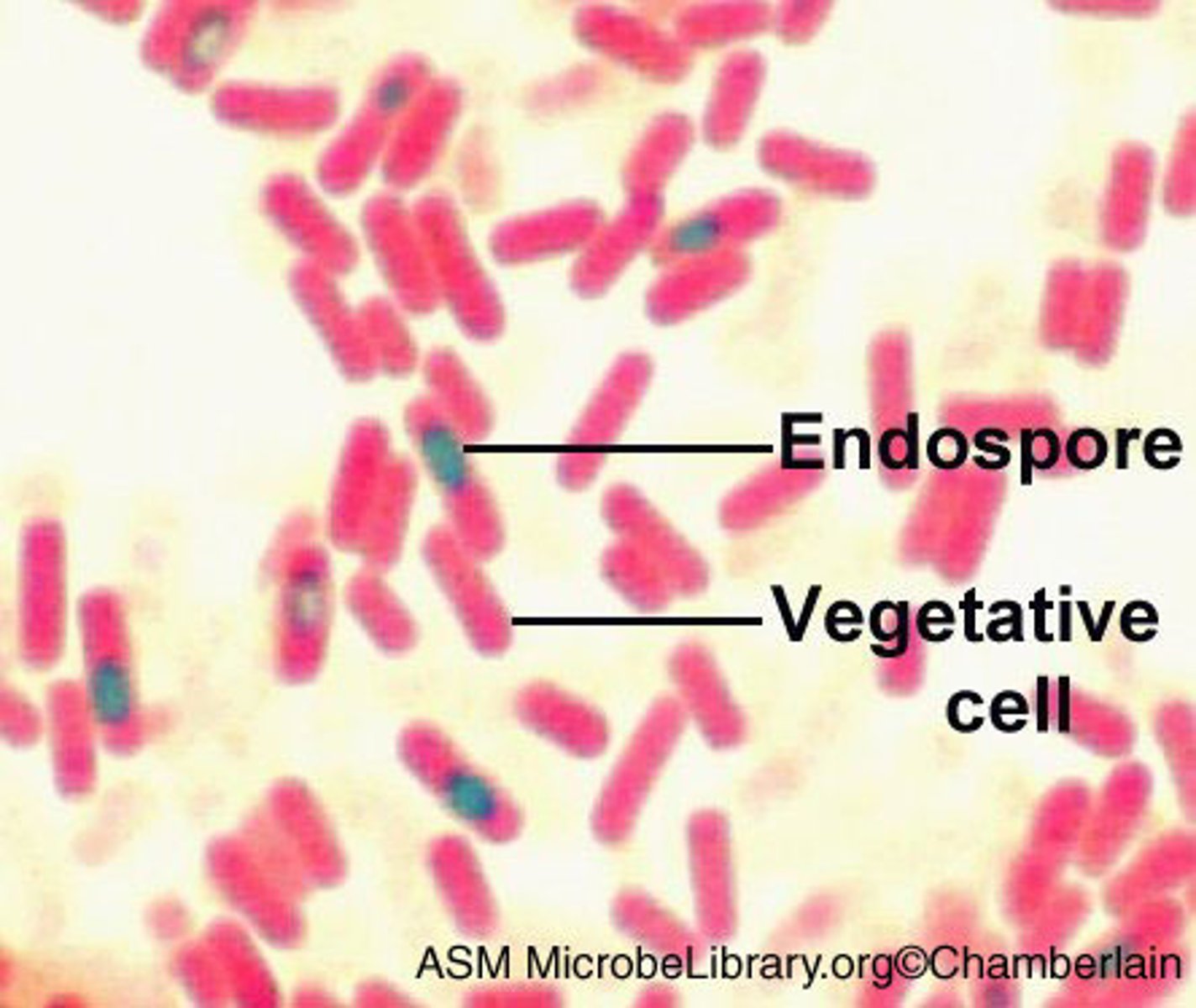
The mother cell that houses the endospore is known as ______________.
Sporangium
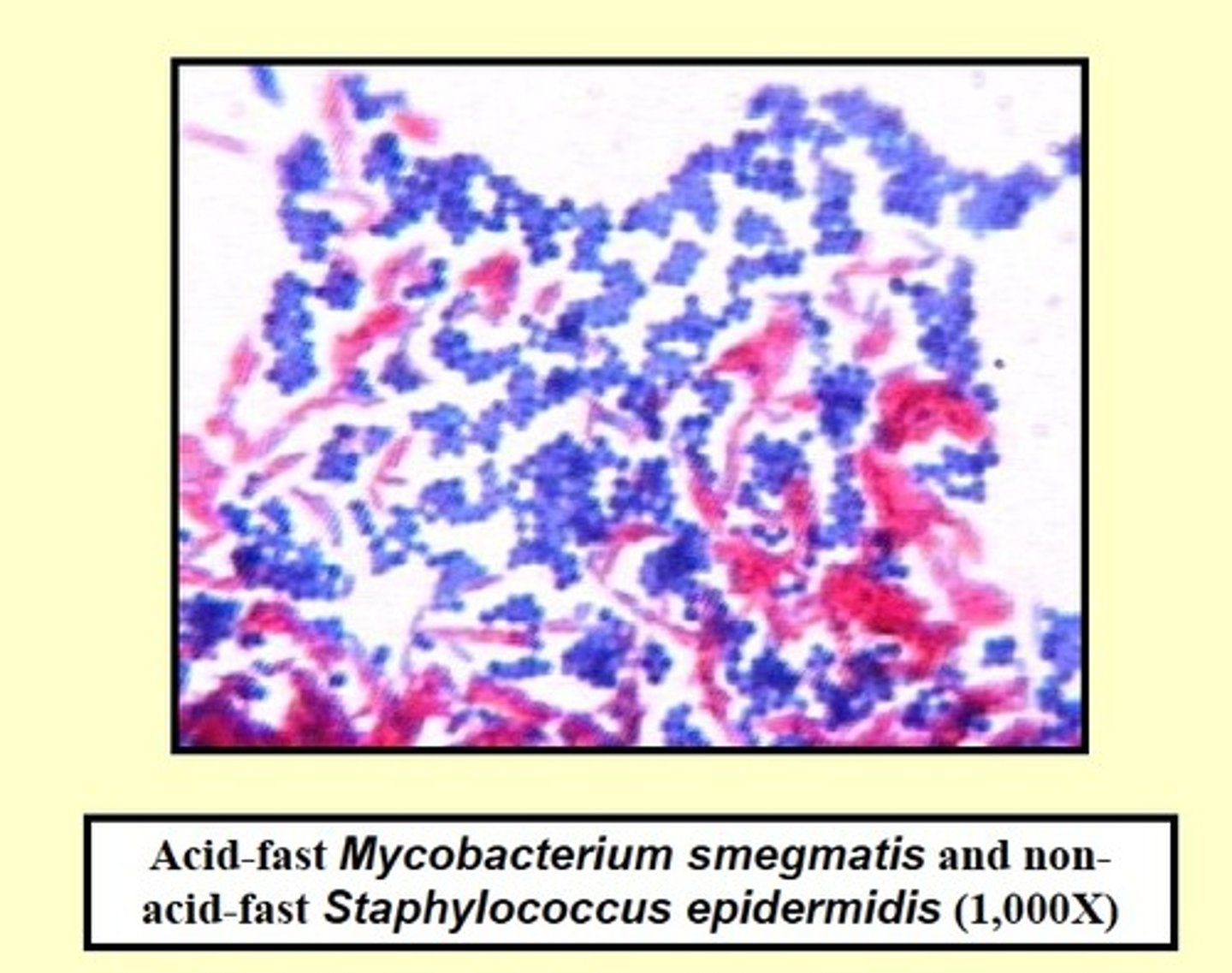
What acid fast organisms (genera/genus of bacteria) cause disease?
