Ch. 17
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Digestive System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Alimentary Canal
mouth to anas
What are the 2 parts of each of the digestive organs? Know the function of each part.
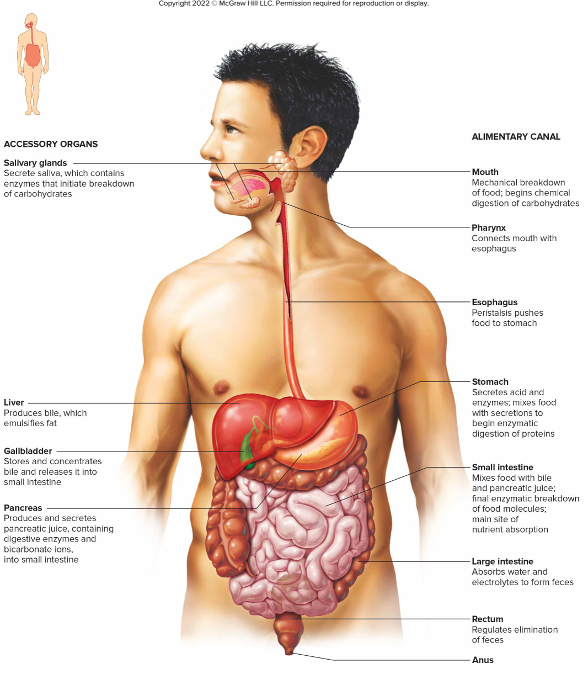
What are the functions of the digestive system?
Ingestion
Propulsion- move food through the digestive tract
*Digestion
Mechanical digestion breaks large pieces of food into smaller ones without altering their chemical composition. This mechanical breakdown increases the surface area of ingested foods, getting them ready for chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion also involves muscular movements that help mix food molecules and digestive juices
BOLUS- mass of chewed food mixed with saliva
Chemical digestion involves enzymes that act to chemically break down larger food molecules into simpler chemicals (building blocks), a catabolic process.
*Absorption
Involves the passage of nutrients from the alimentary canal into the blood after food undergoes mechanical and chemical digestion, it is small enough to be absorbed through the microvilli lining the small intestines- glucose, nucleic acids, etc. Considered to be on one of the main function of the digestive system
Elimination
Defecation of unabsorbed material
MAIN FUNCTIONS ARE DIGESTING AND ABSORPTION
Describe the nervous system’s role for digestion i.e., parasympathetic system
Activities of digestive system increase when stimulated by parasympathetic impulses
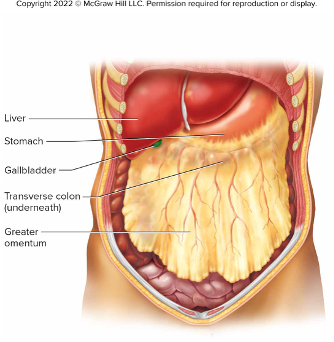
Omentum
A filmy, double fold of peritoneal membrane called the greater omentum
drapes like an apron from the stomach over the transverse colon and the folds of the small intestine (fig. 17.34 below)
If the wall of the alimentary canal becomes infected, cells from the omentum may adhere to the inflamed region and help seal it off, lowering the risk that the infection will spread to the peritoneal cavity.
Note the location of the gallbladder in Fig 17.34 below
Epiglottis
The epiglottis usually upright and allows air to enter the larynx.
During swallowing, muscular contractions raise the larynx, and the base of the tongue presses the epiglottis downward, partially covering the opening into the larynx, helping prevent foods and liquids from entering the air passages.
