Integument Structure and Function in Vertebrates
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Integument (Skin)
The outer covering of the body, also known as the cutaneous layer.
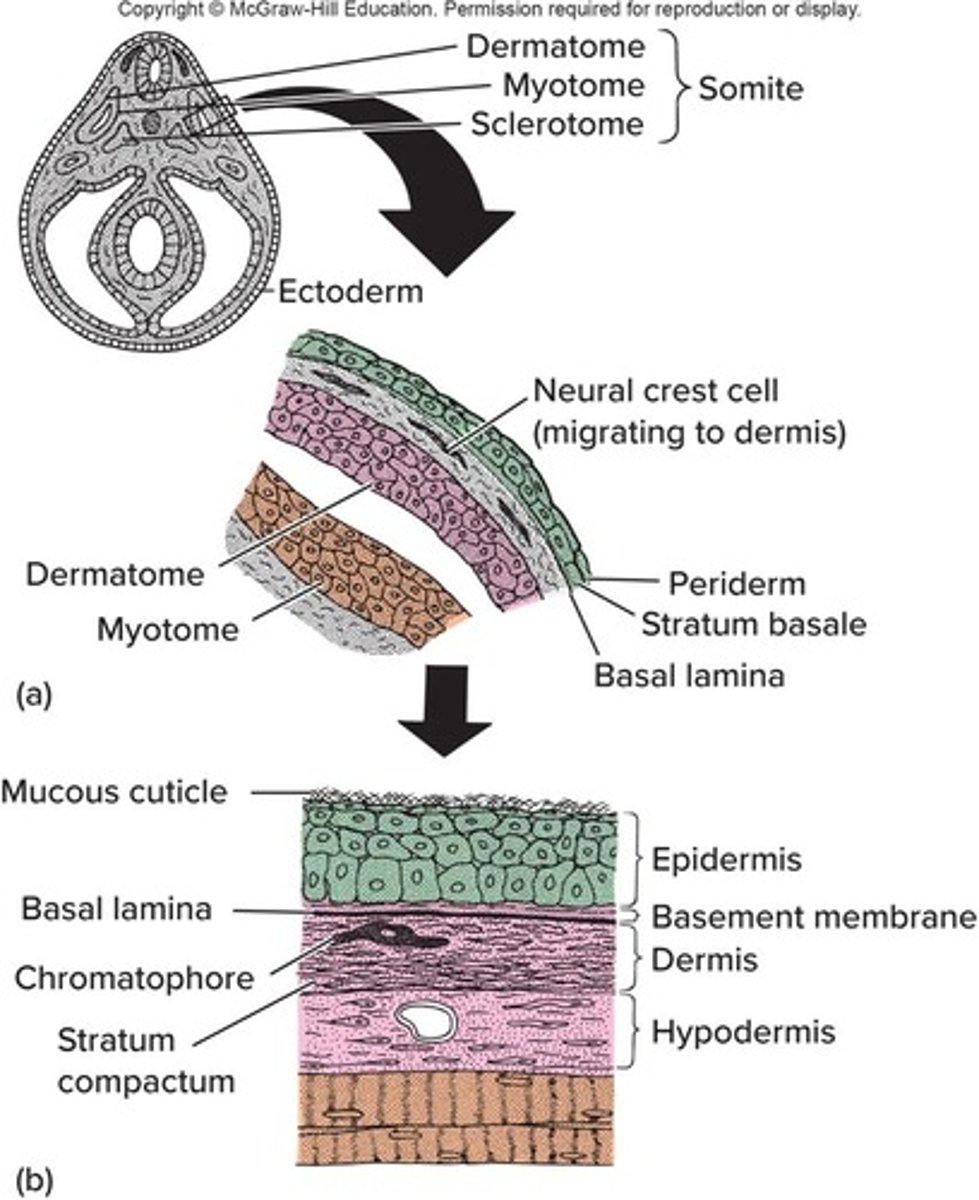
Epidermis
Superficial layer of skin.
