Bio Unit 4
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Will C Wood Leonard (works for most bio classes though, but based off of leonards slides) , please let me know if I need to fix anything!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Cell Membrane (What is it made out of)
Phospholipid Bilayer
Cell Membrane (Function)
Allows material in/out of cell aka SELECTIVE PERMEATION
Where is bacteria found
Soil, water, air, most surfaces, glacial ice
Photosynthesis (aka)
Autotrophic (aka)
Eukaryotes(energy source))
Photosynthetic predation (ingestion)
Golgi apparatus (function)
Packages material in places in the cell and out of the cell
Ribosome (Function)
Manufactures proteins
Lysosome (Function)
Digests macromolecules
Centrioles (Function)
Used in reproduction
Eukaryote (age/skill)
Younger/more advanced
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (er) (function
Just makes proteins in cells
DNA
Cell control center (nucleoid)
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (er) (Function)
Makes AND moves lipids
Pros, bacteria
Decomposes, produces antibodies, vaccines, insulin, produces food, digestion, cleaning up oil spills, defends us
Plant cell (diagram)
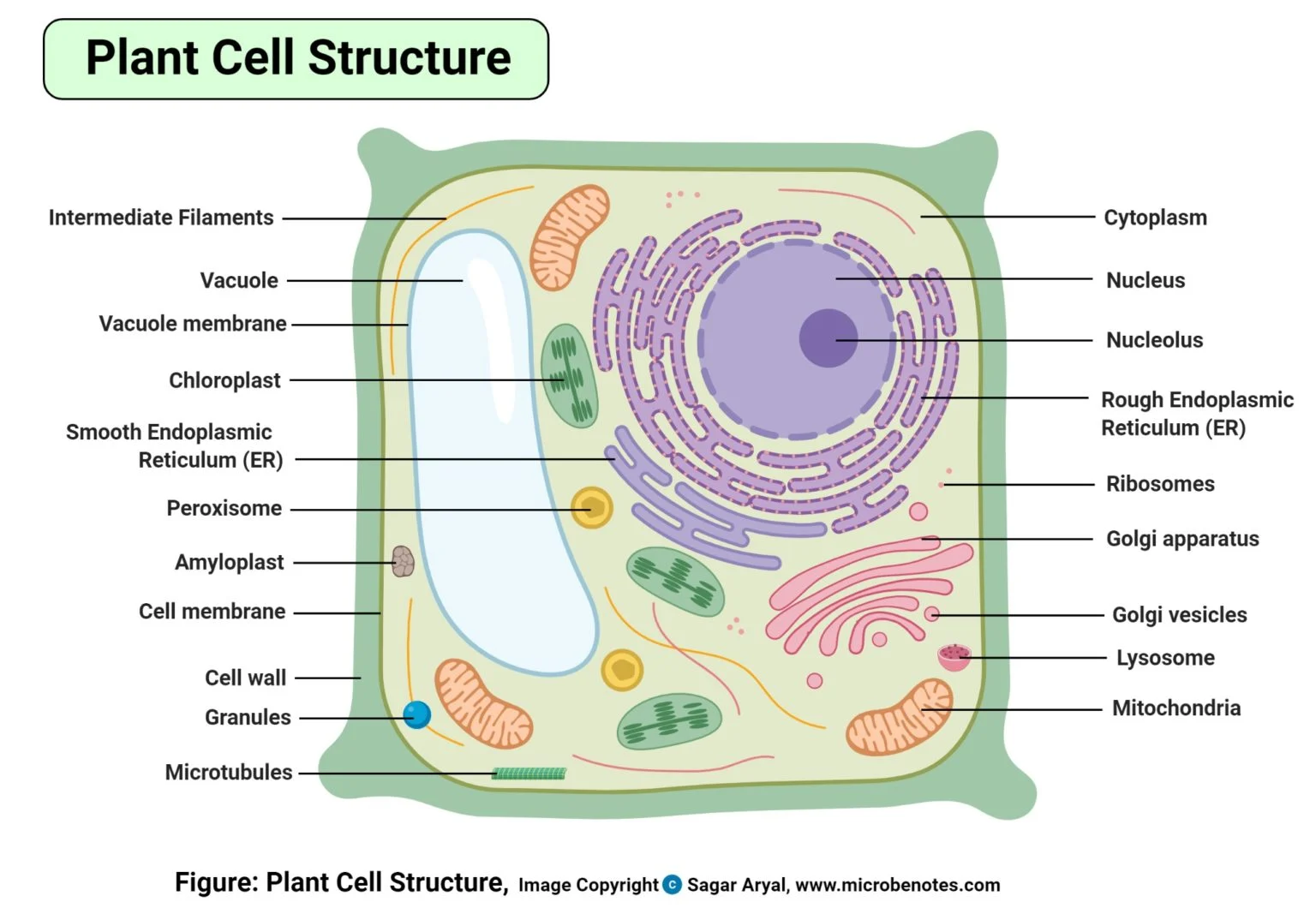
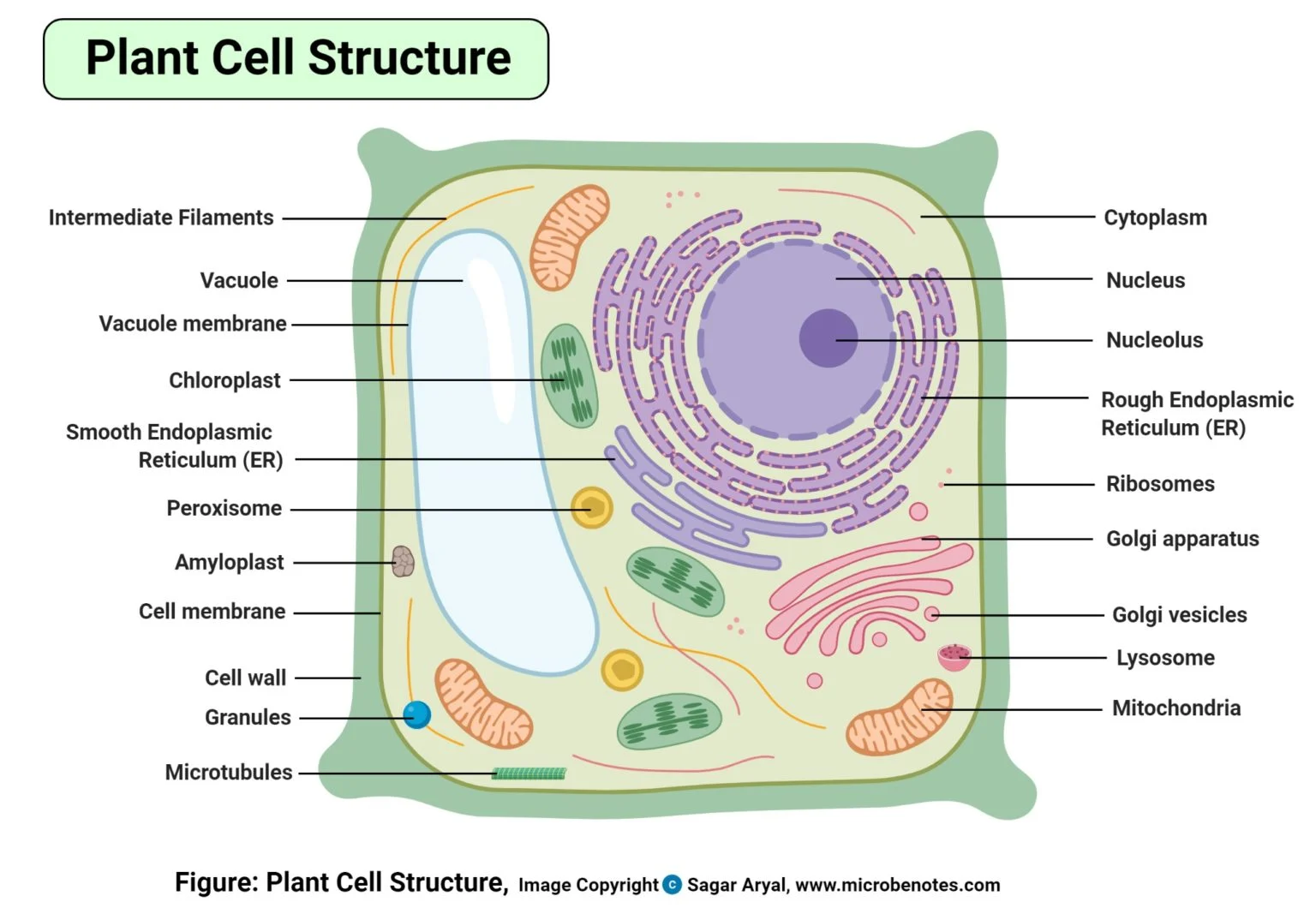
Eukaryotes (description of nucleus)
Large nucleus
Eukaryotes (unicellular/multicellular)
Can be both
Prokaryotes (energy source)
Photosynthesis, disease causing decomposers
Eukaryotic animal cell diagram
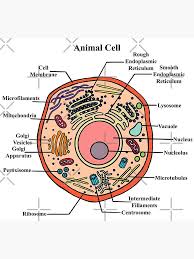
How to control bacteria
