Micro Final Parasitic Infections
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What are "unicellular heterotrophic organisms that are animal like"?
Protozoa.
Characteristics of protozoa.
-Most lack a cell wall
-Majority are free living aquatic organisms; also found in soil or in or on plants and animals
-Many have specialized structures for movement, such as cilia, flagella, or pseudopods
What do protozoans exist as?
Both as a trophozoite (growing, feeding form) and as a cyst (infectious survival form). Think cysts = dormant. Trophozoites = infectious/growing.
When do protozoans develop into cysts?
When they exit as feces. Cysts can survive in harsh environments.
Cysts can release trophozoites how?
Excyst.
"pseudopods that move the cell forward and engulf particles".
Amoebae.
What is an intestinal amoebae that can cause disease?
Entamoeba histolytica.
Are most ameobaes commensals or pathogenic?
Commensals.
What is the reservoir and vector of Amebiasis (Entamoeba histolytica)?
Reservoir - humans.
Fecal oral transmission via cysts.
How to treat infections caused by Entamoeba histolytica?
Metroniadazole (flagyl).
Causative agent of Giardiasis?
Giardia lamblia.
What is a "flagellated protozoan with two side-by-side nuclei, adhesive disc on undersurface, and cysts with CHITIN-LIKE polysaccharide walls".
Giardia lamblia.
Where does Giardia lamblia live?
Intestinal tracts of humans, can be infected by contaminated water (fecal-oral).
Pathogenesis of Giardiasis.
-Cysts infectious, survive stomach acid, unlike trophozoites
-Trophozoites emerge from each cyst that reaches upper part of small intestine
-Some attach to epithelium by adhesive disc
-Others use flagella to move freely in intestinal mucus
-Some migrate to gallbladder, cause cramping or jaundice
-Can interfere with digestive enzymes
-Trophozoites detach, are carried to large intestine
What is one of the most common waterborne illnesses in the US?
Cryptosporidiosis ("Crypto"). It is resistant to chlorine so it can also survive in recreational water.
What is Cryptosporidiosis ("Crypto") caused by?
Cryptosporidium hominis (formerly parvum)
A protozoan.
What is one distinct symptom of crypto?
Profuse watery diarrhea.
Pathogenesis of crypto.
Sporozoites released from ingested oocyst infect small bowel epithelial cells -> profuse diarrhea.
What medication can help treat crypto?
Nitazoxanide.
What protozoan causes toxoplasmosis?
Toxoplasma gondii.
Which protozoan can reproduce sexually, in cats and other felines?
Toxoplasma gondii.
Fetal toxoplasmosis is most severe during which trimester?
During first trimester -> miscarriage, birth defects.
Pathogenesis of toxoplasmosis.
-Organism enters by ingestion of oocysts (feces) or undercooked meat containing tissue cysts
-Infects any kind of nucleated cell
-Tachyzoites destroy infected cell until brought under control by immune response
-Tissue cysts persist
-In immunodeficient, infection can be widespread and uncontrolled, producing widespread tissue necrosis
Why is toxoplasmosis transmitted best in warm, humid, low altitude countries?
Incidence higher in warm, humid, low altitude countries (better survival of oocytes).
How is malaria able to penetrate host cells?
Because it has a apical complex at one end.
Explain the "sexual" and "asexual" life cycle of malaria.
-Sexual reproduction occurs is called the definitive host
-Other host is intermediate host
Sexual vs asexual replication of malaria.
Sexual replication - parasite develops into male and female gametocytes, necessary for transmission to a new human host.
Asexual replication - repeatedly infect and lyse red blood cells (especially in blood and liver).
What protozoan causes malaria?
Plasmodium.
Are humans or mosquitos the definitive host for malaria?
Mosquitoes are definitive host (thats when sexual reproduction occurs).
Are humans or mosquitos the intermediate host for malaria?
Humans are the intermediate host (asexual replication).
Liver stage vs RBC stage of malaria.
Liver stage -exoerythrocytic stage – exo means “outside of”.
RBC stage - erythrocytic stage.
When does the exoerythrocytic stage of malaria begin?
The exoerythrocytic stage begins when female Anopheles mosquito injects sporozoites; carried by bloodstream to liver.
When does the erythrocytic stage of malaria begin?
