Period 1: 1491- 1607 Indigenous societies and Spanish Settlement Diagram | Quizlet
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Centralized
Spain created a system of governing the Colonies that have been described this way- the crown had tight control through viceroys
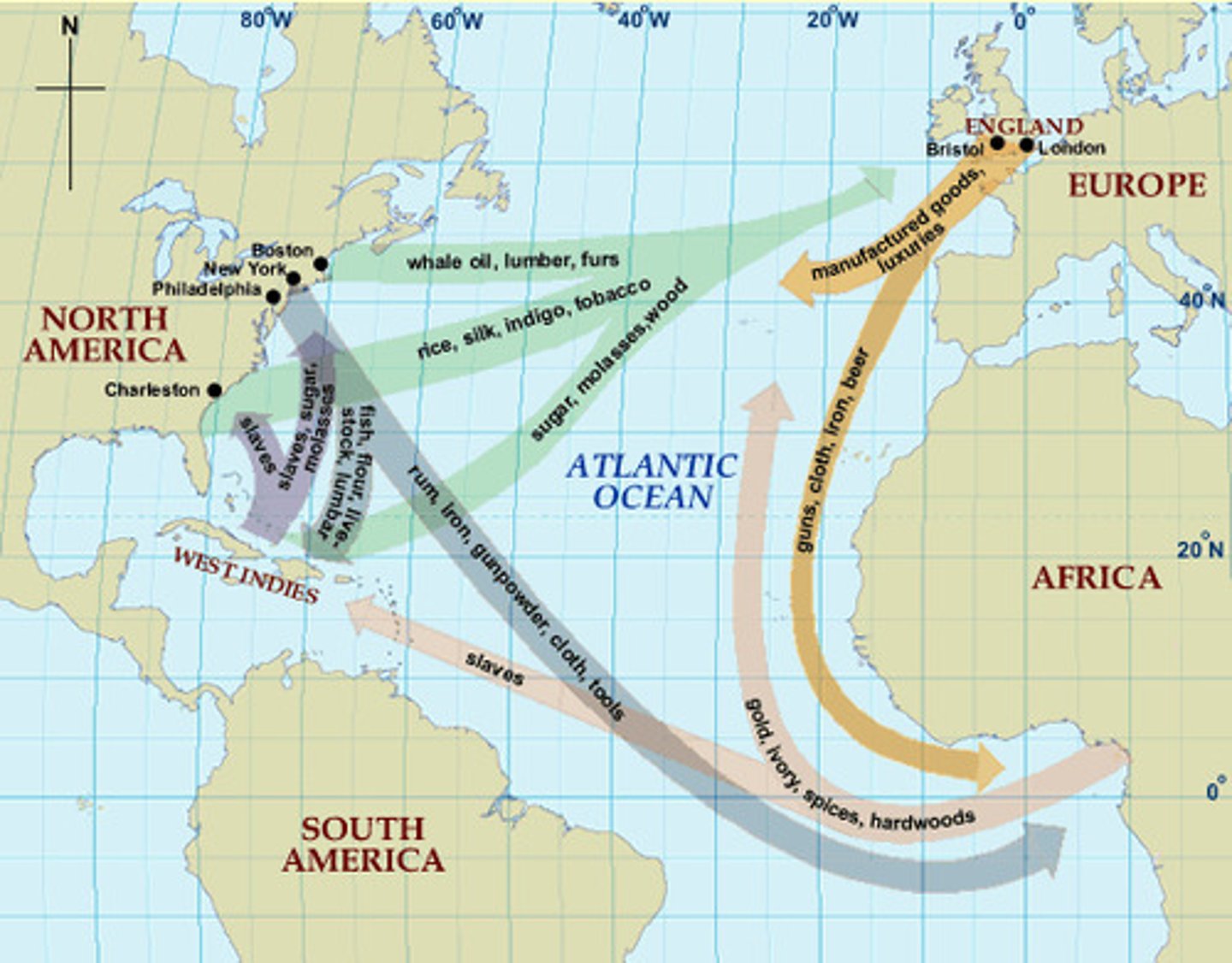
Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
This started as labor was needed in the Americas for cash crops like sugar and mining. The Native population was reduced by disease and warfare.