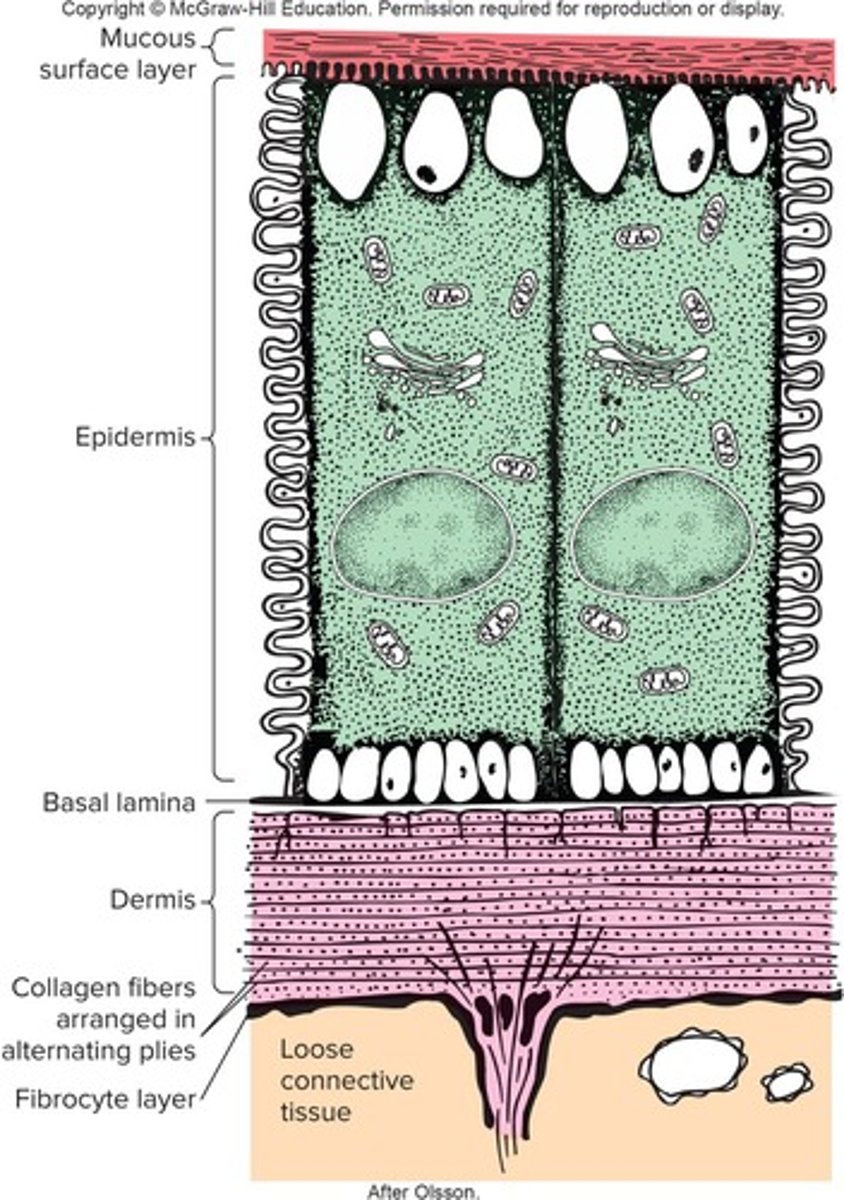
Basement membrane
Separates epithelium from connective tissue.
Dermis
Deep layer of skin.
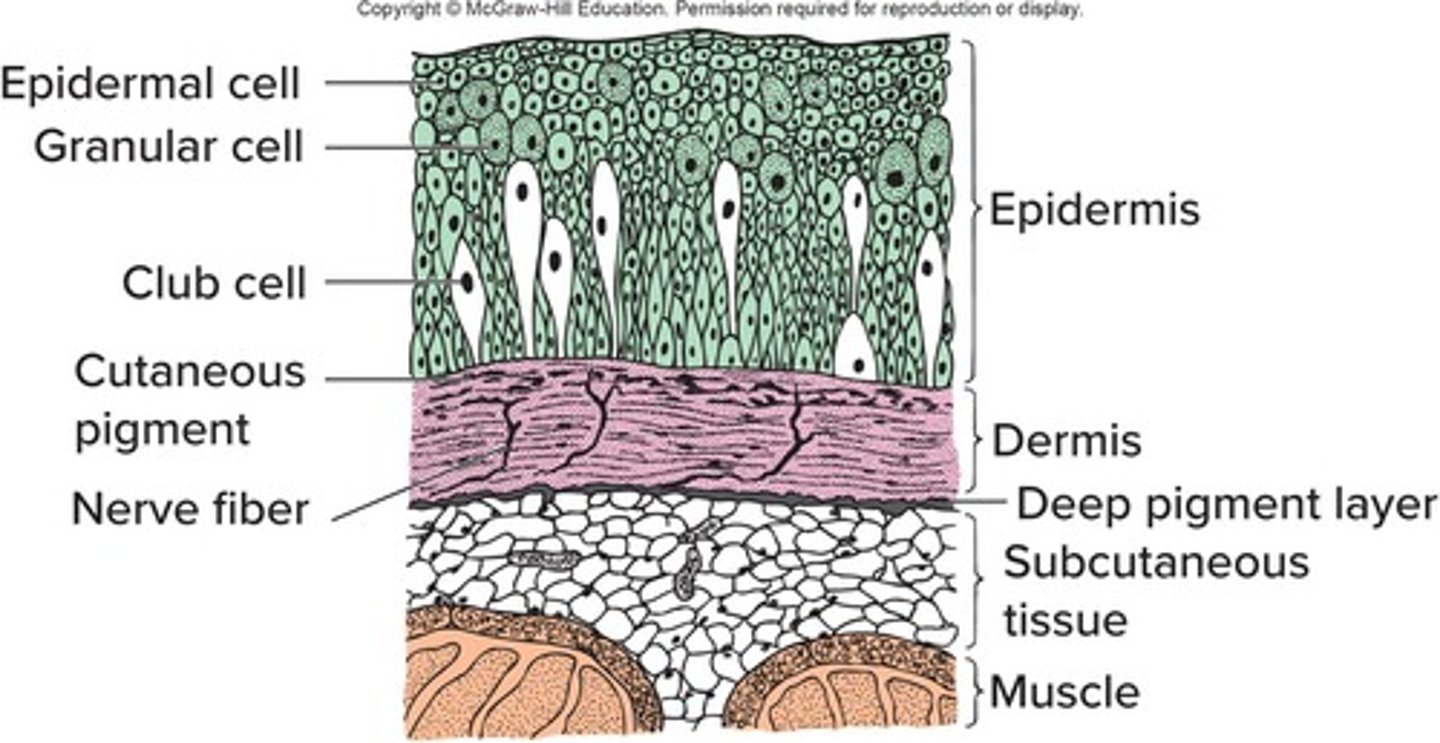
Hypodermis
Layer of connective tissue under the skin; also called superficial fascia or subcutaneous layer.
Integument Functions
Includes protection, shape maintenance, osmotic control, gas exchange, temperature regulation, and sensory functions.