The epiglottis is attached to the larynx
The stomach receives food, mixes it with gastric juice, carries on a limited amount of absorption, moves food into the small intestine
Identify the following structures
Stomach
Esophagus
Liver
Gallbladder
Small Intestine
Large Intestine
Ascending Colon
Transverse Colon
Descending Colon
Functions
Absorb Water
Store Feces
Digest Proteins
Synthesize Vitamin B
Appendix- located in lower right quadrant
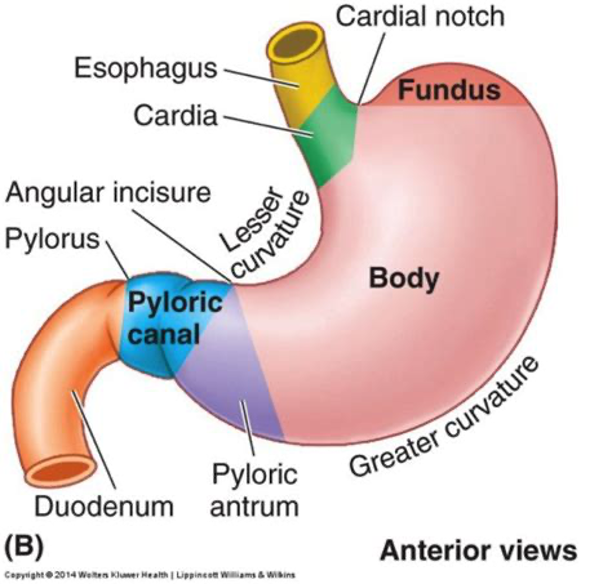
Parts of the stomach- Be able to identify structures- see image below
Cardial Notch- is a temporary storage area and sometimes fills with swallowed air.
Fundus- is a temporary storage area and sometimes fills with swallowed air.
Body- main part of the stomach
Pylorus- is the distal portion of the stomach where it approaches the small intestine
Pyloric Antrum
Lesser Curvature
Greater Curvature
Longitudinal Layer- refer to 2nd image next page
The pyloric sphincter serves as a valve between the stomach and the small intestine.
Layers of Stomach Muscle
Be able to identify longitudinal layer- outer musculature layer- see arrow
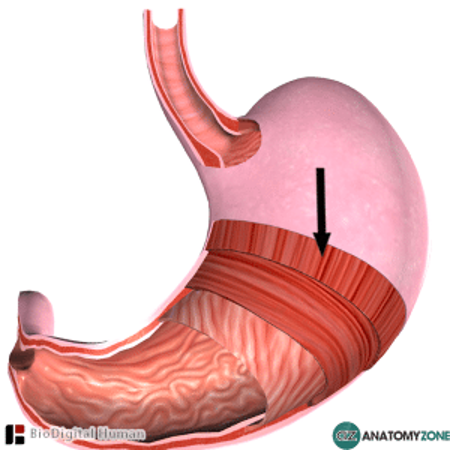
The 2 major types of motor processes in the digestive tract are mixing movements and propelling movements
Peristalsis- A propulsive movement of contents of the lumen from one area to another
Segmentation
Salivary Glands
Produce saliva
Function of saliva- break down food in mouth into smaller pieces
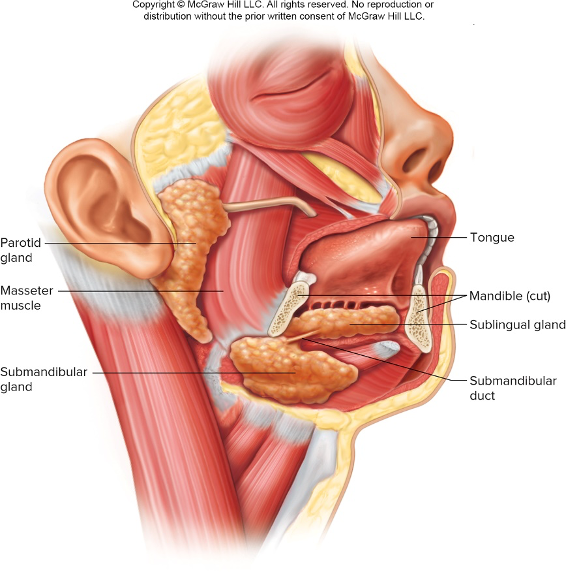
Know location of the 3 glads
Identify the following digestive structures
Parotid gland
Submandibular gland
Sublingual gland
Functions of saliva
Moistens, binds, dissolves food particle
Beginning of chemical digestion of carbohydrates
Cleanses teeth and mouth
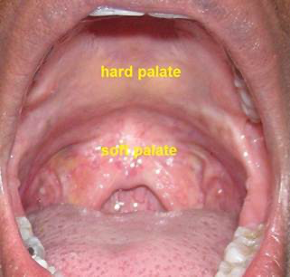
Palate of Mouth- know location and identify - hard and soft palate
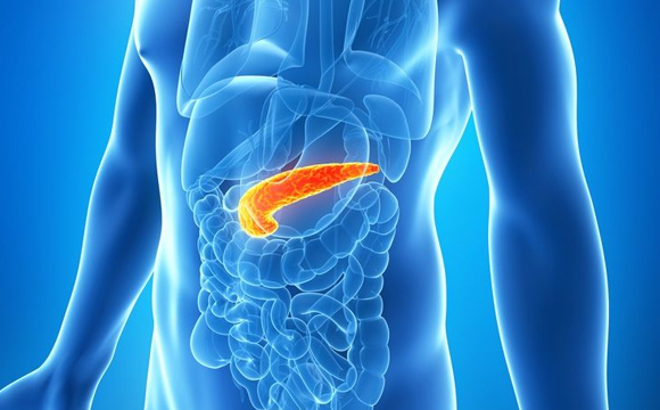
Pancreas location: See picture below- Be able to identify
Pancreatic Acinar Cells- What do they secrete?
The cells that produce pancreatic juice, called pancreatic acinar (a′sĭ-nar) cells, make up the bulk of the pancreas
These cells form clusters called acini (sing, acinus) around tiny tubes into which they release their secretions.
The smaller tubes unite to form larger ones, which join a pancreatic duct that extends the length of the pancreas