cultivation
Preparing the land to grow crops; improvement for agricultural purposes Natives sometimes did this by slash and burn or shifting _____________ by moving when the ground was less fertile to another area

Christopher Columbus
He mistakenly discovered the Americas in 1492 while searching for a faster route to India. Encouraged the exploitation of indigenous labor and support their conversion to Christianity
Increased population in Europe
New world crops such as maize, tomatoes, potatoes and the wealth from minerals extracted caused this
capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state. It started to rise after the age of exploration
Decrease of the Native American population
the Columbian exchange had this effect as diseases brought over by Europeans
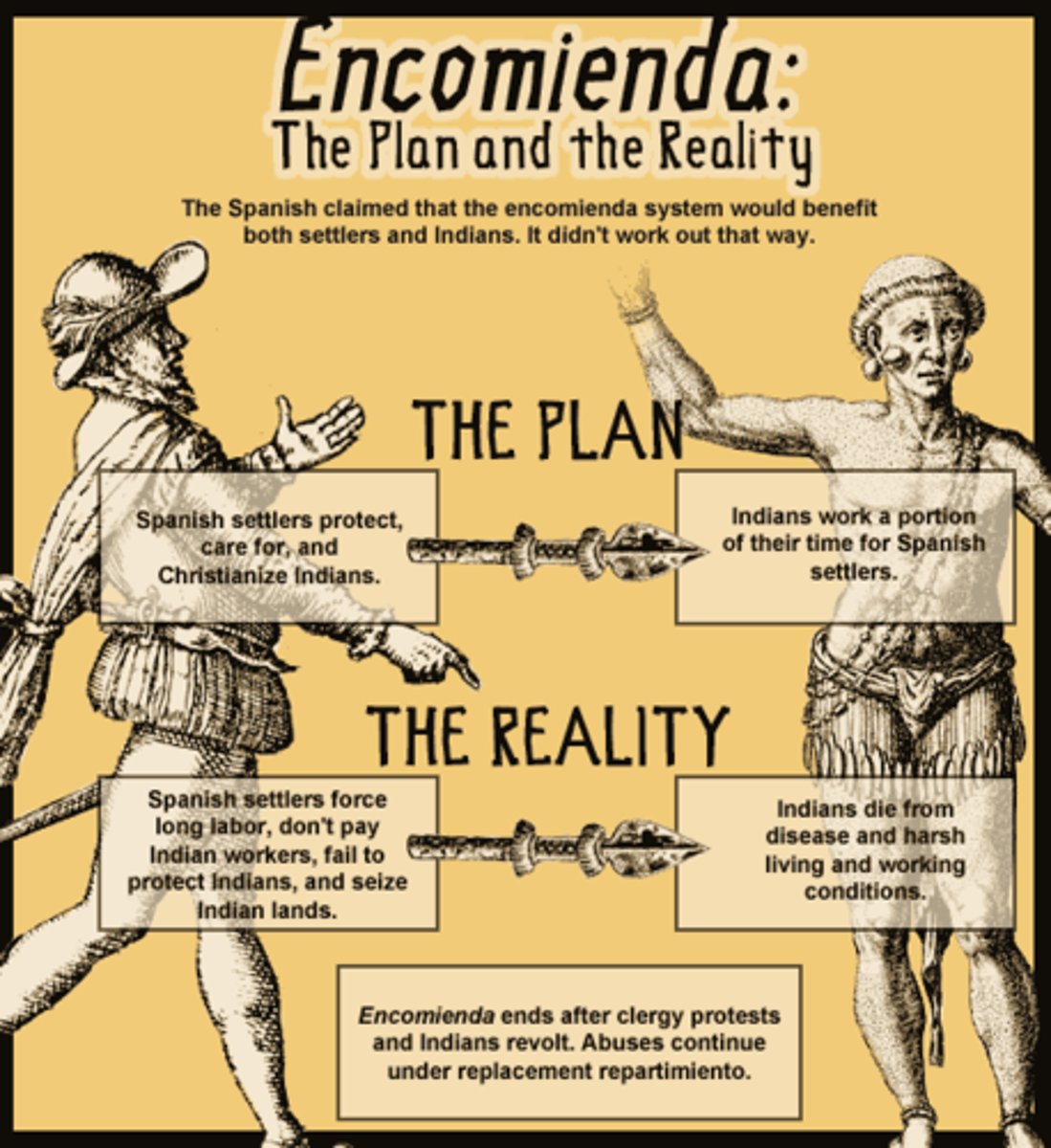
Encomienda
a grant by the Spanish Crown to a colonist in America conferring the right to demand tribute and forced labor from the Indian inhabitants of an area with responsibility of Christianizing the Native population.