Mycobacterium, Nocardia
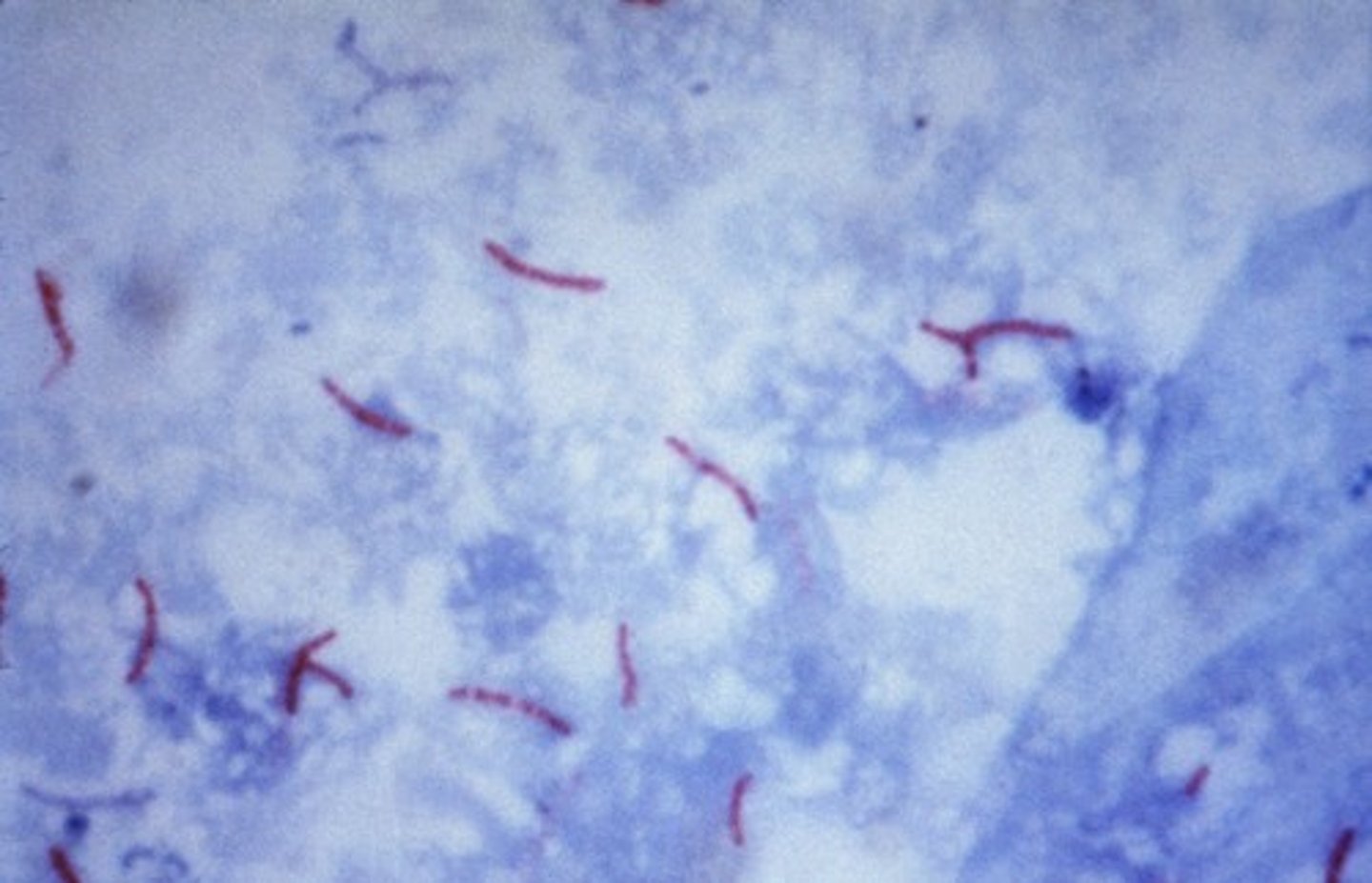
What diseases are caused by acid fast bacteria?
Tuberculosis, leprosy
What is the primary stain of the acid fast stain?
Carbolfuschin
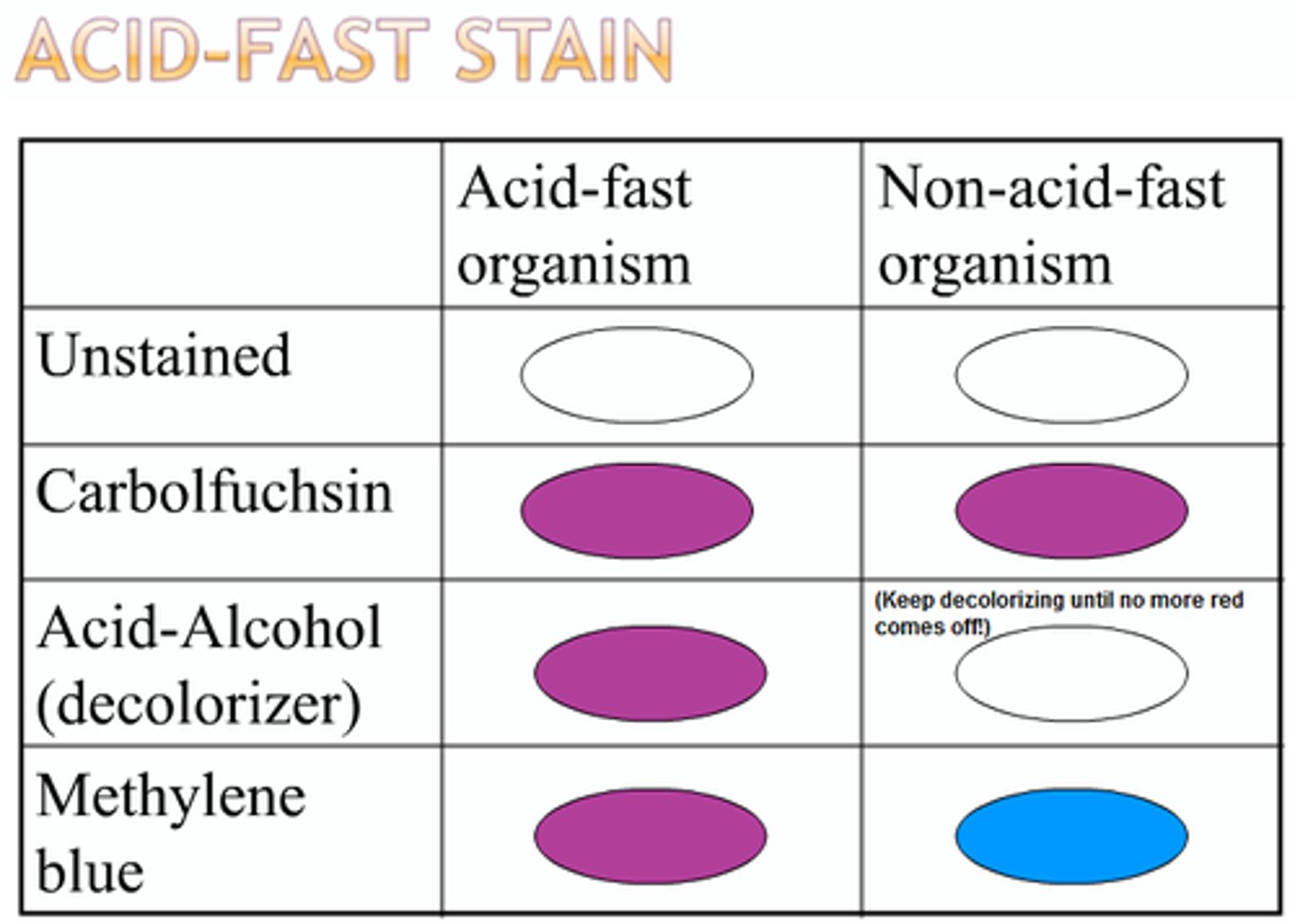
What is the decolorizer of the acid fast stain?
