OCR B Geography GCSE Sustaining Ecosystems
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
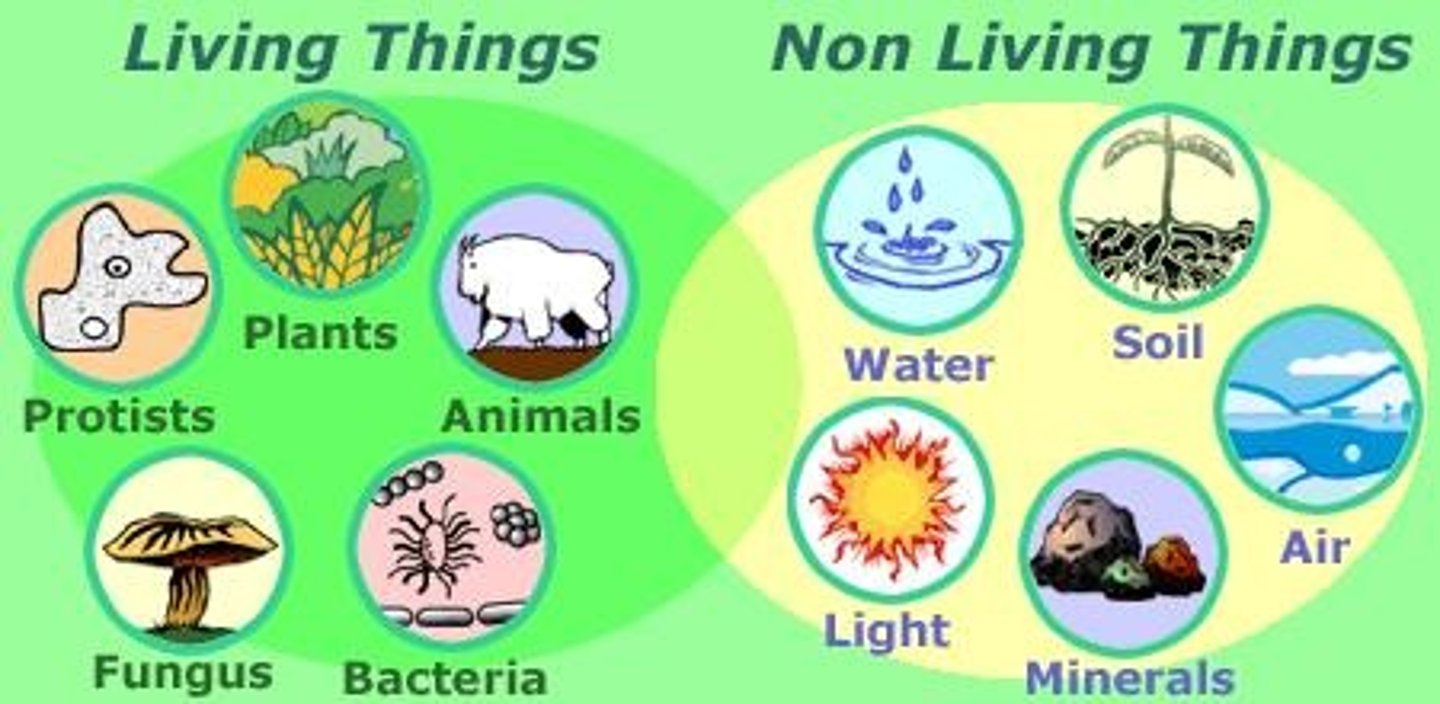
biotic
all of the living elements of the ecosystem including plants, animals and bacteria
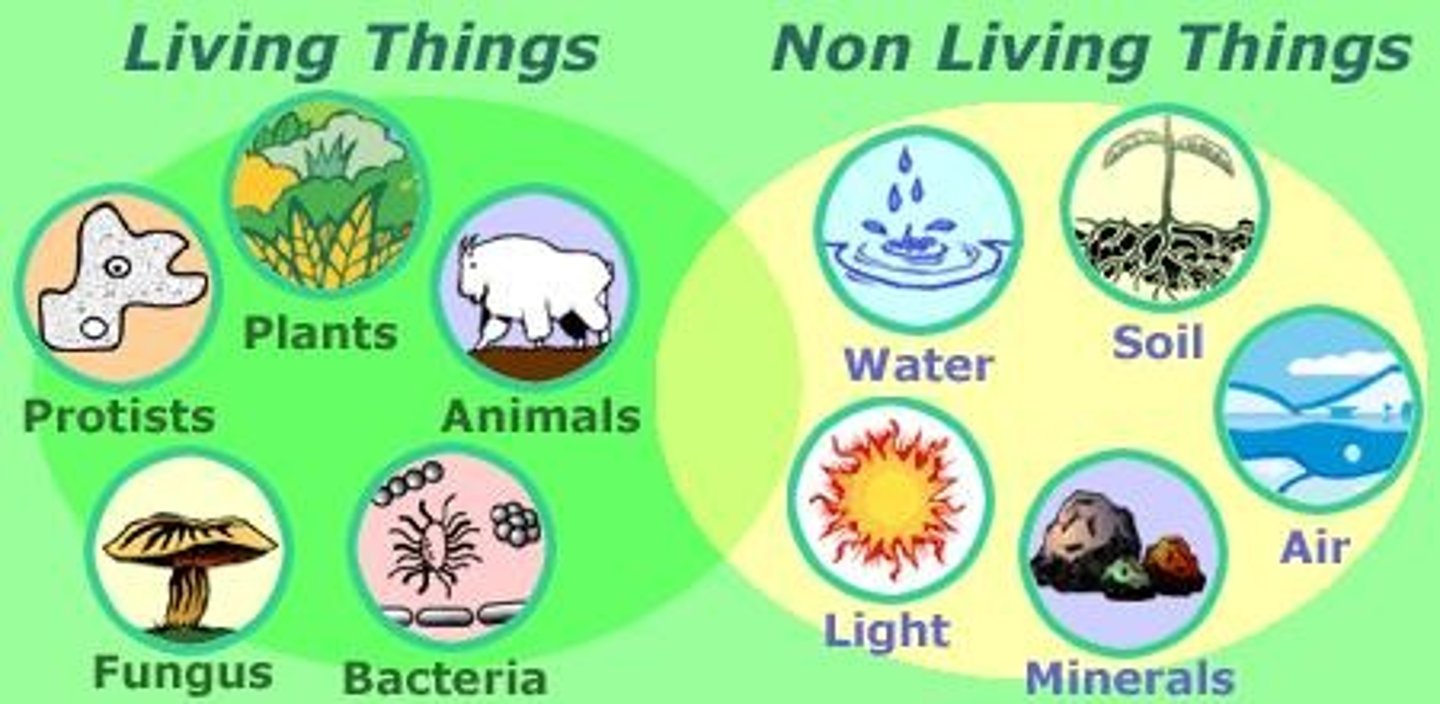
abiotic
the physical, non-living parts of the ecosystem, including temperature, water and light
flora
another term for the plants in an ecosystem