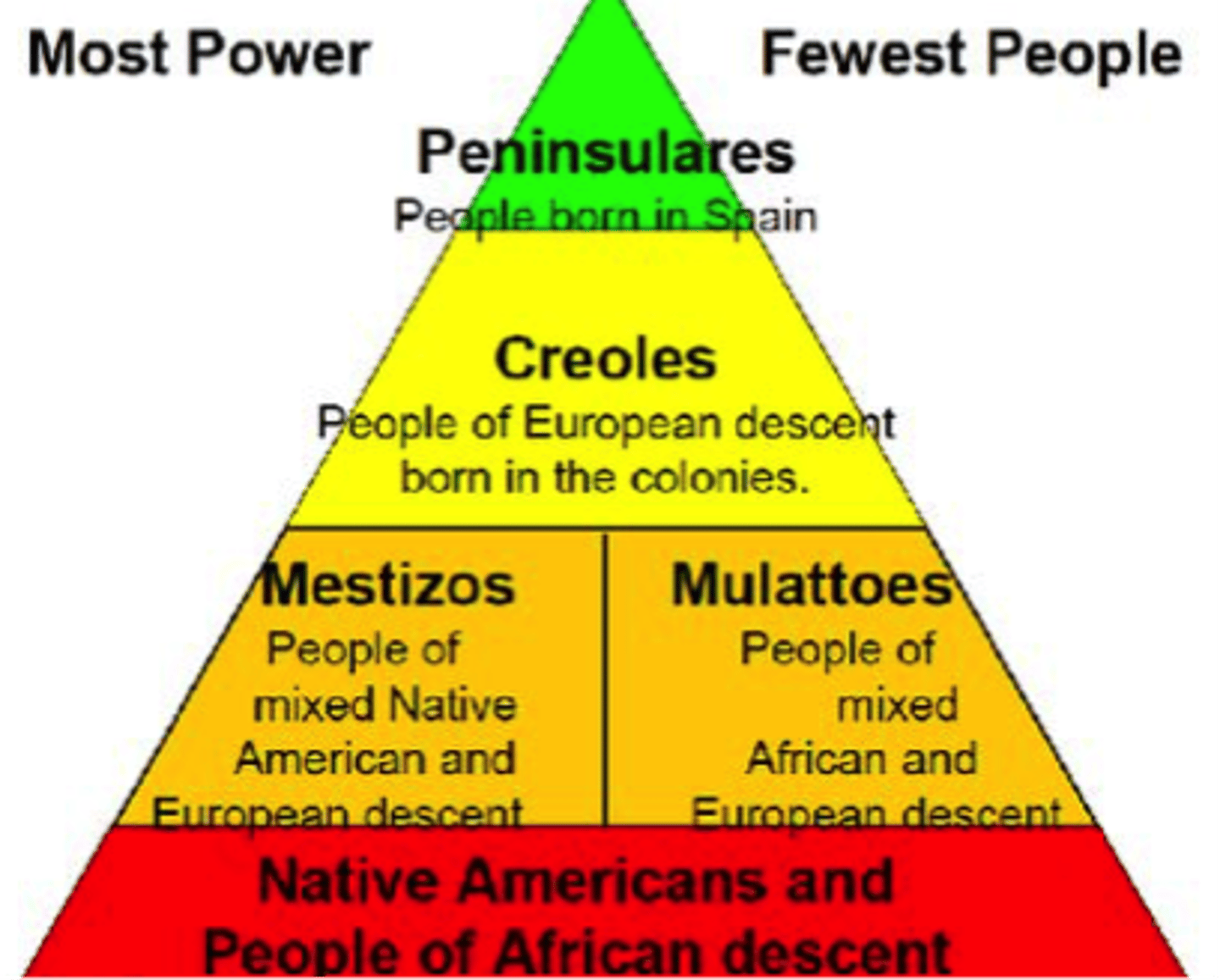
Mestizo
The term used by Spanish authorities to describe someone of mixed native American and European descent. There was a large rate of intermarriage between Spanish Conquistadors and Native women.

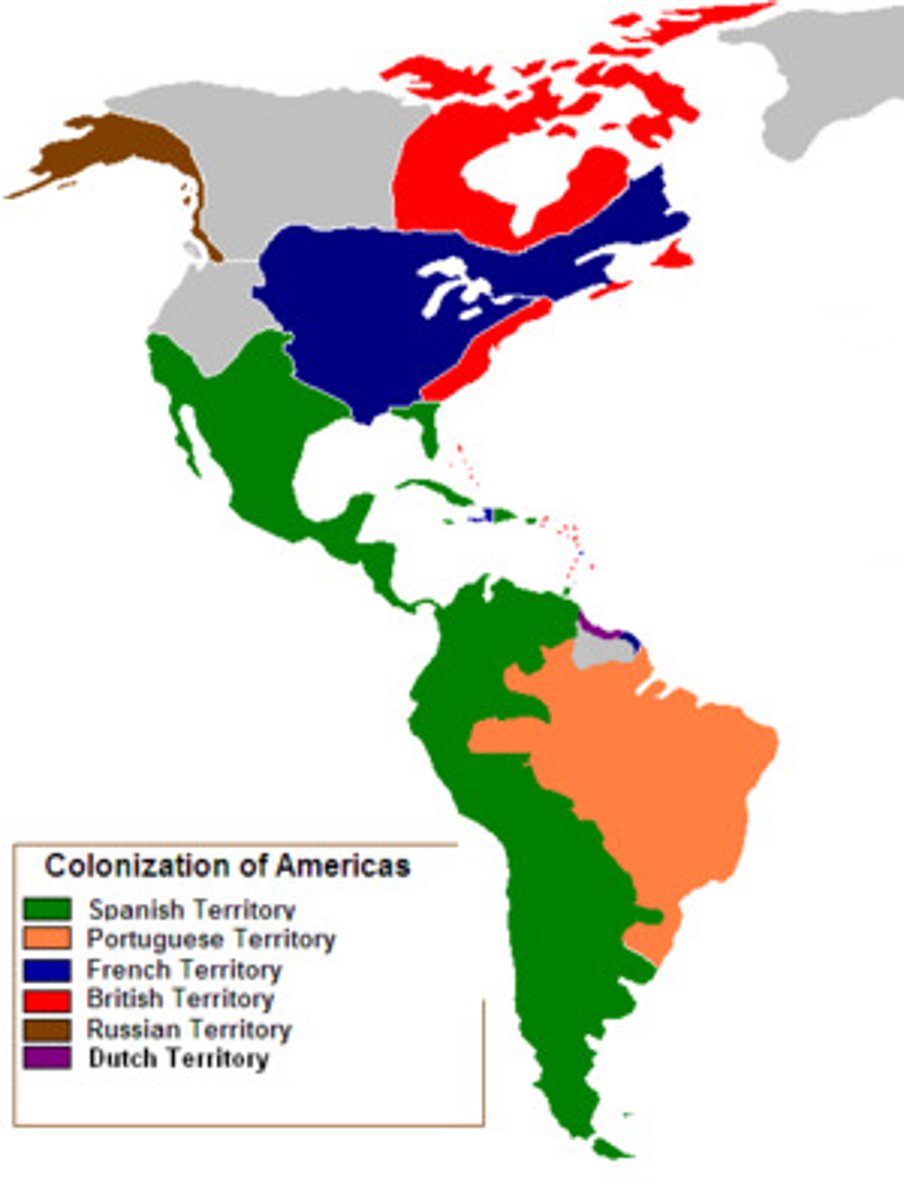
English Colonization
Many colonies created by joint stock companies and mercantile charters (Virginia Company creates Jamestown). Roanoke fails. Plymouth created for religious freedom by Pilgrims (Puritans).
