SHPEP A&P - autonomic system (lecture 7)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
Efferent fibers typically lead to…
…ganglia outside of the cell
Ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
How is the autonomic nervous system divided?
sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (STRESS/fight or flight)
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy (rest & digest)
All of the autonomic nerve fibers are…
…motor (efferent)
preganglioic fibers
Axons of preganglionic neurons. Neuron cell bodies in CNS
Postganglianic fibers
Axons of postganglionic neurons. Neuron cell bodies in ganglia
Adrenal medulla
secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
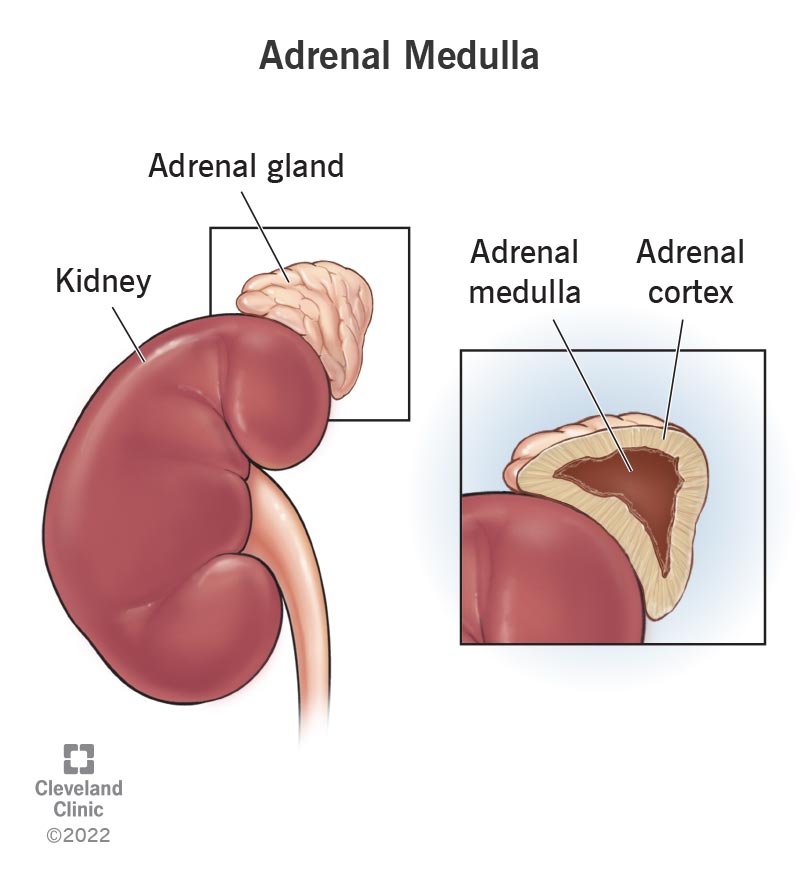
What stimulates the adrenal medulla?
sympathetic nervous system
Where are ganglia of the sympathetic division located?
Thoracolumbar region (close to spinal cord)
Adrenal cortex
outer section of each adrenal gland; secretes cortisol, aldosterone, and sex hormones
What is the adrenal cortex stimulated by
ACTH from anterior pituitary (sympathetic nervous system)
preganglionic fibers leave spinal nerves through _ rami & enter __ ganglia
White, pravertebral
paravetebral ganglia and fibers that connect them make up what?
The sympathetic trunk
Postganglionic fibers extend from sympathetic ganglia to…
…visceral organs
Postganglionic fibers usually pass through rami and return to a spinal nerve before proceeding to an ____
Gray, effector
What kind of preganglionic fibers DO NOT synapse with postganglionic neurons?
Preganglionic fibers to the adrenal medulla
Craniosacral division
Another name for the parasympathetic division.
Where are preganglionic neurons located?
Craniosacral division
Cholonergic fibers release what?
They release acetylcholine
Adrenergic fibers release what?
They release norepinephrine
Cholergenic fibers are…
…preganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers
Adrenergic fibers are…
…postganglionic and sympathetic fibers
think aggravation think STRESS so sympathetic
Cholinergic receptors bind to what?
They bind to acetylcholine (Ach)
Muscaranic Receptors
receptor cites for acetylcholine in the parasympathetic nervous system, where they mediate various functions by interacting with the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
adrenergic receptors
receptor sites for the sympathetic neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine on effector cells
excitatory neurotransmitters
Cause depolarization of postsynaptic membranes. Promote action potentials
Slow neurotransmitters
regulate release of neurotransmitters from synapse over a period of time
nicotinic receptors
cholinergic receptors that also respond to stimulation by nicotine
T/F: nicotinic receptors are found in both sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways
True, nicotinic receptors are found in the ganglia of the post ganglionic neuron
antagonistic effects of dual innervation
the two divisions exerting opposing effects on a target organ. in an emergency, the sympathetic division inhibits many processes of the parasympathetic division. when the emergency is over, the parasympathetic division takes over once again
dual innervation
organs that receive instructions from both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
beta-adrenergic receptors
Portions of the nervous system that, when stimulated, can cause an increase in the force of contraction of the heart, an increased heart rate, and bronchial dilation.
alpha-adrenergic receptors
Portions of the nervous system that, when stimulated, can cause constriction of blood vessels.
What organs are ONLY innervated by the sympathetic nervous system?
Adrenal medulla, arector pilli muscles in skin, sweat glands in skin, most blood vessels
Beta blockers block what
Sympathetic function (they block beta-Adrenergic receptors)
What controls the autonomic nervous system?
hypothalamus and medulla oblongata (CNS)
medulla oblongata
regulates cardiac, vasomotor andrespiratory activities
hypothalamus
regulates visceral functions, such as body temperature, hunger, thirst, and water and electrolyte balance
Limbic system and cerebral cortex
control emotional responses