Chromatophores
Skin pigment cells that provide color to the organism.
Dermal bones
Plates of bone initially positioned in the dermis.
Keratinization
Process by which proteins form keratin with help from keratinocytes.
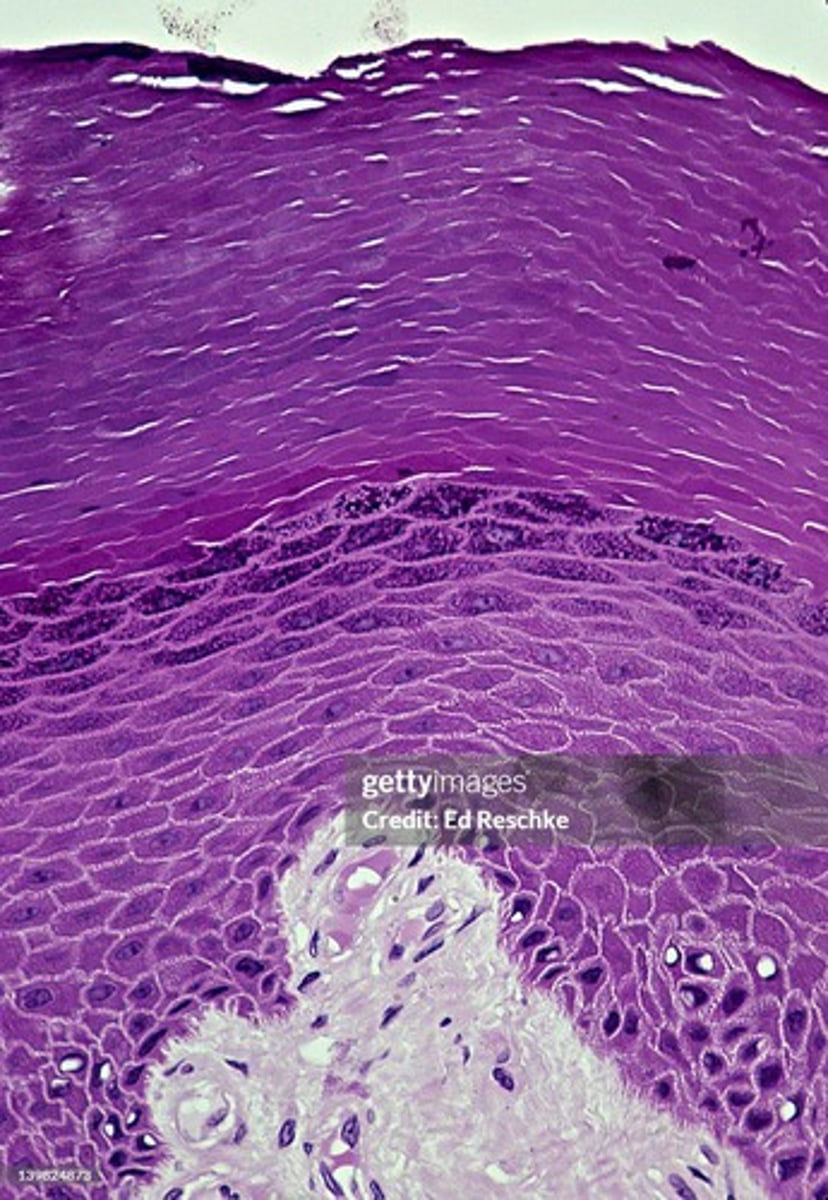
Stratum corneum
Outer keratinized layer of the epidermis in terrestrial vertebrates.