fauna
another term for the animals in an ecosystem

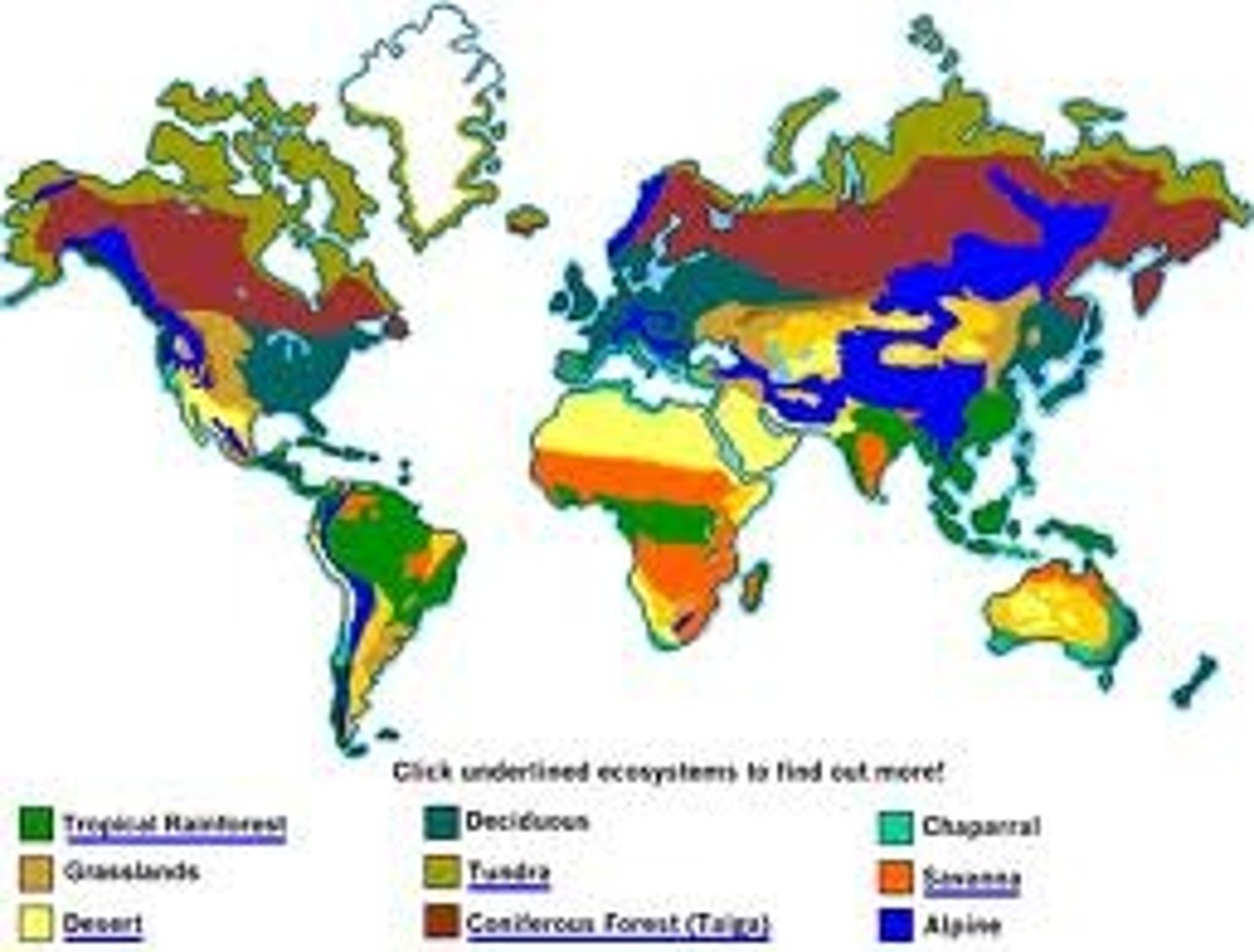
biome
large scale ecosystems that are spread across continents and have plants and animals that are unique to them
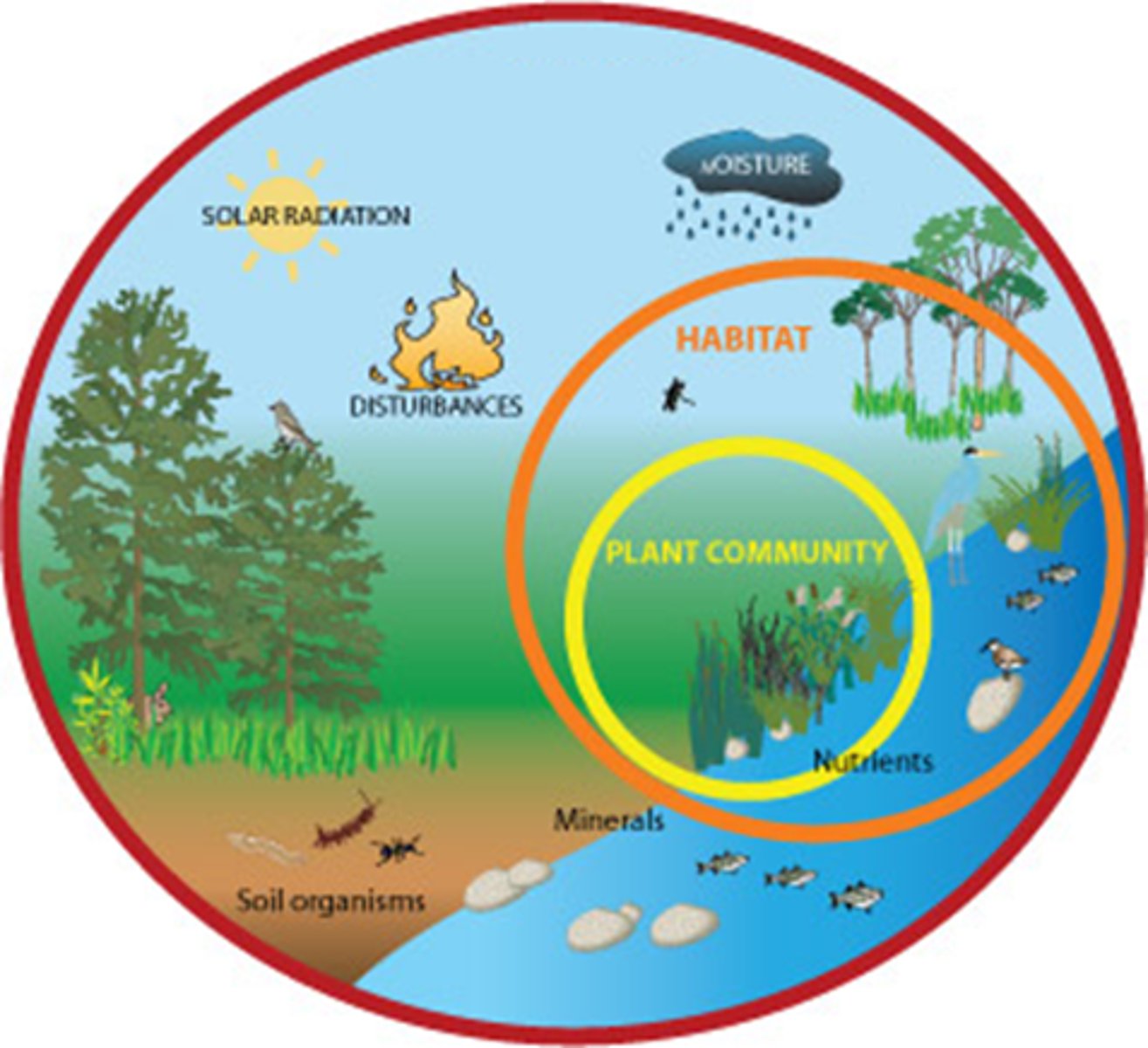
ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
interdependence
the reliance of every form of life on other living things and on the natural resources in its environment, such as air, soil and water
temperate
Mild or moderate
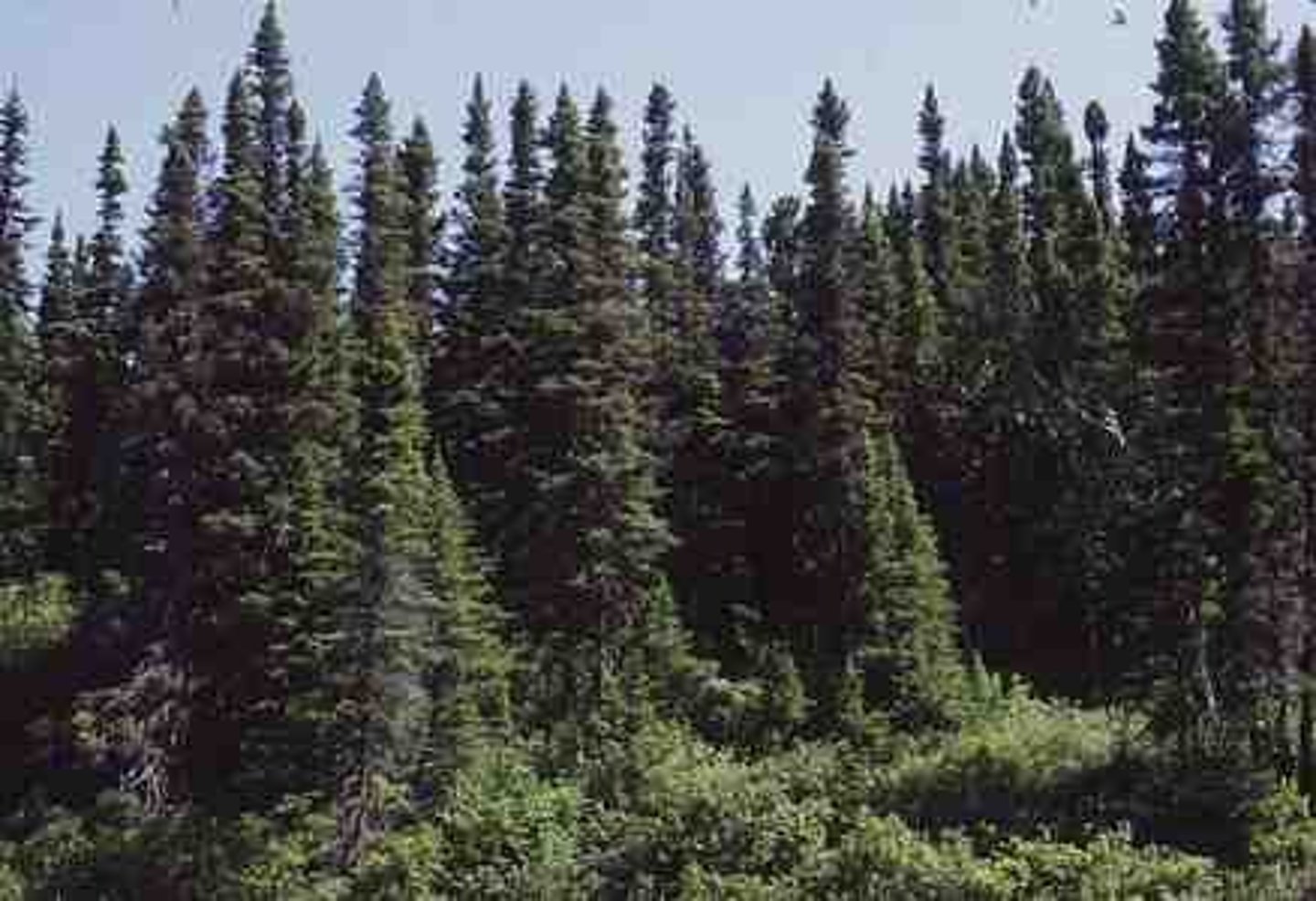
coniferous forest
a forest made up of trees that are evergreen and have needle shaped leaves

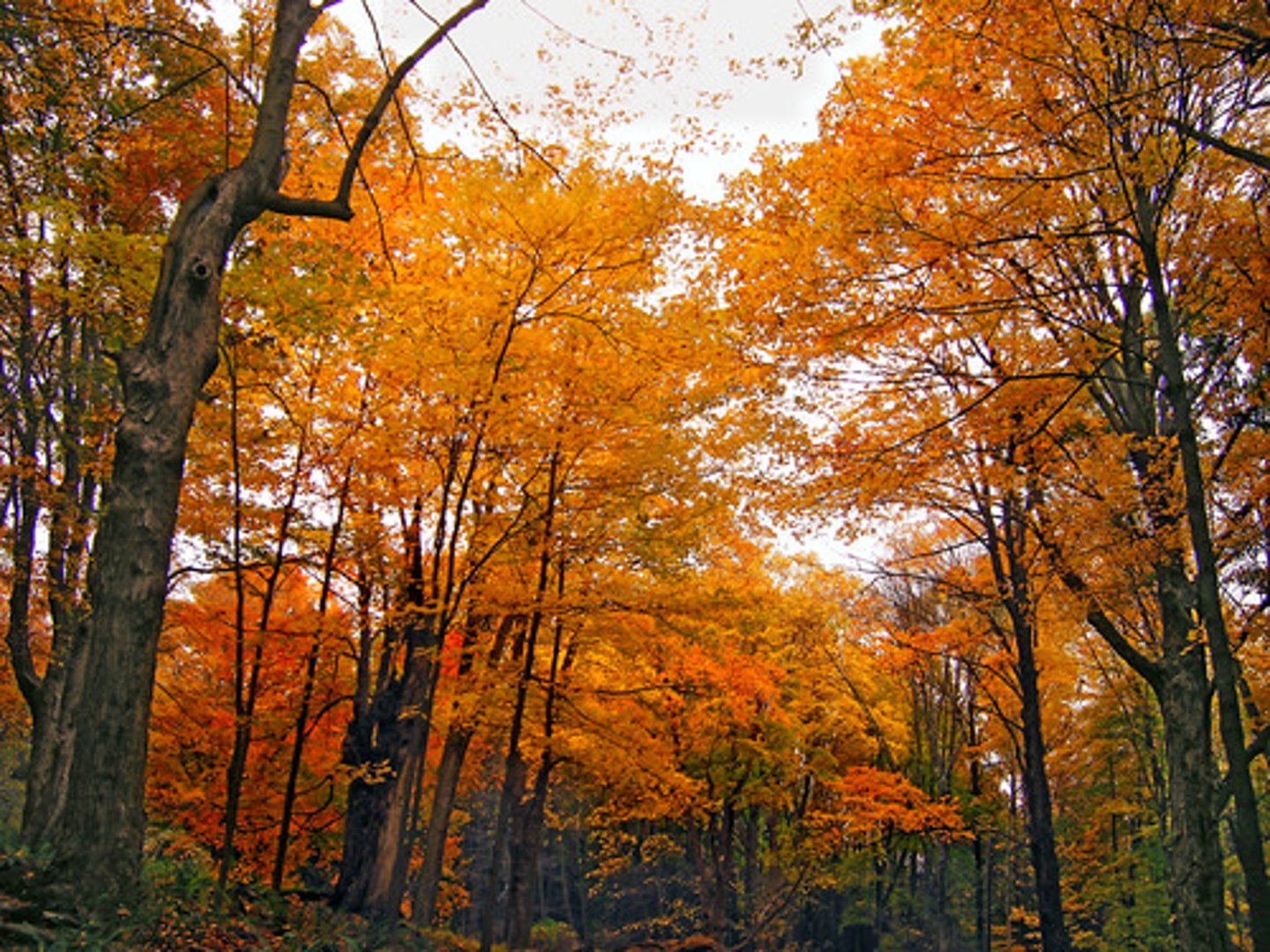
temperate deciduous forest
a forest made up of broad leafed trees which shed their leaves in autumn and grow new ones in spring

