Chapter 10 - Economic Growth, the Financial System, and Business Cycles
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
1
New cards
Long-run economic growth is
the process by which productivity increases the average standard of living
2
New cards
Business cycle
the alternating periods of economic expansion and economic recession
3
New cards
Real GDP per capita
the amount of production in the economy, per person, adjusted for changes in the price level
4
New cards
Economic prosperity and health go hand in hand
richer nations can devote more resources to improving the health of their citizens, and healthier citizens are more productive
5
New cards
Another important measure of our improvement is
the increase in our lifespans
6
New cards
A good measure of economic prosperity is
the amount of time we can spend on leisure
7
New cards
As our lifespans grow
we can spend more time on leisure; and also as we grow more productive, we can devote less time to work, and hence more leisure
8
New cards
Calculate the growth rate (percentage change). In 2021 Real GDP was $21.4 trillion and in 2022 Real GDP was $21.8 trillion.
( ($21.8 trillion - $21.4 trillion) ÷ ($21.4 trillion) ) × 100 = 1.9% Remember ( ( current year - base year) ÷ base year) × 100 = percentage change
9
New cards
Calculate the growth rate over a few years. In 2020: real GDP growth -2.2%. In 2021: real GDP growth 5.8%. In 2022: real GDP growth 1.9%. So, the average annual growth rate over this three year period was?
(-2.2% + 5.8% + 1.9%) ÷ 3 = 1.8%
10
New cards
(Growth rates over longer periods) Rule of 70 can help us determine how long it will take for an economic variable to double:
Number of years to double = 70 ÷ growth rate
11
New cards
Apply Rule of 70. If the growth rate is 5 percent, the variable will double in
70 ÷ 5 = 14 years
12
New cards
Increases in real GDP per capita rely on increases in
labor productivity
13
New cards
What is labor productivity?
The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work
14
New cards
Why can the average American consume more than nine times as many good and services now than in 1900?
Because the average American produces more than nine times as many goods and services in an hour now than in 1900.
15
New cards
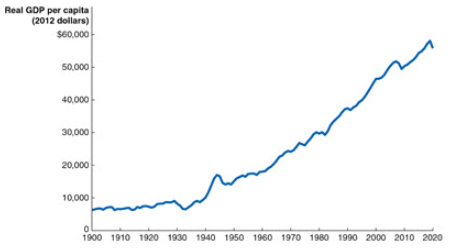
Use the graph to help determine which one of the following statements is true:
The average American in the year 2020 could buy more than eight times as many goods and services as the average American in the year 1900.
16
New cards
What are factors that affect labor productivity growth?
Increases in capital per hour worked, technological change, and property rights
17
New cards
Property rights
A market system can't function unless right to private property are secure. Governments can aid growth by establishing independent court systems to enforce contracts between private individuals.
18
New cards
Technological change
improvements in capital or methods to combine inputs into outputs (new tech) allowing workers to produce more. The role of entrepreneurs here is critical in pioneering new ways to being together the factors or production to produce better, lower cost products
19
New cards
Increases in capital per hour worked
capital is physical assets and intellectual property that are used to produce other goods and services. The more capital a worker has the more productive they'll be.
20
New cards
Potential GDP is
the level of real GDP attained when all firms are operating at capacity. Capacity refers to "normal" hours and sized workforce
21
New cards
What happens when the labor force expands, a nation acquires more capital stock or when new technologies are created?
the Potential GDP rises
22
New cards
Retained earnings
reinvesting profits back into the firm
23
New cards
Firms can finance some of their own expansion through
retained earnings, often firms want to obtain more funds for expansion than are available in this way
24
New cards
How do firms obtain retained earnings?
via the financial system
25
New cards
What is the financial system?
the system of financial markets and financial intermediaries through which firms acquire funds from households
26
New cards
Financial markets are
markets where financial securities, such as stocks and bonds, are bought and sold
27
New cards
What is Financial security
a document (sometimes electronic) stating the terms under which funds pass from the buyer of the security to the seller
28
New cards
What is a stock?
a financial security representing partial ownership of a firm
29
New cards
What is a Bond?
a financial security promising to repay a fixed amount of funds…essentially a loan from a household to a firm
30
New cards
Financial intermediaries are
firms, such as banks, mutual funds, pension funds, and insurance companies, that borrow funds from savers and lend them to borrowers.