TERM
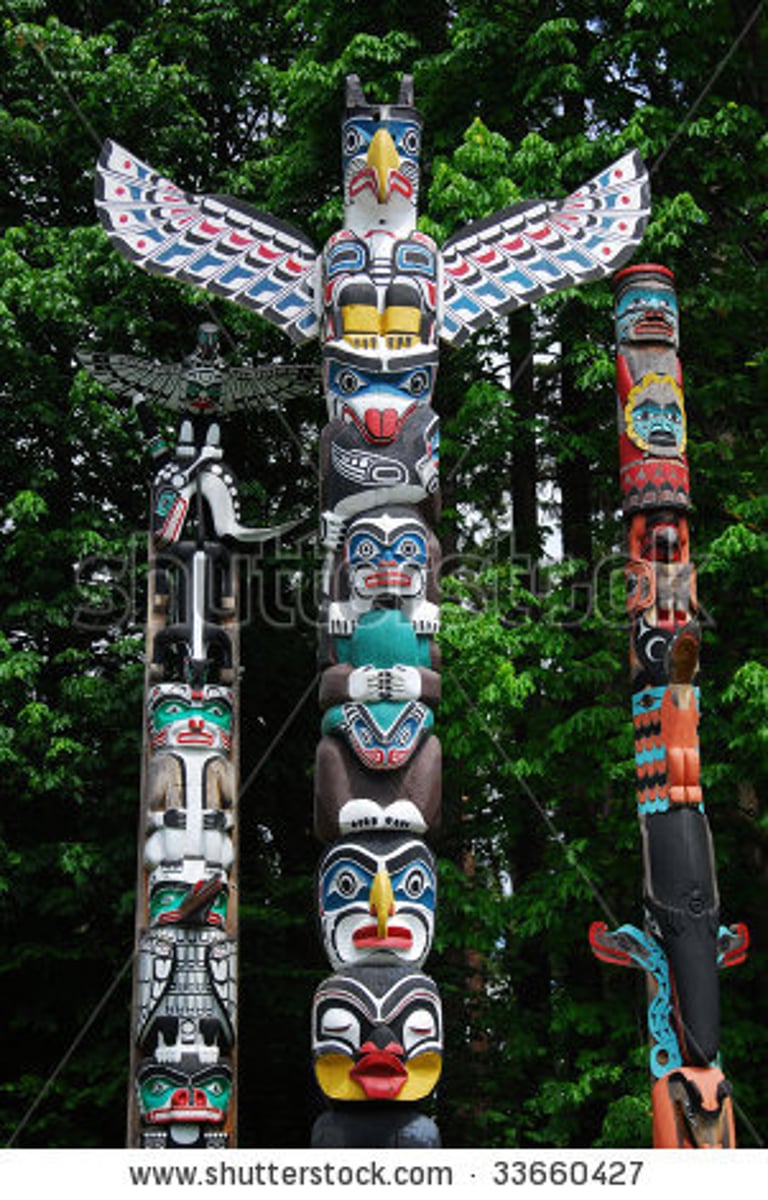
Pacific Northwest Tribes
DEFINITION
Dense population in an abundance of natural resources with dense woods and fishing. There were many distinct groups who controlled small territories and spoke different languages. Stratified societies ruled by wealthy families who nurtured strong warrior traditions to maintain control of their territories. Included the Chinooks; sophisticated fishing using dugout, ocean-going canoes; matriarchal, totem poles

TERM
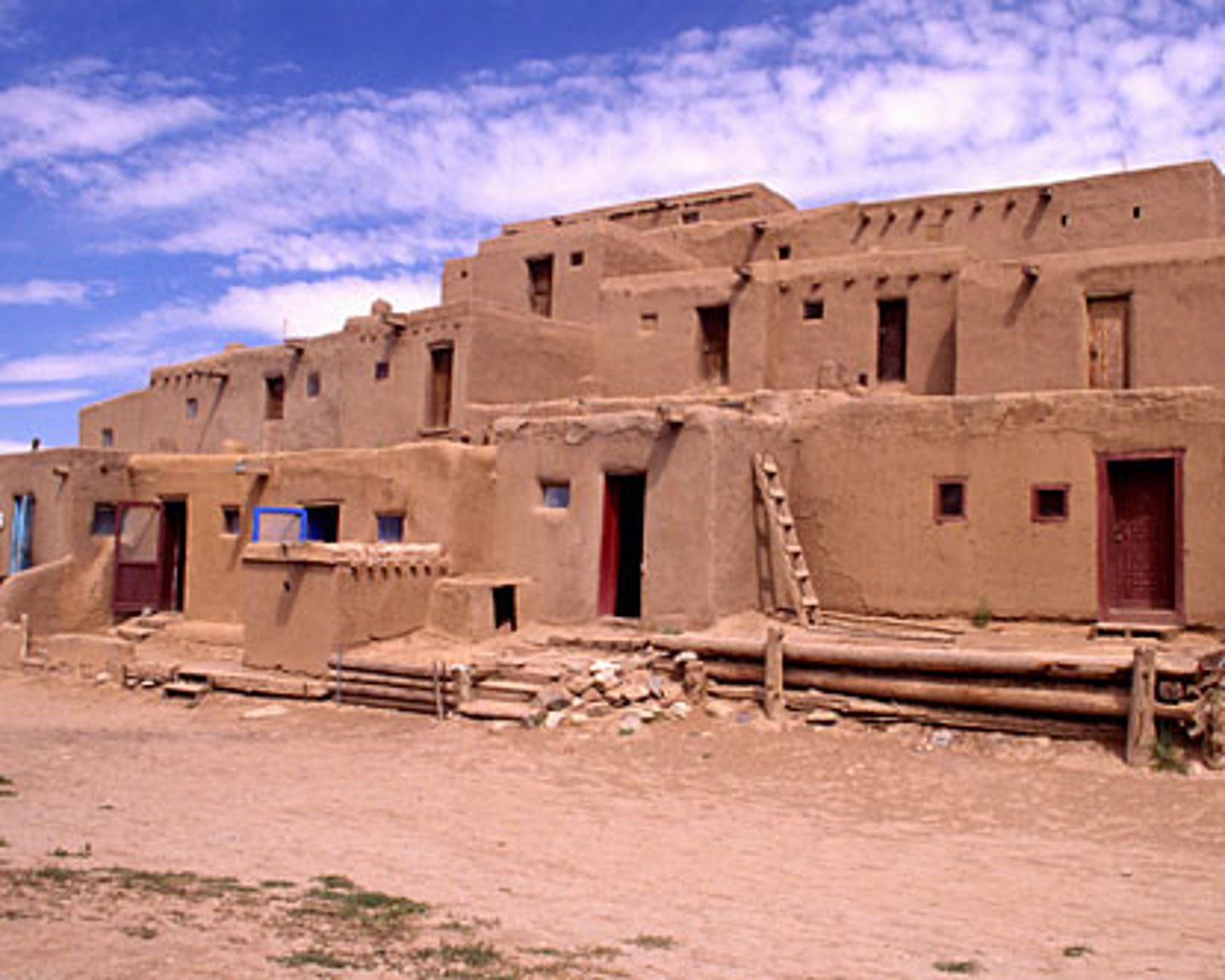
Desert Southwest Tribes
DEFINITION
Drier climate forced tribes to manage water effectively. The Hopi lived near cliffs that were cooler, easlily defended and could collect water in cisterns

TERM
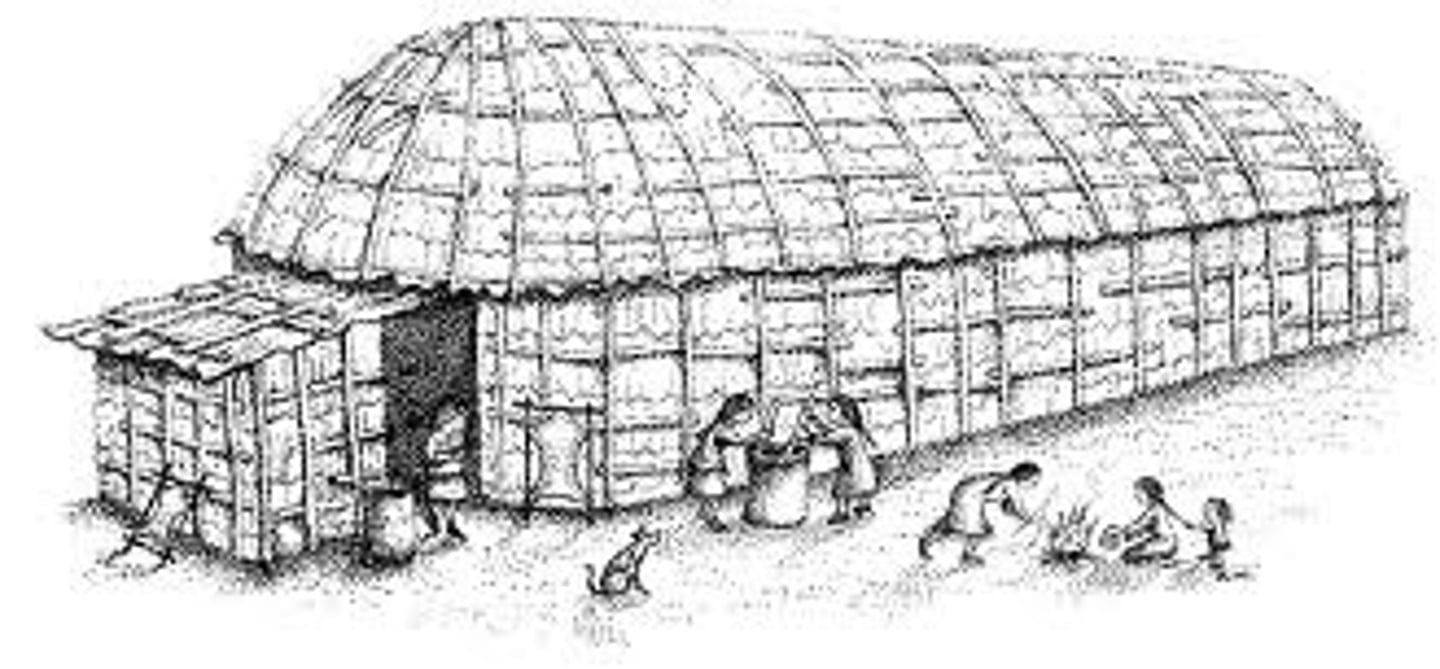
