The Endocrine System Outline Part 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
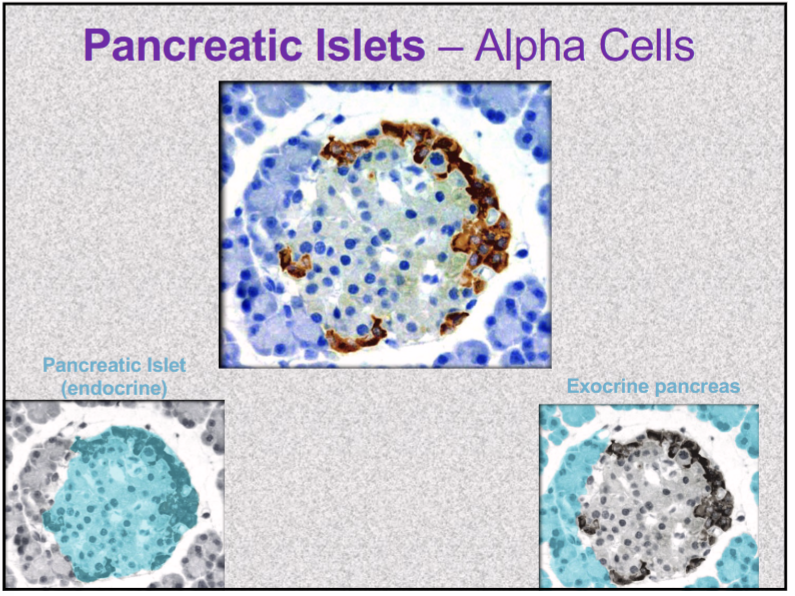
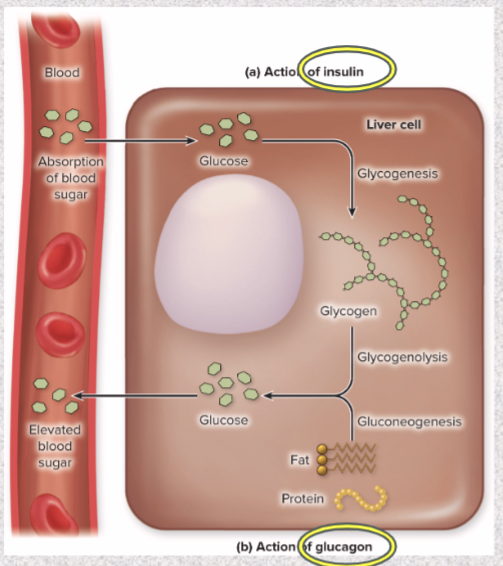
Pancreatic Islets alpha cells secrete what? What does it do?
GLUCAGON
released between meals when blood glucose concentration is falling
in liver, stimulates gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis to release of glucose into circulation- raise blood glucose level
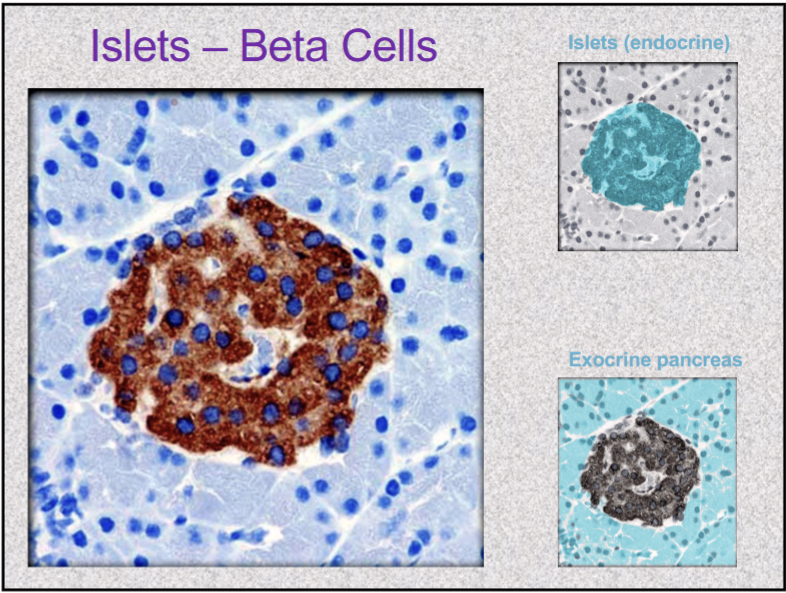
pancreatic islets beta cells secrete what? What does it do?
