Neurophysiology & Pharmacology of Dental LA
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is the SENSORY NEURON that brings signals TOWARD the brain and spinal cord?
Afferent
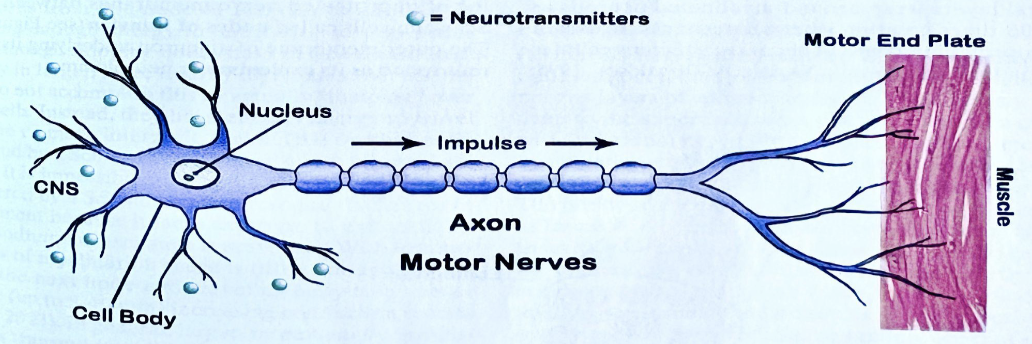
What is the MOTOR NEURON that brings signals AWAY from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands?
Efferent
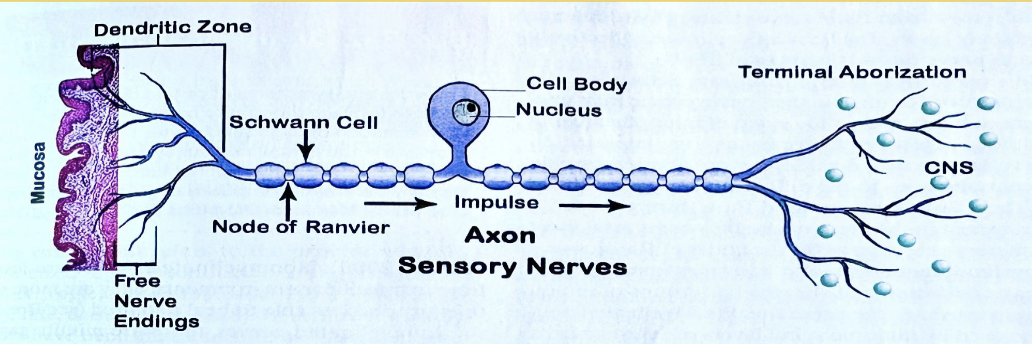
What Nerve carries information from the periphery of the body to the brain
Aferent - Sensory
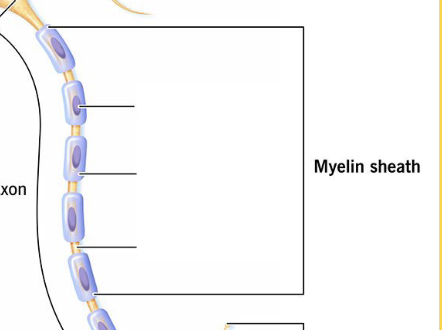
What is the Insulating and protective lipid-rich layer around the Axon?
Myelin
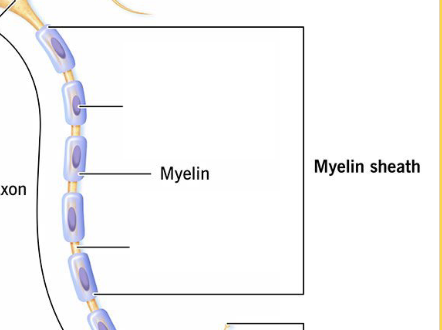
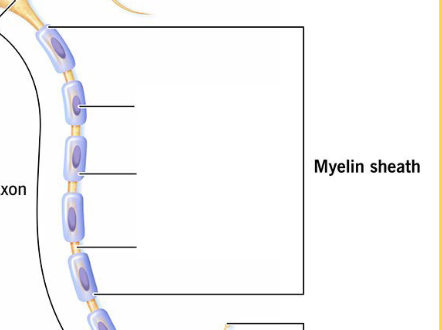
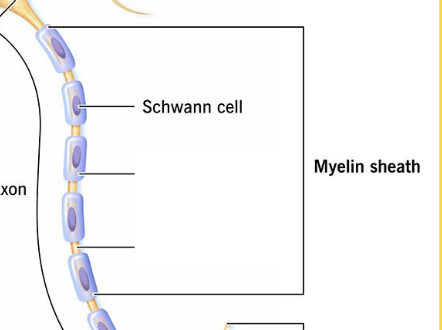
This is responsible for producing and maintaining the myelin sheath.