Once in liver, parasites enlarge, reproduce asexually, produce thousands of merozoites, which infect red blood cells (RBC).
After 2 weeks, malaria symptoms fall into three phases, describe them.
-Cold stage: patient feels cold and develops shaking chills that last for up to an hour
-Hot stage: patient’s temperature rises sharply for 3 to 8 hours often reaching 40℃ Celsius (104℉) or more
-Wet stage: Patient’s temperature falls, drenching sweating occurs for 2 to 4 hours leaving patient exhausted
The cycle of the three stages of malaria is called what?
Paroxysm.
Why can the spleen be affected by malaria?
-Anemia results from RBC destruction
-Spleen enlarges to cope with high levels of foreign material and abnormal red blood cells; may rupture
What antigen could black African Americans have that make them resistant to malaria?
Duffy antigen.
People with what blood disease are partially protected from malaria?
sickle cell.
Why are sickle cell patients partially protected from malaria?
The unusual shape of sickle red blood cells stretches their membranes, making them porous and leaky. This prevents the parasite from getting the nutrients it needs to survive.
What can be used to treat malaria?
Chloroquine, mefloquine.
What is a free living protozoan that enjoys warm temperatures.
Naegleria fowleri.
What protozoan causes meningoencephalitis (PAM).
Naegleria fowleri.
Pathogenesis of meningoencephalitis.
-Enters body when contaminated water is forced or snorted into the nasal passages (NO PERSON TO PERSON TRANSMISSION)
-Penetrates skull along olfactory nerves of nasal mucosa
-Multiplies, migrates to brain, destroys nervous tissue
-Hemorrhage, coma, death occur within a week
Is there a vaccine for meningoencephalitis?
No.
Treatment of meningoencephalitis.
-miltefosine
-minimize brain swelling by inducing hypothermia
What are multicellular protozoan parasites?
Helminths (worms).
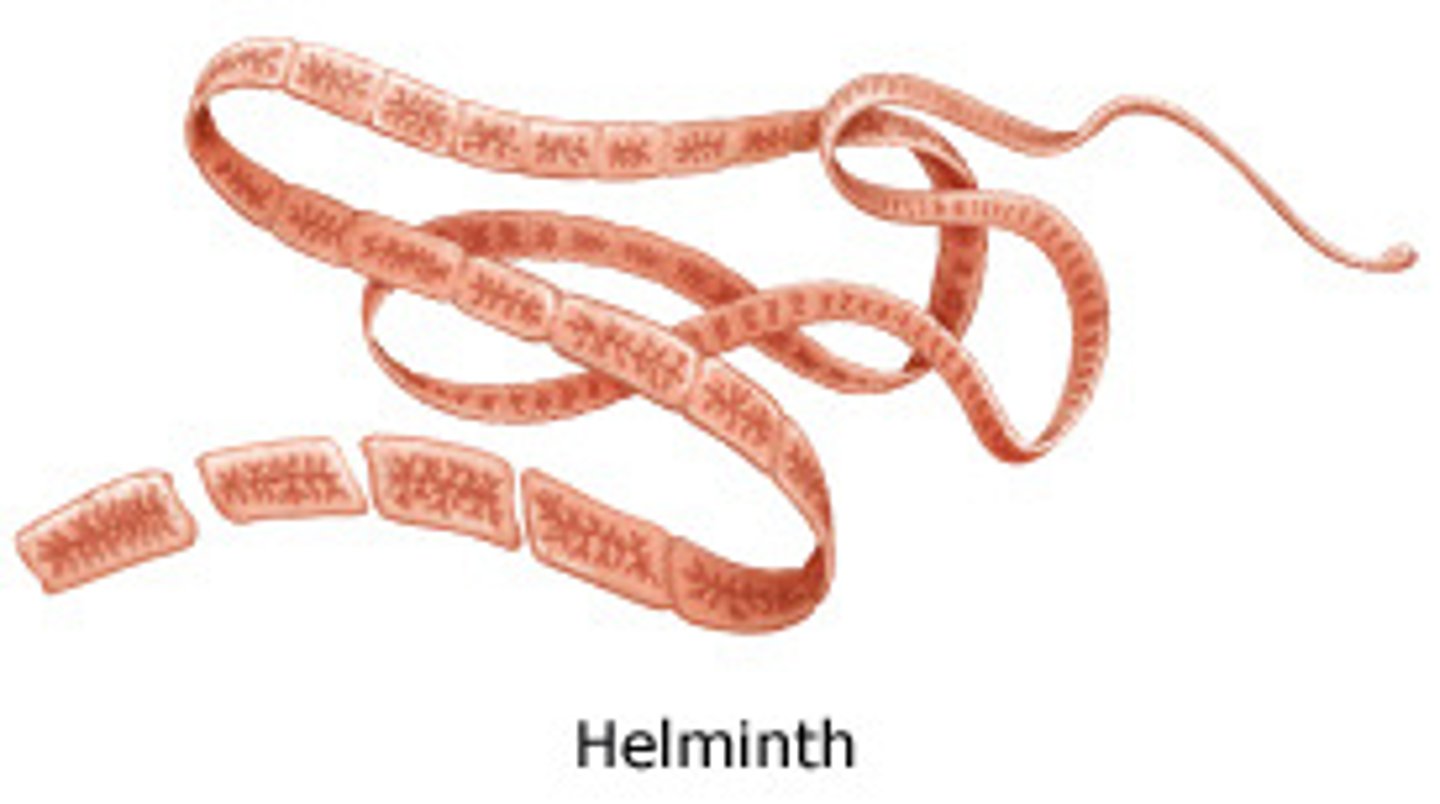
What are the two phyla of helminths?
-Phylum: Nematoda (roundworms)
-Phylum: Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
***Class: cestodes (tapeworms)
***Class: trematodes (flukes)
What is the difference between monoecious and dioecious helminths?
mono - male and female reproductive systems in one animal
dio - separate male and female
Where do hookworm larvae of helminths live vs burrow?
Hookworm larvae live in soil, burrow through human skin (end up multiplying in digestive tract).