INSULIN
secreted during/ after meal when glucose and amino acid blood levels are rising
stimulates cells to absorb these nutrient and store or metabolize them; lowers blood glucose levels
promotes synthesis of glycogen, fat, and protein
suppresses use of already-stored fuels
insufficiency/ inaction= diabetes mellitus
pancreatic islets delta cells secrete what? What does it do?
SOMATOSTATIN
partially suppresses secretion of glucagon & insulin
prolongs absorption of nutrients
pancreatic polypeptide secreted by PP cells does what?
act on brain to reduce pancreatic secretions
Gastrin secreted by G cells does what?
stimulates stomach acid secretion, motility, and emptying
Hyperglycemic hormones … blood glucose concentration
RAISE
glucagon, growth hormone, epinephrine, norepinephrine, cortisol and corticosterone
Hypoglycemic hormones … blood glucose concentration
LOWER
insulin
Ovaries and testes are both…
endocrine and exocrine
exocrine product: whole cells- eggs and sperm
endocrine product: gonadal hormones— mostly steroids
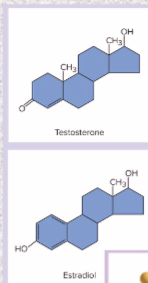
steroids- from, secretion, examples
from cholesterol
secreted by gonads and adrenal glands
estrogens, progesterone, testosterone, cortisol, corticosterone, aldosterone, calcitriol
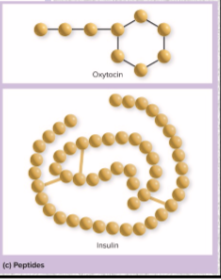
peptides and glycoproteins- from, secretion, examples
from chains of amino acids
secreted by pituitary & HT
oxytocin, ADH, insulin, anterior pituitary hormones
monoamines- from, secretion, examples
from amino acids
secreted by adrenal, pineal, and thyroid glands
epinephrine, norepinephrine, melatonin, and thyroid hormone
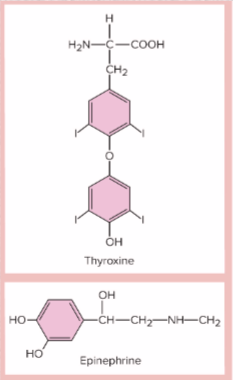
most monoamines & peptides=
hydrophilic
mix easily with blood
steroids and thyroid hormone=
hydrophobic
bind to transport proteins (globulins) (to prevent filtration and degradation)
bound hormones have longer half life
only unbound hormone leaves capillaries to reach target cell