Callus
A thick protective layer that can form on the skin.
Epidermal cells
Cells in the epidermis that include various types such as club cells and goblet cells.
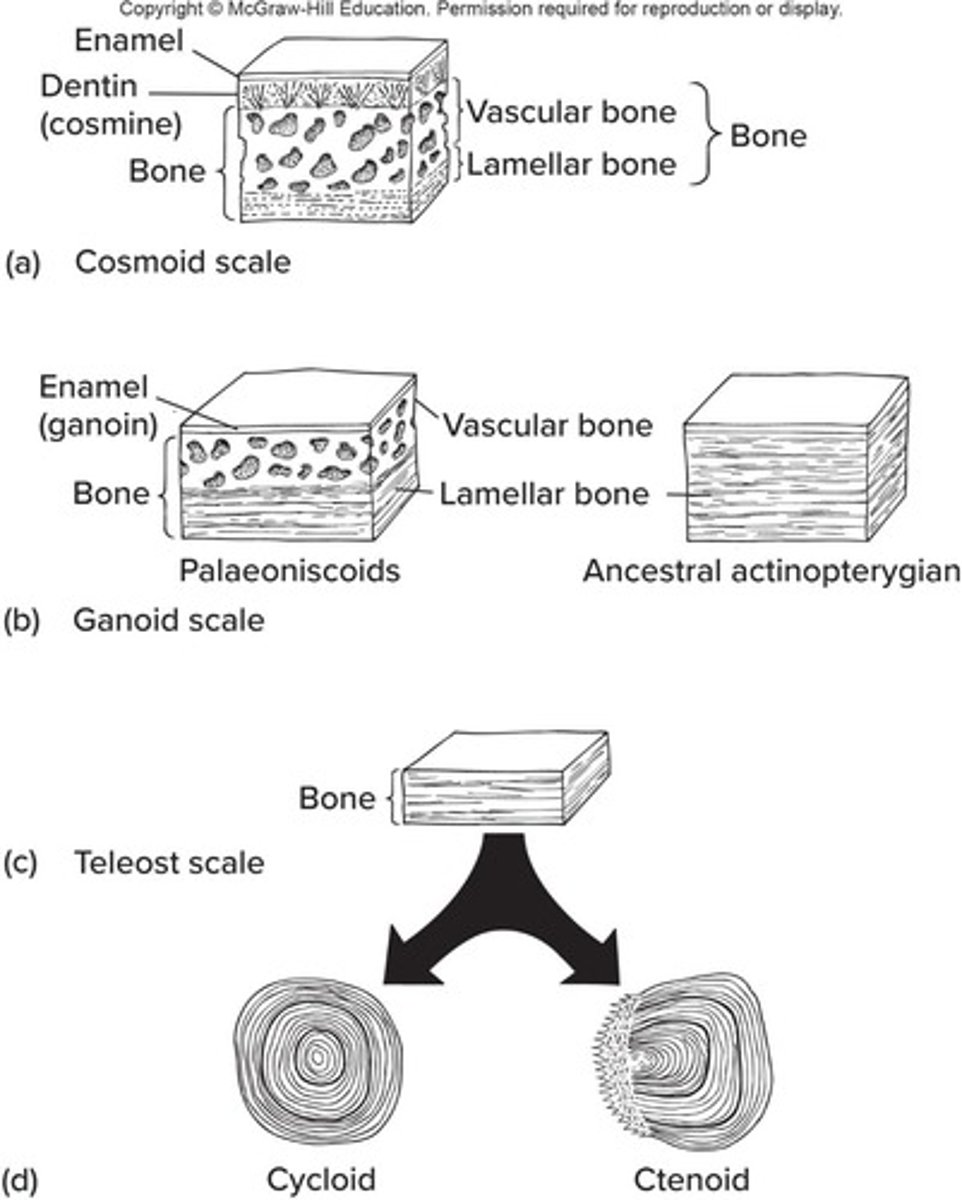
Cosmoid scales
Scales made from enamel, dentin, and bone found in some fish.