The pancreatic duct usually connects with the duodenum at the same place where the bile duct from the liver and gallbladder joins the duodenum, although divisions of the pancreatic duct and connections to other parts of the duodenum may be present
Passage of Food
Passageway of food from pharynx to esophagus to stomach
From stomach to the 3 parts of the small intestine: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum
Function of Gallbladder
The liver and gallbladder are accessory glands that function together in the production and storage of bile.
Bile is a fluid that contains important bile salts, needed for the breakdown of lipids in the small intestine
Teeth
Function to tear and used food
Differentiate between primary and permanent teeth- how many of each?
Primary teeth- 20 teeth
Secondary/Permanent Teeth - 32 teeth
Identify the following
Maxillary canine teeth
Pharynx
Small Intestine
Stomach- located in left upper art
Tooth Enamel
The tooth is composed of a crown that sits above the gum line, and the root which sits below the gum line
The crown is composed of a covering of enamel which is composed of calcium salts, and a deeper layer of dentin which is similar to bone but harder
Enamel thins from years of brushing, teeth grinding, and eating acidic foods
Tooth Root
Blood vessels and nerves found in root canal
What are the overall functions of the digestive system?
The digestive system receives foods, breaks down nutrients into forms that can pass through cell membranes, and eliminated unabsorbed materials
Parietal Cells of Gastric Glands
Secrete Hydrochloric Acid
Amylase
Produced by pancreas to aids in digestion of carbohydrates
Salivary amylase breakdown carbohydrates
Makes Chew bite of bread- gets sweeter bc breakdowns carbs into sugar
Lipase
Fat Splitting enzyme, gastric lipase
Gastric juice contains small quantities of this enzyme
Pepsin
Enzyme that begins the digestion of protein in the stomach
HCL (Hydrochloric Acid)- converts pepsinogen ( inactive form) to pepsin
Pepsinogen: produced by the chief cells of the gastric glands in an inactive form
If medication is given to decrease HCL, then this conversion to pepsin doesn’t occur as it should & digestion of protein can be impaired
Gastrin
is a peptide hormone that acts to increase the secretory activity of gastric glands
Trypsin
Found in pancreatic juice and digest all types of protein
Secretin
Stimulates release of pancreatic juice
Cholecystokinin
Regulates pancreatic secretion of digestive enzymes
What are the layers of walls in order in alimentary canal & which one absorbs nutrients?