(Facilitates the healing process after injury)
Schwann cells
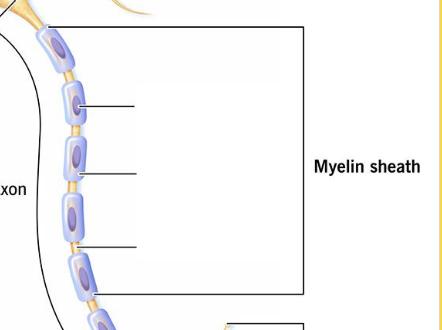
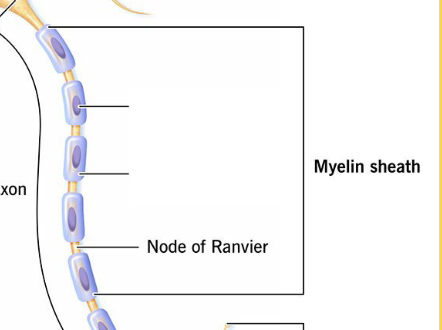
The gap(s) between adjoining Schwann cells and myelin spirals.
Nodes of Ranvier
What ion passes through the nerve membrane easily?
RN (neutral base)
What is NOT true about myelinated nerves?
It slows the transmission of impulses.
What are the steps of electrophysiology of nerve conduction?
1.) Resting state/potential
2.)Membrane Excitation (stimulus)
3.) Nerve Potential Generation
4.) The Wave Effect
5.) Repolarization (reset)
Acts like a battery with different charges inside and outside.
Resting state/potential
What part of the nerve has more (Na+) and (Cl-) and has a positive charge?
Outside or External
What part of the nerve has more (K+) and a negative charge?
Inside or Internal
Pressure, temperature, or chemicals that trigger the nerve and change the inside from negative to positive (depolarization).
Membrane excitation
What is it when sodium rushes through the sodium and changes from negative to positive?
Action potential generation
This is how the messages moves along the nerve ( domino effect).
The wave effect
Returns to resting state, sodium channels close automatically, potassium channels open, and the membrane returns to negative charge.
Repolarization ( reset)
How does dental local anesthetic work?
Blocking sodium channels
Immediate after stimulus has initiated action potential unable for a time to respond to another stimulus.
Absolute Refractory Period
When a new impulse may be generated by A stronger than normal stimulus.
Relative Refractory Period
Fast conduction, jumps between nodes, sharp, precise pain, cold sensitivity, first to be blocked by Local Anes. Sharp tooth pain.
A fibers - myelinated
Facts about myelinated nerves.
Impulses are carries through the Nodes of Ranvier
Insulation along the nerve axon
Schwann cells are responsible for creating myelin sheaths
Slow conduction, most common, dull burning pain, tension and pressure, thermal pain (hot or cold). Lingering toothache.
C - fibers - unmyelinated
What fibers are found in the dental pulp?
Both A & C fibers
The sequence of successful impulse generation
Resting state, stimulation, slow depolarization, firing threshold, rapid depolarization, repolarization, recovery.
What nerves doe the Local Anes effect?
Both Sensory and motor nerves
What nerve is affected first Motor (large) or Sensory (small)?
sensory (small)
What two anesthetic agents can be use topically and subcutaneously
Lidocaine and prilocaine
What is true about nerve membranes (neurolemmas)?
Hydrophilic ends of the membrane are facing out
Lipophilic ends of the membrane are facing in
What is the order of the blockade of Local Anes.
1.) pain sensation fibers
2.) temperature sensation
3.) touch sensation
4.) pressure sensation
The main reason anesthesia fails to occur near an abscessed tooth?
Infection causes a decrease n the tissue pH.
What the factors affect Local Anes success?
pH factor of tissue
Blood flow in the area
Accuracy of placement
type of nerve being blocked
concentration of drug
What element needs to be blocked for there to be no nerve signal?
Sodium
The ACTIONS of a drug on the body
Pharmacodynamics
The manner in which the body MANAGES the drug (absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination)
Pharmacokinetics
The rate of which a drug is removed from the systematic circulation by the kidneys.