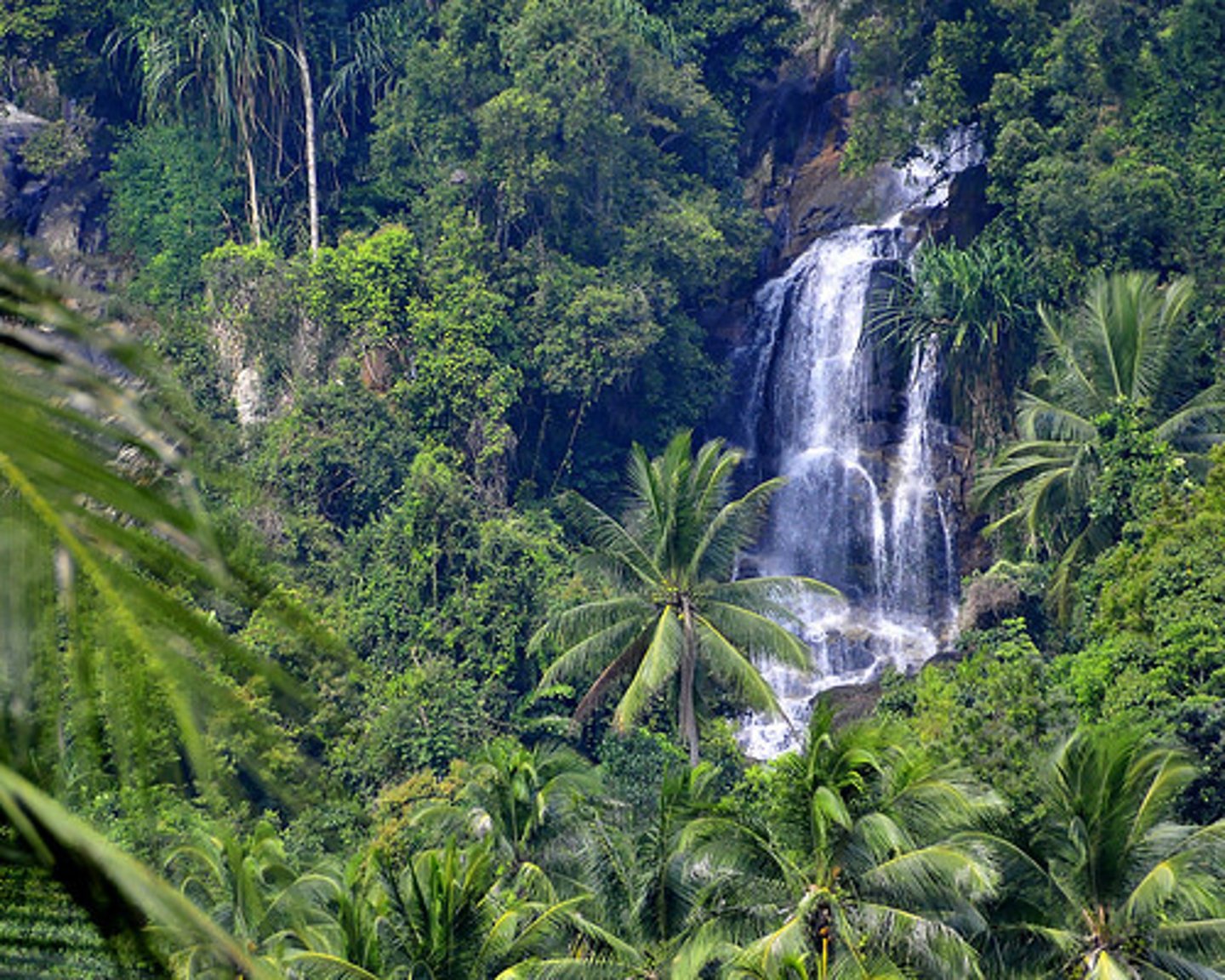
tropical rainforest
forest in the tropics which produces its own rain, have very high levels of bioproductivity and biodiversity

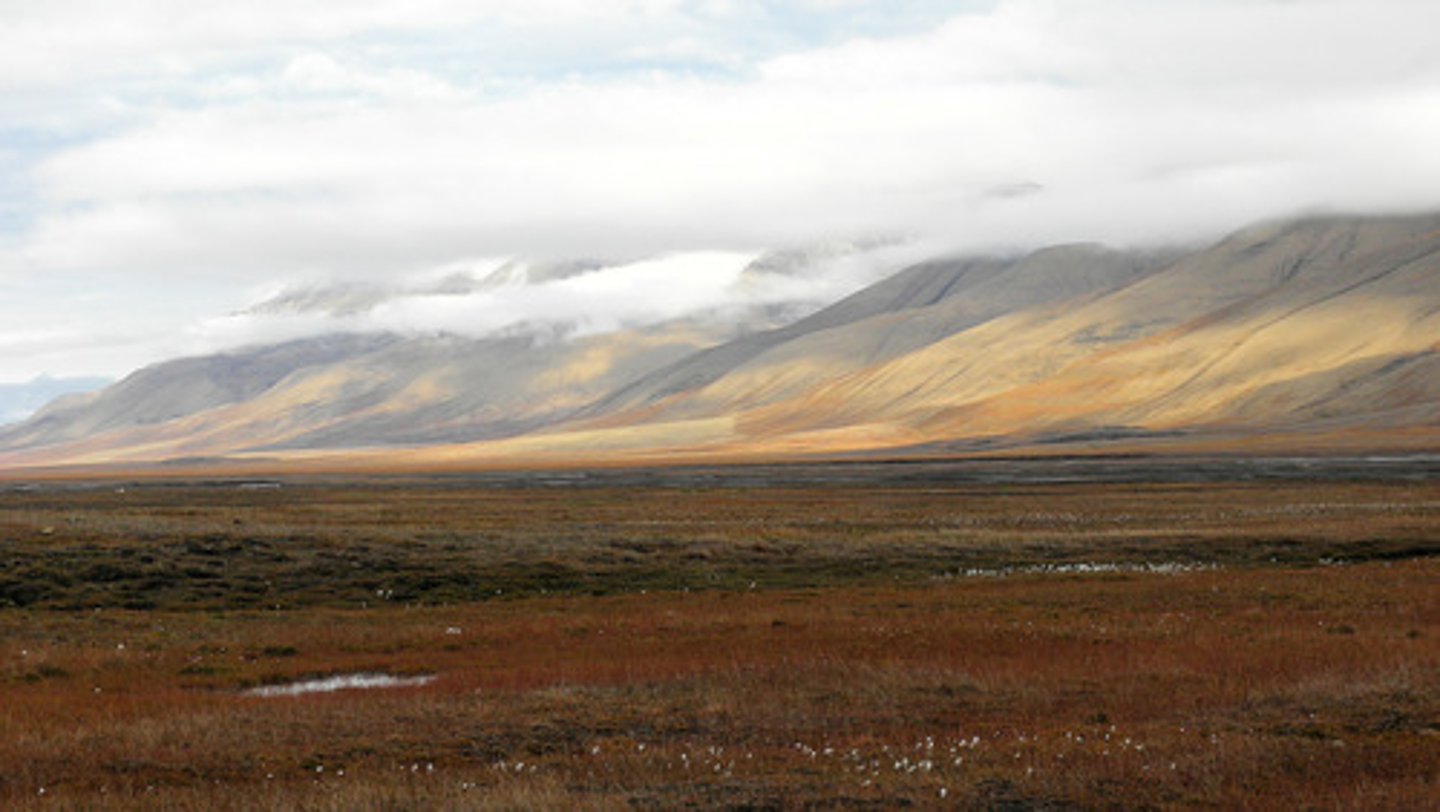
tundra
a vast, flat, treeless Arctic region of Europe, Asia and North America in which the soil is permanently frozen

temperate grassland
grassland with moderate or mild temperatures

tropical grassland
grassland with tropical temperatures

hot desert
Hot area which recieves on average less than 250 mm rainfall per year

circumpolar wind
flow of air around the Earth's poles
deforestation
the cutting down of trees, transforming a forest into cleared land for other uses such as building, growing crops or rearing cattle

emergent
the tallest tree in the rainforest towering above the canopy
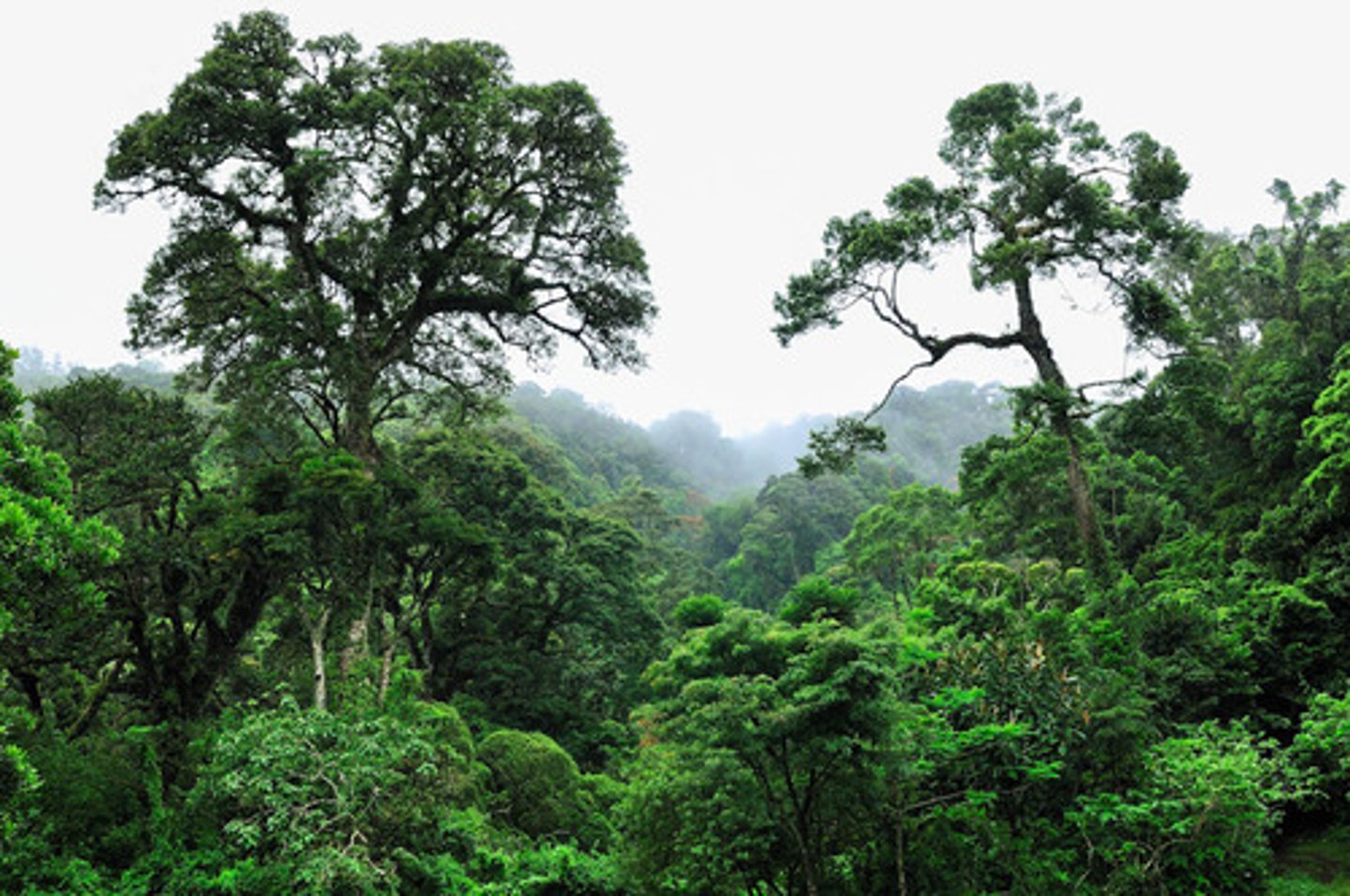

