shapes and IMFs
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
The shapes of and bond angles in molecules and ions with up to 6 e- surrounding the central atom as predicted by EPR including lone pairs
Electron pairs in valence shells repel each other as far apart as possible resulting in these bond angles
Determination of shapes of molecules, ions and poly atomic ions
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the number of electron / bonding pairs surrounding the central atom , for poly atomic ions take into account ionic charge
Relative repulsive strengths of bonded pairs and lone pairs of electrons
Multiple bonds have a similar repelling effect to single bonds but lone pairs of electrons repel more than bonded pairs of electrons reducing bond angles , for each lone pair bond angle is reduced by 2.5°
Electron pair repulsion to explain the following shapes of molecules and ions
Linear : 2 bonding pairs SCA, BA: 180°
Trigonal planar: 3 bonding pairs SCA ,BA: 120°
Tetrahedral: 4 bonding pairs SCA ,BA: 109.5°
Octahedral: 6 bonding pairs SCA ,BA: 90°
Non linear: 2 BP and 2LP SCA ,BA: 104.5°
Pyramidal: 3BP and 1LP SCA ,BA: 107°
Should be able to draw 3d diagrams to illustrate shapes of molecules and ions
Electronegativity
Ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond
Interpretation of Pauling EN values
Pauling EN values are used to compared the ENs of atoms of different elements, the greater the number the greater the EN
Pattern
Fluorine is the most EN element, the closer an element to F the more EN the element so EN increases towards F in the periodic table
Why?
Polar bond
Covalent bond between atoms with different electronegativities with positive and negative partial charges on the bonded atoms
Explanation
In this bond the shared pair of electrons is shared unequally between the bonding atoms, the atom of the more EN element has a partial -ve charge and the atom of the less EN has a partial +ve charge
permanent dipole
positive and negative partial charges separated by a short distance in a molecule, separation of partial charges across a polar bond arising from different electronegativites
When is a molecule polar
When there is a polar covalent bond and there is a dipole across the molecule and the polar bonds with dipoles don’t cancel due to direction as molecules that have more than one polar bond, the dipoles in the polar bond may cancel due to their direction
Determination
To decide whether a molecule is polar draw 3d shape of a molecule and label and polar bonds with partial charges, if the molecule is symmetrical the dipoles in the polar bonds cancel out and the molecule is non polar and if the molecule is not symmetrical the dipoles in the polar bonds don’t cancel out and the molecule is polar
Intermolecular forces
Weak attractive forces between molecules
IMF based on induced dipole-dipole interactions (London forces)
exist between all molecules , electrons in a molecule are always moving and at any instant time the distribution of electrons may be uneven as a result a molecule may have a temporary dipole
Then
The presence of a temporary dipole in one molecule can cause an induced dipole to form in a nearby molecule and the induced dipole can then induce a dipole in another neighbouring molecule
Induced dipole-dipole interactions/ London forced
Attraction between induced dipoles is called induced dipole-dipole interaction or London forces
Strength of London forces
Weakest IMFs, the more electrons a molecule has the stronger the London forces between molecules so more energy will be needed to break London IMF increasing MPs and BPs
Representation
Dipoles are represented using arrows where the head of the arrow shows region of negative charge
IMFs based on permanent dipole-dipole interaction
Exists between two molecule that have permanent dipoles in addition to London forces. Polar molecules with permanent dipoles have regions with different electron densities and when two polar molecules are close they attract each other
Permanent dipole- dipole interaction
Attraction between two polar molecules with permanent dipoles is called permanent dipole-dipole interaction
Example of PD-D interaction
In a HCl molecule the more electronegative Cl atom of a HCl molecule attracts the less electronegative H atom of another HCl molecule
Liquid vs Solid HCl
In liquid HCl these attractions are constant breaking and reforming as molecule move around within the liquid but in solid these interactions hold the molecules in a fixed position
Hydrogen bonding
IMF formed between molecules containing a H atom bonded to an electronegative atom such as N, O, or F AND a lone pair of electronegative element such as N, O, F in a different molecule
Examples include
H2O, NH3 and HF hydrogen bonds drawn as dots must be joining a lone pair of electrons from an EN atom and a H atom of another molecule bonded to an EN atom
Feature of hydrogen bonds
Strong permanent dipole-dipole interactions, strongest type of IMFs between molecules
Anomalous property of water 1 resulting from hydrogen bonding
Density of ice compared with water; ice has a regular lattice structure in which H2O molecules are held in an open lattice structure by hydrogen bonds between molecules allowing ice to float on water
Then
When ice metals the open lattice structure collapses allowing water molecules to move closer together increasing the density
Explanation of anomalous property of water 2 resulting from hydrogen bonding
Relatively high MP and BP : hydrogen bonds greatly increase the strength of the overall IMFs in ice and water so a lot of energy is needed to break hydrogen bonds increasing MP and BP compared with similar molecules without hydrogen bonding
Solid structures of simple molecular lattices
Covalently bonded molecules attracted by intermolecular forces , in a solid state a SML contains molecules held together in a regular structure where the atoms within each molecule are bonded together strongly by covalent bonds and the molecules are held in place by weak IMFs
So the molecules
Are attracted by intermolecular forces such as ice and iodine (I2)
Explanation of the effect of structure and binding on the physical properties of covalent compounds with simple molecular lattice structures
SM substances / covalent compounds with SML structures have
low MPs and BPs
Poor electrical conductors
Soluble in non polar solvents, insoluble in water
Low MP and BP
But can be solid liquid of gas at room temp, weak IMFs are easily overcome at low temps, strong covalent bonds between atoms in molecules don’t break on changing state
Poor electrical conductors
As they don’t have charge
Solubility
In general, they have weak dipoles and tend to be soluble in non polar solvents and insoluble in water but highly polar molecules are soluble in water as they can interact with dipoles in water molecules
EQs
What is meant by the term electronegativity
Ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
Explain why molecules of H2O are polar
Dipoles don’t cancel out, has an overall dipole, water is non symmetrical
Show hydrogen bonding between two H2O molecules including dipoles, partial charged and lone pairs
Explain why ice has a lower density than water
In ice molecules are held apart by hydrogen bonds, ice has an open lattice due to hydrogen bonds
Solid ammonia has hydrogen bonds suggest why it has a lower MP than ice
Ammonia has weaker hydrogen bonds than ice as Nitrogen has one lone pair whilst oxygen has 2 lone pairs
Nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show bonding in NH4 + ion, how to test for presence of NH4 + ion in solution
Don’t forget the lone pairs and big brackets to show overall + charge
Heat with hydroxide, litmus/ indicator paper turns blue or purple
predict bond angles and names of shapes and explain why bond angles are different
Shape… number of bonding regions around .. (central) atom , bond angle
Explanation: Electron pairs/ bonded pairs repel as far apart as possible
Explain why both SO2 and SO3 have polar bonds but only SO2 has polar molecules
Sulfur and oxygen have different electronegativities , S-O bonds are polar
SO2 has uneven electron charge density, dipoles don’t cancel
SO2 lone pair gives non linear shape/ asymmetrical so dipoles don’t cancel as dipoles don’t act in op’s life directions WHEREAS SO3 has a trigonal planar shape/ symmetrical, dipoles cancel as dipoles act in opposite directions
Explanation of trend of BP3 across period 3 in question 10 first paper for shapes and IMFs 6 marks
If there are 3 bonded regions around a central atom but one of them is lone pair such as O-N-O
Say 3 bonded regions around N , bond angle 120° so it is not a trigonal planar but the lone pair didn’t change much it is still 120°
Given first 36 elements give the 3 elements that when in a molecule can form hydrogen bonds with other suitable molecules
N, O, F
Given first 36 elements give an element that is a solid at RTP with a simple molecular lattice structure
Sulfur or Phosphorus
Given first 36 elements give the p block element in period 3 that forms a compound with fluorine with octahedral molecules
Sulfur (remember diagram to show drawing of shapes we drew)
Failed to recognise which compound has a polar molecule between multiple choice HCN, BCL3, CO2, C2F4
Explain why NF3 and BF3 molecules have different shapes and bond angles
NF3 have 3 bonded pairs and one lone pair do electrons and lone pairs repel more than bonded pairs
BF3 has 3 bonded pairs of electrons
What is the correct explanation for the trend in BPs down group 7
London forces increase

Answer was A: all 3
Explain why bond angles for CO2 and H2O are different
CO2 has 2 bonding regions
H2O has 2 bonded pairs and is lone pairs
Like Paris repel more than bonded pairs

Give that one another shot- key is that N doesn’t only give 3 electrons gives all 5 use guidance of the arrows and double bonds drawn
Solid chlorine and solid bromine have a similar structure name the structure
Simple molecular lattice
Explain why it has a bond angle of 104.5
there are 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs around the central atom
Bonded pairs repel, lone pairs repel more than bonding pairs
Explain the difference in MPs of phosphorus P8 and Chlorine
Phosphorus has more electrons so it has stronger London forces, more energy is required to break the IMFs/ London forces
Explain the term electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
Explain why this molecule is polar
The dipoles don’t cancel out, the molecule is non symmetrical
Drawing hydrogen bonds
Don’t forget partial charged, dot is between lone pairs on N, O, F and H of other side, other molecule
State and explain 2 anomalous properties of ice caused by hydrogen bonding
Ice is less dense than water as molecules in ice are held apart by hydrogen bonds , ice has an open lattice stricture
Ice has a relativity high MP as hydrogen bonds are relatively strong, stronger than other IMFs, more energy is needed to overcome hydrogen bonding
Explain why SbCL3 molecules are polar
there is a difference in electronegativities between Sb and Cl, Sb-Cl bonds are polar, have a dipole
The molecule is not symmetrical so dipoles don’t cancel
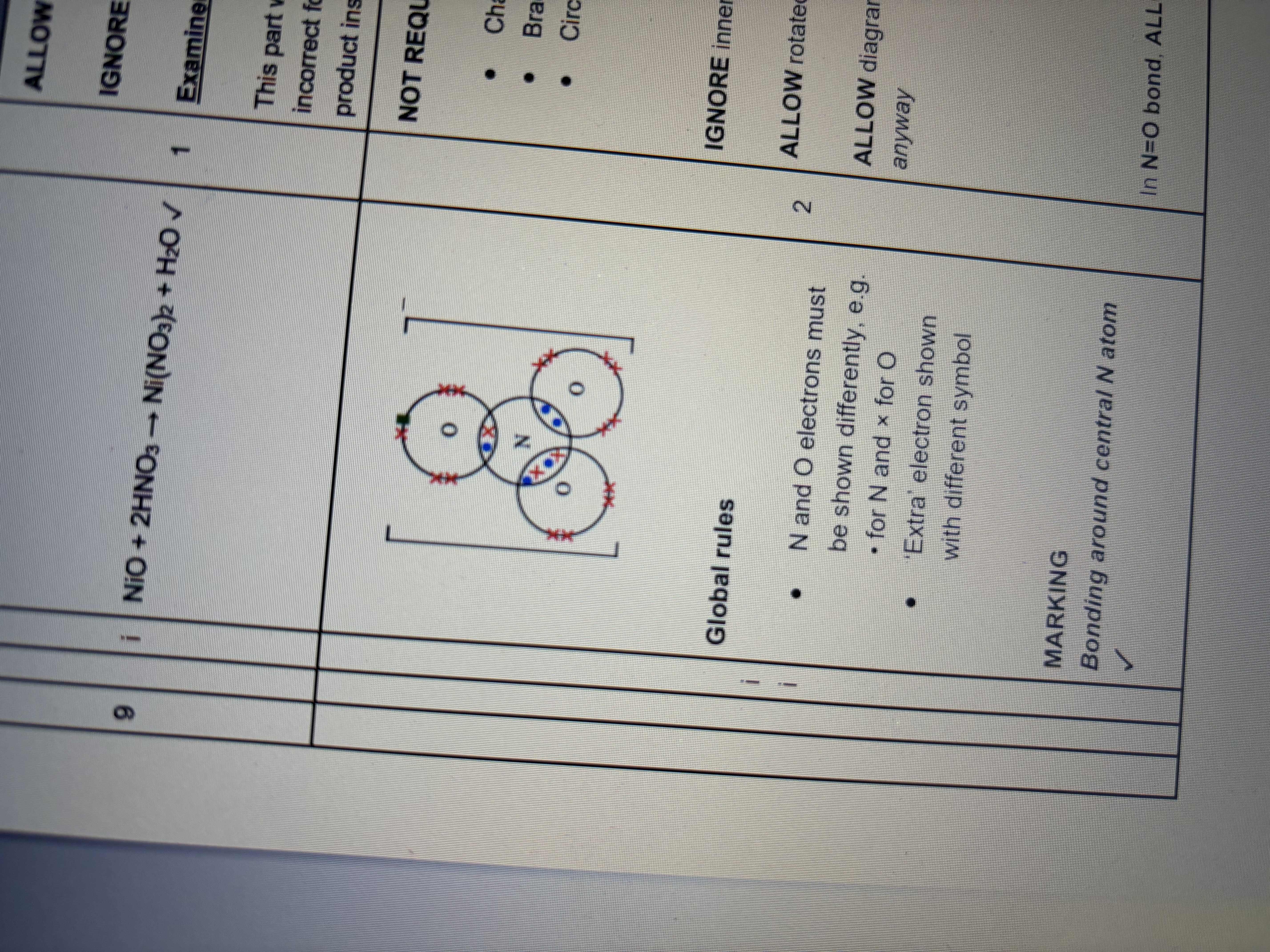
Carbon monoxide has a triple bond and includes a dative covalent bond draw D+C diagram to show it, you failed
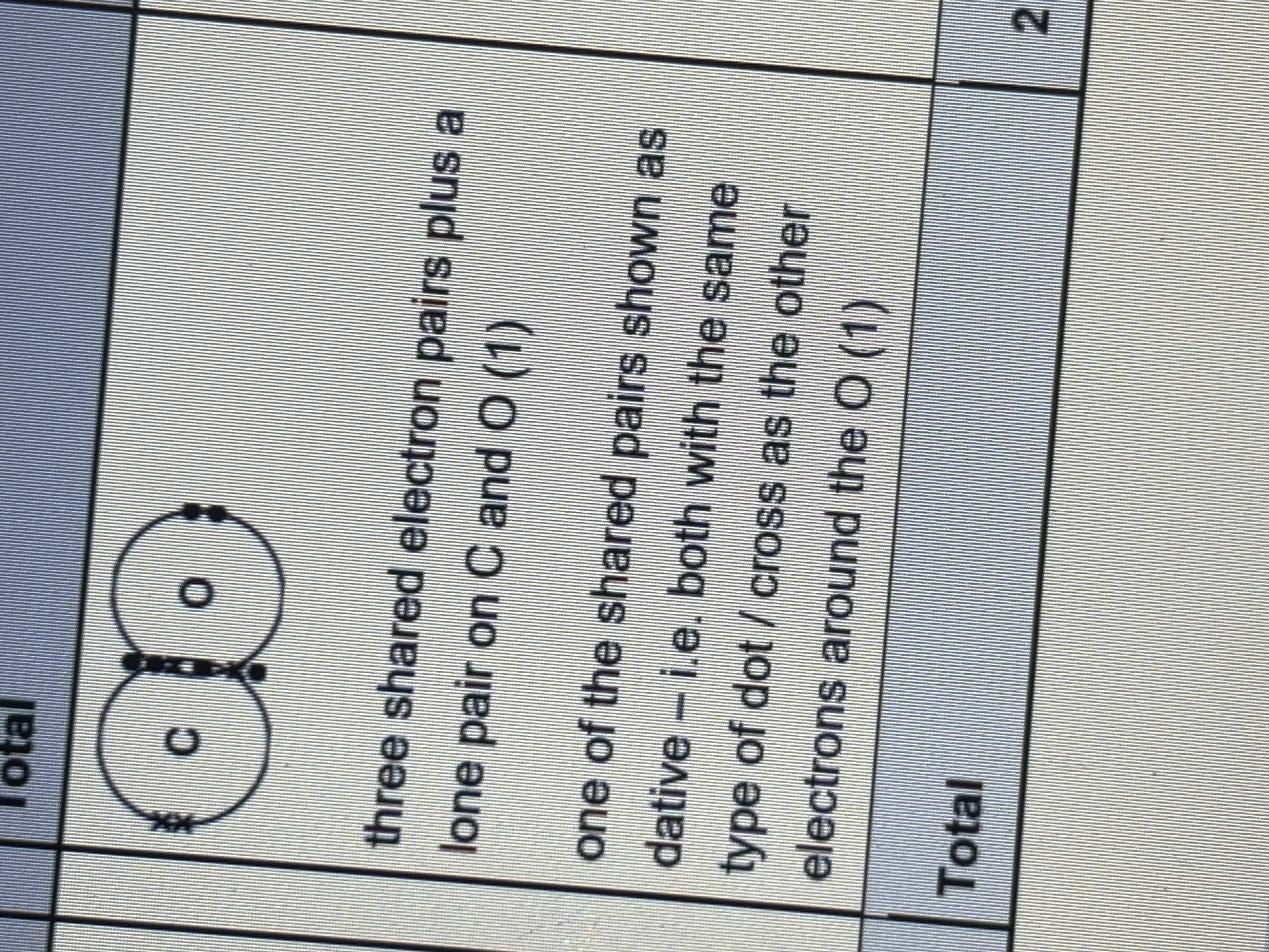
Predict the type of structure and bonding of SO2 and MgO and explain difference in their MP
can’t talk about each one individ must use comparative sentences- MgO is giant ionic, SO2 is simple molecular, ionic bonds in MgO are much stronger than IMF in SO2 , ionic bonds in MgO need more energy to overcome/ break than IMFs in SO2
Explain why the BP of H2S is lower than H2O
H2O has hydrogen bonding, hydrogen bonding is stronger , more energy is required to overcome hydrogen bonding
Explain why BP of H2S is lower than H2Se
London forces in H2S are weaker as H2s has fewer electrons, less energy required to overcome ID-D interactions/ London forces
5 mark explanation given increasing BP from Fluorine —> NH3 —> Bromine
MUST COMPARE: NH3 has hydrogen bonding, F2 and Br2 have London forces
Forces or attractions are between molecular/ are intermolecular for ammonia and for fluorine, bromine
London forces in bromine are greater than in fluorine because bromine has more electrons than bromine
London forces in bromine are greater than hydrogen bonding in NH3
Hydrogen bonding in NH3 is greater than h London forces in fluorine
Each C-Cl bond within the molecule is polar explain why
The covalent bond is between 2 atoms with different electronegativities, so the more electronegative chlorine atom will attract the bonding electrons more leading to partial charges and a dipole
Explain why ammonia will have a higher BP than PH3 hydride
Ammonia has hydrogen bonding which is stronger than permanent dipole-dipole forces in between phosphine molecules
Suggest why water has a high surface tension
There is hydrogen bonding in between water molecules
When a drop of liquid soap is added to water paperclip it sinks suggest why
Soap interrupts hydrogen bonding between water molecules
Explain how structure and bonding in iodine accounts for its relatively low BP
Iodine has simple molecular structure
London forces between molecules are weak
So relatively easily overcome
Would astatine, another group 7 element have higher or lower BP than iodine
Astatine would have a higher BP as it has more electrons so London forces are stronger