Alimentary canal extends from mouth to anus
Wall of alimentary canal is composed of 4 layers: from innermost to outermost, the layers are
Mucosa- composed of epithelial tissue & may contain folds & mucus-secreting glands
Innermost layer, mucous membrane
Folded in some areas, to increase surface area
Absorbs dietary nutrients, secretes mucus & enzymes
Submucosa- Connective tissue layer
Nourishes cells, transports absorbed food molecules
Muscularis or muscular layer (externa)- Muscle tissue
*Contains circular & longitudinal layers
Moves tube & food materials
Serosa- Outermost layer; serous fluid eliminates friction
Visceral peritoneum of organs within abdominal cavity
Rugae- The folds of mucosa & submucosa in the stomach are known as rugae
Medulla Oblongata
Sensory Signals from the stomach & small intestine sent to medulla oblongata to trigger a vomiting reflex
What are the macronutrients?
Nutrients required in large amounts, provide energy, & other specific functions
Include:
Carbohydrates
Protein
Fat
What are micronutrients?
Required in small amounts. They don’t directly provide energy, but make possible the biochemical reactions thatt extract energy from macronutrient molecules
Vitamins
Organic compounds that are required in small amounts for normal metabolic processes
Vitamins don’t directly supply energy; they aid in the release of energy from carbohydrates, fats, proteins
Essential nutrients; can’t be synthesized by body cells in adequate amounts
Classified on the basis of solubility;
Fat-soluble vitamins: A, D, E, & K
Water-soluble vitamins: B vitamins & vitamin C
*B vitamins involved in the oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Minerals
Inorganic elements required in metabolism
Usually extratced from the soil by plants
Obtained from plant foods or animals that have eaten plants
Liver
Largest internal organ in body
Located in right upper quadrant of body
Accessory organ in digestive system
Function of liver: See chart below
Removes toxins such as alcohol & certain drugs from the blood
Common Bile Duct
The bile duct (common bile duct) is formed by the union of the common hepatic & cystic ducts
What is bile? How does it work? What constituent has digestive function?
Bile
Is a greenish-yellow fluid made by your liver & stored in the gallbladder
In addition to bile salts, bile contains cholesterol, water, bile acids, & the pigment bilirubin
Digestive function of Bile salts:
Bile salts promote fat-soluble vitamin absorption A, D, E, K
Bile salts aid in digestive of fat
Jaundice
Jaundice is the abnormal yellowish-tint of tissues, such as the sclera of the eye, skin, mucous membranes
Due to accumulation of bile pigments
FYI Causes: Obstructive jaundice, bile ducts are blocked perhaps by gallstones or tumors
Hepatocellular jaundice the liver is diseased, as in cirrhosis or hepatitis
Hemolytic jaundice, red blood cells are destroyed too rapidly, as happens with a incompatible blood transfusion or a blood infection
Chylomicrons
Large molecule of lipoproteins
Chylomicrons transport dietary fats to muscle & adipose cells
What is heartburn?
Stomachache results from eating a lot of food too quickly
Takes up to 20 minutes for hypothalamus to sense full stomach
Excess fullness leads to abdominal pain & gastric reflux, as stomach contents enter esophagus
Stomach contents in esophagus cause inflammation, called esophagitis; feels like the pain is derived from the heart, so it is called heartburn
Antacids can provide some relief
Prevention: eat small meals, eat slowly, stay upright after eating, & avoid caffeine, nicotine, & alcohol
Over the counter antacids
Sodium, aluminum, calcium, or magnesium