canopy
top layer of a rain forest, where the tops of tall trees form a continuous layer of leaves
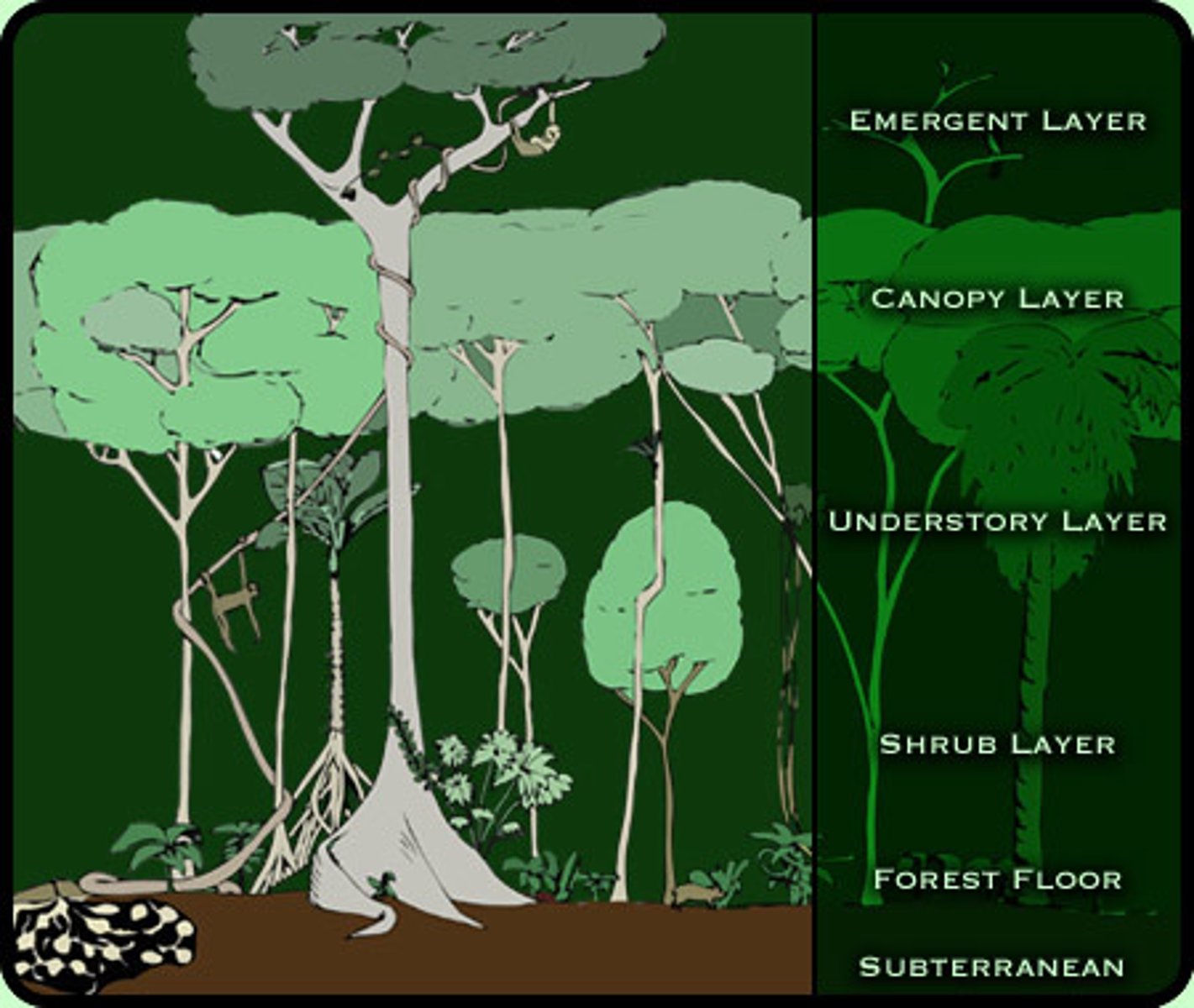
under canopy
young trees awaiting an opportunity to grow into the light
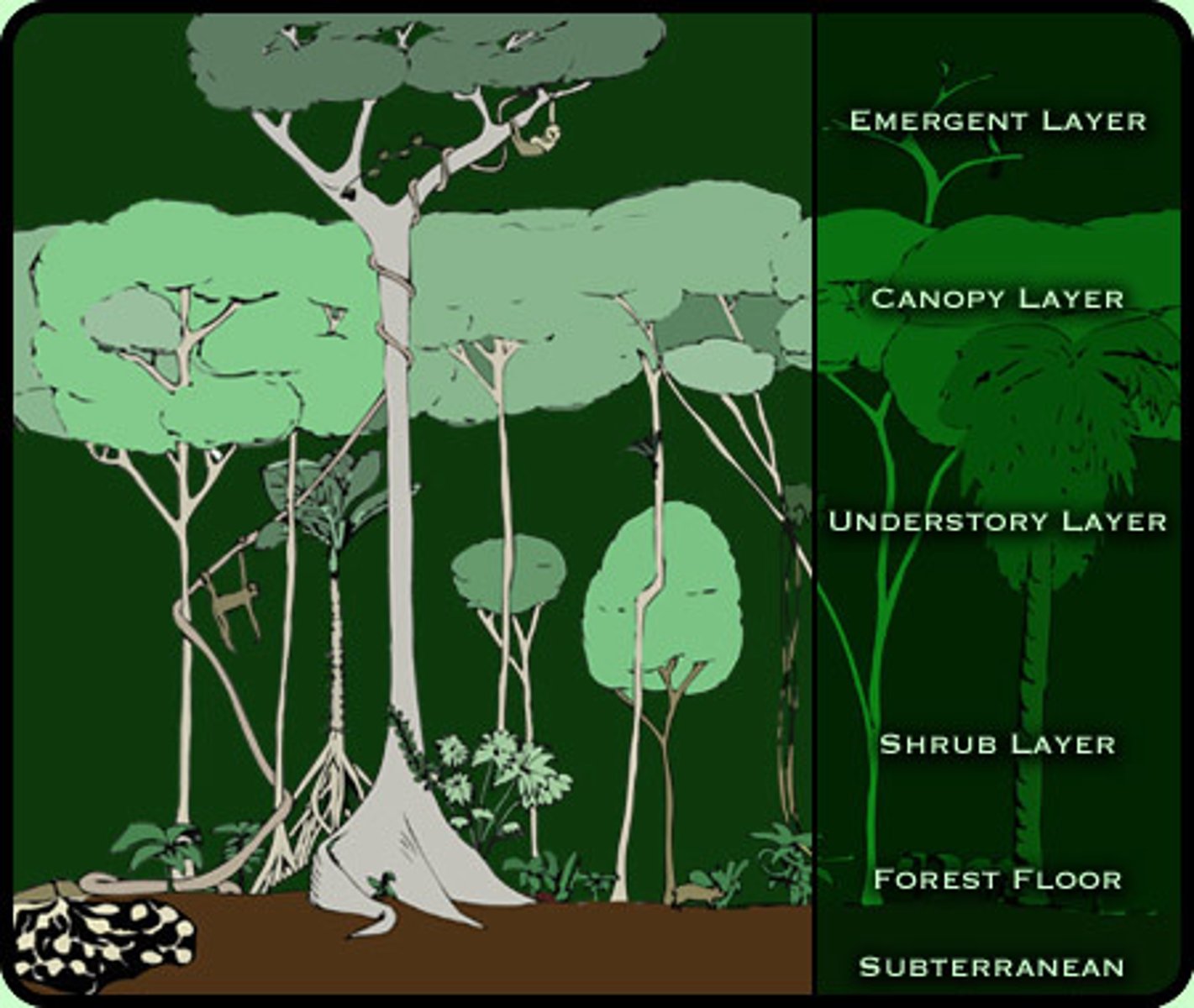
shrub layer
layer of forest containing shrubs and other short plants
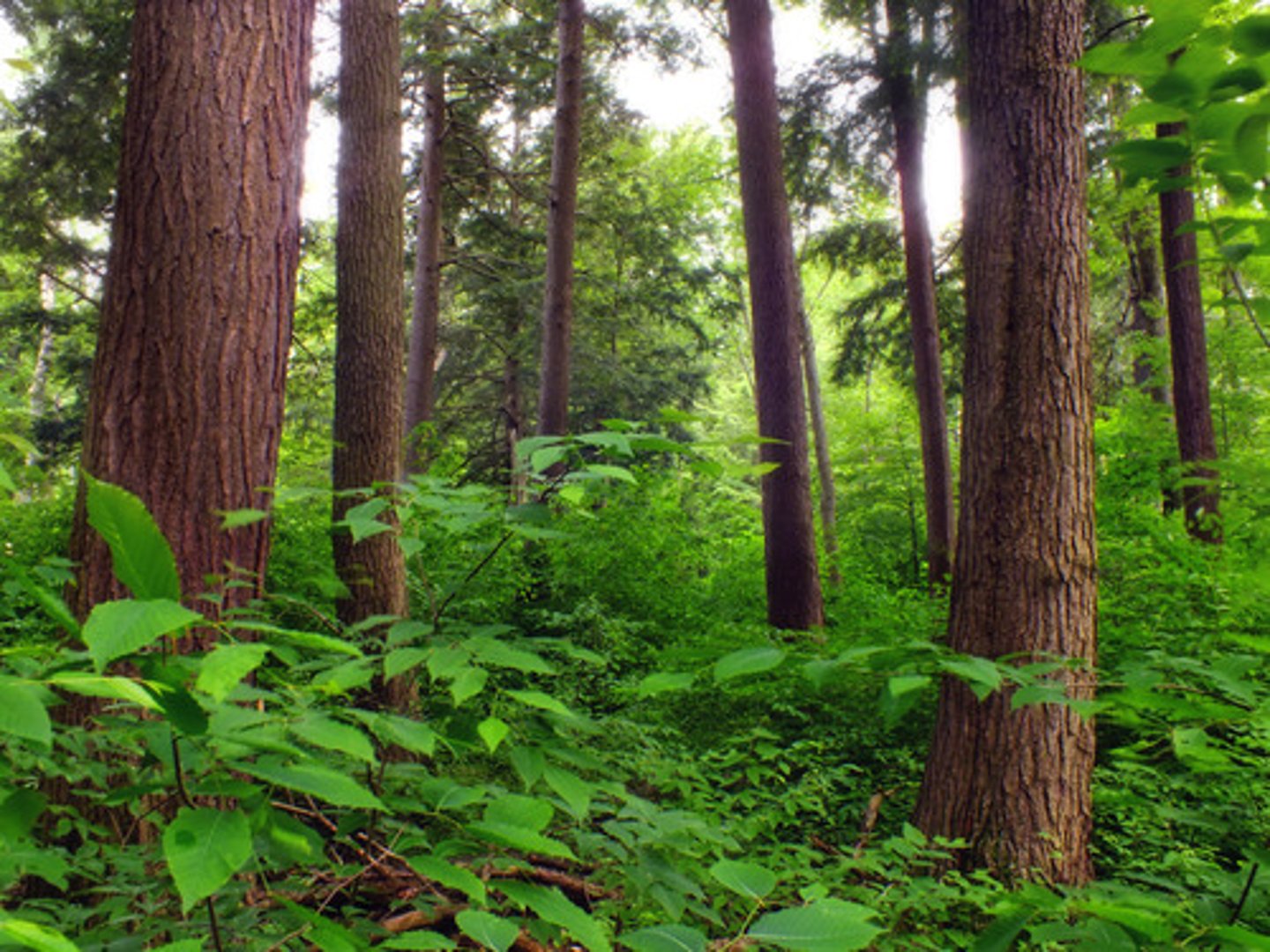

buttress root
Root that is shallow to soak up nutrients in thin soils, but big for stability
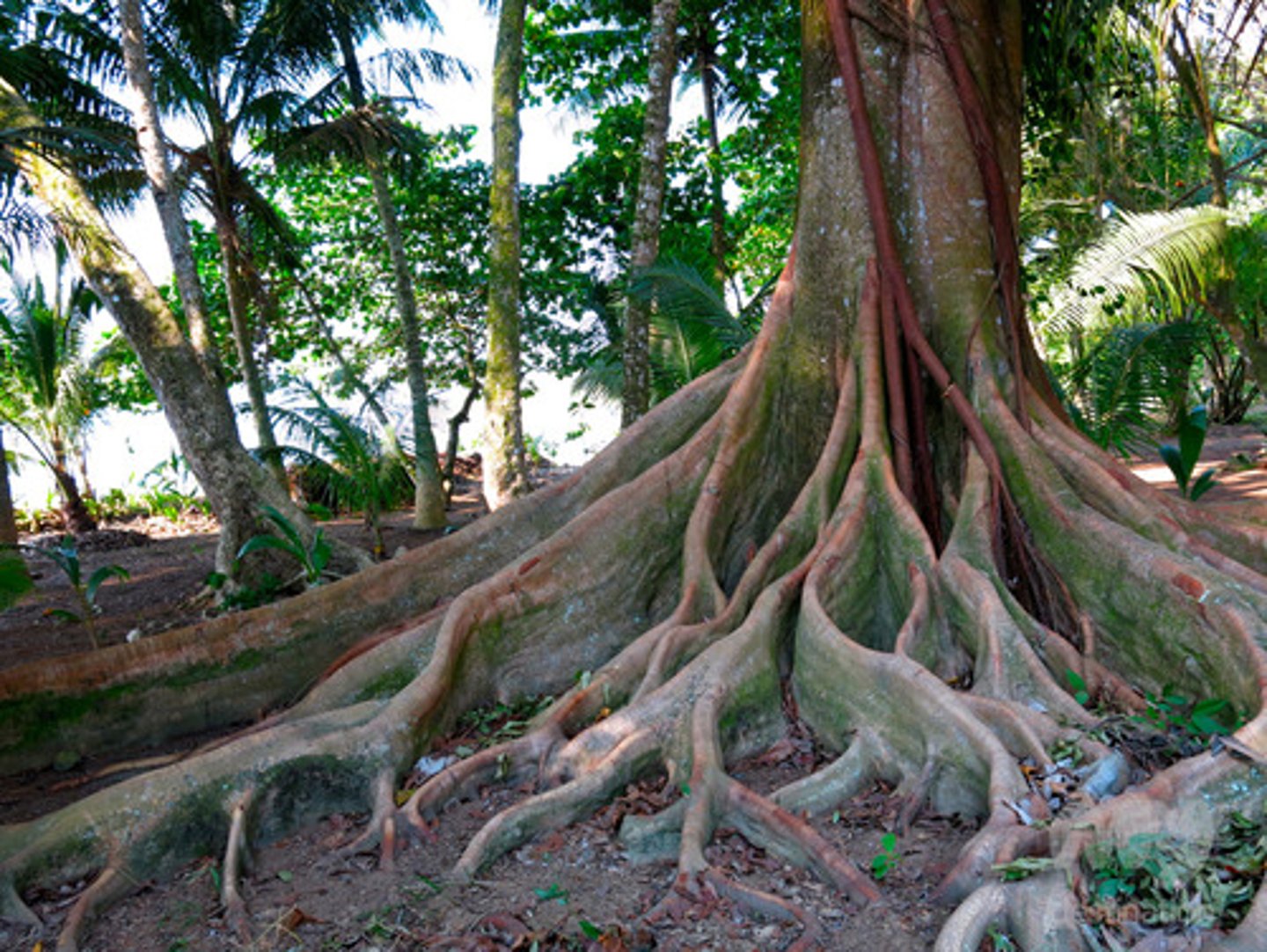

coral reef
a structure built up by coral animals in warm (mean of 18°C), shallow (less than 30m) ocean water.