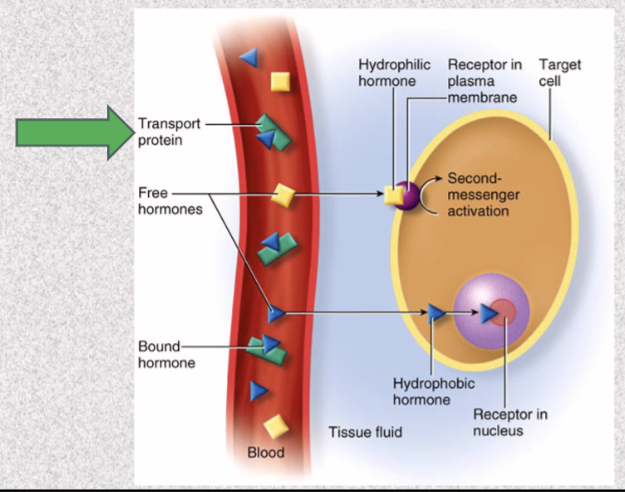
Thyroid hormone binds to 3 transport proteins in plasma
albumin, thyretin, thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)
specific receptor for each hormone. Saturated when…
all receptor molecules occupied by hormone molecules
receptors are
protein/ glycoprotein molecules
act like switches, turn on metabolic pathways when hormone binds
Hydrophilic hormones mode of action
peptide hormone
need membrane receptor
changes physiology via second messenger
quick
does NOT enter cell
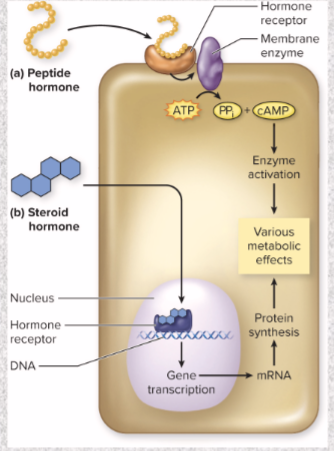
Hydrophobic hormones
steroid hormone
goes INTO cell
act directly on genes to change target cell physiology
take several hours to days to show effect
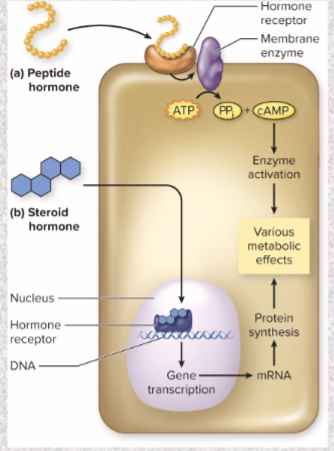
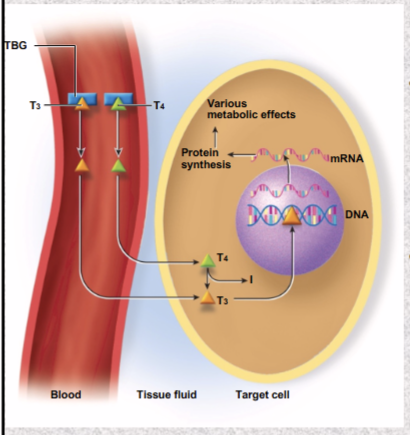
Thyroid hormone mode of action
thyroid hormone enters target cell by diffusion, mostly as T4 (little metabolic effect)
within target cell, T4 converted to more potent T3
T3 enters target cells, binds to receptors in chromatin
activates genes makes
myosin, strengthens heartbeat
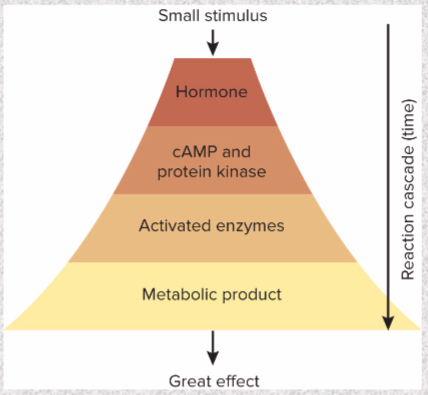
(Don’t worry too much about this) Peptides and Catecholamines mode of action
most common: activates G protein—activates adenylate cyclase—produces cAMP
enzyme amplification
one hormone molecule—synthesis of many enzyme molecules
small stimulus—large effect
circulating concentrations very low
Up vs Down regulation to adjust response to hormones
UP= increase receptor density and stronger response
DOWN=reduce receptor density and diminished response
synergist effects def and example!!!
Multiple hormones act together for greater effect
ex- FSH & testosterone on sperm production
permissive effects def and example!!!
one hormone enhances target organ’s response to second later hormone
ex: estrogen preps uterus for progesterone
Antagonistic effects def and example!!!