Amphibian skin
Specialized for cutaneous respiration and lacks scales.
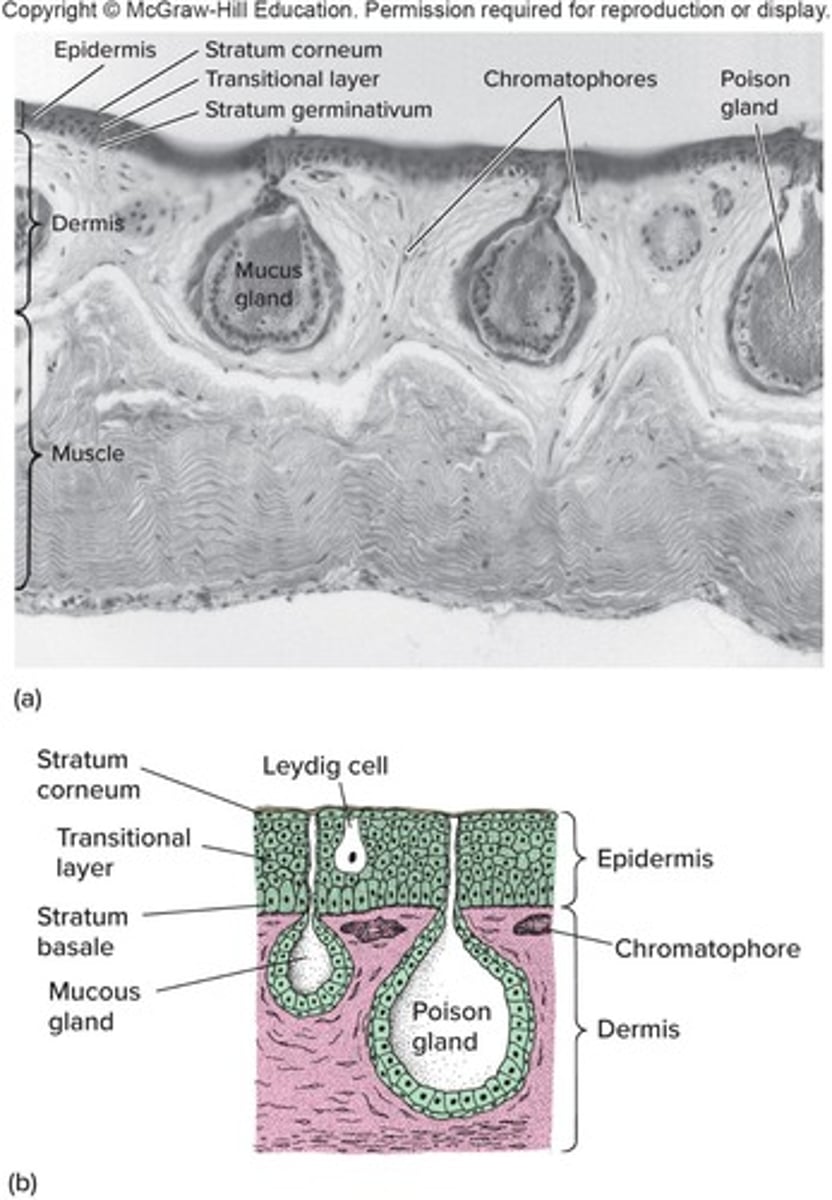
Mucus glands
Glands in the dermis of amphibians that produce mucus.
Gastralia
Bones in the abdominal area of some reptiles.
Uropygial gland
Gland at the base of the tail in birds that produces a lipid/protein product.
Salt gland
Gland on the head of some birds that excretes excess salt.
Langerhans cells
Cells in the epidermis that assist in immunity.
Papillary layer
Upper layer of the dermis made from dermal papillae.