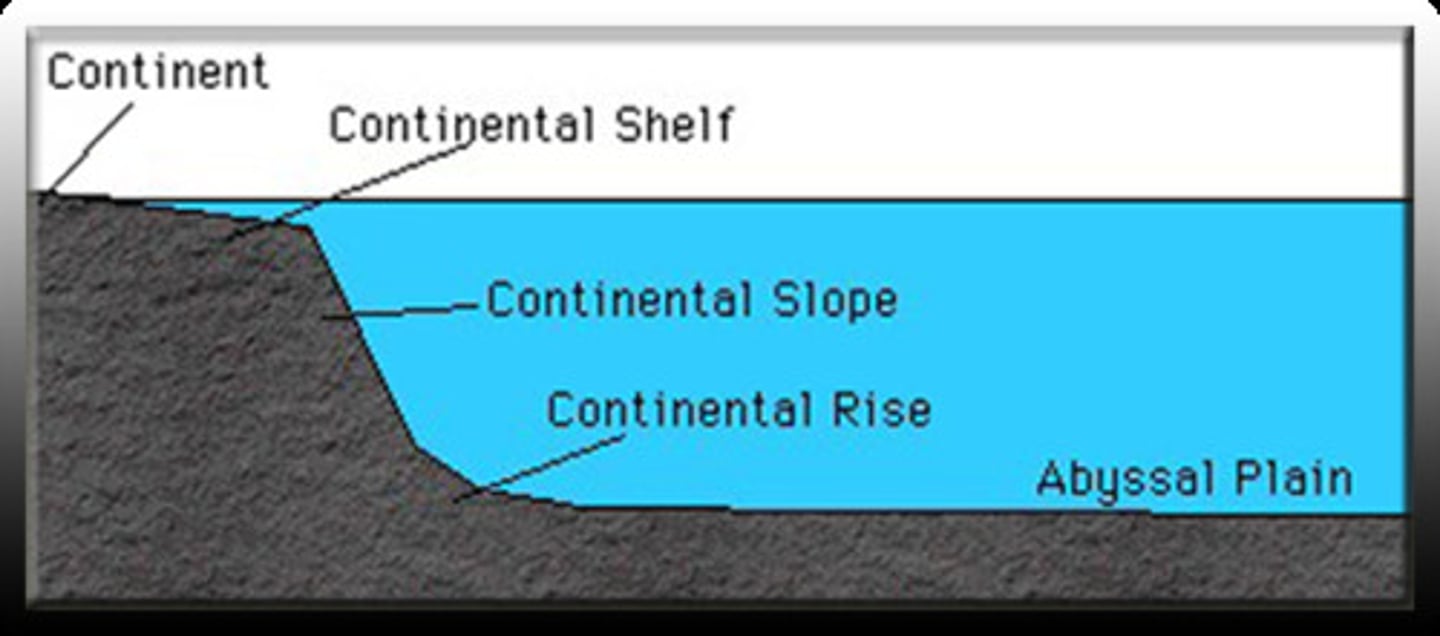
continental shelf
a gently sloping, shallow area of the ocean floor that extends outward from the edge of a continent
parrot fish
a type of fish which feeds on coral

starfish
a marine echinoderm with five or more radiating arms

clam
a shellfish which feeds on plankton

eel
a long, thin fish that looks like a snake

mollusc
soft bodied creatures like sea snails and octupuses
dugong
a large plant-eating mammal, related to the manatee, that lives in shallow tropical coastal waters

herbivore
eats only vegetation

carnivore
eats meat

omnivore
eats both meat and vegetation

xerophytic
a type of plant that can survive on very little water

microclimate
the climate of a relatively small area, which is likely to be different from the climate of the surrounding area
biomass
the total mass of plants and animals in an ecosystem
litter
the total amount of organic matter, including humus (decomposed material) and leaf litter