Eastern Woodlands Tribes
DEFINITION
Native Americans who adapted to a forest environment, hunters of deer and cultivated crops such as corn beans and squash. Complex societies such as the
TERM
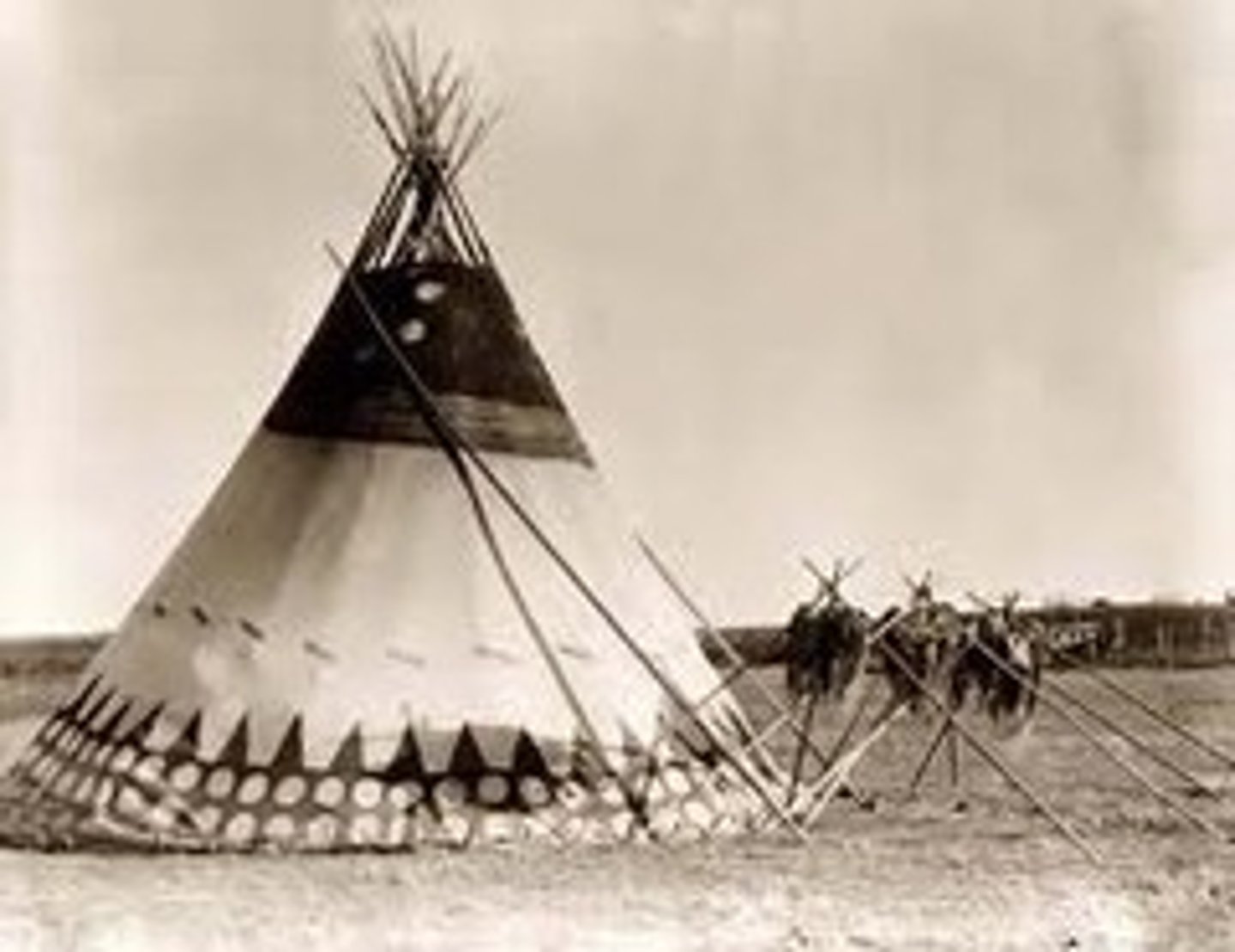
Great Plains Tribes
DEFINITION
These nomadic tribes, such as the Sioux and the Pawnee engaged in some agriculture of corn, beans and squash but primarily migrated with the herds of bison/ buffalo to survive and built homes out of buffalo skin called teepees

private property
this concept was not developed in traditional societies in America but was brought over by Europeans especially capitalist English settlers

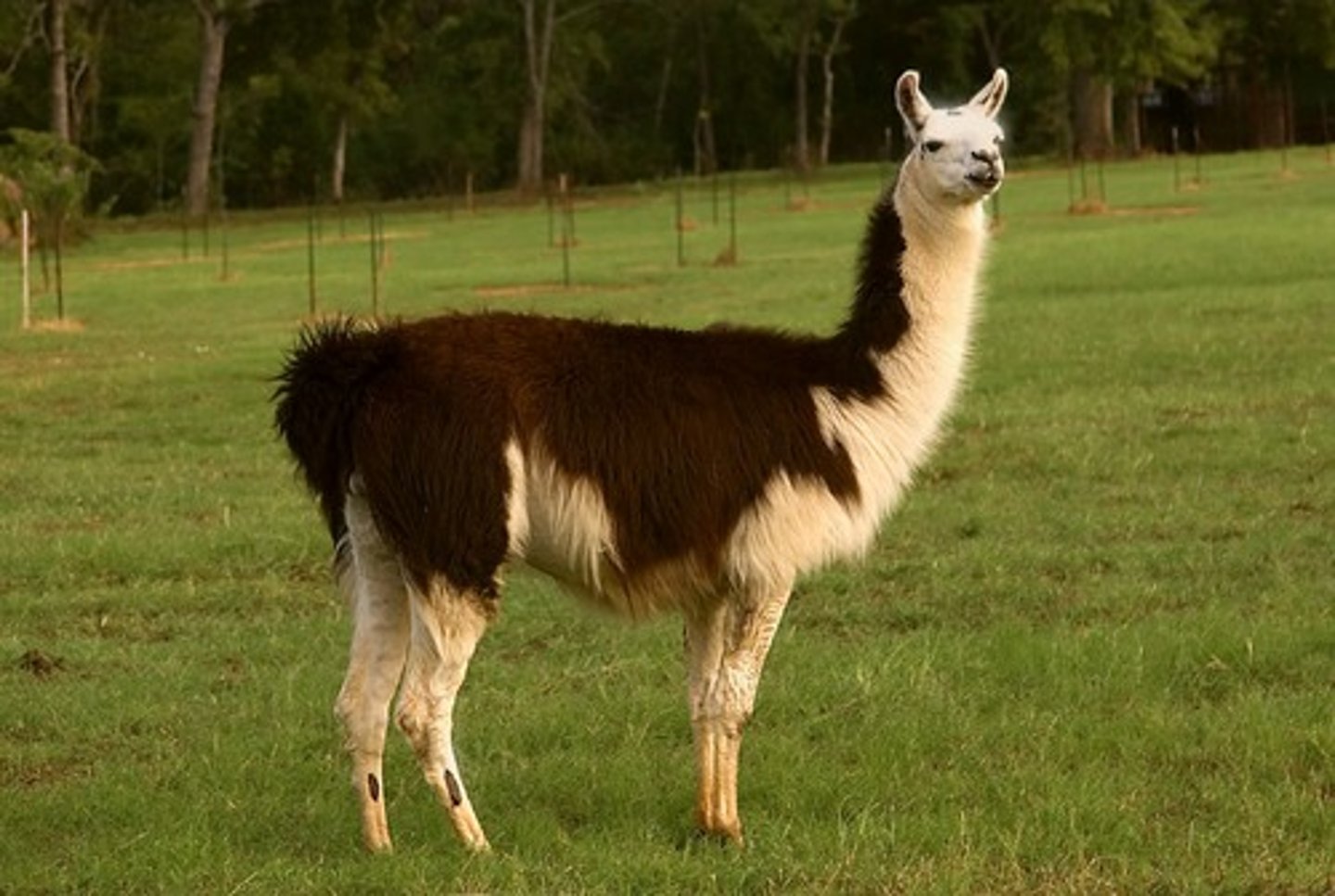
domesticated animals
Native Americans hunted or fished for meat because these were not brought to the Americas before the Columbian Exchange except the Llama