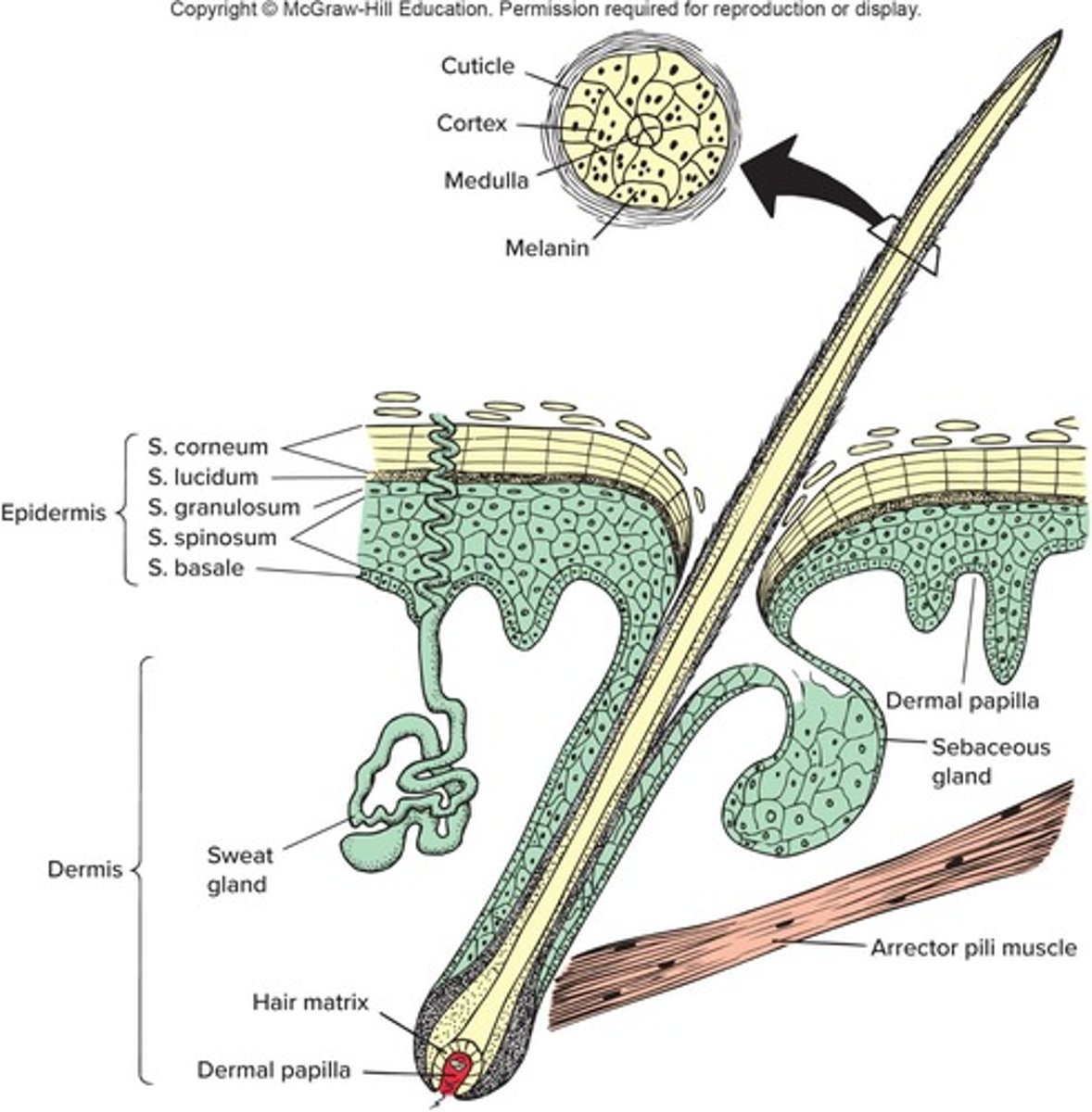
Sebaceous glands
Glands that produce oily secretion (sebum) released into hair follicles.