Acid alcohol
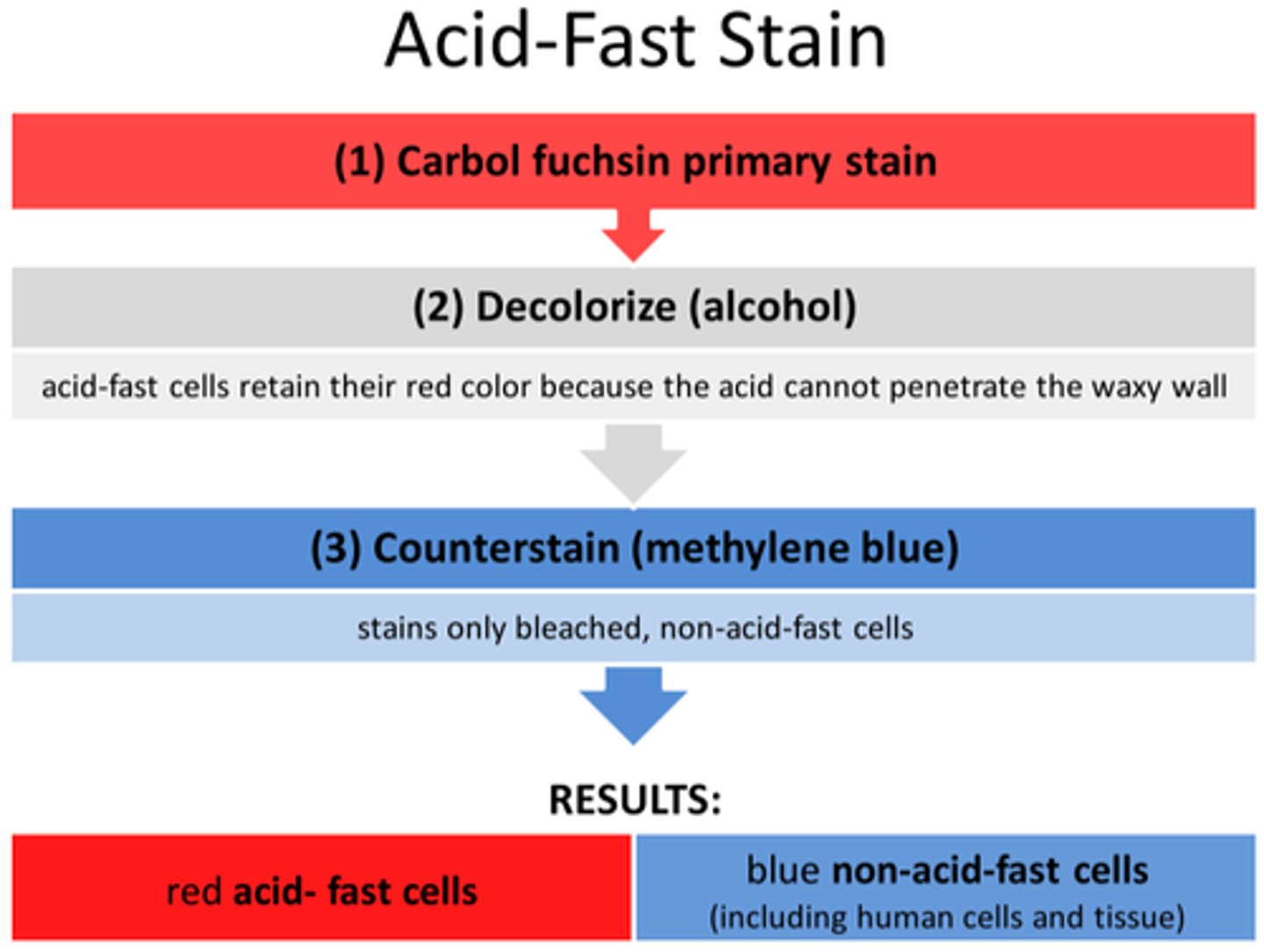
What is the counterstain of the acid fast stain?
Brilliant green/Methylene blue
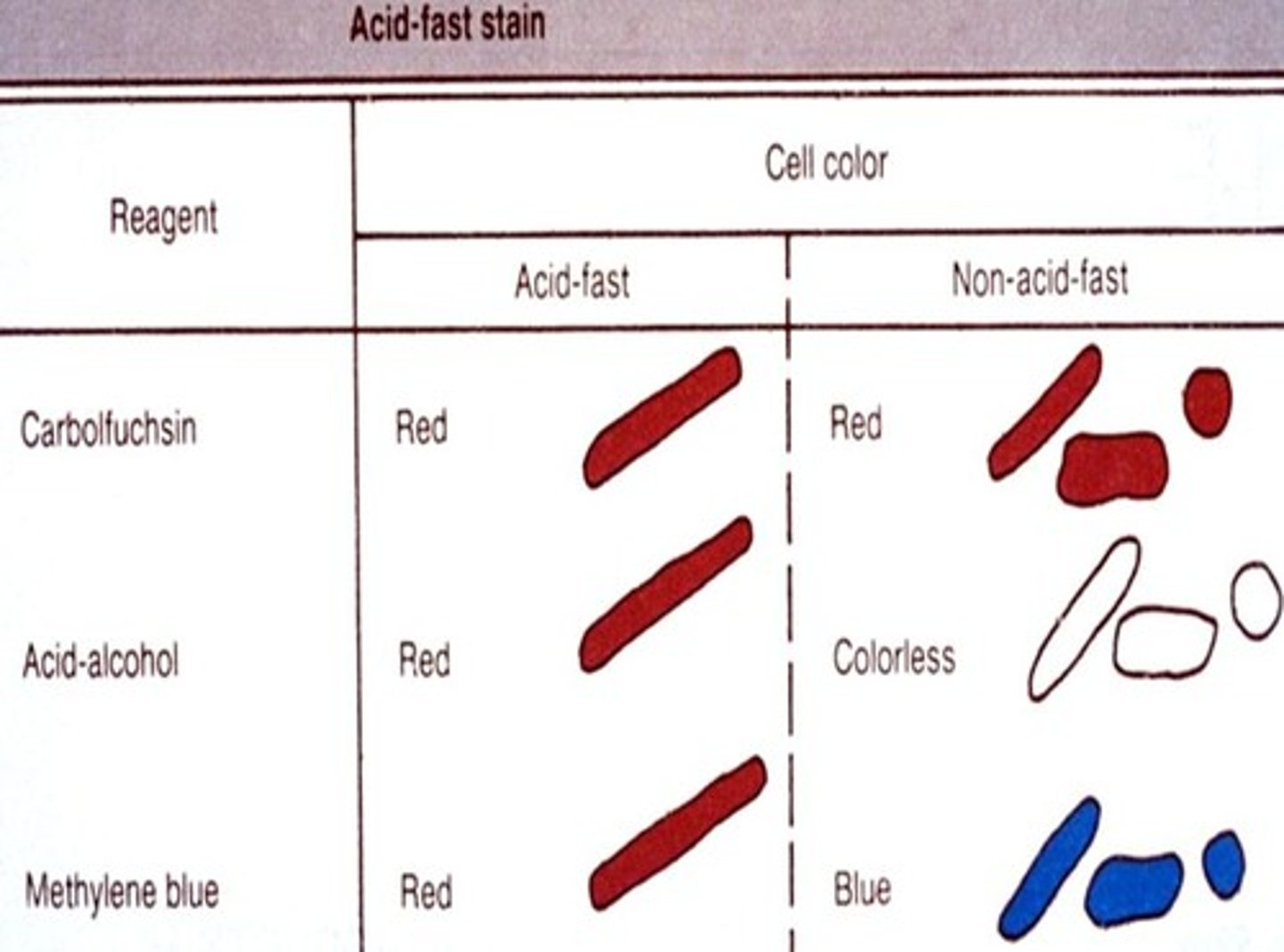
What color are acid fast positive cells?