31
New cards
Risk sharing
by allowing investors to spread their money over many different assets, investors can reduce their risk while maintaining a high expected return on their investment
32
New cards
Liquidity
the financial system allows savers to quickly convert their investments into cash
33
New cards
Information
This aggregation of information makes funds flow to the right firms: the prices of financial securities represent the beliefs of other investors and financial intermediaries about the future revenue stream from holding those securities.
34
New cards
Recall that we can express the GDP of a nation (Y) as
the sum of consumption C, investment (I), government purchases (G), and net exports (NX)
35
New cards
The equation for the GDP of a nation is
Y = C + I + G + NX
36
New cards
The equation for a closed economy is
Y = C + I + G
37
New cards
The expression for investment spending by businesses is
I = Y - C - G
38
New cards
Savings is composed of
private savings (by households, S-private) and public savings (S-public)
39
New cards
Private saving or S-Private is
household income that is not spent
40
New cards
Private saving is equal to
Y - C - T
41
New cards
Private savings with transfers is equal to
Y + TR - C - T
42
New cards
Labor productivity is
The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work.
43
New cards
Increases in real GDP per capita depend on
increases in labor productivity
44
New cards
Labor productivity is affected by two factors:
Capital per hour worked and Technological change
45
New cards
Technological change refers to
the processes a firm uses to turn inputs into outputs of goods and services. Technological change is the increase in the quantity of output that firms can produce given a quantity of inputs.
46
New cards
Capital Hours Worked refers to
the manufactured goods that are used to produce other goods and services, such as computers, factory buildings, machine tools, and warehouses.
47
New cards
Which of the following does NOT lead to long-run economic growth?
increase in average wages
48
New cards
Which of the following do lead to economic growth?
Increase in the capital stock, technological change, improved labor productivity
49
New cards
Long-run economic growth is
the process by which rising productivity increases the average standard of living
50
New cards
Potential GDP
increases over time as technological change occurs AND increases over time as the labor force grows.
51
New cards
A firm's capacity is measured by
its production during normal business hours. This changes as the economy experiences long-run growth.
52
New cards
Math Practice: Real GDP in 2006 = $11,567 and Real GDP in 2007 = $11,916. Assuming the population is constant over the two years, how many years will it take for real GDP per capita to double? (Rule of 70)
First find percentage change: ((11,916 - 11,567)÷11,567) × 100 = 3.0172% Now apply the rule of 70: 70 ÷ 3 = 23.3333….23.3 Years to double
53
New cards
Which of the following statements about real and potential GDP is true?
potential GDP increases every year (as technological change happens and labor force grows)
54
New cards
What other key services do financial intermediaries provide to savers and lenders?
allows savers to spread their money through investments, provides easy method of exchanging money or financial security, collect and communicate info about borrowers to savers
55
New cards
Market for loanable funds is
the interaction of borrowers and lenders that determines market interest rate and quantity of loanable funds exchanged
56
New cards
The demand for loanable funds is determined by the
willingness of firms to borrow money for investment spending
57
New cards
The supply of loanable funds is determined by the
willingness of households to save and the extent of government saving or dissaving.
58
New cards
Evaluate the statement: "Saving money is not lending. How can it be? When I save my money, I put it in a bank. I don't loan it out to someone else." The statement is
incorrect. The supply of loanable funds is determined by household saving
59
New cards
During expansions
inflation and employment increase.
60
New cards
During recessions
inflation and employment decrease.
61
New cards
Expansion: During a business cycle
spending by firms and households is strong. As sales increase, firms increase production and hire more workers. With spending strong, firms find it easier to raise prices.
62
New cards
Recession: A recession will often begin with
A decline in spending by firms on capital goods or by households on consumer durables leads to lower sales. As sales fall, firms cut production and lay off workers, causing rising unemployment and lower incomes. This further reduces spending, and during a recession, firms struggle to sell goods and are unlikely to raise prices.