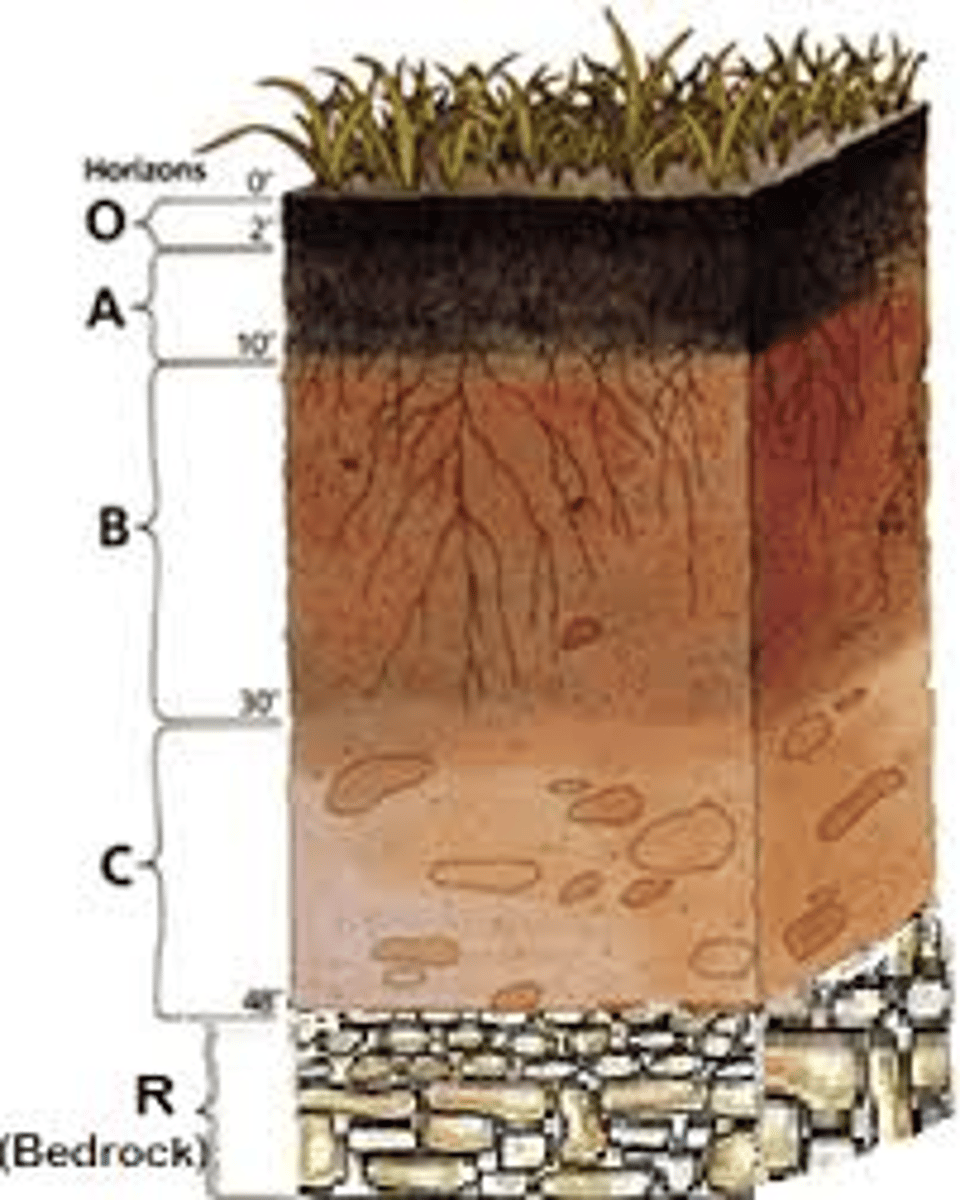
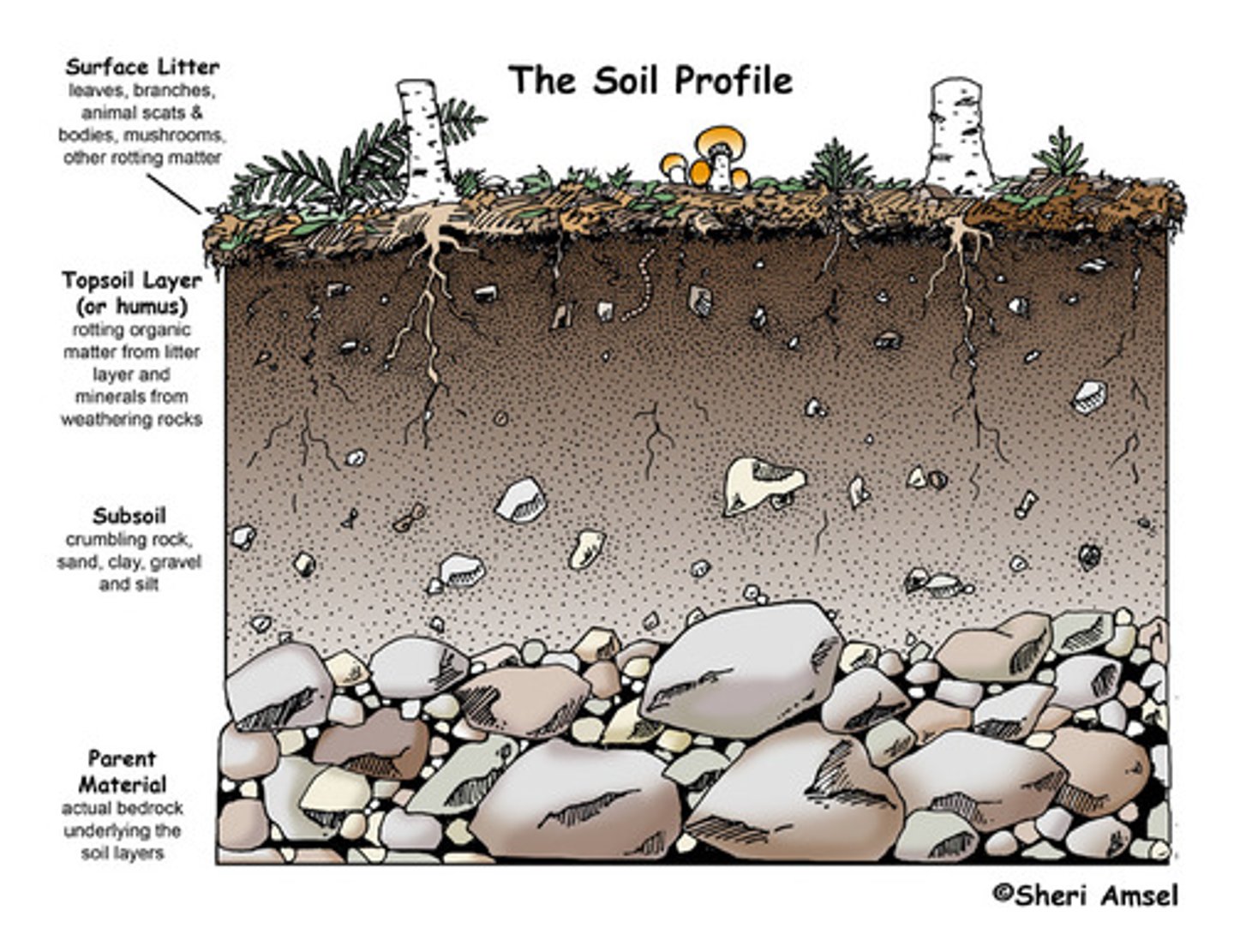
soil
A loose mixture of rock fragments, organic material, water, and air that can support the growth of vegetation
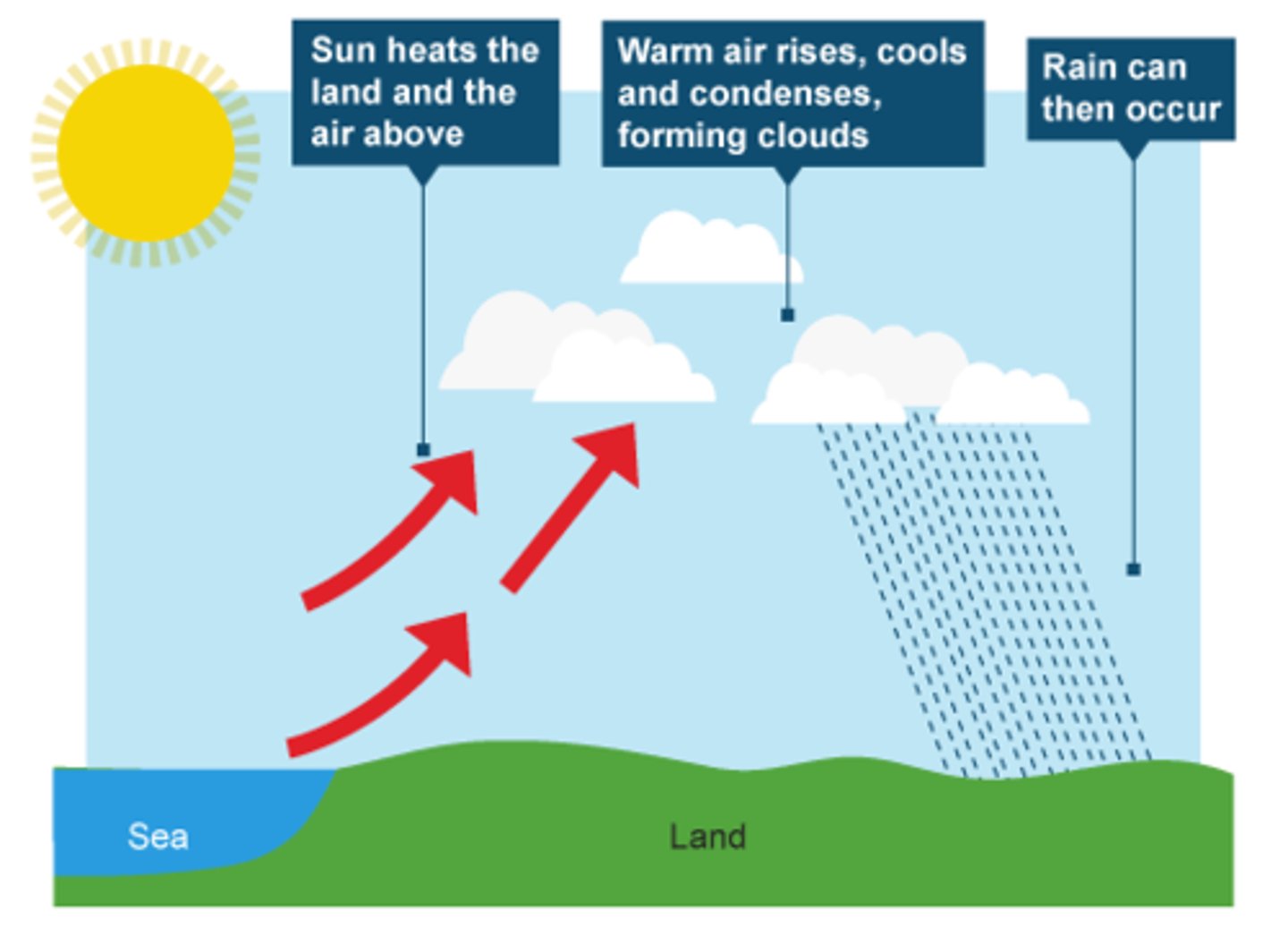
convectional rainfall
occurs frequently in the tropics where it is hot; hot air close to the ground rises, cools and condenses to form rain; if the air is hot enough, it rises very quickly and can lead to thunderstorms
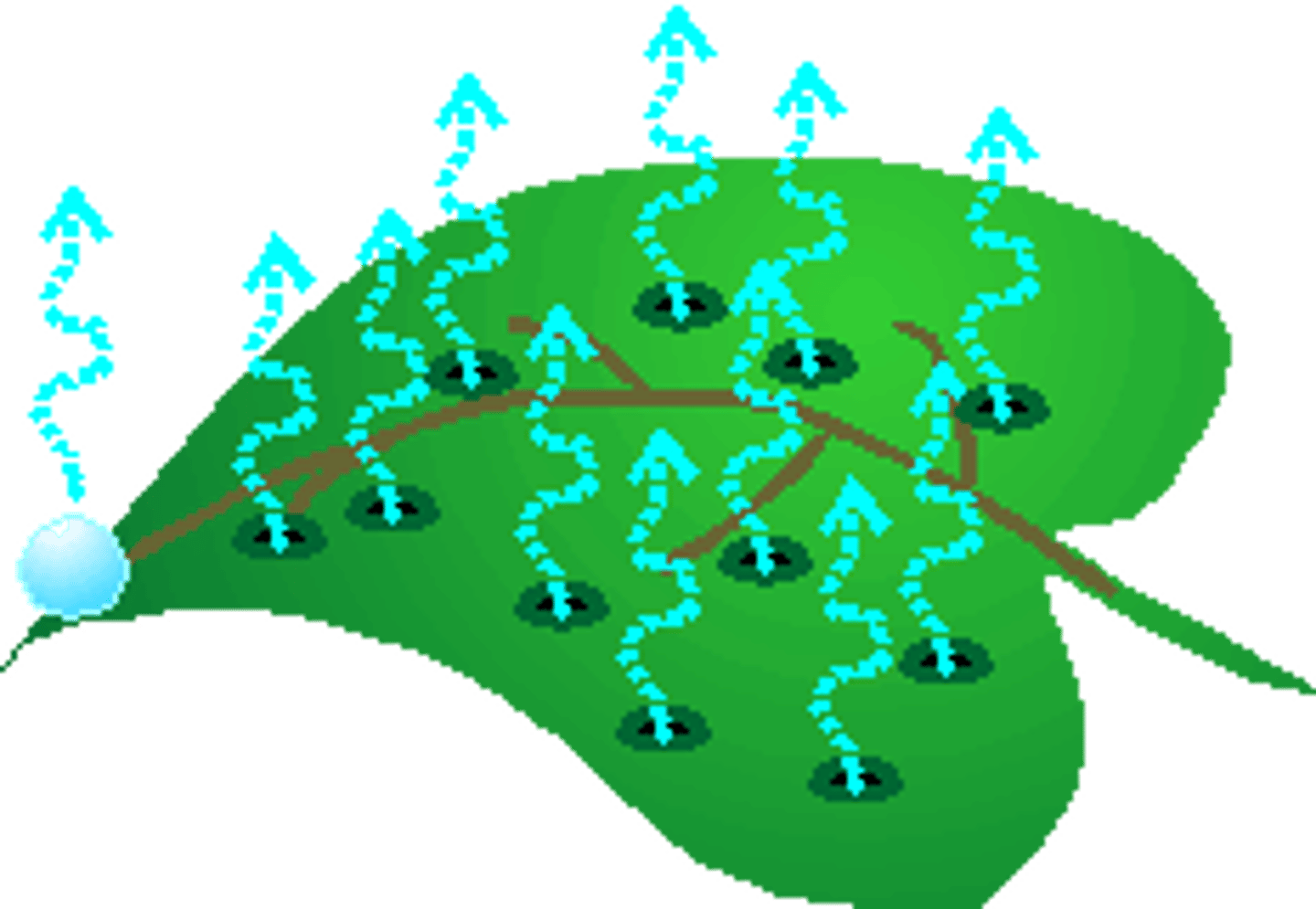
evapo-transpiration
the process by which water is transferred to the atmosphere by evaporation from surfaces and by transpiration from plants

transpiration
loss of water from a plant through its leaves
latosols
soils found under tropical rainforests with a relatively high content of iron and aluminium oxides
humus
rich, dark organic material formed by decay of vegetable matter, essential to soil's fertility

parent rock
the upper layer on rock on which soil forms
hunter-gatherers
nomadic people who move from place to place, hunting, fishing and harvesting (gathering) wild food
shifting cultivation
the use of tropical forest clearings for crop production until their fertility is lost. Plots are then abandoned, and farmers move on to new sites

ecosystems goods
tangible items such as crops, wood, drinking water, fish, and wildlife
ecosystems services
the services which are provided by a natural ecosystem to people; these can be seen as benefits of keeping the ecosystem functioning efficiently

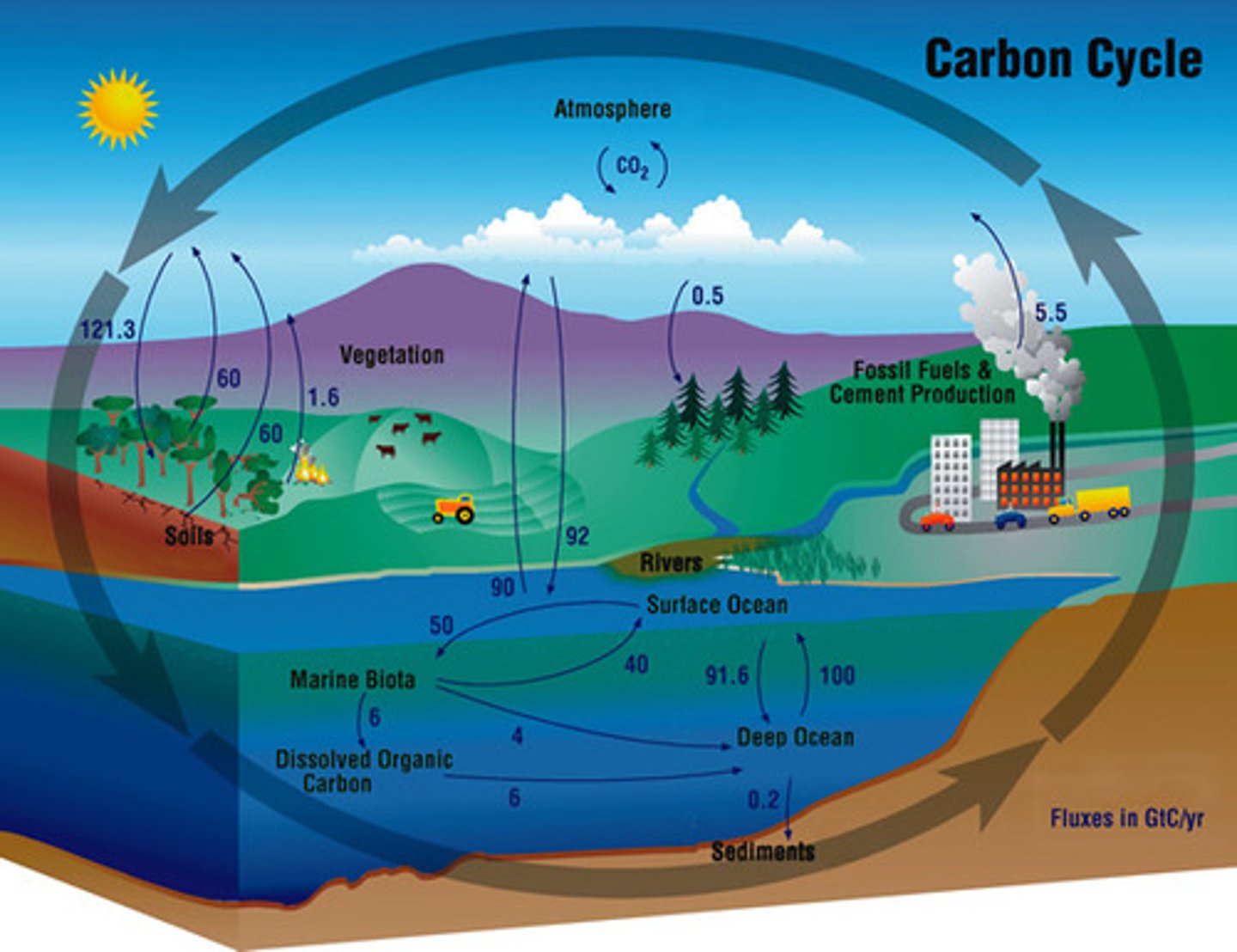
carbon sink
a forest, ocean or other natural environment that is able to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
cash crops
crops grown and produced to be sold for a profit, such as wheat or cotton