Pink
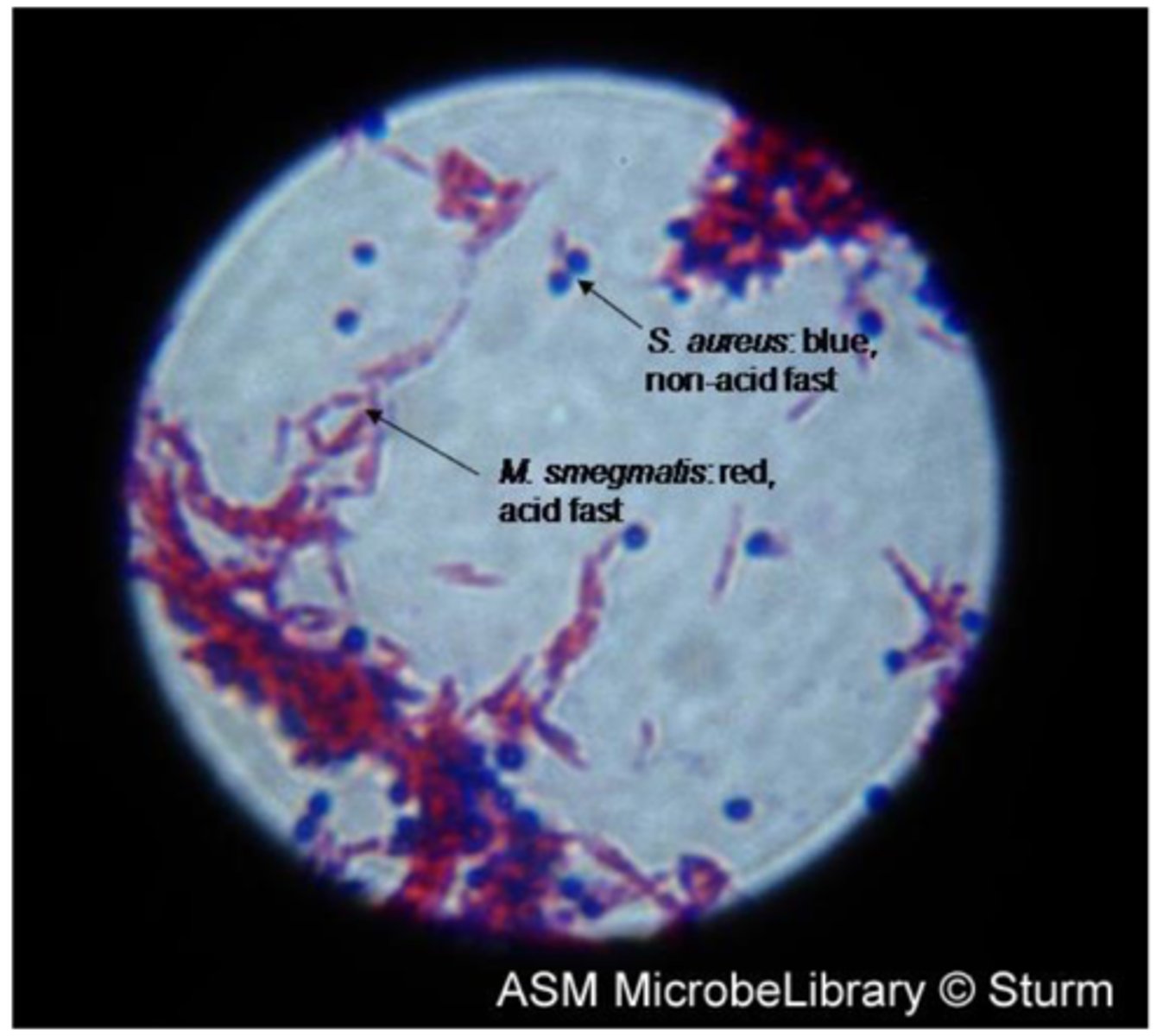
What color are non acid fast cells?
Green or blue depending on the counterstain
________ bacteria that have no flagella.
Atrichous
________ bacteria that have flagella at each pole.
Amphitrichous

