DNA Condensation
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Chromatin refers to:
DNA interacting with particular proteins
In the classic "beads-on-a-string" structure during DNA condensation, which components are required to hold the "beads" in place?
linker histones or H1
A string of nucleosomes coils up with the help of Histone __ to form the more compact structure 30nm chromatin fiber.
N tails interactions facing outward
A __ model describes the structure of the 30 nm fiber.
zigzag
Genes that are being transcribed (active) are thought to be packaged in a __ condensed type of euchromatin and usually show particular epigenetic modification; less methylation and more acetylation.
less
The 30 nm chromatin fiber is further compacted by the formation of __ that emanate from a central axis.
Loops
The structure of the DNA-protein complex, called __, is highly dynamic (active) over time.
euchromatin
True or False: Chromosomes exist at different levels of condensation, depending on the stage of the cell cycle.
True
True or False: Eukaryotic chromosomes contain many different sites with different degree of condensation, euchromatin & heterochromatin, where DNA replication and transcription can be initiated.
True
Cytogeneticists can determine large-scale chromosomal abnormalities, like Down syndrome, by looking at a patient's __.
karyotype
The cri du chat syndrome represents a chromosomal mutation type termed
deletion
DNA segments called _____ are at the ends of chromosomes and as they shorten they eventually signal the cell to enter apoptosis.
telomeres
True or False: In an older cell the telomeres should be shorter since the cell has gone through repeated cell divisions.
True
Loose chromatin is to tighter chromatin like euchromatin is to __________.
heterochromatin
An individual who has an XXY sex chromosomes is said to have _____ syndrome.
Klinefelter
Genes on the ___ chromosome determine if the sex of a child will be male or female.
Y
Structures made of DNA wrapped (twice) around Histones (core) and some DNA linking between are called:
nucleosomes
True or False: Telomeres are sequences at the center of the chromosomes that protect the genetic information by allowing cells to go through repeated divisions without loss of genes.
False
Which of the following would not be the same in a male and female?
the types of sex chromosomes
When the sheep Dolly was successfully cloned, it was produced by growing an in vitro fertilized egg where the normal egg nucleus had been removed and replaced by a nucleus from an adult. Since this nucleus is from an old mature animal, we would expect it to ______. Interestingly, tests show that this did not happen, a fact that currently puzzles researchers.
have shorter telomeres
While there are __ core Histones, there is only one H1 outside.
8
The most common autosomal abnormality present in people is
an extra chromosome 21
A person with an XO genotype is classified as having
Turner
True or False: Gametes typically have long telomeres on their DNA because germ cells have not gone through repeated cell divisions. This is important since the zygote will need to undergo repeated cell division to develop into a fetus and then into an adult.
True
A female that does not undergo puberty or menstruate or lacks breast development may have
Turner
Segments of DNA that are NOT part of the gene are called
introns
True or False: Most normal cells have a built-in limit to the number of times they can divide before they die. One of the reasons normal cells stop entering the cell cycle is that the telomeres become shortened.
True
True or False: With each cell division, the telomeres shorten, eventually becoming short enough to signal apoptosis.
True
Nucleosomes are kept in place by the H1 histone and forces between DNA and histones, such as hydrogen bonds and ____________ interactions.
hydrophobic
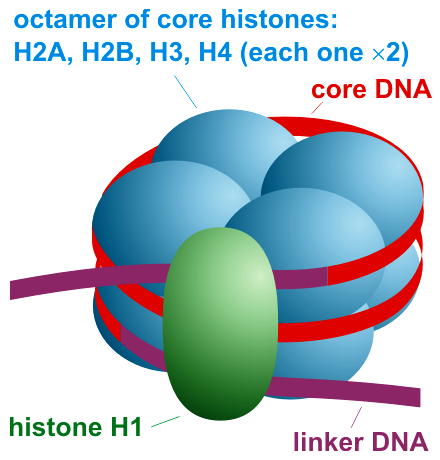
The structure in the picture is representing a single _________.
nucleosome