1.c. carbon and water cycles have processes and pathways that operate within them
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
flows in water cycle
fluxes are measurements of the rate of flow of material between stores. are the physical mechanisms which drive the flux of material between stores
drainage basin
an area of land that is drained by a river and its tributaries. enormous, from small local to major river systems like mississippi, nile and amazon. confluence= point where two rivers join. watershed= boundary between two drainage basins
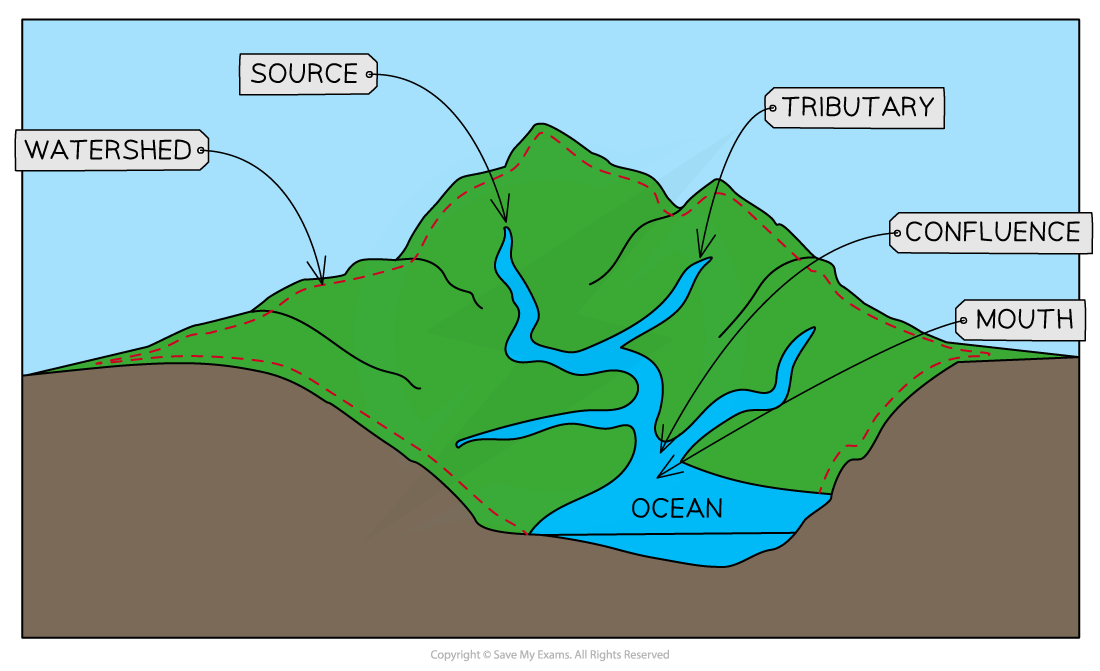
drainage basin open system
interacts with its surroundings by exchanging both matter and energy. receives inputs from outside the basin- solar energy and precipitation, and has outputs, river discharge, evaporation and transpiration.
water balance
equilibrium of water inputs and outputs within a drainage basin, typically expressed as precipitation, runoff and evapotranspiration.
water budget
annual balance between water inputs and outputs within a specific area
flows of water process or flow
precipitation- water in any form which falls from the atmosphere to the surface of the earth
sublimation- ice sheets, glacier and snow fields release water by the direct change of state from solid to a gas
ablation- melting of ice and mass loss from the glacier
infiltration- passage of water downwards into the soil by gravity
percolation- downward vertical movement of water within a soil then enters the groundwater store
throughflow- transfer of water from soil storage zone to the channel. slower than overland flow
overland flow- rainfall is greater than rate at which water can infiltrate the soil. thin layer of water forms on the surface