________ bacteria that have flagella all over the surface.
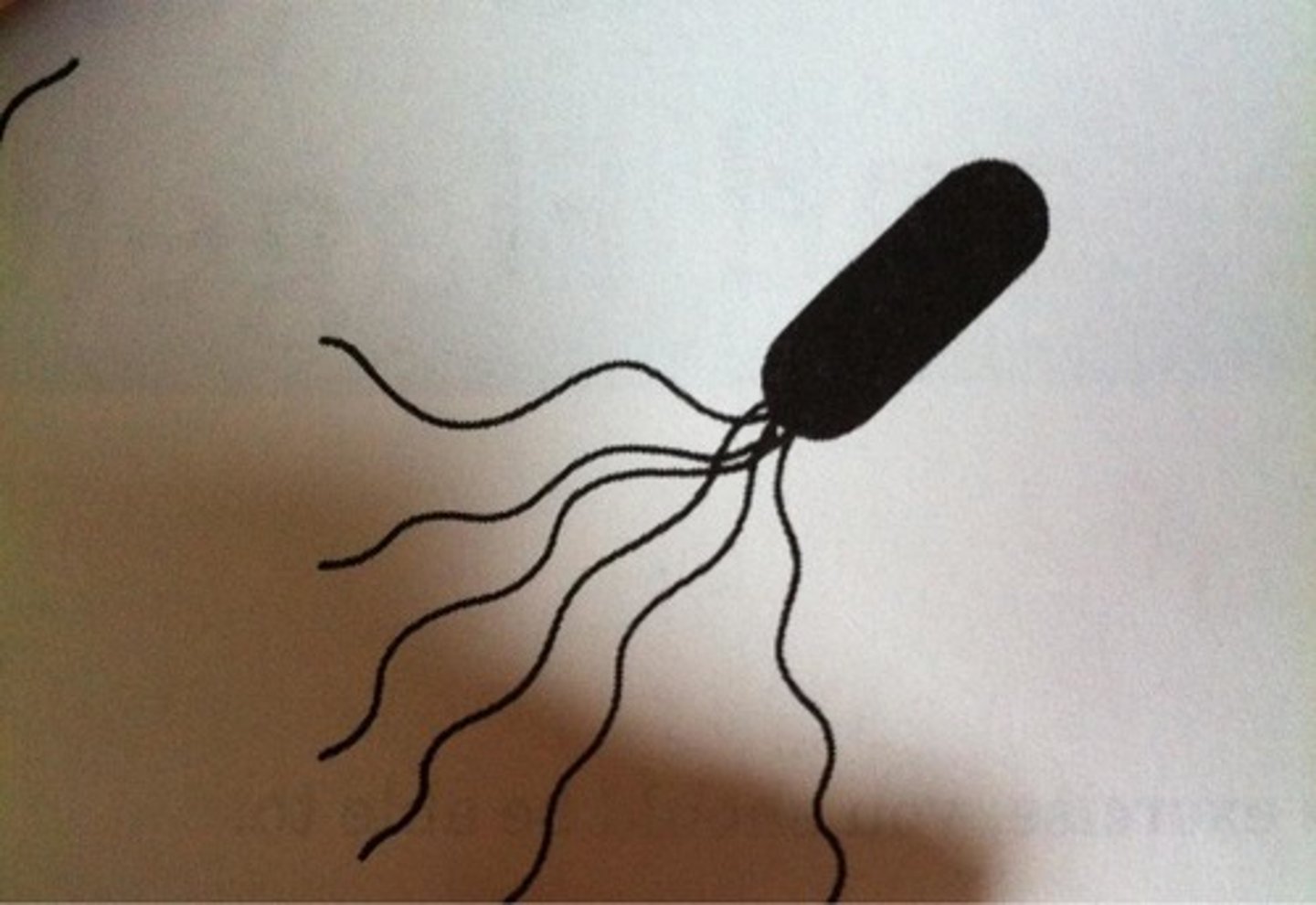
Peritrichous
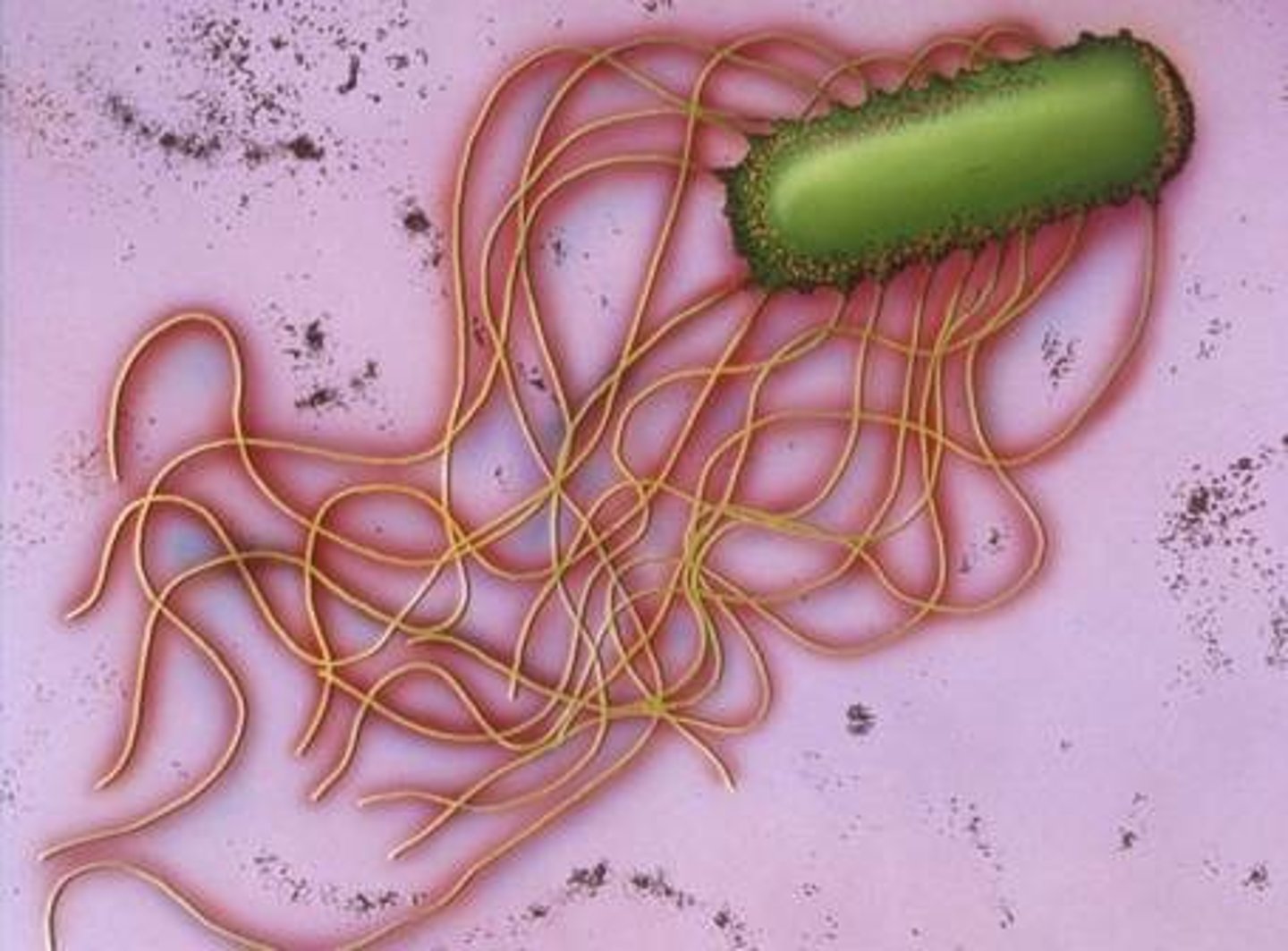
________ bacteria that have a tuft of flagella at one end.
Lophotrichous
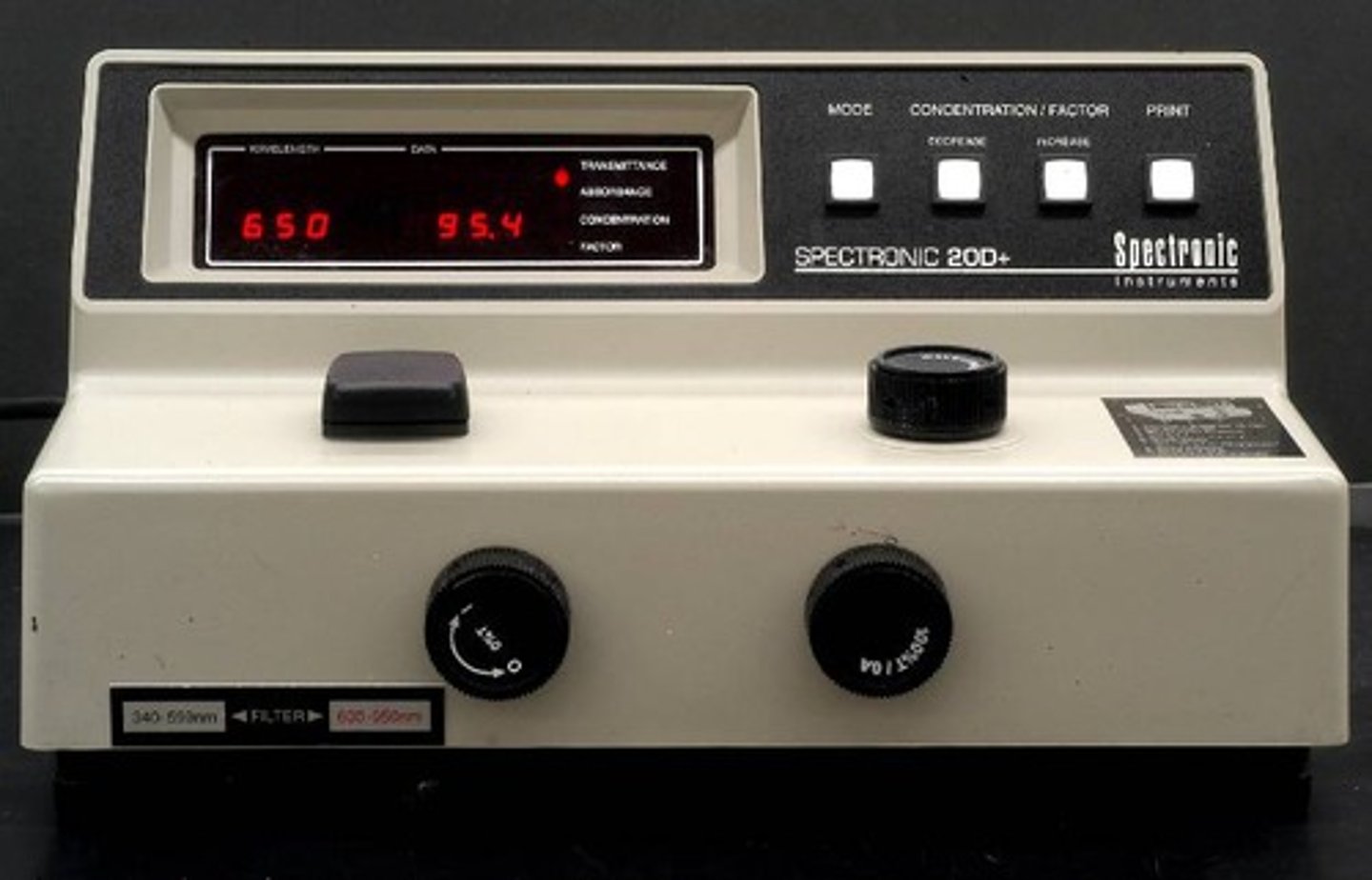