Pasteurization (heating), dehydration, freezing/cooling, disenfectant
Bacteria shape
Spherical, spiral, or Mike n ikes
Prokaryotes (age/skill)
Older/more primitive
Cytoplasm (function)
Jelly like matrix, contains all organelles and dissolved substances
Prokaryotes (unicellular/multicellular)
Unicellular/ bacteria
Bacteria cons
Causes disease, blue/green blooms (toxic), food spoilage
Mitochondria (function)
Cellular respiration, breaks down glucose
Cell membrane (function, made out of)
Protective layer made from carbohydrate complex
Cell theory
All living things made out of cells, cells come from other cells, cells basic unit of structure and function
Cell wall (function made out of)
Protects, provides structure, made out of cellulose
Vacuole (where is it found)
Plant only
Cell wall, (found where)
Plant only
Prokaryotes (description of nucleus)
No nucleus
Eukaryotes (description of organelles)
Many membrane bound organelles
Nucleus (diagram)
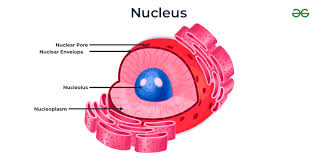
Central vacuole (function)
Stores water and dissolved substances
Prokaryotes (organelle description)
No membrane bound organelles
Parasites energy definition
Feeds off of other organisms, causes disease
Decomposer energy definition
Feeds off of dead matter
What is cellular transport used for?
Maintaining homeostasis
What makes up a phospholipid bilayer
Phosphate head and fatty acid tail
Phosphate head (attraction to h2o)
Hydrophilic (attraction to water)
Fatty acid tail (attraction to h20)
Hydrophobic (repulsion to water)
Are proteins embedded in cell membranes?
yes
Cell membranes are what type of permeable
Selectively permeable
Characteristics of molecules
Molecules have some type of attraction to other molecules, all molecules are moving constantly, all molecules are in different size/shape/arrangement
Passive transport
Cell dosen’t use energy to transport
Diffusion definition
The process of molecules spreading from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Equilibrium definition
A state in which the concentrations of molecules are equal in different areas.
Osmosis definition
The movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
What is water is in a solution
Solvent (dissolves)
What sugar or salt is in a solution
Solute (dissolved substance)
Can water move freely through a cell membrane?
yes
Definition of tonicity
Environmental conditions
Hypotonic definition
The solution around the cell has a higher number of water compared to inside the cell
Effects of hypotonic diffusion
Animal cells may swell and burst because the cell is trying to absorb all the water
Definition of hypertonic
The solution around the cell has a lower number of water compared to inside the cell
Effects of hypertonic diffusion
Shrinking of a cell because the water is exiting the cell
Isotonic definition
Concentration of water inside cell is equal to concentration of water outside cell
Effects of isotonic diffusion
The cell stays the same because the exit of water is equal to the entering of it.
Thank you for using my flashcards!!
Remember to drink water, eat, and get enough sleep for finals!!❤