1491
DATE of Pre-Columbus (Start of Period 1)
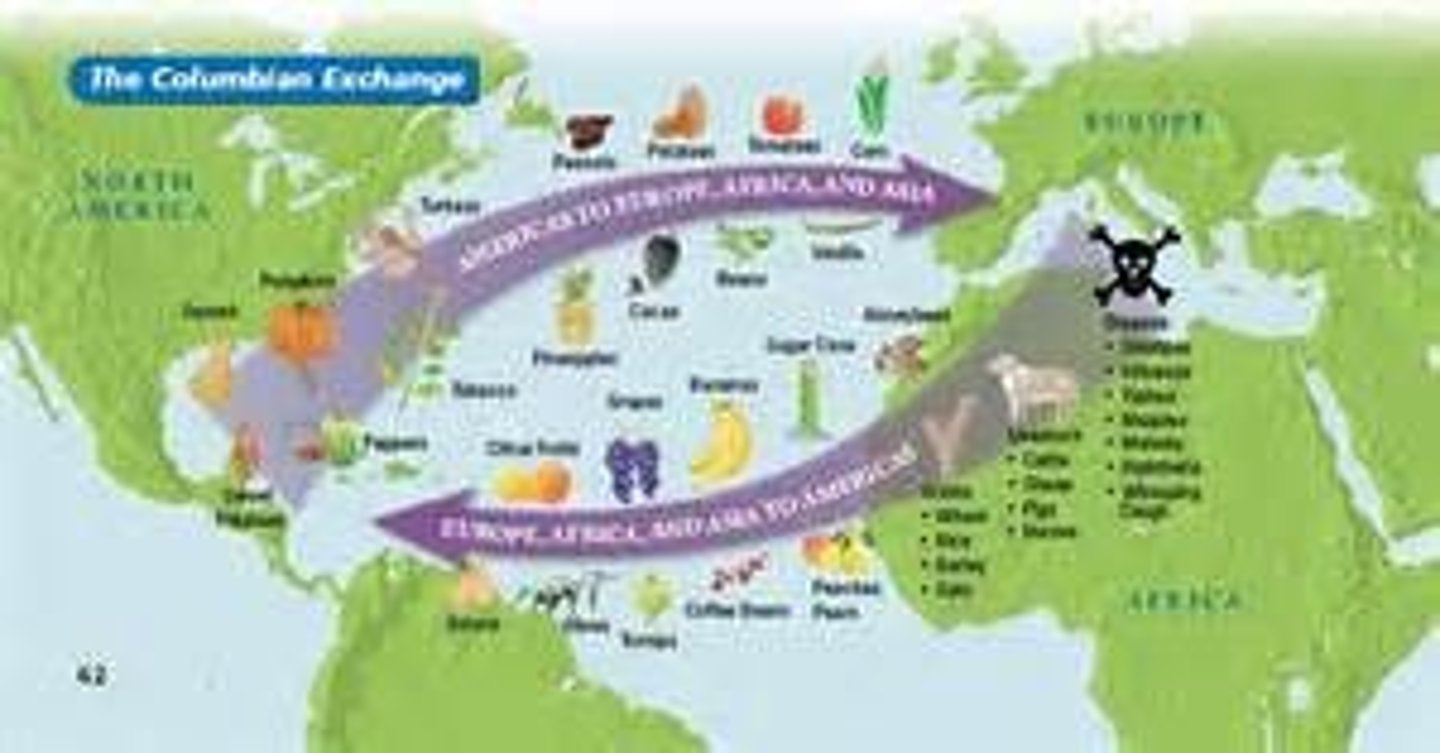
Colombian exchange
the biological exchange between the new world and the old world consisting of the old world bringing wheat, cows, horses, sheep, pigs, sugar, rice, coffee, smallpox, malaria and yellow fever. while the new world sent gold, silver, corn, potatoes, tobacco, and syphills
1607
DATE of Foundation of Jamestown- First Permanent English Settlement (Start of Period 2)
De Las Casas, Bartolome
Spanish Dominican priest, his father sailed on Columbus's second voyage to Cuba who Wrote "A Very Brief Account of the Destruction of the Indies", detailing Spanish Christians' cruel treatment of the Indians and advocating for their freedom
Transatlantic Slave Trade
By 1518 the Spanish brought the first captives were shipped directly from Africa to America. The majority of African captives were exported from the coast of West Africa, some 3,000 miles between what is now Senegal and Angola, and mostly from the modern Benin, Nigeria and Cameroon
Conquistadores
Sixteenth-century Spaniards who colonized the Americas, from Colorado to Argentina, eventually conquering the Aztec and Incan empires. Most of these Spanards were upper class males.
Catholic
This was the religion promoted by the Spanish empire
Casta system
A system in colonial Spain of determining a person's social importance according to different racial categories.
Pueblo Revolt
Native American revolt against the Spanish in late 17th century; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years; Spain began to take an accommodating approach to Natives after the revolt.

Spanish Colonization
Colonial expansion under the crown of Castile was initiated by the Spanish conquistadores and developed by the Monarchy of Spain through its administrators and missionaries. The motivations for colonial expansion were trade and the spread of the Catholic faith through indigenous conversions.
French Colonization
they colonized the interior, where they controlled the fur trade. Most immigrants were single men, and there were few towns and only loose governmental authority. They lived closely with the Indians, trading with them for furs and sometimes taking Indian wives.
Still learning (10)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!