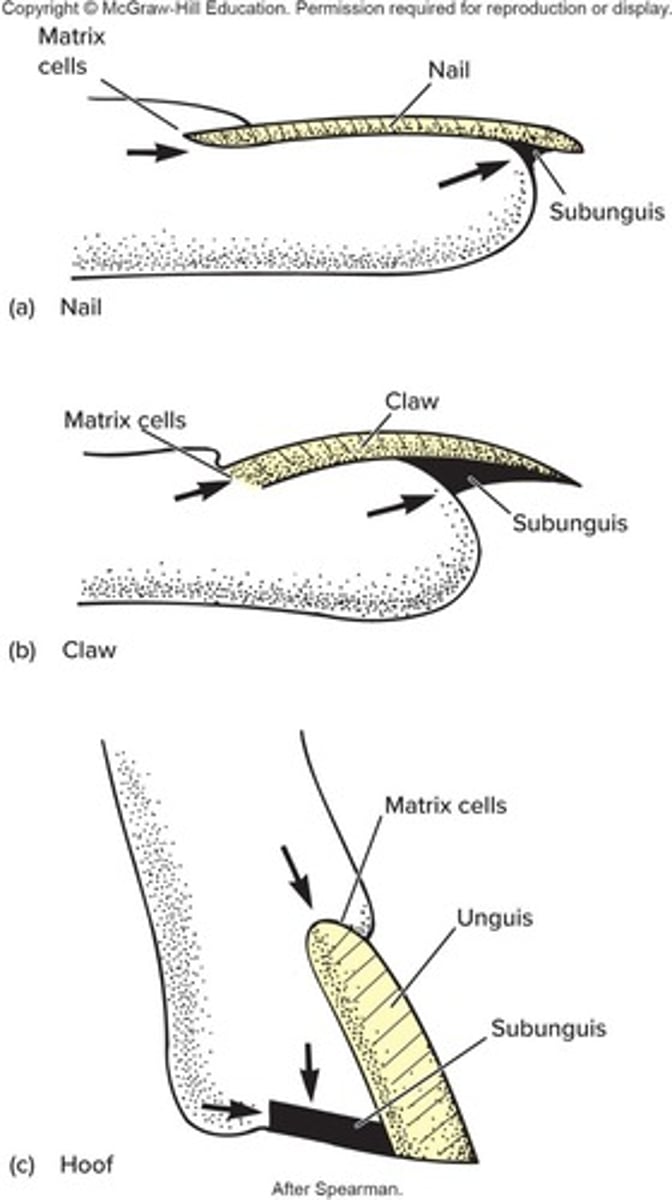
Nail
Plate of tightly compacted, cornified epithelial cells on the surface of fingers and toes.
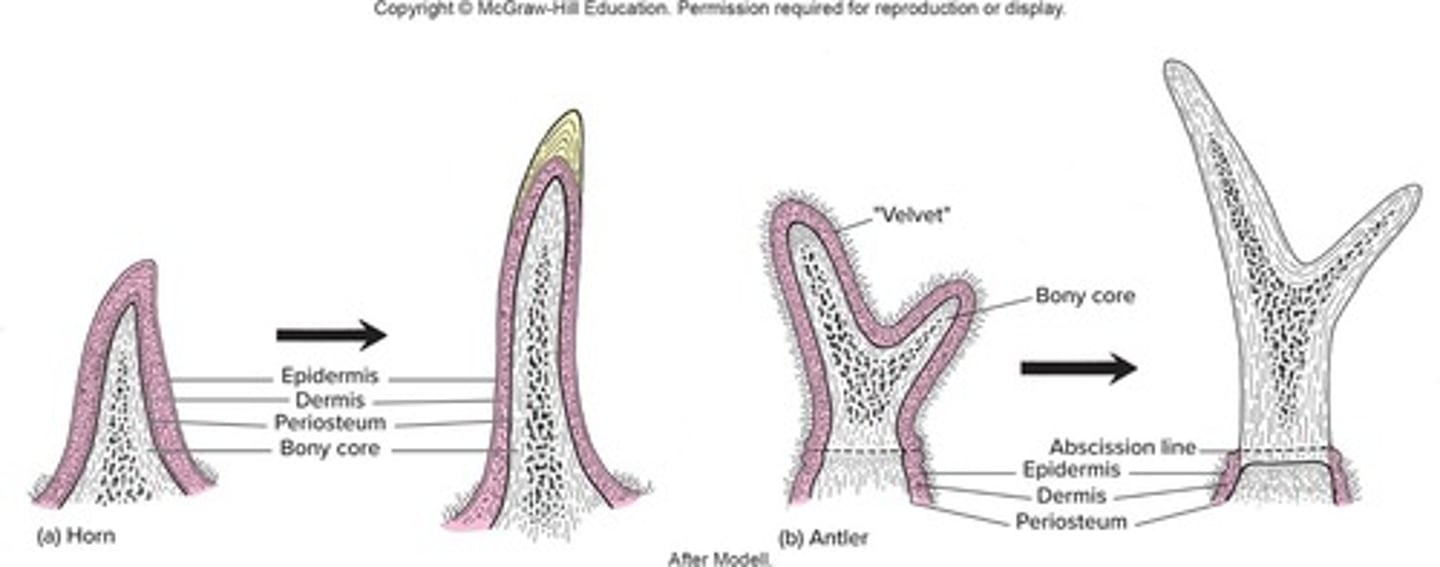
Horn
Tough, cornified sheath that fits over a bony core and is never branched.