biofuel
a fuel that comes from living matter, such as plant material

slash and burn
a form of shifting cultivation where the natural vegetation is cut down and burned to clear the land for cultivation; when the plot becomes infertile the farmer moves on to a fresh plot and does the same again

infrastructure
the basic structures and facilities needed for a society to function, such as buildings, roads and power supplies

mass tourism
Tourism that involves large numbers of people going to the same place at the same time

logging
cutting down trees for commercial purposes

agriculture
use of land to grow crops or raise livestock

cattle ranching
use of land exclusively to rear cows for their meat, makes up 80% of the use of deforested areas in Brazil

palm oil
a highly profitable cash crop used in food products and as a biofuel
mineral extraction
the mining of valuable resources e.g. gold, copper, silver and diamonds

energy exploitation
the mining of energy resources e.g. oil and gas
endemic
a plant or animal species which is unique, or native to a particular area
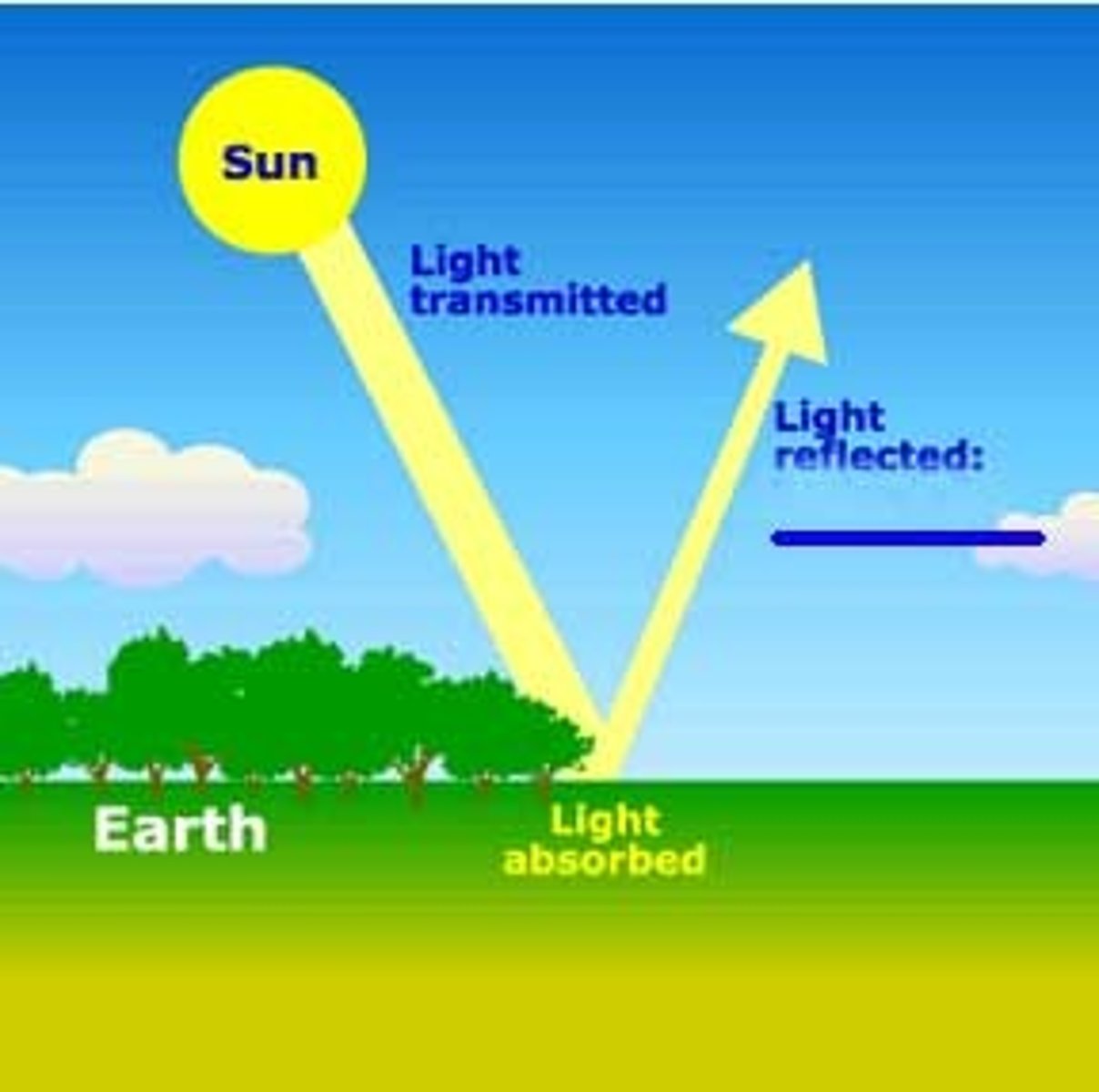
albedo