This machine is used to measure transmittance and absorbance of light to determine an estimated bacterial population growth.
Spectophotometer

These organisms grow better at cold temps (below 15C).
Psychrophiles
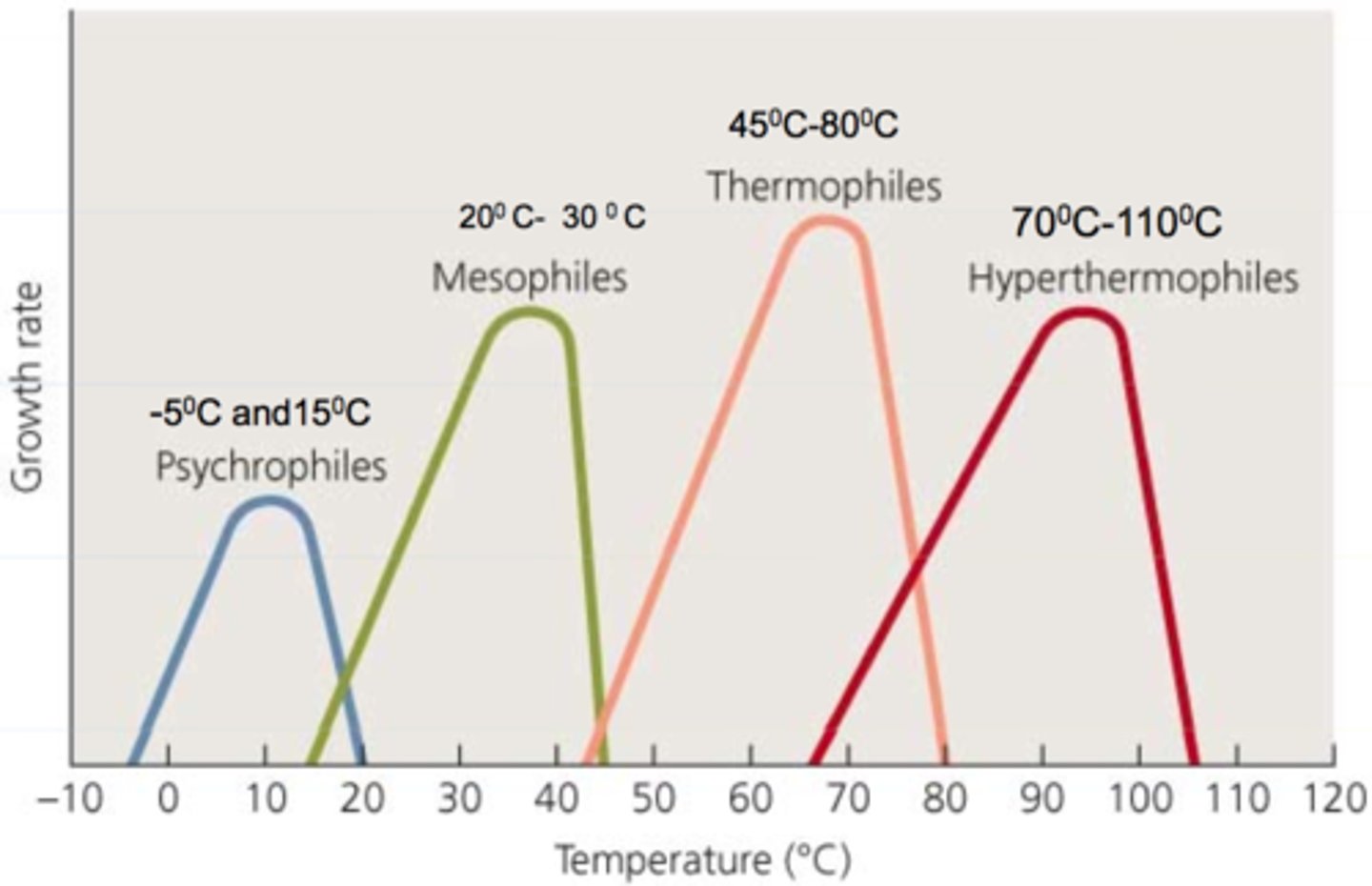
These organisms grow better at moderate temps.