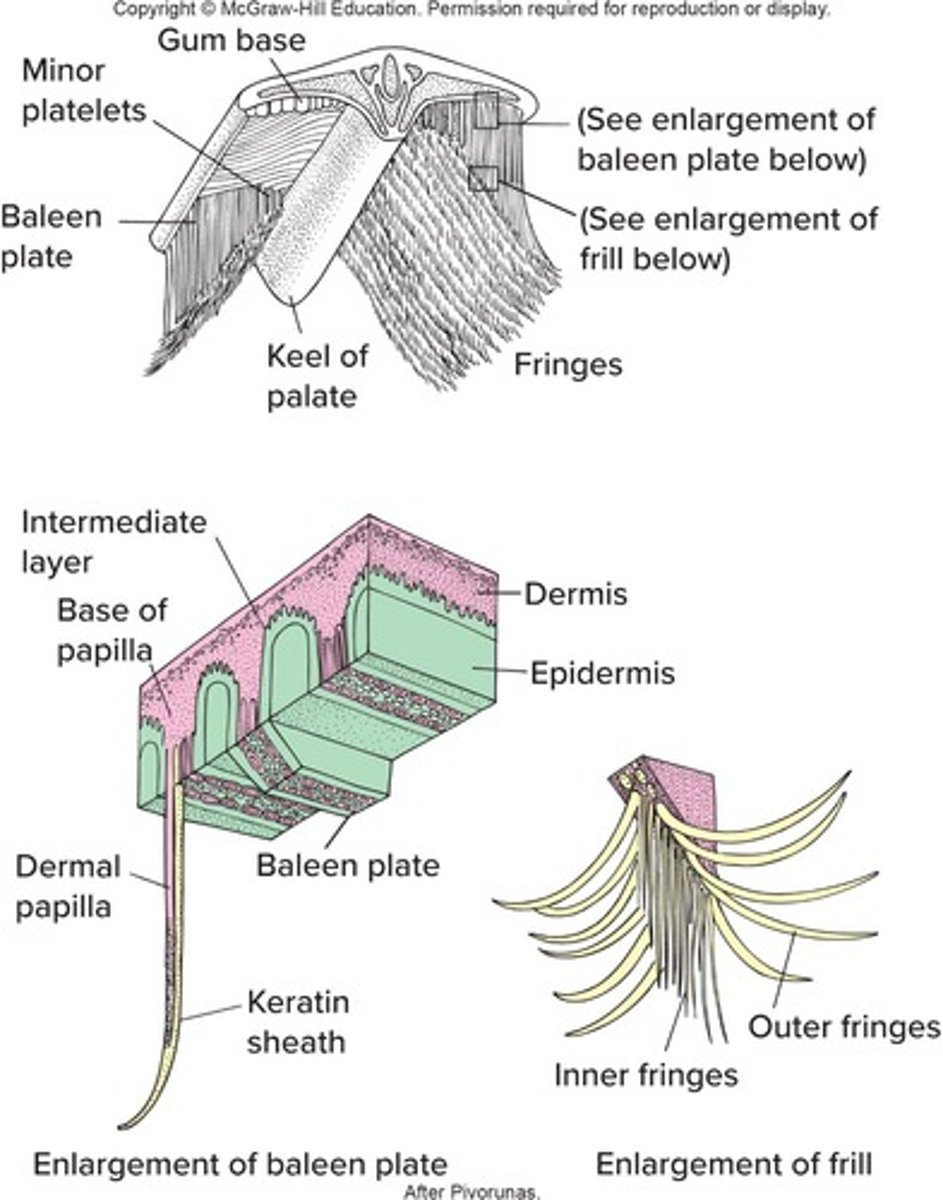
Baleen
Plate that acts as a strainer for whales, made from integument.
Integument
Skin, also known as the cutaneous layer.
Functions of integument
Forms part of exoskeleton, protects entry of microbes, helps hold shape of organism, regulates osmotic control and gas exchange, controls temperature, senses stimuli, and provides color through chromatophores.
Ganoid scales
Reduced scales in teleost fishes, mostly made of lamellar bone.
Cutaneous respiration
Specialized skin function in amphibians for gas exchange.
Ecdysis
Molting process in reptiles.
Merkel cells
Cells associated with nerve endings that detect light touch and pressure.
Eccrine glands
Sweat glands found in humans but not in all mammals.
Mammary glands
Glands that produce milk.
Claw
Curved, laterally compressed keratinized projections from the tips of digits.
Hoof
Enlarged keratinized plate on the tips of ungulate digits.
Antlers
Branched bone; finished antlers have shed their 'velvet', the integument.
5 layers of the epithelium in mammals
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale