Unit 1: Maps & Geography (LARKINS AP HUMAN)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
Distortion and Projection
all maps have _____________ because the world is 3D and it doesn't lay out flat
2
New cards
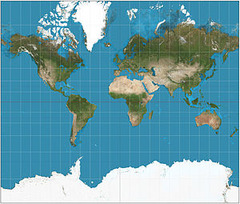
Mercator projection (1569)
Designed to aid ships; good at finding location; bad at distortion of poles; makes land masses around the equator more accurate
3
New cards
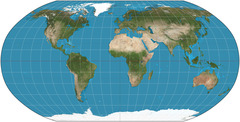
Robinson projection
Good at fixing pole distortion; good for general use/common in classrooms; spreads out the distortion
4
New cards
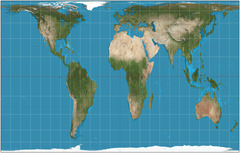
Peters projection (1974)
Controversial because it distorts familiar land shapes; corrects distortions of Africa and South America; land masses around equator become bigger
5
New cards
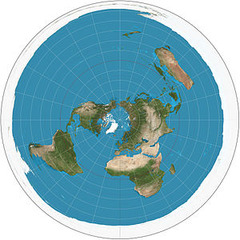
Polar projection
United Nations uses this map; Airlines use it when planning flight directions so it's not centered on one land mass; most of the land mass is in the northern hemisphere; this shows that most of the world's surface is water
6
New cards
Goode's Interrupted projection (equal areas)
Shows the land mass more accurately
7
New cards
Dot map
Uses a dot symbol to show the presence of a feature; shows spatial pattern
8
New cards
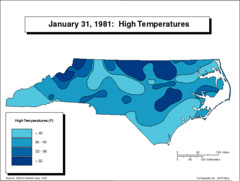
Isoline map
Lines that connect points of equal value
9
New cards
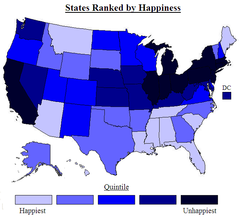
Chloropleth map
Color-coded map that indicate average values of property or quantity in those areas
10
New cards
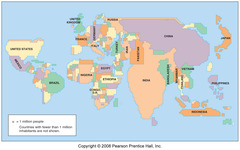
Cartogram map
size of country is determined by population, not by actual size
11
New cards
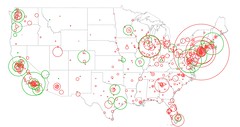
Proportional Symbol map
Type of map that uses a symbol in varying sizes to show the magnitude of a characteristic
12
New cards
Site
the physical character of a place (includes climate, water sources, topography, soil, vegetation, latitude, elevation)
13
New cards
Situation
the location of a place relative to other places; helps us find an unfamiliar place by comparing its location with a familiar one
14
New cards
Latitude and longitude
also called mathematical location
15
New cards
cultural landscape
a region derives its character through the _______________. (ex. language, religion, agriculture, etc.)
16
New cards
Formal region
also called a uniform region, that is an area within which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics
17
New cards
Functional region
also called a nodal region, is an area organized around a node or focal point
18
New cards
Perceptual region
most vague regions, people believe this region exists as a part of their cultural identity (ex. The South, The Middle East)
19
New cards
Scale
From local (small) to Global (large)
20
New cards
Space
How is it organized?
21
New cards
Density
the frequency with which something occurs in space
22
New cards
Concentration
the extent of a feature's spread over space
23
New cards
Pattern
the geometric arrangement of objects in space
24
New cards
Hearth
Where an idea originates
25
New cards
Distance decay
the farther away from one group is from another, the less likely the two groups are to interact
26
New cards
Relocation
the spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
27
New cards
Expansion
The spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in a snowballing process
28
New cards
Hierarchical
The spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places
29
New cards
Contagious
the rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend though out a population; person to person spread of culture.
30
New cards
Stimulus
the spread of an item or idea, it is introduced for the purpose of spreading it, not by accident
31
New cards
environmental determinism
human behavior is strongly affected by the physical environment/climate (ex. cold climate= cold, harsh, cruel people, temperate climate= calm, intelligent people)
32
New cards
Possiblilism
Human action is a result of many factors like individual choice; humans can overcome their environmental constraints; "science will save us"
33
New cards
Location
Position on the Earth's Surface
34
New cards
Absolute location
The exact position of a place on the earth's surface (answers "where is it?")
35
New cards
relative location
The position of a place in relation to another place
36
New cards
Place
physical and human characteristics
37
New cards
Human/Environment Interaction
Shaping the landscape (depend, modify, adapt)
38
New cards
Movement
Humans Interacting on the Earth
39
New cards
Regions
How they form and change; distinguished by physical and human characteristics
40
New cards
location
Latitude and longitude are examples of ____________
41
New cards
Place
"What's it like there?"
42
New cards
place
physical and human characteristics
43
New cards
Human Environment Interaction
Army Corps of Engineers dredges the Great Dismal Swamp to build a canal is an example of _______________
44
New cards
Region
There are many ways to define The South in the USA. This is an example of ___________________
45
New cards
Location
Richmond, VA is located on the fall line of the James River. This is an example of _____________
46
New cards
movement
Amazon has decided to ship Christmas trees this Holiday season. This is an example of ______________
47
New cards
Movement
How are places connected?
48
New cards
Human Environment Interaction
Air conditioning is an example of _____________
49
New cards
Region
In the USA, the Corn Belt, Rust Belt, and Bible Belt are all examples of ____________
50
New cards
Region
How and why is one region similar to another?
51
New cards
Place
Monument avenue is unique to Richmond
52
New cards
location
40 degrees North, 30 degrees West is an example of ________________
53
New cards
Region
The Rocky Mountains are an example of _____________
54
New cards
Location
Singapore became wealthy when China opened up their economy. This is an example of________________