63
New cards
What is the general relationship between the business cycle and unemployment and inflation?
During an expansion, unemployment falls and inflation increases.
64
New cards
During the expansion phase of the business cycle, production, employment, and income
increase
65
New cards
During the recession phase of the business cycle, production, employment, and income
decrease
66
New cards
Increasing importance of services and the declining importance of goods:
During a recession, households reduce purchases of durable goods more than they reduce purchases of services, such as medical care.
67
New cards
Unemployment insurance and government transfer programs are:
programs that make it possible for workers who lose their jobs during recessions to have higher incomes. As a result, they spend more than they would otherwise.
68
New cards
Government policies:
Arguably, policies, such as monetary policy (conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank) and fiscal policy (conducted by the federal government), have played a key role in stabilizing the economy.
69
New cards
Which of the following contribute(s) to shorter recessions, longer expansions, and less severe fluctuations in real GDP?
a service based economy, monetary policy, and social security benefits, fiscal policy,
70
New cards
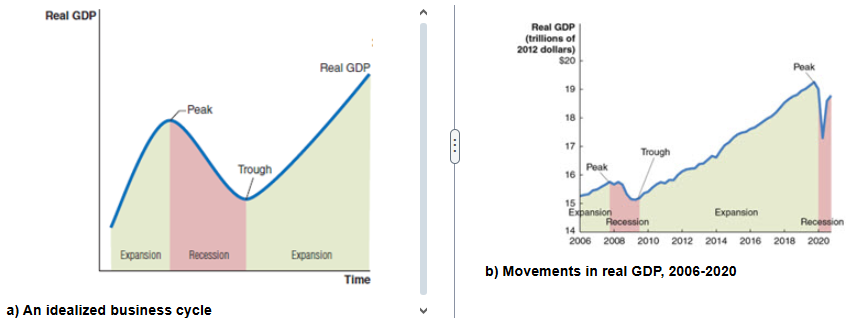
Panel (a) shows an idealized business cycle. Panel (b) shows an actual business cycle by plotting fluctuations in real GDP during the period from 2006 to 2020. Use the graphs to help determine which one of the following statements is NOT true:
Inconsistent movements in real GDP around the business cycle peak can mean that the beginning and ending of a recession are clear-cut.
71
New cards
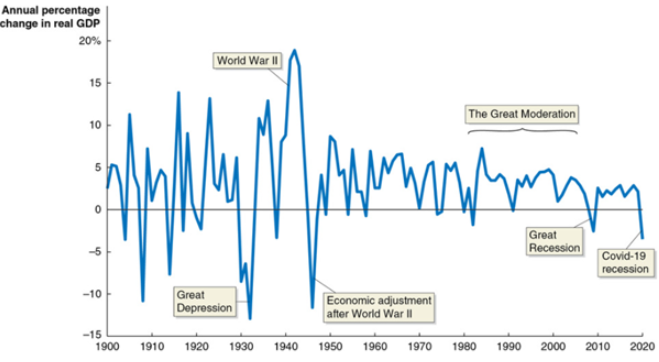
Use the graph to help determine which one of the following statements regarding fluctuations in real GDP is true:
In the first half of the twentieth century, real GDP had much more severe swings than in the second half of the twentieth century.
72
New cards
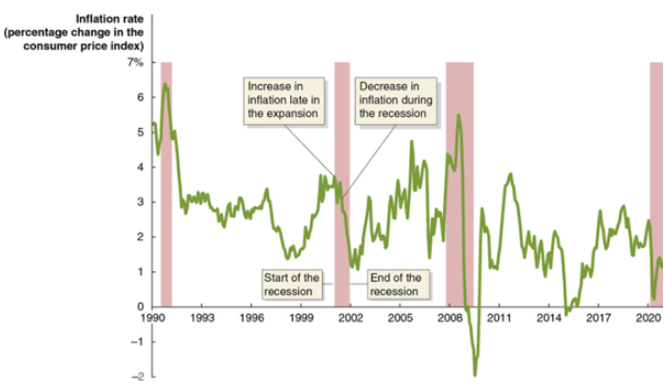
Use the graph to help determine which one of the following statements regarding inflation and business cycles is true. Note: The points on the figure represent the annual inflation rate measured by the change in the consumer price index (CPI) for the year ending in the indicated month.
Toward the end of the 1991-2001 expansion, the inflation rate began to rise.
73
New cards
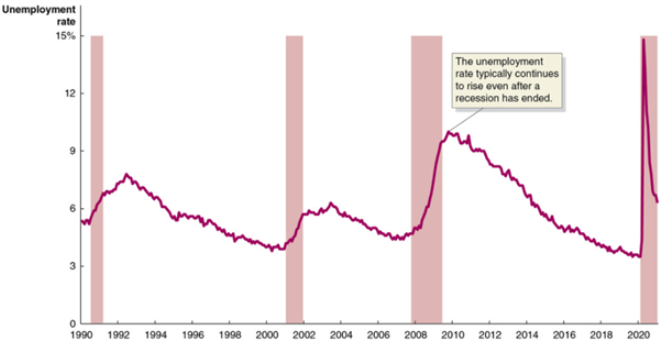
Use the graph to help determine which one of the following statements regarding unemployment and business cycles is true.
The unemployment rate usually continues to rise even after the recession has ended.
74
New cards
The computation of the average annual growth rate of real GDP
is more complex when examining data for a long period of time than when examining data for only a few years.
75
New cards
What is the best use of the rule of 70 among those listed below?
to judge how rapidly real GDP per capita is growing over long time periods
76
New cards
Which of the following changes does not cause an increase in the quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker, or in one hour of work?
an increase in the number of workers
77
New cards
Which of the following changes will ensure that an economy experiences sustained economic growth?
technological change
78
New cards
Potential GDP is
sometimes greater, sometimes less, and sometimes equal to actual real GDP.
79
New cards
Which of the following are financial securities that represent promises to repay a fixed amount of funds?
bonds
80
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a service that the financial system provides for savers and borrowers?
guaranteeing savers high rates of return
81
New cards
Which of the following equals the amount of public saving?
Government tax revenue minus the sum of government purchases and transfer payments to households.
82
New cards
A government that collects more in taxes than it spends experiences
a budget surplus.
83
New cards
In determining whether to borrow funds, firms compare the rate of return they expect to make on an investment with
the interest rate they must pay to borrow the necessary funds.
84
New cards
Which of the following factors determines the supply of loanable funds?
the willingness of households and governments to save
85
New cards
Holding all else constant, a federal government budget deficit will
decrease the supply of loanable funds and increase the equilibrium real interest rate.
86
New cards
From a trough to a peak, the economy goes through
the expansionary phase of the business cycle.
87
New cards
Typically, when will the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) announce that the economy is in a recession?
a year or more after the recession has begun
88
New cards
As the economy nears the end of an expansion, which of the following typically occurs?
Interest rates are usually rising, the profits of firms will be falling, and wages are usually rising faster than prices
89
New cards
Purchases of which types of goods are business cycles most likely to affect?
durable goods
90
New cards
Recessions cause the inflation rate to _________, and the unemployment rate to _________.
decrease; increase
91
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a reason that the economy is considered to have been more stable in the 1950-2007 period than in other periods?
continually falling oil prices
92
New cards
During the last half of the twentieth century, the U.S. economy experienced
long expansions, interrupted by relatively short recessions.
93
New cards
Long-run growth in GDP is determined by
capital, labor productivity, and technology.
94
New cards
Technological progress is affected by
entrepreneurship, private property rights, new software developments, investment capital
95
New cards
In a closed economy, the values for GDP, consumption spending, investment spending, transfer payments, and taxes are as follows: Y = $11 trillion, C = $8 trillion, I = $2 trillion, TR = $1 trillion, T = $2 trillion. Using the information above, what is the value of private saving and public saving?
Private saving equals $2 trillion and public saving equals $0 trillion.