groundwater flow- water transferred slowly through rock into the bed of the river when all pores are saturated
ocean runoff- all water which enters a river and flows out of the drainage basin
evaporation- liquid water is transformed into water vapour, large amount of energy required to change state
interception- raindrops are prevented from falling directly onto the soil surface by a layer of vegetation
evapotranspiration- total amount of moisture removed by evaporation and transpiration from a vegetated land surface
transpiration- process by water is lost from a plant through the stomata
condensation- water droplets or ice are formed when water vapour is cooled to dew point. latent heat of condensation released
flows of water stores
glacier, groundwater, clouds, rivers and lakes, atmosphere, ocean
clouds
formed by condensation, topography or orographic uplift- shape of land in particular area. air is forced to rise over a barrier of mountains or hills it cools as it rises. layered clouds are often produced this way- stratus cloud. air flow forced up then precipitation and falls down same side, rain shadow desert as airflow lowers
convergence- streams of air flowing from different directions are force to rise where they flow together or converge. this can case cumulus cloud and showery conditions. cold air are more dense, warm air are less dense
DALR
dry adiabatic lapse rate- is the rate at which a parcel of dry air cools. cooling caused by adiabatic expansion is around 10 degrees/km
ELR
environmental lapse rate- is the vertical temp profile of the lower atmosphere at any given time. on average the temp falls by 6.5 degrees for every km of height gained