one hormone opposes action of another
ex: insulin lowers blood glucose; glucagon raises it
hormone clearance def
turning off hormone signals when they have served purpose
Metabolic clearance rate (MCR)
rate of hormone removal from blood
half-life: time required to clear 50% of hormone from blood
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
consistent way body reacts to stress; involves elevated levels of epinephrine & glucocorticoids (especially cortisol)
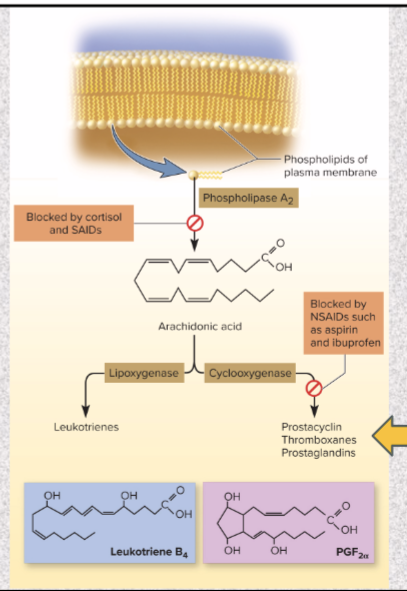
cortisol & corticosterone type of anti-inflammatory drugs and what it does
steroidal anit-inflammatory drugs (SAIDs)
blocks release of arachidonic acid & inhibits eicosanoid synthesis
disadvantage- cushing syndrome symptoms (excess cortisol)
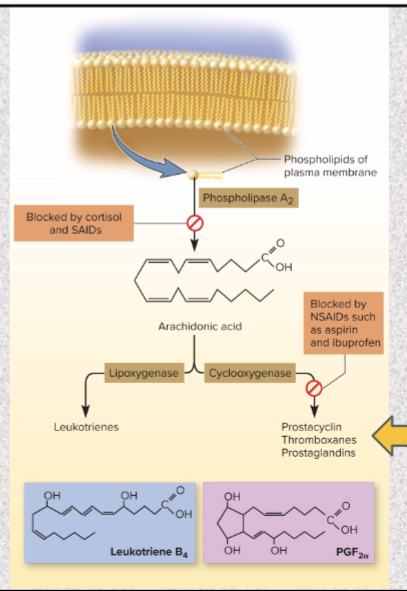
Aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen (Aleve) type of anti-inflammatory drugs and what it does
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
COX (enzyme converts arachidonic acid to thrombox, etc.) inhibitors: block cyclooxygenase
treats fever & thrombosis
Ibuprofen blocks the production of prostaglandins which reduces aches and fever
Hyposecretion def and example
inadequate hormone release
gland destroyed or lost ability to receive signals
ex: pituitary’s inability to secrete ADH (retain water)— Diabetes insipidus: chronic polyuria from lack of ADH (causes you to pee more— dehydration)
Addison’s disease
deficiency of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
Hypersecretion def
excessive hormone release
tumors or autoimmune disorder
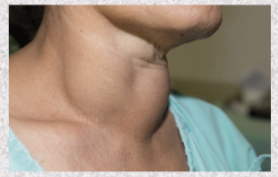
Toxic goiter (Graves disease)
autoantibodies mimic effect of TSH on thyroid, causing thyroid hypersecretion
Pheochromocytoma
tumor of adrenal medulla secretes excessive epinephrine and norepinephrine
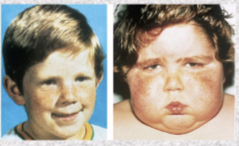
Cushing syndrome
excess of cortisol
Diabetes mellitus
most prevalent metabolic disease
disruption of metabolism due to hyposecretion or inaction of insulin
symptoms: polyuria, polydipsia (extreme thirst), polyphagia
Transport maximum: limit to how fast glucose transporters can reabsorb
excess glucose enters urine and water follows it— dehydration
Type 1 (IDDM) problem
insulin INSUFFICIENCY (something wrong with beta cells)
Insulin used to treat
monitoring blood glucose levels and controlling diet
auto-antibodies attack and destroy pancreatic beta cells
Type 2 (NIDDM) problem 90-95% of diabetics
insulin RESISTANCE
failed response of target cells to insulin
risk factors: heredity, age, obesity, etc.
treated with weight loss program and exercise
Ozempic how does it work?— Increase insulin production and reduce cravings
Pathogenesis
cells cannot absorb glucose; rely on fat and proteins for energy, thus weight loss and weakness
fat catabolism increase fatty acids and ketones in blood
ketonuria promotes
osmotic diuresis, loss of sodium and potassium, irregular heartbeat, and neurological issues
Ketoacidosis
ketones decrease blood pH
diabetic coma
Diabetic neuropathy
nerve damage from poor blood flow can lead to erectile dysfunction, incontinence, poor wound healing, loss of sensation