Mesophiles
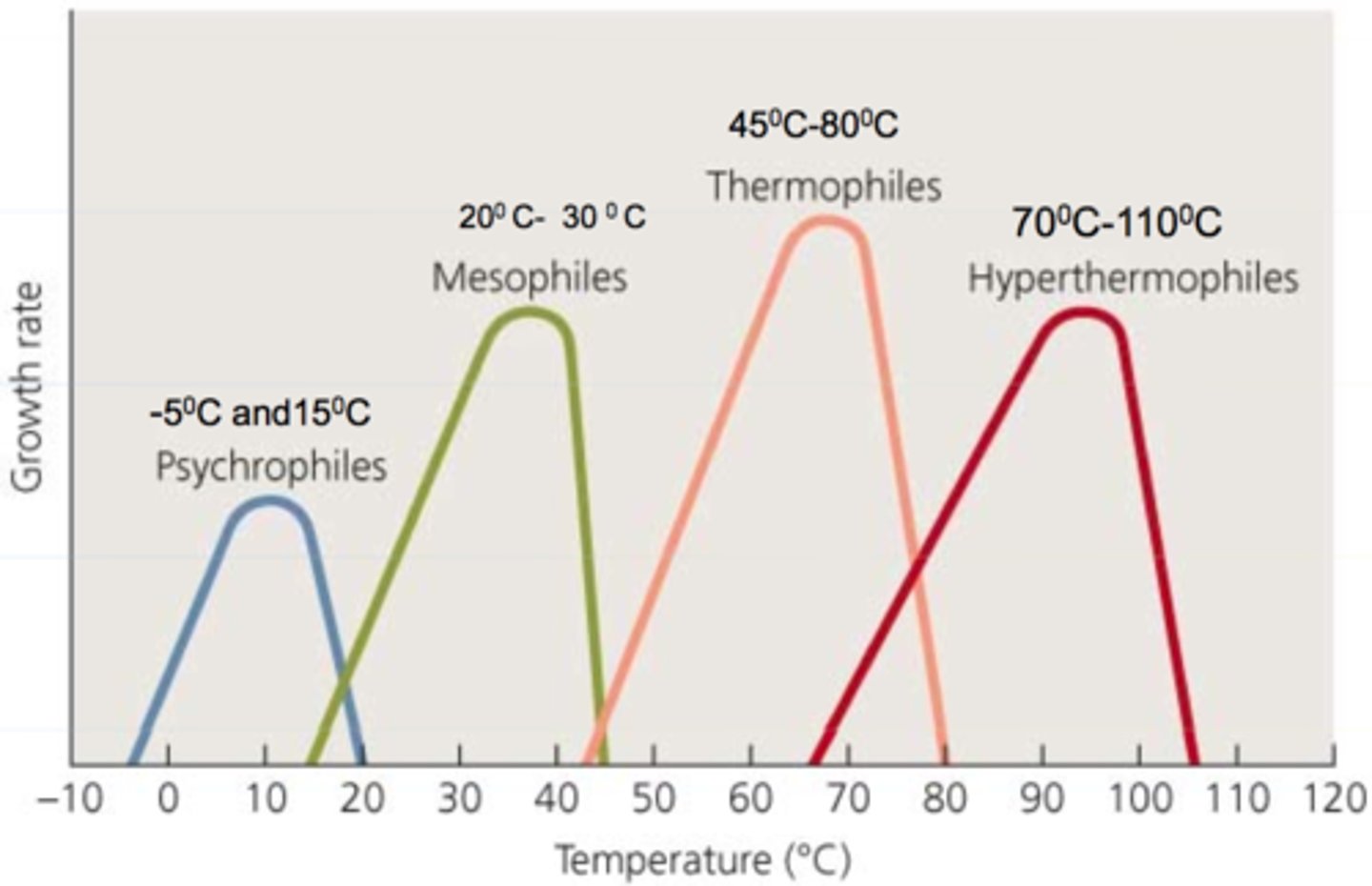
These organisms grow better at warm temps.
Thermophiles
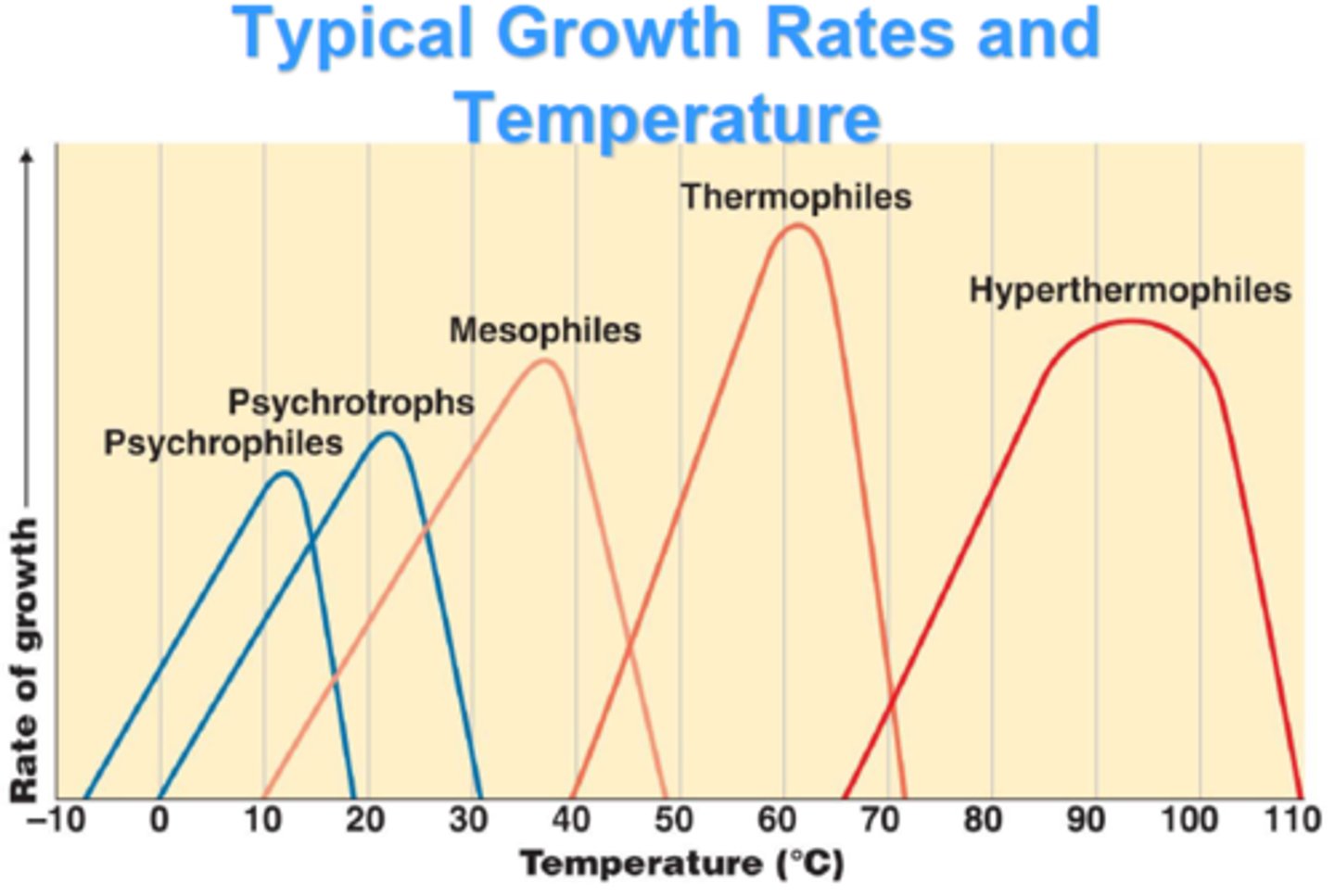
These organisms grow in temperature ranges between psychrophiles and mesophiles.