SALR
saturated adiabatic lapse rate- is the rate at which a saturated parcel of air cools as it rises through the atmosphere. because condensation releases latent heat the SALR at around 7 degrees/km is lower than DALR
absolute instability- rainfall
DALR is right of ELR, parcel of air is warmer than its surroundings. as parcel rises it cools less rapidly than surrounding air and remains warmer and lighter. towering cumulus or cumulonimbus clouds form and thunder storms likely. conditions of instability arise in Britain on hot days
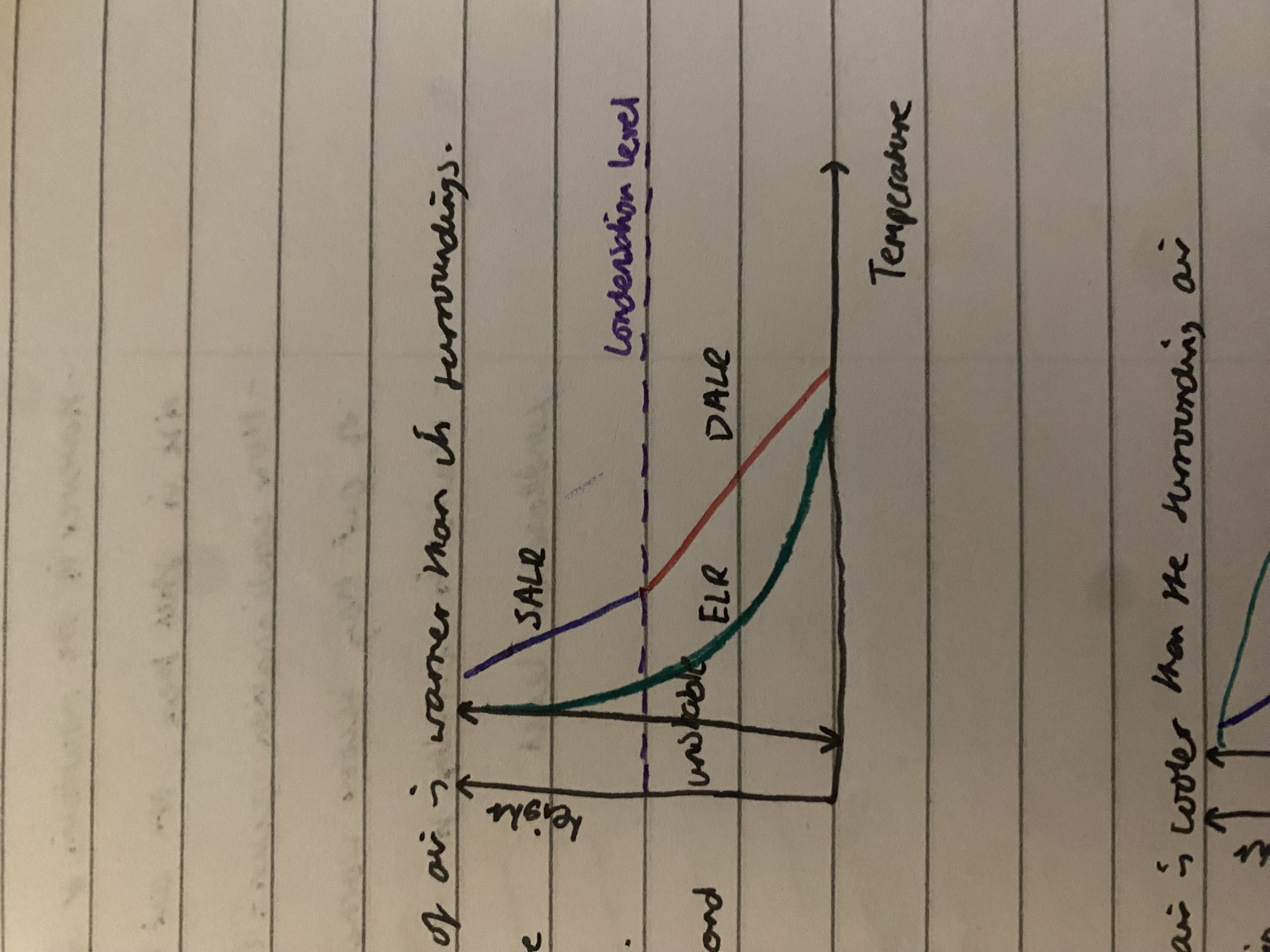
absolute stability
DALR is left of ELR, parcel of air is cooler than the surrounding air. air may be forced to rise but the parcel cools more rapidly than the air surrounding it- by time parcel has reached condensation level it is much colder than surrounding. if nothing to force this continual rise it will sink back down to starting point. air is stable because few clouds form and sinking air= high pressure= temp dry and sunny conditions
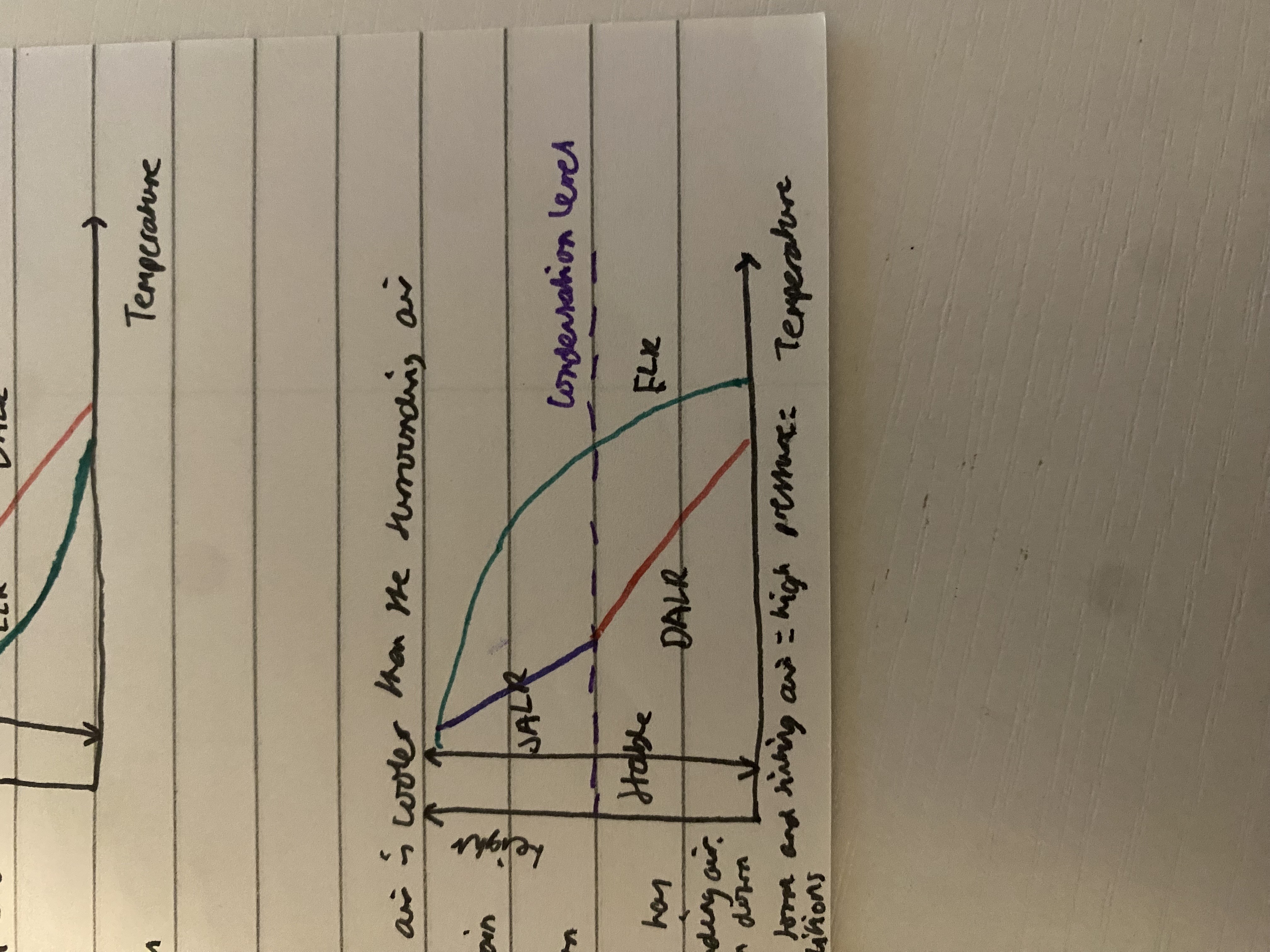
conditional instability
initially ELR is to right of DALR= parcel is colder than surrounding= stable. if parcel is forced to rise it will continue to be colder than surrounding air- normally would sink back down however mountains or cold air mass that originally caused the rise is still there the air will be cooled to its dew point. noe condensation= latent heat is released= air cools more slowly at the SALR and the parcel may become warmer than its surroundings= rise frrely= unstable atmosphere. weather is normally fine in low altitude areas but cloudy and showers at height above the condensation level