Some can be eaten with food or insect bites.
What are two helminths ingested with food?
Trichinella spiralis and Enterobius vermicularis.
What helminth is transmitted via mosquitos and causes elephantiasis?
Wuchereria bancrofti.
What helminth is transmitted via flies and causes river blindness?
Onchocerca volvulus.
What is a nemotode that causes ascariasis, most common roundworm disease.
Ascaris lumbricoides.
What parasite has a flat leaf shape with two suckers to attach or move along a surface. And a mouth, but no anus?
Flukes (Trematodes).
What is the definitive host for flukes?
Mammals or other vertebrates (where sexual reproduction occurs).
What is the intermediate host for flukes?
Snails. Larval form is called cercaria.
What does hermaphroditic mean?
Both male and female reproductive systems - common in tissue flukes.
Which type of flukes have separate sexes (are NOT hermaphroditic)?
Blood flukes (schistosomes).
Bloody diarrhea and iron deficiency are symptoms of which helminth disease?
Schistosomiasis from flukes (Trematodes).
Which helminth has flat, ribbon-shaped bodies that absorb nutrients across body surface. Head end attaches to the intestines of host.
Tapeworms (Cestodes).
The head end of a tapeworm is called what?
scolex.
The segments of a tapeworm contain what?
Proglottids (segments) contain M/F structures. These segments also contain eggs.
What is the beef tapeworm?
T. saginata***
What is the pork tapeworm?
T. solium***
What class are beef tapeworms in?
Cestodes (tapeworms).
What are the definitive host of tapeworms?
Humans (sexual reproduction - reproduces).
What are the intermediate host of tapeworms?
Cattle.
Tapeworms develop where in cattle?
In their muscle. When humans ingest undercooked poultry, the tapeworms can attach to intestines.
How is beef/pork tapeworm diagnosed?
Detection of eggs and/or proglottids in feces.
Eggs of T. solium and T. saginata are indistinguishable. Proglottids differ (thats how they are told apart).
Pork tapeworm can cause what problems in the CNS and eyes?
-seizures, hydrocephalus, ocular dz.
Proglottids and eggs of tapeworms are passed how?
In feces.
What is Neurocysticercosis?
Tapeworm lavae encyst in the brain due to the ingestion of eggs. With clinical sxs of
-Headaches
-Confusion
-Seizures
What is anti-helminth therapy for neurocysticercosis?
Anti-helminthic therapy:
-praziquantel
-niclosamide
-albendazole