Psychrotrophs
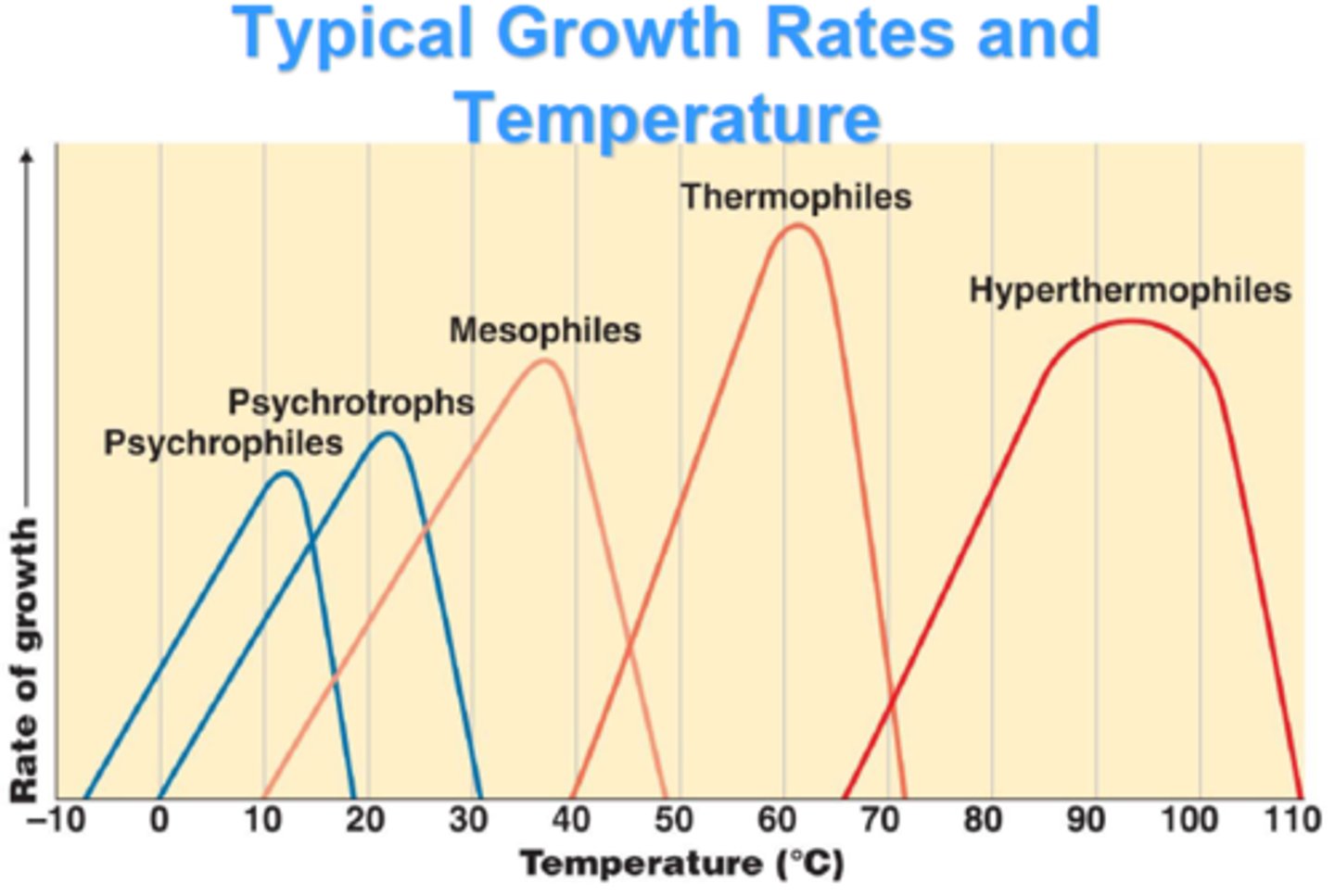
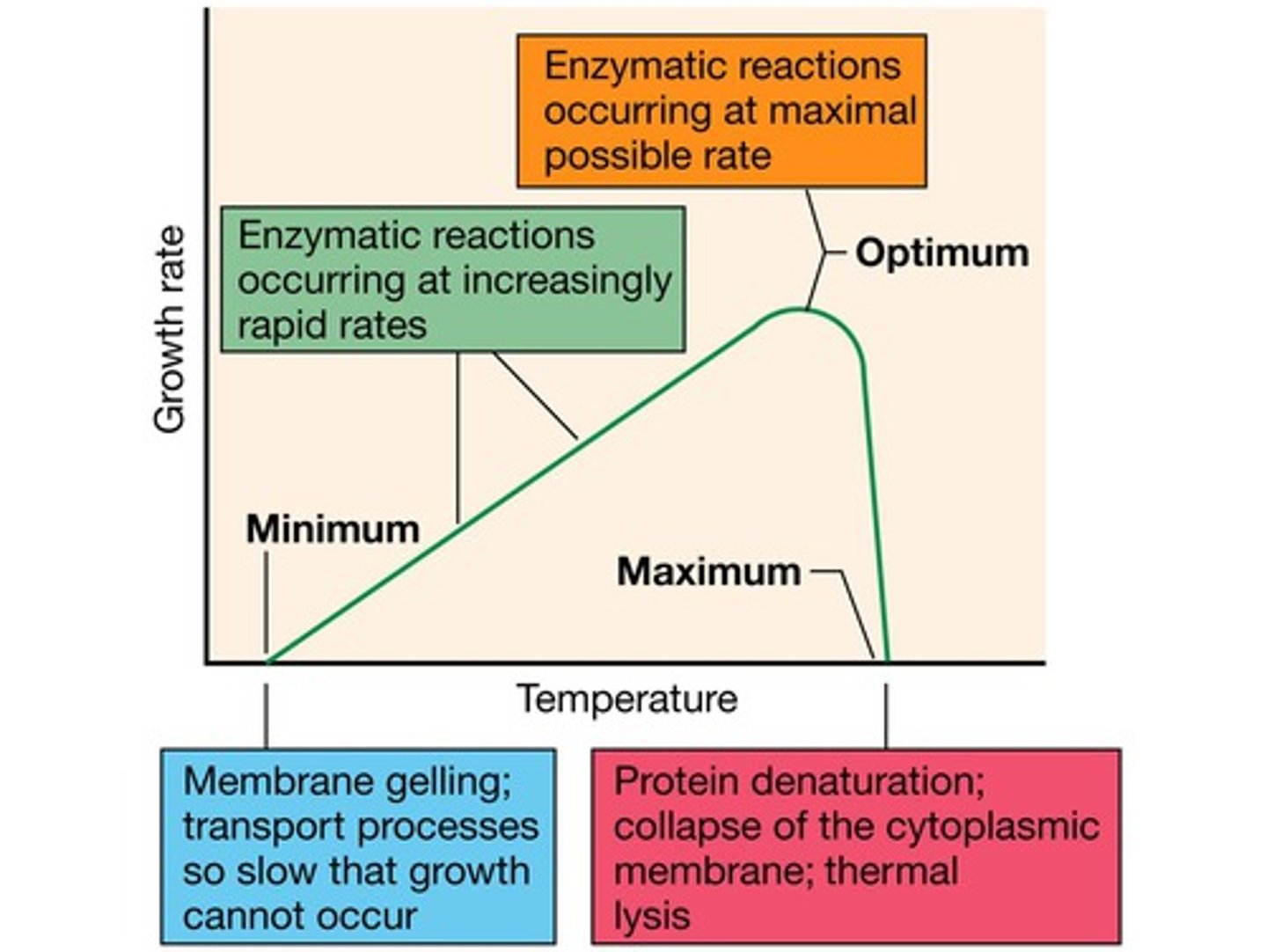
What are the three cardinal temperatures used to determine the temperature range of a microbe?
Minimum, maximum and optimal temps