the amount of incoming solar radiation which is reflected by the Earth's surface (and the atmosphere); fresh snow and ice reflect up to 90% of energy
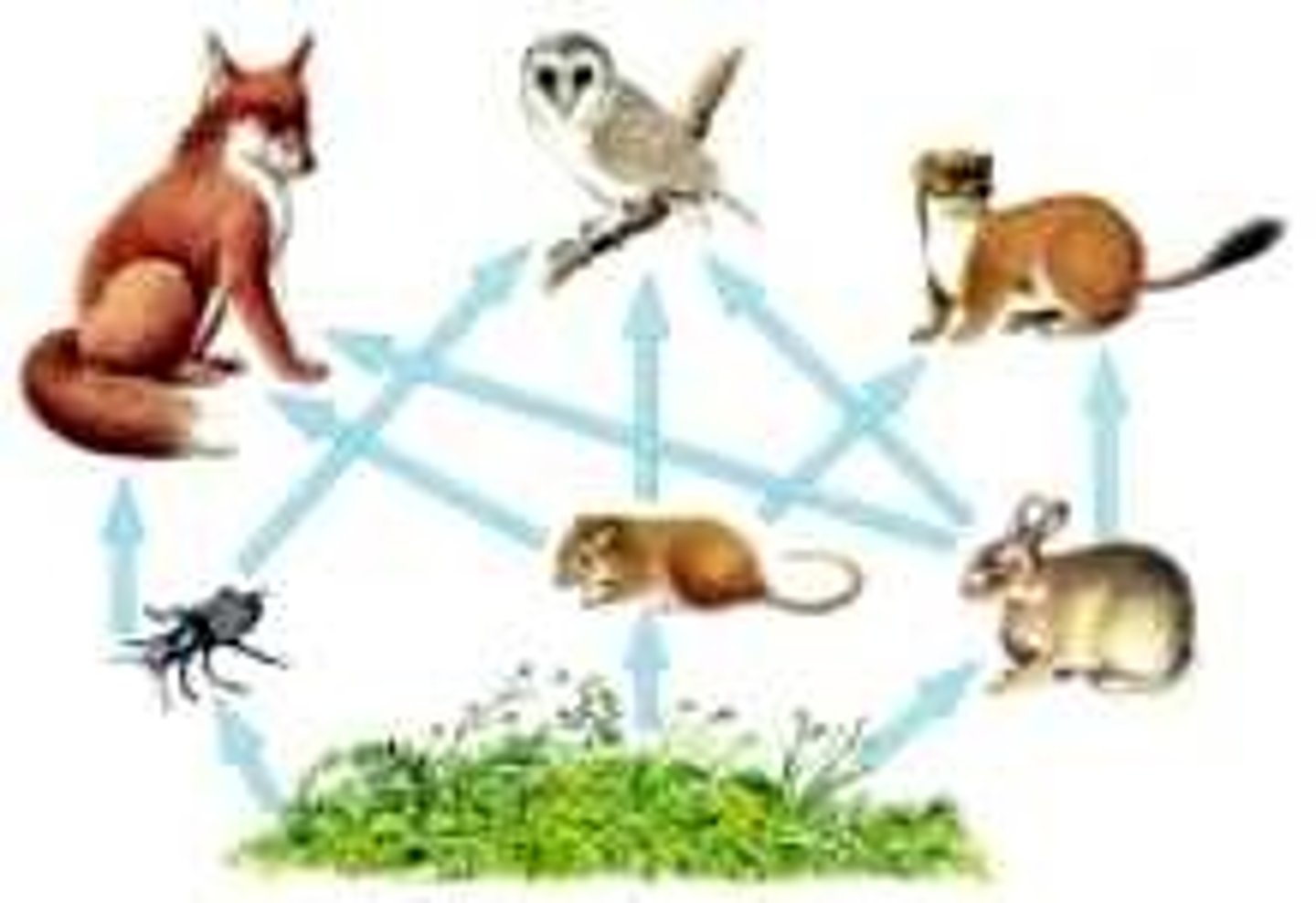
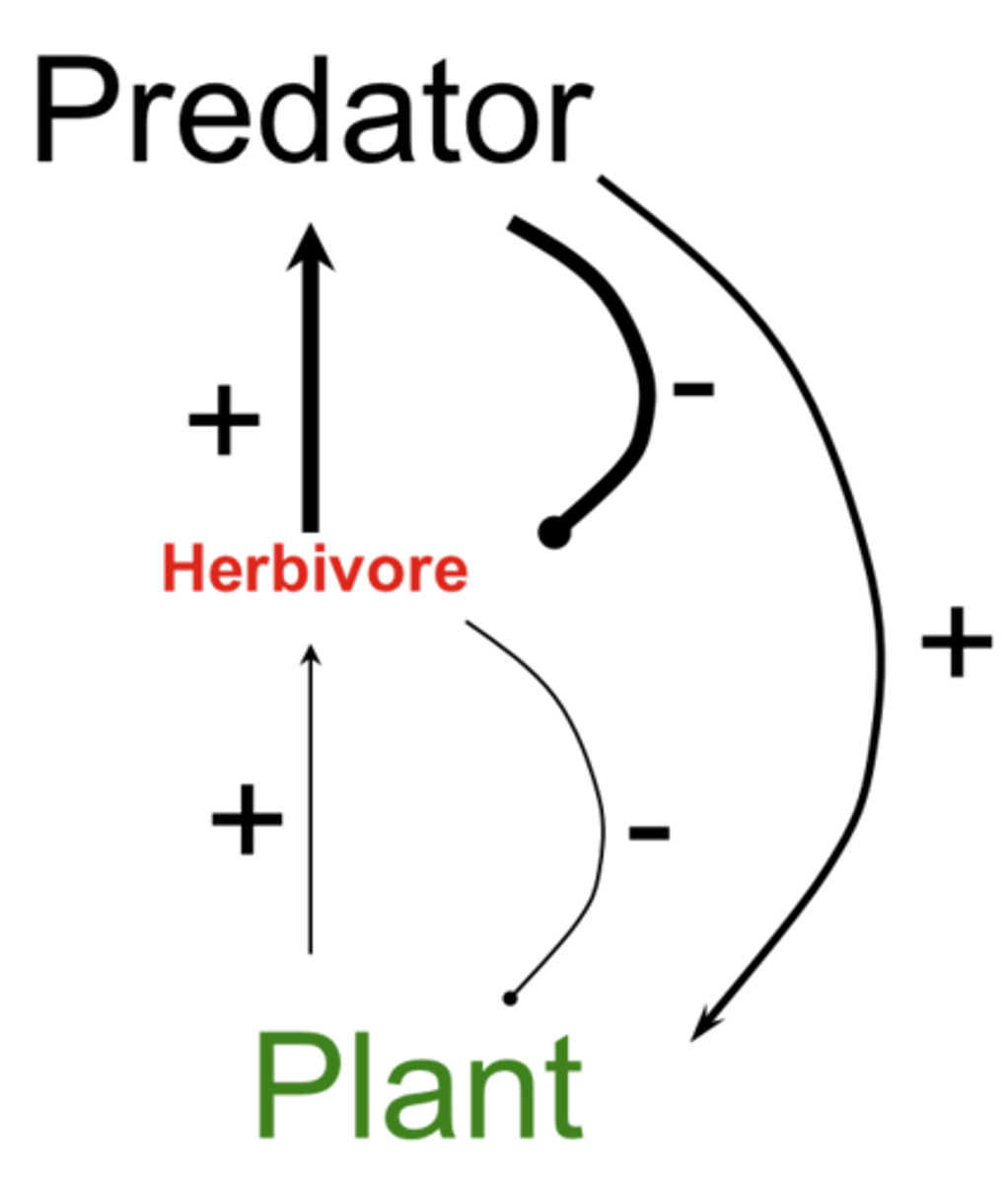
trophic cascade
the transfer of energy through an ecosystem as a result of food chains, at each level some energy is lost
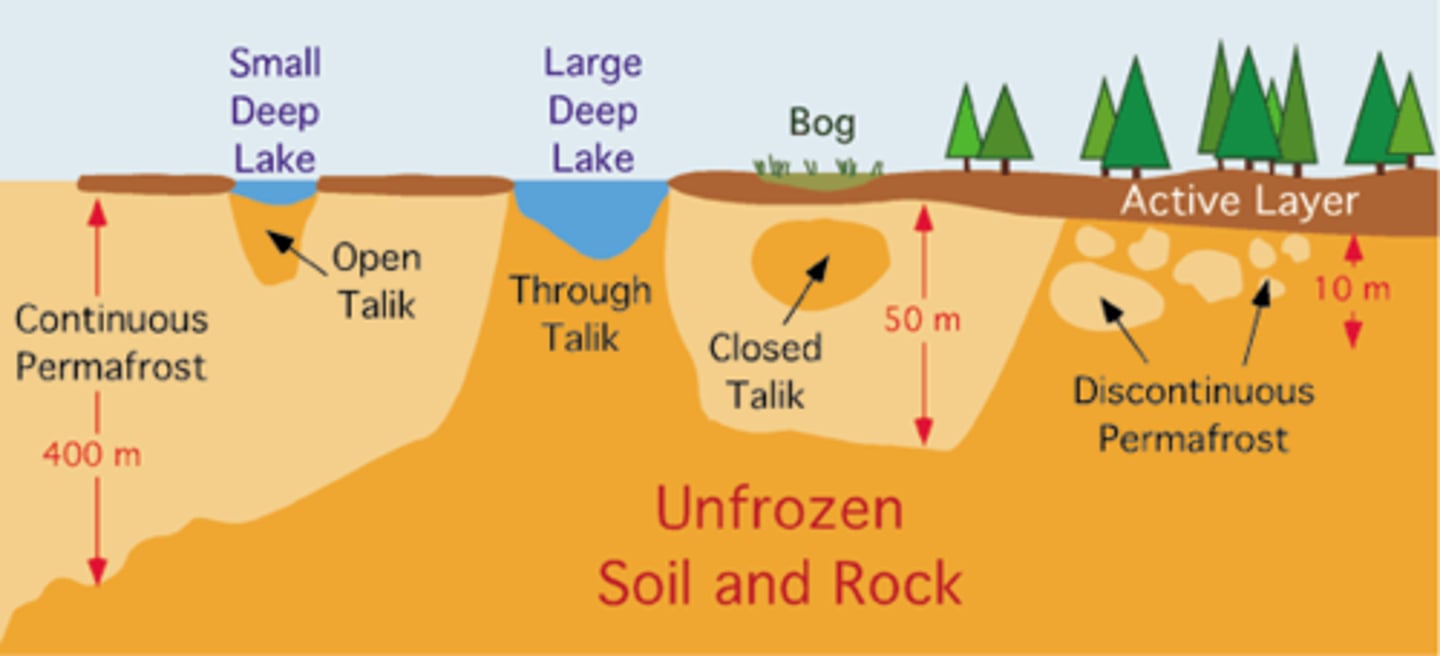
permafrost
an area of land which is permanently frozen
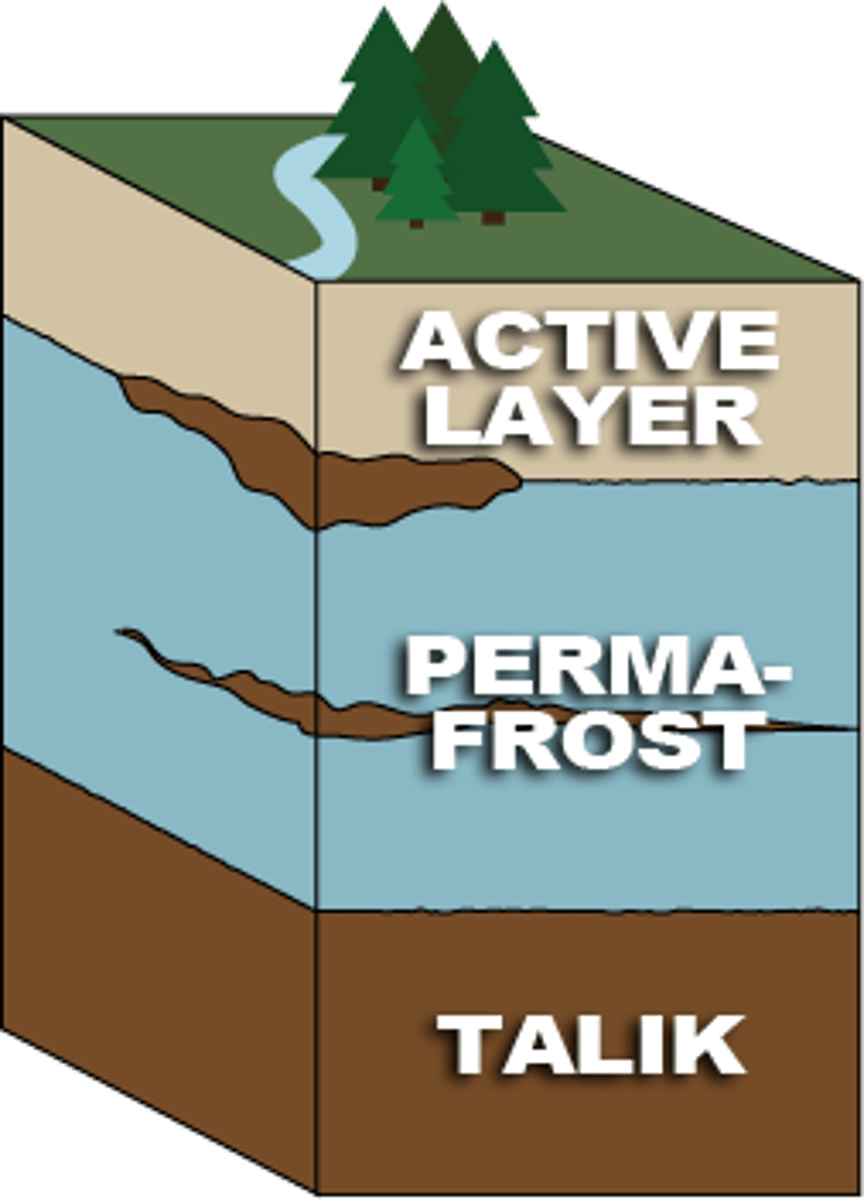
active layer
the upper layer above permafrost which thaws and refreezes during the summer
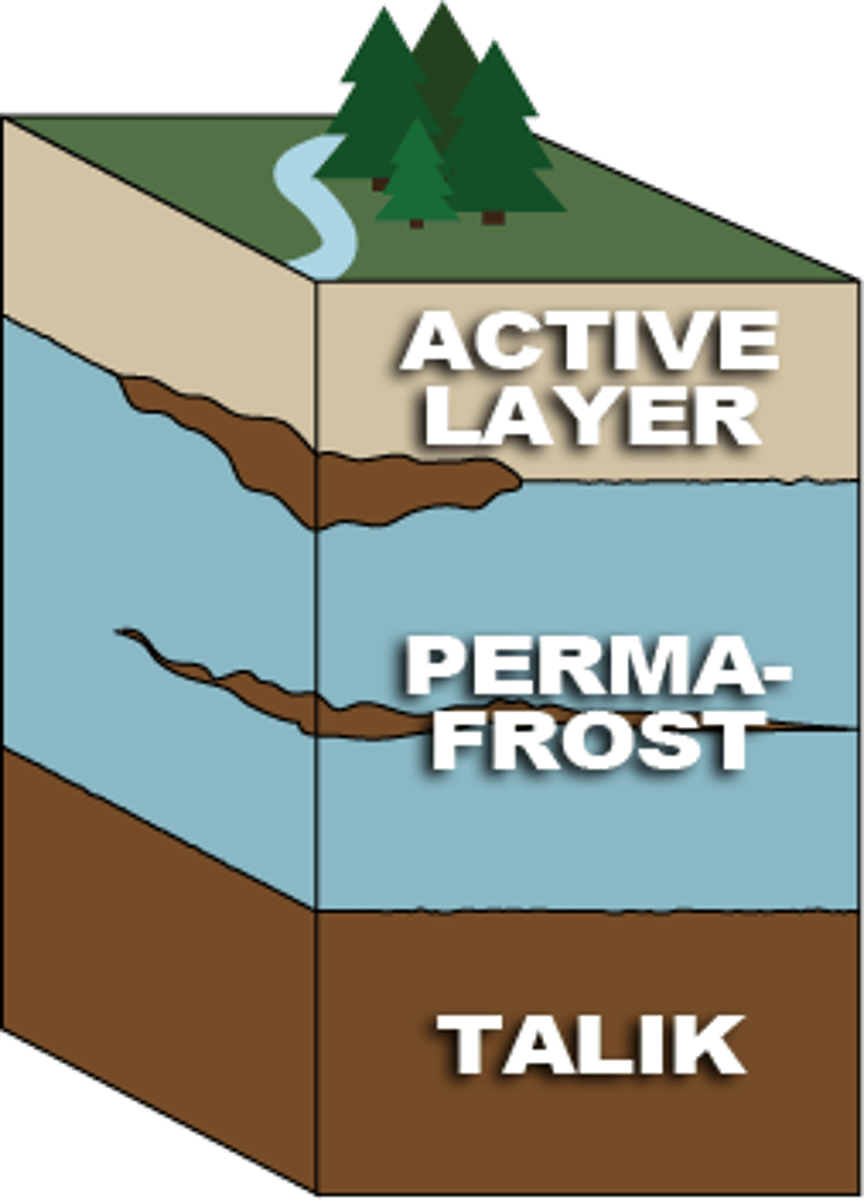
talik
an area of unfrozen ground surrounded by permafrost
biodiversity
the diversity of plant and animal life in a particular habitat (or in the world as a whole)

indigenous people
people who have lived in a given area for thousands of years

whaling
hunting for whales

moratorium
a temporary ban on an activity

fishing
the activity by which 70% of global white fish is caught in Arctic waters

Antarctic treaty
agreement signed by twelve countries coming into force in 1961 and now backed by a total of 53 agreeing to preserve Antarctica for peaceful and scientific use