Half - life
How much of a drug would be life in the system on the 3rd half - life?
25%
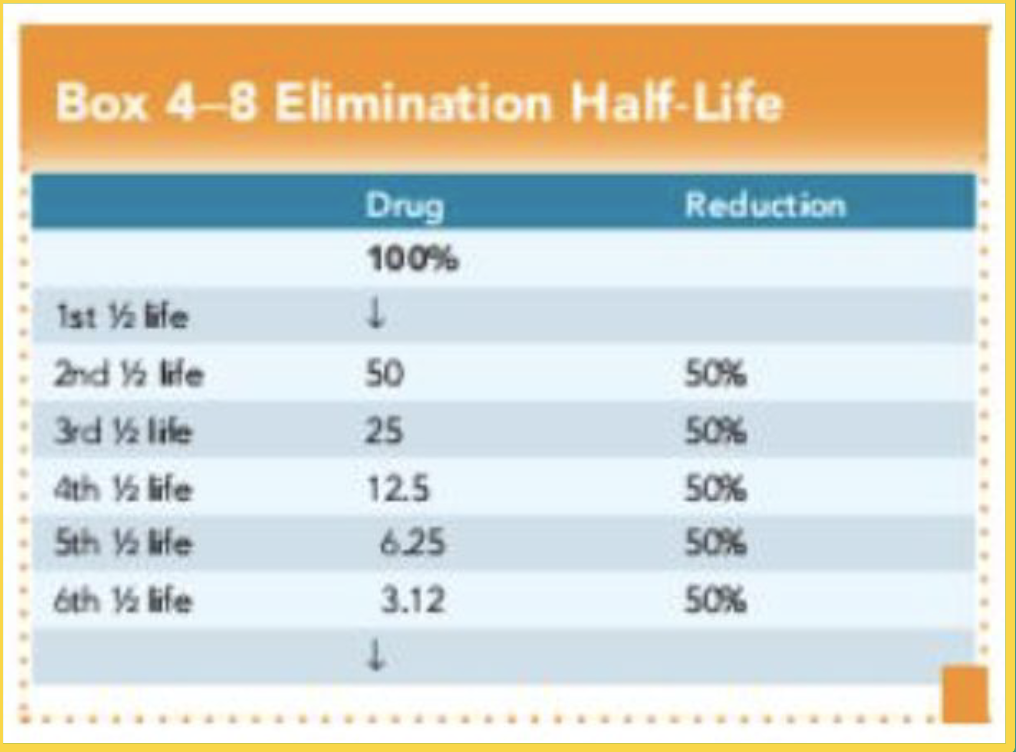
What is elimination half-life refers to what?
The time it takes for half of the drug to be out of the circulation
What anesthetic is primarily metabolized in the blood (cholinesterase)?
Articaine
Local Anesthetics works by penetrating the nerve to inhibit?
Na+ influx
What component of Local Anes renders the molecule water-soluble?
Hydrophilic amino group
Uncharged form of (RN), neutral pH base, can NOT attach to the receptor in channel.
Lipophilic
Charged from (RNH+) cation, low pH, attaches to the receptor in NA+ channel
Hydrophilic
What are examples of Local Anes Amides?
Lidocaine
Bupivacaine
Mepivacaine
Prilocaine
Articaine
Where does the metabolism of the amide anesthetics occur?
The Liver
What are examples of Local Anes Esters?
Cocaine
Procaine
Benzocaine
Tetracaine
chloroprocaine
The metabolism of the anesthetic esters occurs by?
an enzyme cholinesterase
The drug that constricts peripheral blood vessels
Vasoconstrictors
What may be a sign of epinephrine overdose?
Resemble CNS depression which include: drowsiness, slurred speech, confusion, dizziness, poor coordination, slowed breathing and heart rate.
What is Phase I of CNS?
Excitation - signs of fear and anxiety.
What is Phase II of CNS?
Depression - tonic clonic seizures, coma and respiratory arrest.
What is Phase I in CVS?
Heart rate and blood pressure increase.
What is Phase II in CVS
Vasodilation continues leading to a fall in BP, reduced cardiac output, and respiratory arrest.
Facts about RNH+ of the local anesthetic ion?
Blocks the nerve impulse
the working form of the drug
blocks the calcium channel
What is true about the cation RNH+ charged form?
it has low pH